Curriculum for Pre-kindergarten
Students lay the foundation of number sense and mathematical thinking as they progress through very concrete, hands-on exercises that prepare them for future success in math.
MODULE 1 Counting to 5
Topic A: Identifying Attributes
Students learn the meaning of same, different, alike, larger, and smaller. They identify and match objects based on size, color, shape, and even purpose.
Pretest: Sorting and labeling objects by attribute
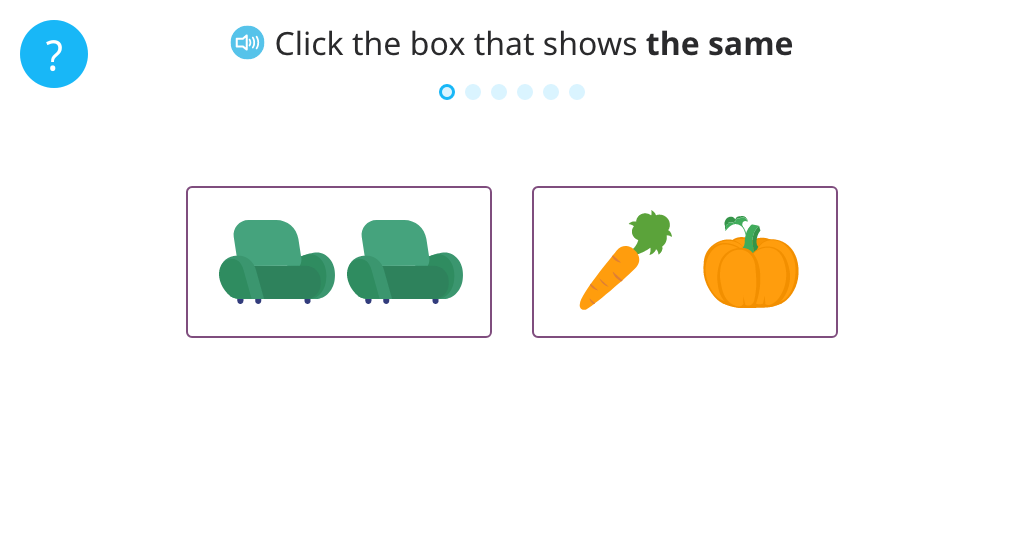
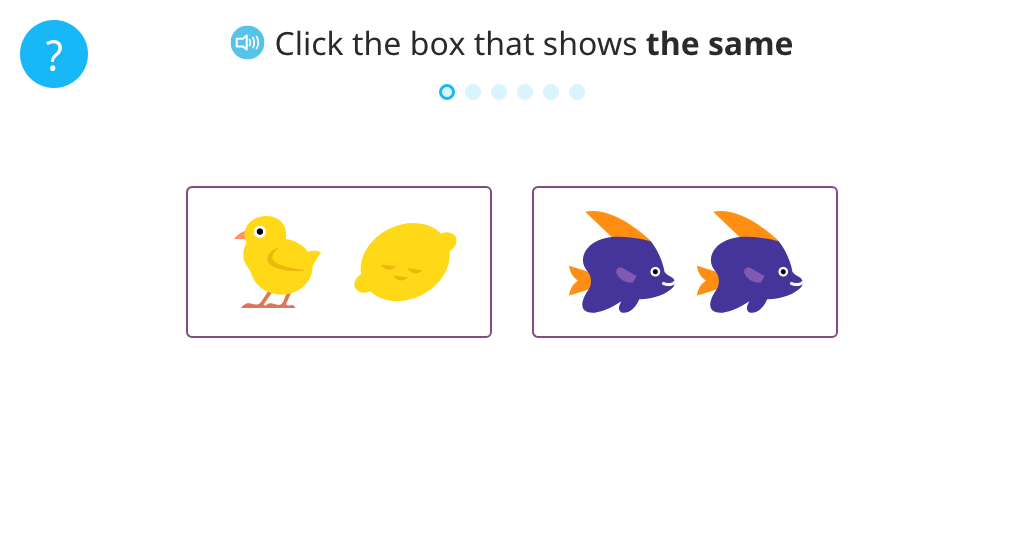
Identify two out of three objects that are the same

Identify two out of three objects that are different

Identify whether two objects are the same or different

Identify which of two similar objects is larger

Identify which of two similar objects is smaller

Match pairs of similar items that differ in size and/or color

Match pairs of similar items that differ in size and color

Match pairs of different items that are used together

Topic B: Sorting Objects by Attribute
Students build upon their understanding of size, color, shape, and purpose to sort dissimilar objects based on a common attribute. They must also ignore objects that do not fit the given descriptors.
Identify objects that belong to a given category

Identify objects of a given color

Sort objects based on two given categories (Level 1)

Sort objects based on two given categories (Level 2)

Sort objects based on two given colors

Exit ticket: Sorting and labeling objects by attribute
Topic C: How Many Questions with 1, 2, or 3 Objects
Students learn to count objects with 1:1 matching by interacting with each object, either by tapping it or by moving it. They work with uniform objects that are both aligned and scattered. Automatic voice prompts give directions and guidance.
Pretest: Counting to 5

Count uniform objects (Part 1)

Count uniform objects (Part 2)

Align groups of uniform objects and identify the total

Count scattered uniform objects

Topic D: Exploring Numbers 1 to 3
Students learn the numeric representation and value of numbers 1-3. They learn to identify and write the numerals and count from 1-3 with concrete objects.
Identify and write the numeral 1

Identify and write the numeral 2

Determine if a set has 1 or 2 objects

Identify and write the numeral 3

Identify the correct numeral from 1-3

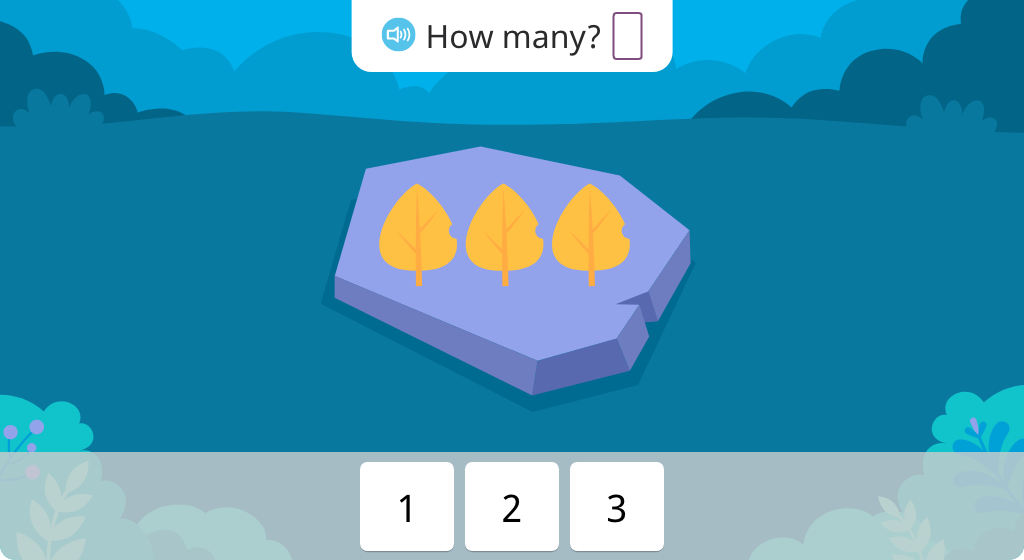
Count to determine the number of objects in a set (Level 1)

Count to determine the number of objects in a set (Level 2)

Count concrete objects to show 1-3 (Level 1)

Count concrete objects to show 1-3 (Level 2)

Count concrete objects in sets
Identify sets of 1-3 objects (Level 1)

Identify sets of 1-3 objects (Level 2)

Identify numerals from 1-3

Topic E: Exploring the Number 4
Students learn the numeric representation and value of number 4. They learn to identify and write the numeral and count from 1-4 with concrete objects.
Identify and write the numeral 4

Identify the correct numeral from 1-4

Count and label the number of objects in a set

Explore the concept of pairs

Count sets of 4

Count to determine the number of objects in a set

Count concrete objects to show 1-4
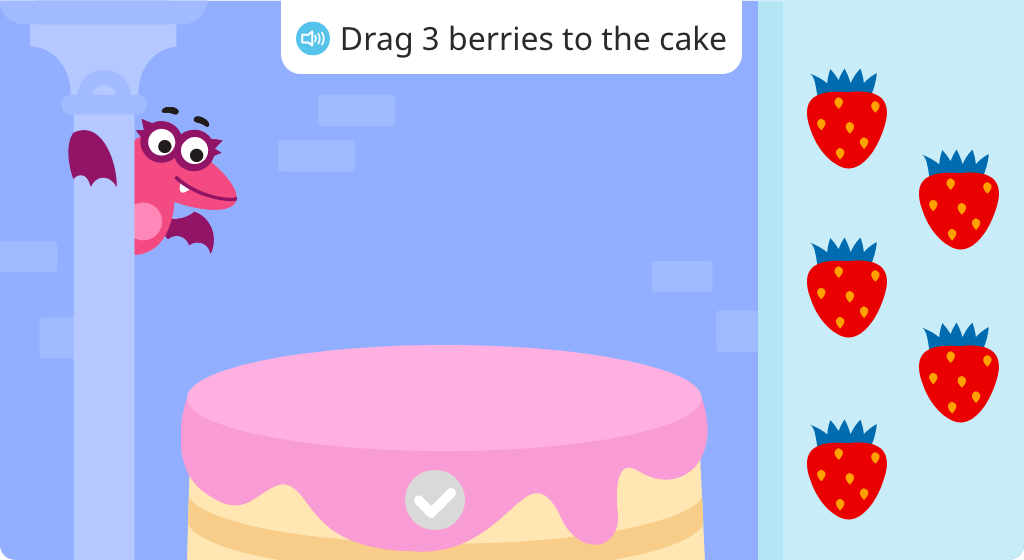
Identify sets of 1-4 objects

Topic F: Exploring the Number 5
Students learn the numeric representation and value of number 5. They learn to identify and write the numeral and count from 1-5 with concrete objects.
Write and count to 5

Count concrete objects up to 5 (Level 1)

Count concrete objects up to 5 (Level 2)

Count concrete objects to show 1-5

Identify sets of 1-5 objects

Topic G: One More with Numbers 1 to 5
Students work with sets of identical objects to determine the total when one more is added. They may or may not count each object as they begin to rely on their ability to visually recognize totals up to five.
Determine the total after "one more" is added to a set of identical objects (Part 1)

Add "one more" object to a set and determine the total

Determine the total after "one more" is added to a set of identical objects (Part 2)
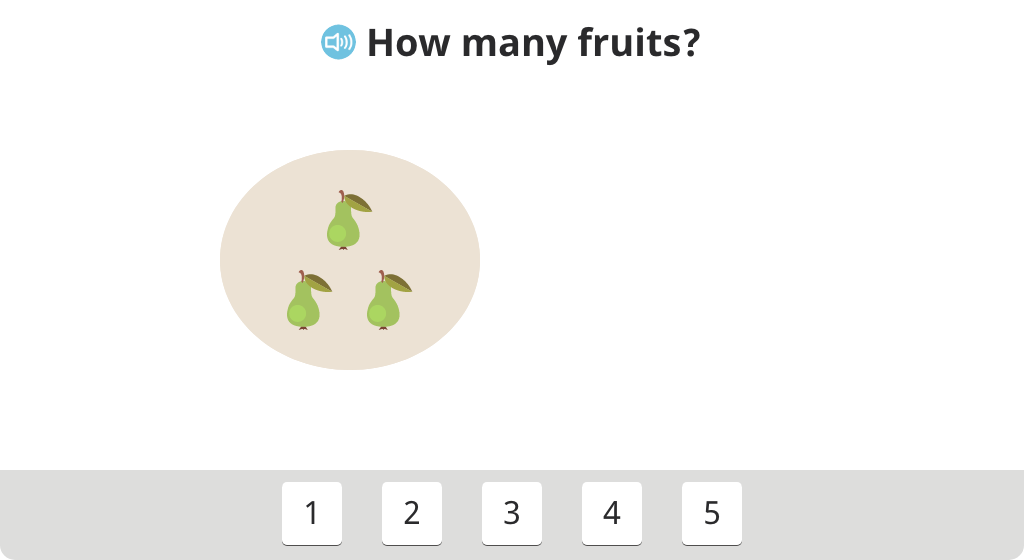
Determine the missing numbers on a number line numbered 1-5

Topic H: Counting 5, 4, 3, 2, 1
Students work with sets of identical objects to determine what remains when one is taken away. Students learn to count backward from 5 and identify missing numbers in this series.
Determine what remains after one is taken away

Count backward from 5

Identify the missing number in a series

Exit ticket: Counting to 5

MODULE 2 Shapes
Topic A: Two-Dimensional Shapes
Students identify circles, squares, triangles, and rectangles of different sizes, colors, and orientation. Students also work with triangles and rectangles with different proportions. They learn the positions above, below, next to, in front of, and behind.
Pretest: 2-D shapes and relative positions

Identify circles from among a set of two-dimensional shapes

Identify squares from among a set of two-dimensional shapes

Identify triangles from among a set of two-dimensional shapes

Identify rectangles from among a set of two-dimensional shapes

Identify the position above or below a given object (Part 1)

Identify the position above or below a given object (Part 2)

Move objects up or down as instructed

Position a shape above or below another shape as instructed

Position an object next to another object as instructed

Position an object in front of or behind another object as instructed

Exit ticket: 2-D shapes and relative positions

MODULE 3 Counting to 10
Topic A: How Many Questions with up to 7 Objects
Students continue developing their ability to count with 1:1 matching, moving in a left to right progression as well as from top to bottom to count objects in rows. They continue to develop their visual recognition of totals without counting.
Pretest: Counting to 10

Recognize that one more than 5 is 6

Count 6 similar aligned objects from left to right

Tap objects to count the total to 6

Identify totals of up to 6 identical objects

Recognize that one more than 6 is 7

Count 7 similar aligned objects from left to right

Tap objects to count the total to 7

Identify totals of up to 7 identical objects

Align groups of identical objects and identify the total

Count identical objects in two rows from left to right, top to bottom

Topic B: Matching One Numeral with up to 7 Objects
Students work with groups of identical objects to split totals in different ways (a precursor to learning fact families). They count objects in different alignments, including circular, two rows, and vertical column. In the final exercise, they see that when objects are rearranged, the total remains the same.
Combine and split groups of 6 identical objects and determine totals

Split a group of 6 identical objects into two groups in different ways

Combine and split groups of 7 identical objects and determine totals

Split a group of 7 identical objects into two groups in different ways

Distribute and count 7 identical objects aligned in a circular arrangement

Distribute and count 6 identical objects aligned in two rows

Distribute and count 5 or 6 identical objects aligned in a column

Topic C: How Many Questions with up to 8 Objects
Students continue developing their ability to count with 1:1 matching, moving in a left to right progression as well as from top to bottom to count objects in rows.
Recognize that one more than 7 is 8

Count 8 similar aligned objects from left to right

Identify totals of up to 8 identical objects
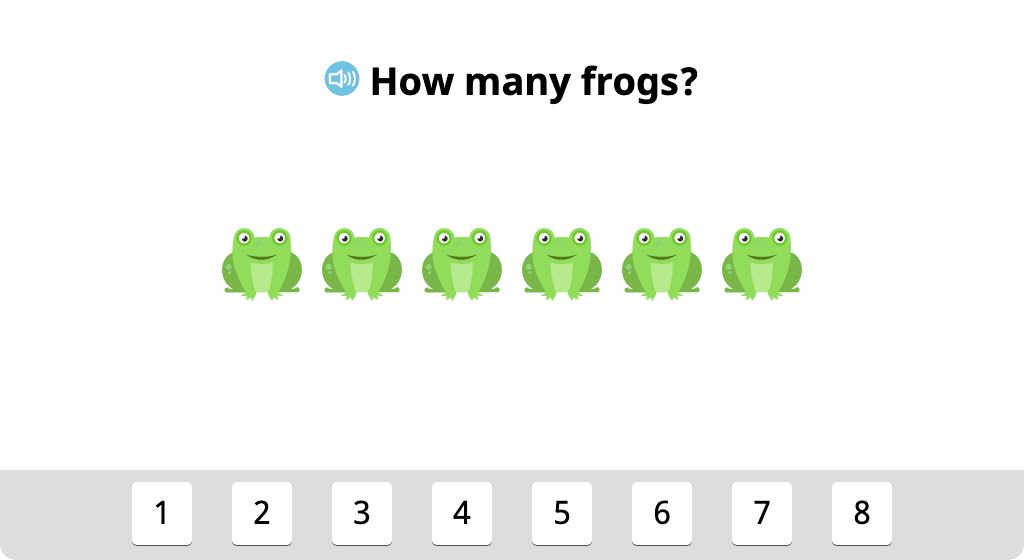
Align groups of identical objects and identify the total

Count identical objects in two rows from left to right, top to bottom

Topic D: Matching One Numeral with up to 8 Objects
Students match groups of uniform objects to a total written in digits. They work with both aligned and scattered objects to match objects to a number or match a number to objects. Students begin to create parts (or groups) for totals of up to eight objects.
Identify the total of 8 identical objects aligned in two groups

Split a set of 8 objects into two groups in different ways

Identify the total of 8 identical objects aligned in a circle

Identify the total of 8 identical objects aligned in two rows

Identify the total of 7 identical objects aligned vertically

Topic E: How Many Questions with 0 up to 9 Objects
Students are introduced to the concept of 0. They continue developing their ability to count with 1:1 matching, moving in a left to right progression as well as from top to bottom to count objects in rows.
Recognize that 0 is an amount that is one less than 1

Determine which set of identical objects has a total of 0

Determine totals of identical objects, including 0
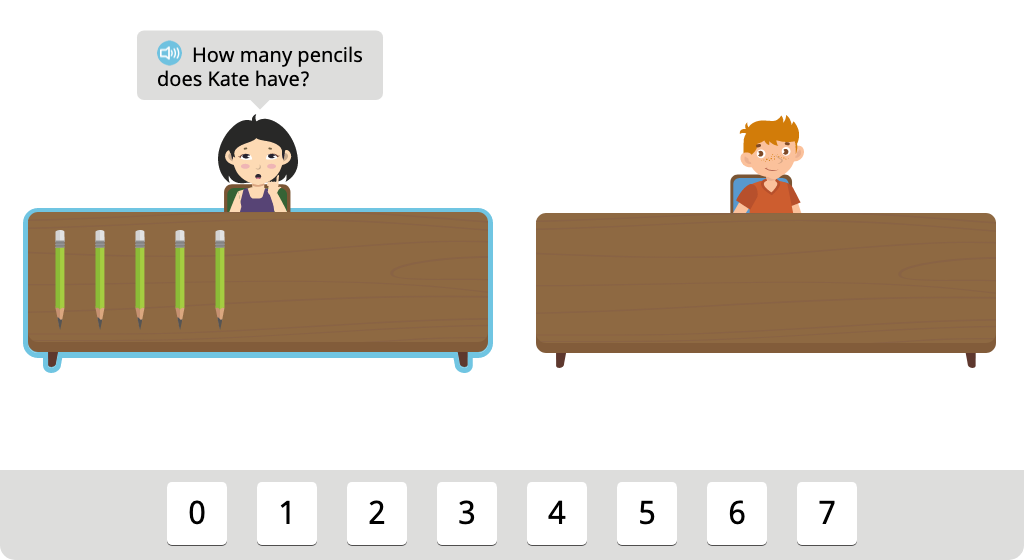
Recognize that one more than 8 is 9

Count 9 similar aligned objects from left to right

Identify totals of up to 9 identical objects
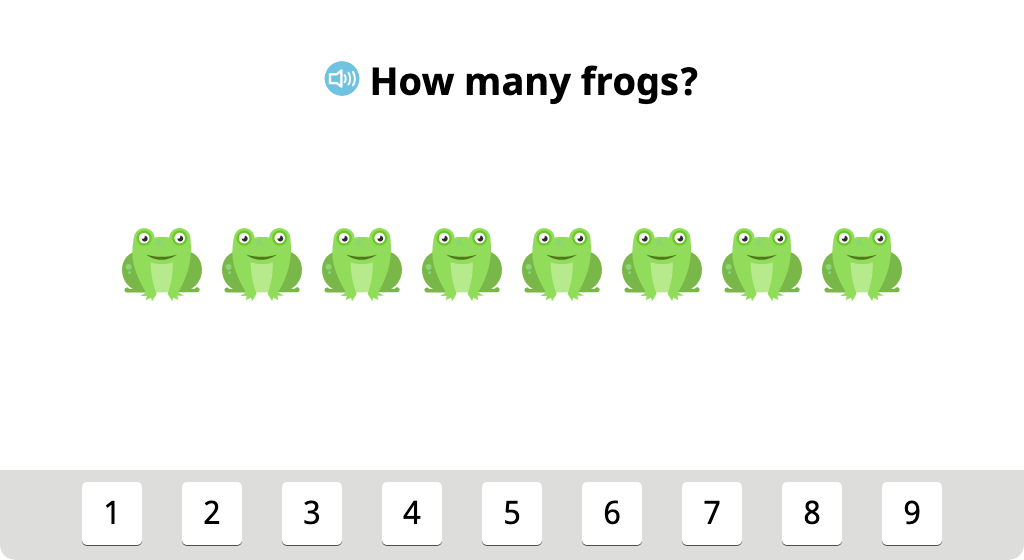
Align groups of identical objects and identify the total

Topic F: Matching One Numeral with 0 up to 9 Objects
Students work with groups of identical objects to split totals in different ways (a precursor to learning fact families). They count objects in different alignments, including circular and rows. In the final exercise, they see that when objects are rearranged, the total remains the same.
Combine and split groups of 9 identical objects and determine totals

Split a group of 9 identical objects into two groups in different ways

Count 7 identical objects aligned in a circular arrangement

Distribute and count 9 identical objects aligned in a circular arrangement

Topic G: How Many Questions with up to 10 Objects
Students continue developing their ability to count with 1:1 matching, moving in a left to right progression as well as from top to bottom to count objects in rows.
Recognize that one more than 9 is 10

Count 10 similar aligned objects from left to right

Identify totals of up to 10 identical objects
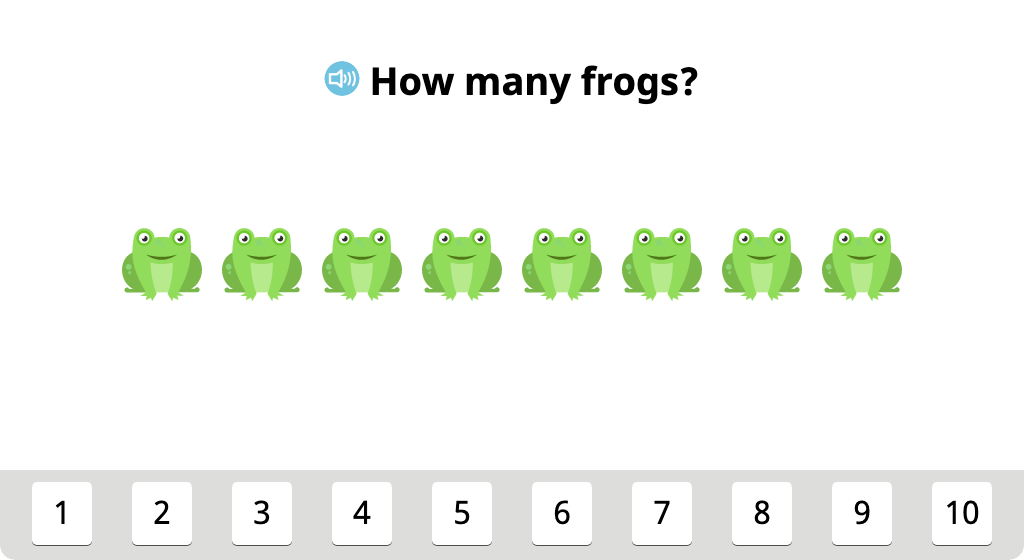
Align groups of identical objects and identify the total

Count identical objects in two rows from left to right, top to bottom

Exit ticket: Counting to 10

Topic H: Matching One Numeral with up to 10 Objects
Students work with groups of identical objects to split totals in different ways (a precursor to learning fact families). They count objects in different alignments, including circular and two rows. In the final exercise, they see that when objects are rearranged, the total remains the same.
Combine and split groups of 10 identical objects and determine totals

Split a group of 10 identical objects into two groups in different ways

Distribute and count 10 identical objects aligned in two rows

MODULE 4. Comparison of Length, Weight, Capacity, and Numbers to 5
Topic A: Comparison of Length
Students are introduced to the terms "taller," "higher," and "about the same" regarding height and length. They work with familiar objects to make determinations about height or weight, eventually manipulating objects to create the desired height or weight.
Determine which of two objects is taller

Determine which of two objects is longer or shorter

Identify two objects that are about the same height

Identify two objects that are about the same length

Identify an object that is about the same length or height as a given object

Add cars or take them away to make a train the same length as a given train

Add cubes or take them away to make a tower the same height as a given tower

Topic B: Comparison of Weight
Students are introduced to the concept of weight, including the terms "lighter" and "heavier." Students will compare familiar objects to make determinations about weight.
Explore the concepts of "lighter" and "heavier"

Determine which object is heavier

Determine which object is lighter

Topic C: Identifying Objects That Are First and Last
Students are introduced to the terms "first" and "last," then use this knowledge to identify which items are first and last in a series of 5 or less. Then, students are introduced to the concept of one-to-one correspondence.
Develop the concept of "first" and "last"

Identify objects that are first and last in a series

Begin to understand the concept of one-to-one correspondence

Topic D: Comparing Sets
Students are introduced to the concepts of "more," "less," "same," and "different." Given two sets of 5 or less objects, students will compare the number of items in each group and identify which shows more or less, or same or different amounts.
Determine which of two sets shows "more"

Determine which of two sets shows "fewer"

Identify the number of cubes in two given stacks and compare them

Begin to understand the concepts of "same" and "different" amounts of objects

Determine if two sets of base-10 cubes show the same amount

MODULE 5 Addition and Subtraction Stories
Topic A: Contextualizing Addition Stories to Solve
Students count identical objects aligned in a row. Then additional objects, identical except for the color, are added to the row. Students count those objects and then determine the total.
Count two groups of objects and determine the total (Part 1)

Count two groups of objects and determine the total (Part 2)
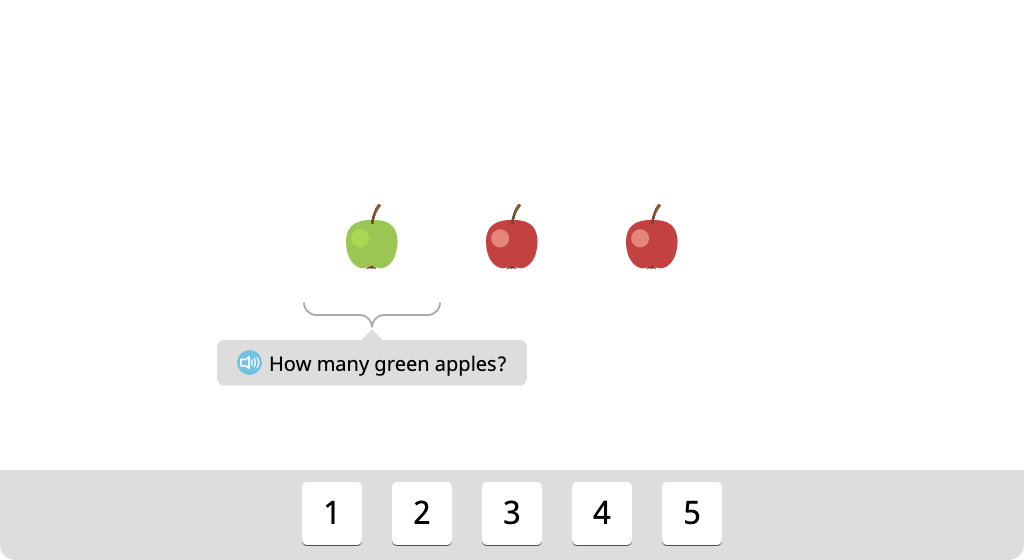
Topic B: Contextualizing Subtraction Stories to Solve
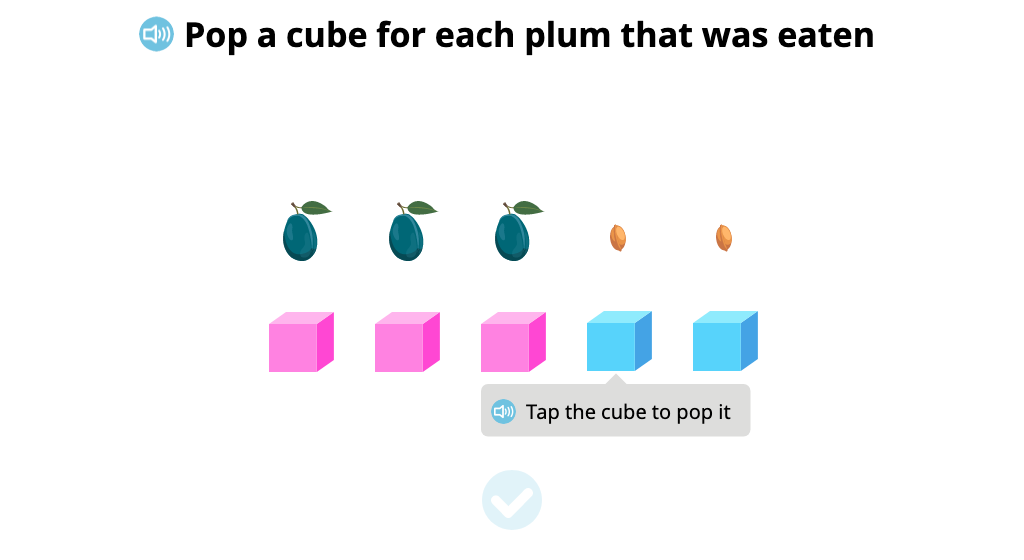
Students count identical objects aligned in a row. Then some of the objects are taken away (balloons pop, pears are eaten, etc.). Students count the remaining objects to determine the difference.
Determine the number of objects at different points in a subtraction scenario (Part 1)

Determine the number of objects at different points in a subtraction scenario (Part 2)

Topic C: Decontextualizing Addition Stories to Solve Using Fingers, Objects, and Drawings
Students move toward more abstract thinking by using cubes to represent real objects (birds, balloons, apples, etc.). They build understanding that the number of cubes represents the objects with 1:1 matching and can be used in determining totals in simple addition stories.
Match cubes 1:1 with objects aligned in a row (Level 1)

Match cubes 1:1 with objects aligned in a row (Level 2)

Determine the number of objects represented by cubes

Match cubes 1:1 with objects aligned in a row (Level 3)

Determine the number of objects represented by cubes in an addition scenario (Level 1)

Determine the number of objects represented by cubes in an addition scenario (Level 2)

Determine the total of two groups of objects based on their representation in cubes

Topic D: Decontextualizing Subtraction Stories to Solve Using Fingers, Objects, and Drawings
Students move toward more abstract thinking by using cubes to represent real objects . They build understanding that the number of cubes represents the objects with 1:1 matching and can be used in determining totals in simple subtraction stories.
Represent subtraction scenarios using cubes to match objects 1:1

Determine the number of objects represented by cubes in a subtraction scenario