Curriculum for Kindergarten
From number recognition to counting and operations, students build the number sense and conceptual understanding they'll need for grade 1.
MODULE 1 Numbers to 10
Topic A: Identifying Same, Different, and Alike
Students consider the size, shape, and color of objects to determine whether they are the same, different, or alike. Additionally, they are introduced to dissimilar objects that "match" because of a related function, such as a sock and a shoe.
Identify two out of three objects that are the same

Identify two out of three objects that are different

Identify differences between two similar images

Identify items that belong together based on their use

Identify whether two objects have the same shape (with different colors and patterns)

Identify whether two objects have the same color (with different shapes and patterns)

Identify whether two objects have the same pattern (with the same and with different colors)

Identify whether two objects have the same pattern (with different shapes and colors)

Topic B: Sorting and Counting Similar Objects
Students sort similar objects based on narrow categories (such as "bears"), broad categories (such as "clothes"), and self-determined categories. They identify objects that do not belong in a group without being given the name of the category. Finally, students count to determine the total number of objects in a group.
Sort similar objects into given categories

Sort objects into self-determined groups

Identify which of four objects does not fit with the group

Identify objects that belong to a category and count the total

Count totals of objects in a category

Identify sets of objects with a given total

Identify a set of objects with a given total

Sort objects into two groups and identify totals

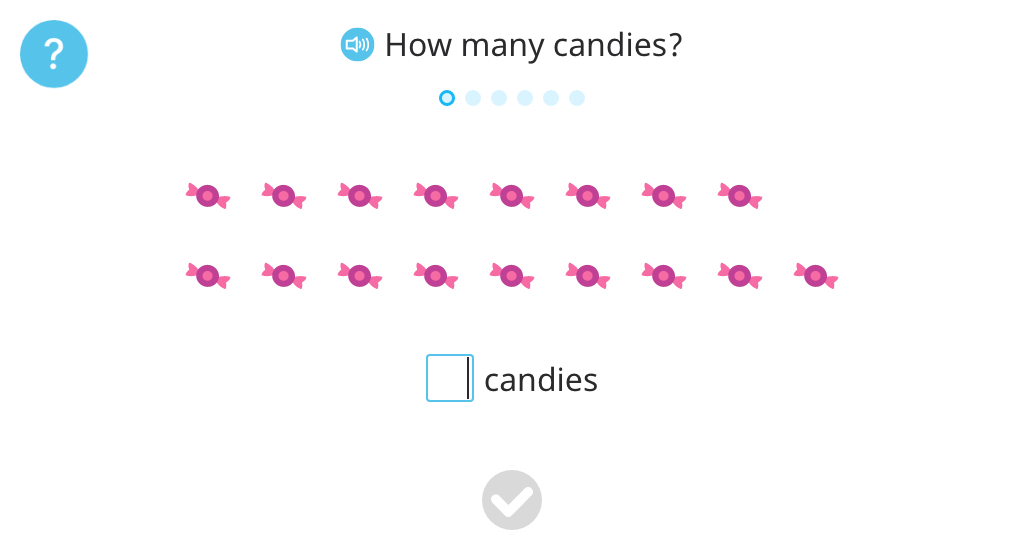
Pretest: Counting to 10

Topic C: Numbers to 5 in Different Configurations, Math Drawings, and Expressions
Students count in sequence to determine position or total up to 5. They relate objects to digits and see digits in a variety of fonts. They work with aligned objects, scattered objects, fingers, and the number line. Students learn strategies for counting with 1:1 match and learn that sets of objects with the same total can be aligned in different ways.
Match a numbered set of 1, 2, or 3 cubes to an identical numbered set of cubes

Match numbered and non-numbered sets of cubes to a number 1-3

Match sets of cubes to numbers 1-3

Match numbers 1-3 to their positions on a number line labeled with numbers and dot patterns

Identify a numbered set of cubes that matches an identical set of 4 or 5 numbered cubes

Match numbered and non-numbered sets of cubes to number 4 or 5

Count 2-5 aligned objects to determine the total

Match numbers 1-5 to arrangements of fingers displayed on a hand

Match sets of cubes to numbers 1-5

Identify numbered sets of cubes that match a given total up to 5

Match numbers 1-5 to their positions on a number line labeled with numbers and dot patterns

Align scattered objects to count and determine the total

Count to find the total of scattered objects by matching 1:1 numbers to objects

Identify a set of scattered objects that matches a given total up to 5

Topic D: The Concept of Zero and Working with Numbers 0 - 5
Students use digits 1-5 to sequence objects and to determine position or total. They work with aligned objects, scattered objects, and the number line. They explore the composition of the number 3 and begin using +, -, and = signs.
Identify sets of 0 among sets of scattered objects

Identify a set of scattered objects that matches a given total up to 5

Sequence scattered objects numbered 1-5 in ascending order

Continue a count sequence on a number line from a given point to reach a given position

Identify missing numbers up to 5 on a numbered number line

Identify the object at a given position in a set of aligned objects

Identify the position of an object in a set of aligned objects

Topic E: Working with Numbers 6 - 8 in Different Configurations
Students count in sequence to determine position or total up to 9. They relate objects to digits and see digits in a variety of fonts. They work with aligned objects, scattered objects, fingers, and the number line. Students learn strategies for counting with 1:1 match and learn that sets of objects with the same total can be aligned in different ways.
Recognize that one more than 5 is 6

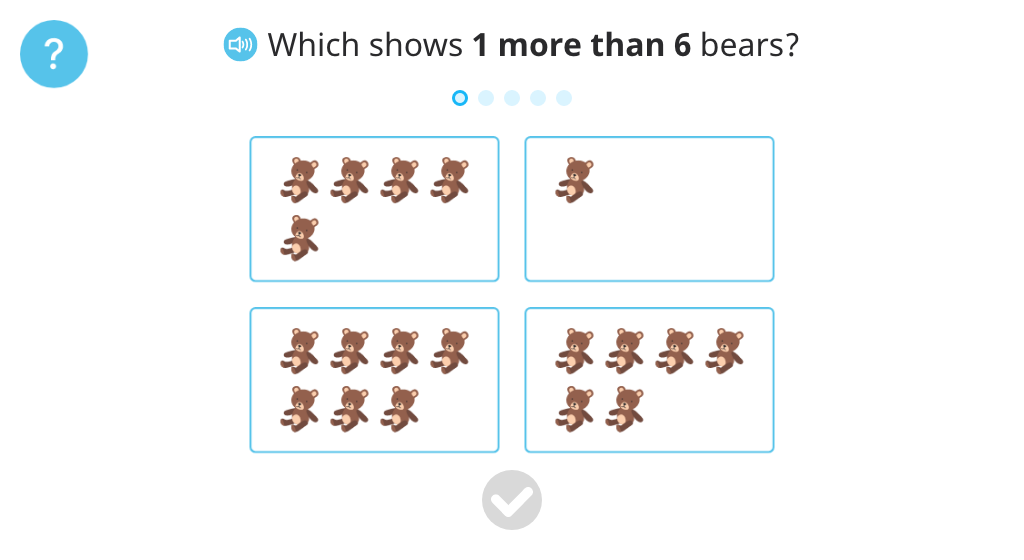
Recognize that one more than 6 is 7

Identify the number of fingers up to 7 displayed on two hands

Match numbers 0-7 to arrangements of fingers displayed on two hands

Identify a set of aligned objects that matches a given total up to 7

Match numbered patterns of dots to an identical numbered pattern of dots up to 7

Identify sets of numbered cubes that match a given total of 6 or 7 (Part 1)

Identify sets of numbered cubes that match a given total of 6 or 7 (Part 2)

Place numbers below 10 on a number line marked at intervals of 5

Count objects as they move away from a set and identify the total

Count scattered objects two different ways to arrive at the same total

Recognize that one more than 7 is 8

Identify the number of fingers up to 8 displayed on two hands

Match numbers 0-8 to arrangements of fingers displayed on two hands

Identify a set of aligned objects that matches a given total up to 8

Identify sets of numbered cubes that match a given total up to 9 (Part 1)

Identify sets of numbered cubes that match a given total up to 9 (Part 2)

Count objects as they move away from a set and identify the total

Count scattered objects two different ways to arrive at the same total

Identify the total number of scattered objects after a known total has been rearranged

Topic F: Working with Numbers 9 - 10 in Different Configurations
Students work increasingly with 0 and with numbers 6-10 to determine totals and recognize digits. They work with scattered objects, non-identical objects, fingers, and the number line.
Recognize that one more than 8 is 9

Determine the total of up to 9 scattered objects (Part 1)

Count out a given number of objects from a larger set

Determine the total of up to 9 scattered objects (Part 2)

Determine the total of up to 9 non-identical scattered objects

Match sets of non-identical objects to numbers up to 9

Match numbered patterns of dots to an identical numbered pattern of dots up to 9

Identify a set of scattered objects that matches a given total up to 10

Match numbered patterns of dots to an identical numbered pattern of dots up to 10

Match numbers 0-10 to their position on a number line labeled with numbers and dot patterns

Continue a count sequence on a number line from a given point to reach a given position

Identify missing numbers up to 9 on a number path

Exit ticket: Counting to 10

Pretest: 1 more and 1 less with numbers up to 10
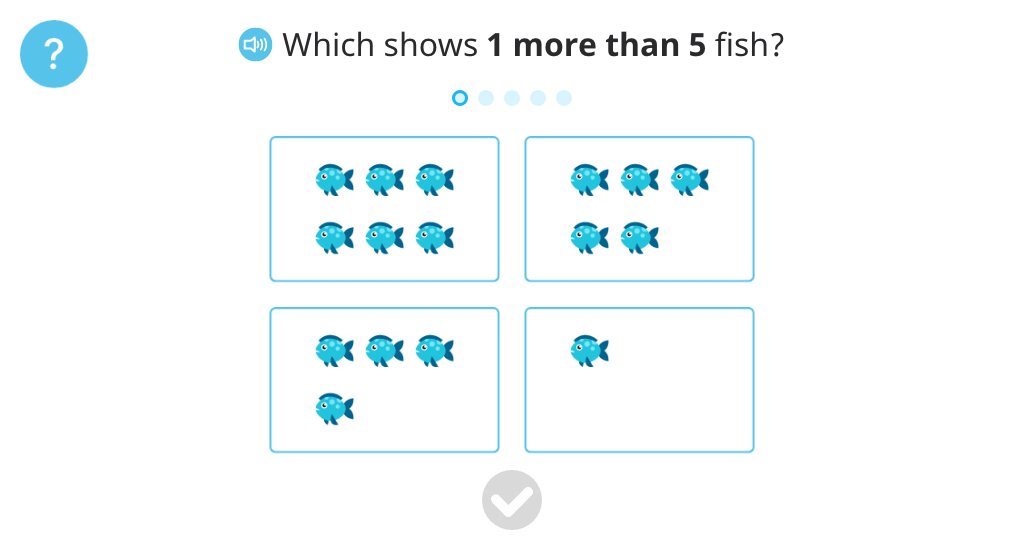
Topic G: One More with Numbers 0 - 10
Students use familiar representations (cubes, base-10 blocks, a number path, and real-world objects) to explore the concept of one more. They begin to count on rather than count all.
Identify numbers 1-5

Complete number path with missing numbers

Identify the number that comes next in a series

Explore the concept of one more with cube models

Explore the concept of one more with base-10 block models

Explore the concept of one more on a number path

Explore the concept of one more using real-world objects

Count on from a given number to find one more

Topic H: One Less with Numbers 0 - 10
Students use familiar representations (cubes, base-10 blocks, a number path, and real-world objects) to explore the concept of one less. Then, they use their understanding of one more and one less to solve +/- 1 equations.
Count and explore the concept of one less

Explore the concept of one less with cube models

Explore the concept of one less with base-10 block models

Explore the concept of one less on a number path

Explore the concept of one less using real-world objects

Exit ticket: 1 more and 1 less with numbers up to 10
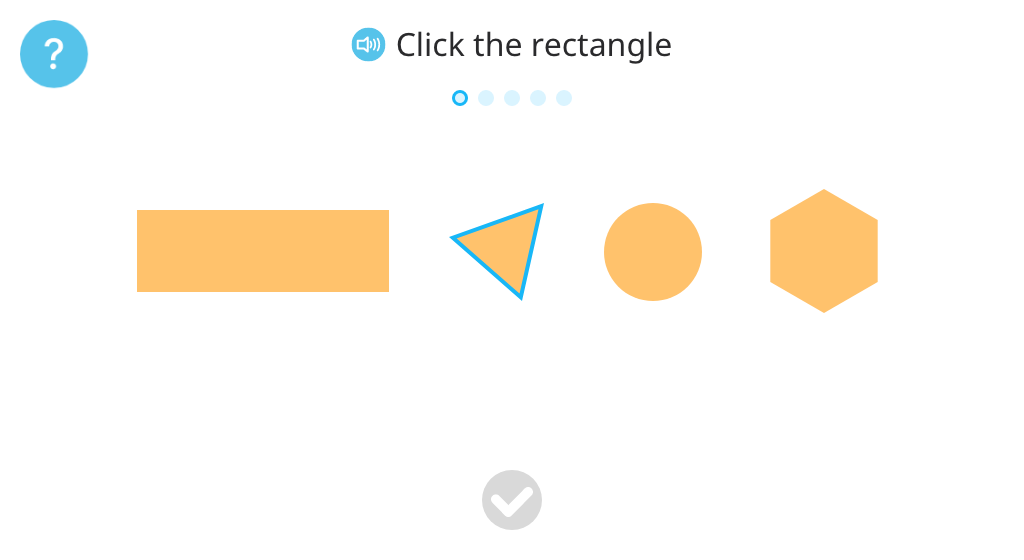
Pretest: 2-D shapes and types of lines
MODULE 2 Two-Dimensional and Three-Dimensional Shapes
Topic A: Two Dimensional Flat Shapes
Students become familiar with the appearance and names of two-dimensional shapes. They work with squares, circles, triangles, rectangles, and hexagons. Students identify examples from among non-examples. Our sound feature allows non-readers access to shape names.
Identify positions above and below an object

Position objects above and below an object

Position an object in front of or behind an object (Part 1)

Position an object in front of or behind an object (Part 2)

Identify the lines

Identify curved lines

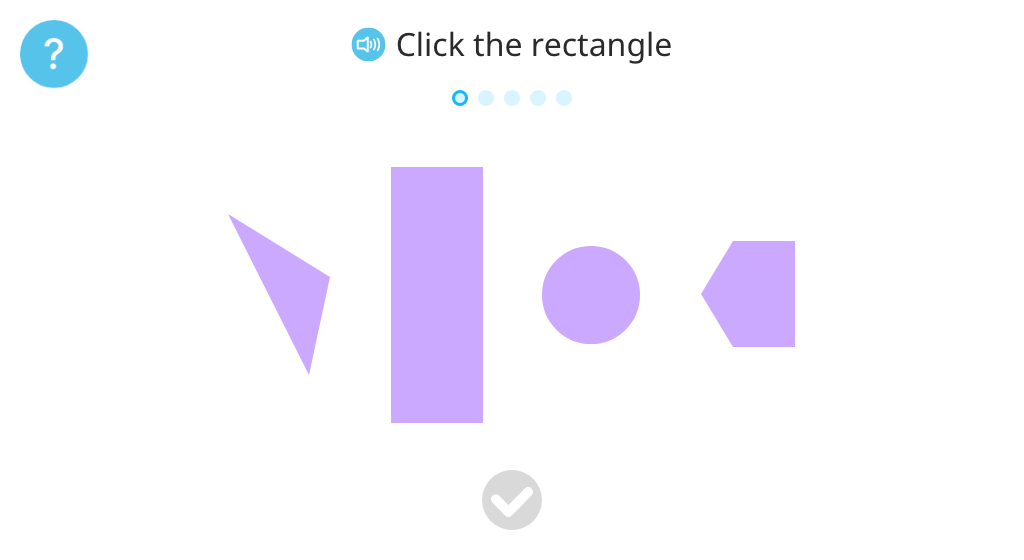
Identify rectangles, triangles, or circles from among a set of shapes

Identify properties of triangles

Identify properties of rectangles

Identify hexagons from among a set of shapes

Identify properties of hexagons

Identify real world objects composed of 2D shapes

Match real world objects to their 2D shapes

Match a 2D shape to its name

Identify shapes with a given number of sides, corners, or curved lines

Identify and sort triangles and rectangles

Identify 2D shapes and move them into positions above, below, in front of, and behind

Exit ticket: 2-D shapes and types of lines
Pretest: 3-D shapes and relative positions
Topic B: Three-Dimensional Solid Shapes
Students become familiar with the appearance and names of three-dimensional shapes. They work with cubes, spheres, cones, and cylinders. Students also reinforce their understanding of positions (above, below, in front of, next to, and behind). Our sound feature allows non-readers access to shape names.
Sort shapes into the categories flat and solid

Match shapes to real-world objects

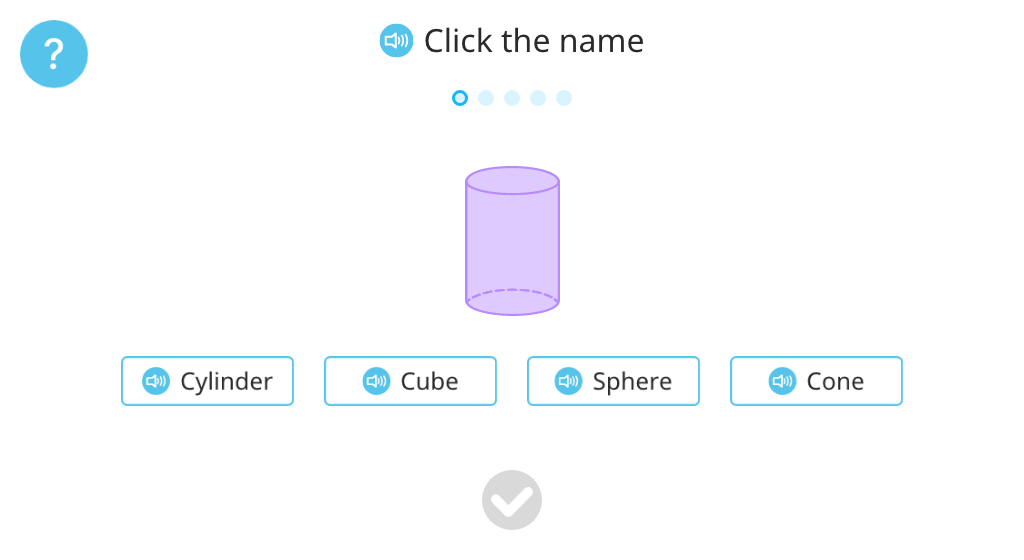
Identify cylinders from among 3-D shapes

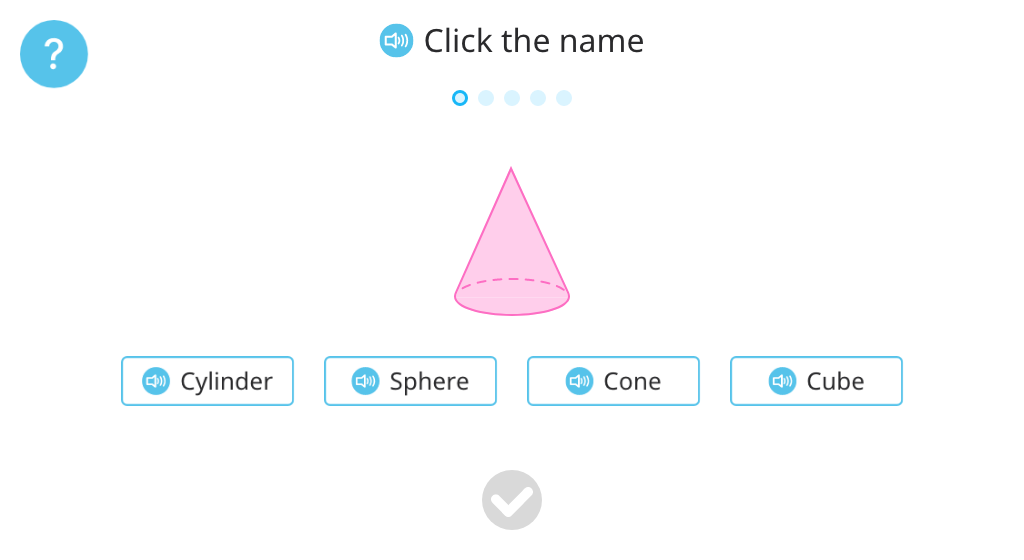
Identify cones from among 3-D shapes

Identify cones and cylinders

Identify cubes from among 3-D shapes

Identify cones, cubes, and cylinders

Identify spheres from among 3-D shapes

Identify cones, cubes, cylinders, and spheres

Identify 3-D shapes by name

Identify 3-D shapes among real-world objects

Identify and position 3D shapes above, below, in front of, or behind an object

Position 3-D shapes above, below, in front of, and behind an object

Practice position terms

Deepen understanding of the terms "next to" and "far from"

Practice using position terms in context

Identify objects in positions above, below, next to, and in front of

Exit ticket: 3-D shapes and relative positions
Topic C: Two-Dimensional and Three-Dimensional Shapes
Students apply their previous understanding of flat and solid shapes to distinguish between the two.
Distinguish between flat and solid shapes

Identify which shape in a set of three is not like the others

Pretest: Comparing numbers up to 10 and sizes
MODULE 3 Comparison of Length, Weight, Capacity, and Numbers to 10
Topic A: Comparison of Length and Height
Using familiar, real objects, students use the language of comparison (tallest, taller, longest, longer, shortest, shorter) as they explore length.
Determine which of two objects is longer or shorter

Identify the longest or shortest object in a set

Compare objects based on longer/shorter

Determine which of two objects is taller

Compare objects based on taller/tallest and shorter/shortest

Topic B: Comparison of Length and Height of Linking Cube Sticks Within 10
Students work with familiar linking cubes to count cubes to determine length of sticks. They compare lengths using longer, shorter, and the same as.
Identify the longer or shorter of two linking cube sticks (aligned and unaligned)

Identify two out of three linking cube sticks that are the same length

Build a stick of a given length of cubes or shorter, longer, the same as a given stick

Complete a statement comparing length of sticks

Identify sticks that are longer than a given length (unaligned)

Topic C: Comparison of Weight
Using familiar, real objects, students use the language of comparison (heavier, lighter, about the same) as they explore weight. To do so, they employ a virtual balance scale to compare.
Determine which of two objects is heavier or lighter

Determine which of two objects on a balance scale is heavier or lighter

Determine which of two balance scales holds objects that are about the same weight

Identify which picture of objects on a balance scale matches a description of their weight (Level 1)

Identify which picture of objects on a balance scale matches a description of their weight (Level 2)

Topic D: Comparison of Volume
Students learn the word capacity and use it to measure the amount of liquid a container can hold. Using the unit "glasses," they measure by pouring glasses into a larger container and by pouring from a larger container into glasses. They also compare measured capacities of two containers.
Identify which of two containers has a greater capacity

Measure capacity by pouring

Compare two containers based on measured capacities

Topic E: Are There Enough?
To prepare for comparing numbers, students work with real world objects to determine if there are "enough" to make pairs. They then determine whether a set of real objects has more than, fewer than, or the same as another set of objects.
Pair objects and determine whether there are enough to complete each pair

Compare paired objects to determine more, fewer, and the same as

Compare sets of objects to determine which shows fewer

Show more, fewer, or the same number of objects as a given set of objects

Topic F: Comparison of Sets Within 10
Students compare two sets of objects using the words "more," "fewer," "greater," and "less." They work with aligned objects and numbers.
Compare sets to determine which shows "more" objects

Use cubes to show "more" than a given set

Count and compare two sets of objects (Part I)

Identify numbers that are greater than others

Compare sets to determine which shows "fewer" objects

Use cubes to show "fewer" than a given set

Count and compare two sets of objects (Part II)

Identify numbers that are less than others

Topic G: Comparison of Numerals
Students compare two sets of objects using the words more, fewer, and same. They work with similar and dissimilar objects, both aligned and scattered, in vertical and horizontal alignments. Finally, they begin to compare numbers.
Explore number path

Use number paths to compare numbers within 10 (Level 1)

Use number paths to compare numbers within 10 (Level 2)

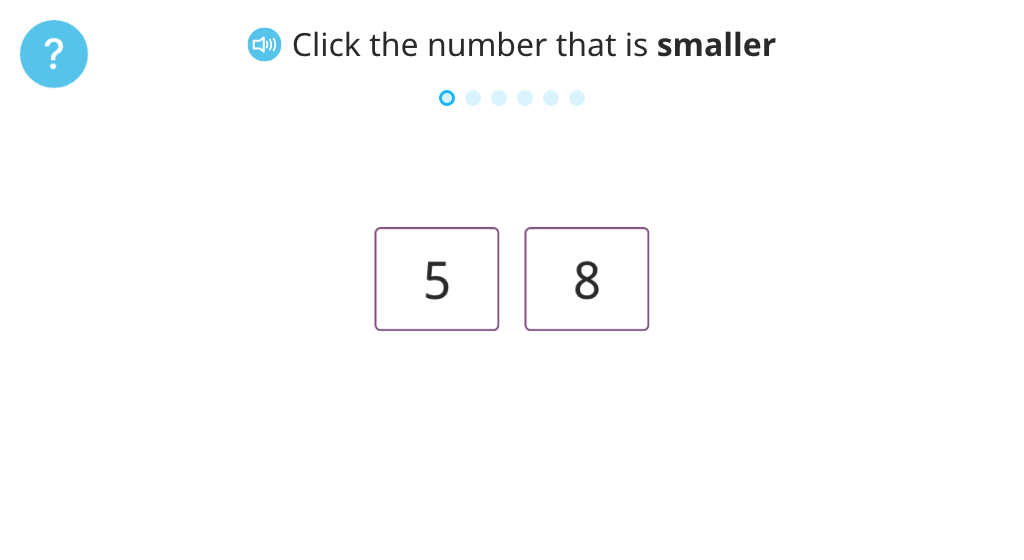
Identify the greater number

Identify the smaller number

Exit ticket: Comparing numbers up to 10 and sizes
MODULE 4 Number Pairs, Addition and Subtraction to 10
Topic A: Addition with totals of 2, 3, 4, and 5
Students learn the basics of addition with totals to 5. They work with real-world objects and math cubes in two colors to represent addends. They learn the meaning and use of the + and = symbols and solve equations based on real-world and cube models. Students also compose number bonds and addition statements based on the models.
Identify totals to 4

Identify totals to 5 and state as addition (Part 1)

Identify totals to 5 and state as addition (Part 2)

Identify and use + and = signs

Solve addition equations to 5 based on a model

Solve addition equations to 5 based on a word problem

Use cubes in two colors to represent a set of real-world objects

Solve addition equations to 5 based on a model of cubes

Solve addition equations to 5

Identify correct addition sentences to 5

Topic B: Addition to 6, 7, and 8
Students extend their addition skills to totals of 8 using familiar tools and methods. They use and build models using real-world objects and math cubes. They compose number bonds, addition statements, and equations.
Identify addition and find the sum

Solve addition equations to 6 based on a model

Solve addition equations to 6 based on a model of cubes

Solve addition equations to 7 based on a model (Part 1)

Model addition to 7 and solve

Solve addition equations to 7 based on a model (Part 2)

Solve addition equations to 8 based on a model

Model addition to 8 and solve

Topic C: Addition concepts to 8
Students deepen their understanding of addition by strengthening the connection between concrete objects, base-10 blocks, and equations. They determine both sums and missing addends. They record equations, including the + symbol.
Identify correct addition sentences to 8

Write addition sentences based on a model and see that different combinations of addends can result in the same sum

Select models that show the same sum and match a model to the correct equation

Sort items by shape and color to create addition models. Identify whether the sums are the same or different in two equations

Observe models and write many addition equations with the same sum

Solve simple word problems with the help of a model and learn where to place the plus sign

Solve word problems by selecting the addition equation that best represents it

Topic D: Subtraction from Numbers to 8
This topic introduces formal subtraction concepts including writing and solving expressions and equations. Students acting out take away stories and working at the pictorial level. Then the concrete objects and pictorial representations are tied to or matched to the representative subtraction expression or equation using the minus sign with no unknown.
Solve subtraction problems (5 or less objects)

Solve more subtraction problems (5 or less objects). Rephrase subtraction as "taking away."

Solve subtraction problems (5 or less objects) phrased as "taking away."

Learn about the meanings of the minus and equals signs

Identify minus and plus signs

Rewrite word problems as subtraction equations

Solve word problems and number sentences involving subtraction within 5

Solve subtraction problems within 5 using picture models for support

Match number sentences to associated word problems

Match linking cubes to a set of objects

Represent subtraction problems with linking cubes. Write number sentences to match models

Use models to complete subtraction number sentences within 5

Solve subtraction equations with and without using linking cube models

Solve expressions involving subtraction of numbers less than 5

More practice solving subtraction equations within 5

Solving subtraction problems using greater numbers (6 or less)

Solve subtraction problems with greater numbers (6 or less) using linking cubes for support

Create number sentences to represent word problems involving subtraction (7 or less)

More practice making number sentences representing subtraction of 7 or less objects

More practice using cubes to model subtraction problems and create number sentences

Select equations that represent a model of subtraction

Write number sentences to represent subtraction problems with support

Topic E: Addition to and decomposition of 9 and 10
Students use the connections between concrete objects, base-10 blocks and equations to build upon their understanding of addition. They find missing addends and sums and record equations, including the + symbol.
Use linking cubes to solve addition sentences to 9

Create models and write corresponding addition sentences

Complete and solve addition equations with linking cube models (Part 1)

Model different ways to compose 8 and 9

Select models that show a given sum (Part 1)

Use linking cubes to solve addition sentences to 10

Complete and solve addition equations with linking cube models (Part 2)

Select models that show a given sum (Part 2)

Use picture models to solve word problems with addition up to 10

Solve word problems by selecting the addition equation that best represents it

Topic F: Subtraction from 9 and 10
Students use the connections between concrete objects, number sentences and word problems to explore subtraction from 9 and 10. They learn to see subtraction as "taking away" and associate the minus sign with subtraction.
Complete and solve subtraction equations with linking cube models

Match pictures to the number sentences

Solve word problems involving subtraction from 8 or 9

Complete and solve equations based on linking cube models that show "taking away"

Solve more number stories involving subtraction from 8 or 9

Match a number sentence to the word problem

Solve word problems involving subtraction from 10

Write number sentences to represent subtraction from 9 and 10

Write number sentences to represent subtraction

Solve subtraction equations within 10

Topic G: Patterns with Adding 0 and 1 and Making 10
Students use concrete objects, a number path, and equations to practice adding and subtracting 0 or 1 from a number. Students find number pairs that make 10 and use ten-frames and cube models to solve missing addend equations.
Solve addition equations by adding 1

Solve subtraction equations by subtracting 1

Review that 0 represents no objects

Add 0 to a number

Subtract 0 from a number

Add or subtract 0 from a number

Add sets of concrete objects to complete a ten-frame

Identify the amount of concrete objects needed to make 10

Identify amounts that make 10 when added together

Identify pairs of numbers that make 10

Identify the missing addend to make 10

Pretest: Numbers and counting to 100

MODULE 5 Numbers 10 - 20 and Counting to 100
Topic A: Count 10 Ones and Some Ones
Students differentiate a "ten" from ones using a ten-frame or rod. They begin to explore the composition of 2-digit numbers and number names. These exercises form a foundation for later learning about place value and addition strategies. Students use a number line for the first time.
Count objects and learn the concept of a ten-frame

Learn the numbers 10-12 using a ten-frame and additional objects

Use cubes and ten-rods to count to 11 and 12

Use a number line and practice the numbers 11 and 12

Learn the numbers 13, 14, and 15 using ten-frames and remaining objects

Count and identify the numbers 13 through 15 using cubes and ten rods

Identify numbers on a number line and reinforce knowledge of numerals 1-15

Learn the numbers 16, 17, 18, and 19 using ten-frames and remaining objects

Learn the number 20

Use a number line to fill in missing numbers, especially focusing on numbers 10-20

Form 2-digit numbers within 20 using ten rods and additional cubes

Count to 2-digit numbers within 20 using partially filled ten frames and additional dots

Topic B: Decompose Numbers 11 - 20, and Count to Answer "How Many?"
Students further their understanding of teen numbers by applying them to positions on a number line and simple equations.
Count to 2-digit numbers within 20 with or without separating a group of ten objects into a ten-frame

View an incomplete number line and put missing 2-digit numbers within 20 in the correct spot

Use 10-frames and remaining dots to add and solve for 2-digit numbers within 20

Count 11 to 19 objects in different arrangements

Decompose numbers 11-20 using models involving 10-frames

Decompose numbers 11-20 without using models

Complete number sentences involving numbers 11-20

Topic C: Extend Count Sequence to 100
Students will explore how multiples of 10 are represented by 10-frames or number names. Students begin to order multiples of 10 on a number path to practice skip-counting by 10s. They begin to see 2-digit numbers as groups of 10 and some 1s.
Use 10-frames to explore multiples of 10 (20, 30)

Use 10-frames to explore multiples of 10 (40, 50)

Match number names to their numeric forms (0-50)

Skip count by 10s to 50, using 10-frames. Identify missing multiples of 10 in a set

Use 10-frames to explore multiples of 10 (60, 70)

Use 10-frames to explore multiples of 10 (80, 90)

Given the number name, identify the numeric form of multiple of 10

Use 10-frames to explore the concept of 100

Match number names to their numeric forms (60-100)

Count by 1s and 10s

Order multiples of 10 on a number path

Begin to understand that 2-digit numbers are composed of multiples of 10 and some ones

Given a number name, identify the numeric form of a 2-digit number

Order 2-digit numbers on a number path

Exit ticket: Numbers and counting to 100