Curriculum for Grade 2
Students master operations in the hundreds, perform exchanges confidently, and take first steps toward multiplication as they rely on number sense, place value understanding, and number flexibility.
MODULE 1. Sums and Differences to 100
Topic A: Foundations for Fluency with Sums and Differences Within 100
Students extend their understanding of addition and subtraction within 100. Use of base-10 blocks reinforces the concept of "tens" and "ones" to build place value understanding. Students move quickly from concrete models to more abstract equations. Students build their fluency with addition and subtraction facts by modeling the underlying concept of exchanging and memorizing number bonds of 10.
Review addition facts with a sum of 10

Adding to groups of ten

Use models to practice addition equations with a one- and two-digit addend

Solve addition equations with a one- and two-digit addend

Use models to solve subtraction equations with a one- and two-digit number

Solve subtraction equations with a one- and two-digit number

Add groups of ten to a two-digit number (Part 1)

Adding one- and two-digit numbers

Use models to solve subtraction equations with two-digit number

Add groups of ten to a two-digit number (Part 2)

Develop fluency with addition and subtraction of one- and two-digit numbers

Topic B: Initiating Fluency with Addition and Subtraction Within 100
Students build fluency with addition and subtraction problems within 100. They use number bonds and base-10 block models to practice the strategy of breaking an addend/subtrahend into parts to make a 10, then solving.
Identify the connection between a number bond and a fact family

Complete number bonds

Use a number bond to make 10

Use number bonds to solve related addition and subtraction equations

Use number bonds to solve addition equations that cross a ten

Solve addition equations that cross a ten, where one addend is 9

Solve more addition equations that cross a ten, where one addend is 8

Solve more addition equations that cross a ten, where one addend is 7

Find the missing subtrahend in subtraction equations

Use number bonds to make 10 and solve subtraction equations

Solve subtraction equations that cross a ten (Level 1)

Solve subtraction equations that cross a ten (Level 2)

Build fluency solving subtraction equations that cross a ten

Subtract single-digit numbers from a tens number, using base-10 blocks for support

Use number bonds and base-10 blocks to subtract a 1-digit number from a 2-digit number

Use number bonds to subtract a 1-digit number from a 2-digit number, crossing a ten
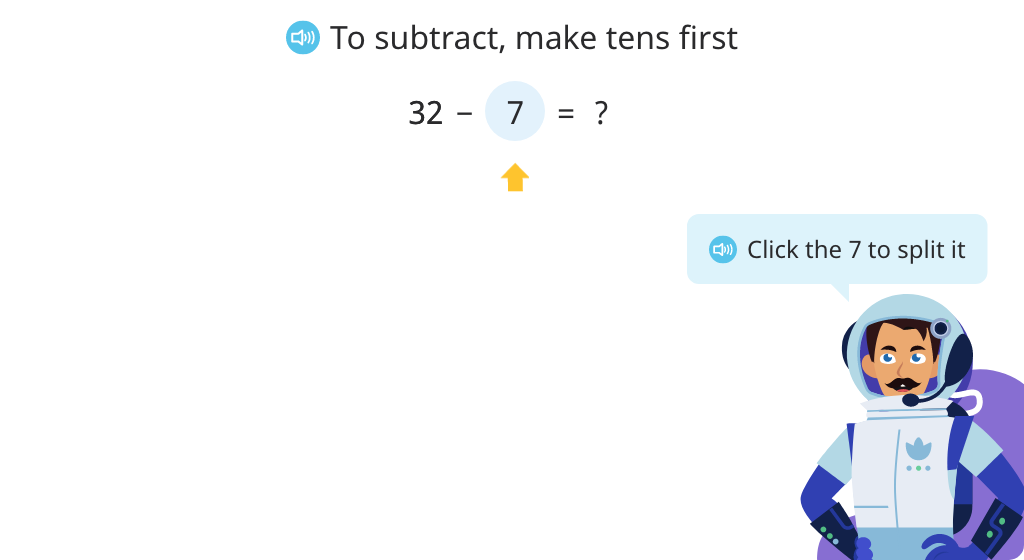
Build fluency solving subtraction equations that cross a tens number

Build fluency solving subtraction equations with a 1- and 2-digit number

MODULE 2. Addition and Subtraction of Length Units
Topic A: Understand Concepts About the Ruler
Students learn the basic principles of linear measure. They measure objects and line segments arranged horizontally, vertically, and randomly. They practice with increasingly abstract units of measure, from real objects to bricks to isolated centimeters to a centimeter ruler. Students learn to align an object to 0 on the ruler to measure length.
Count to measure lengths of objects in non-standard units

Measure lengths of objects from endpoint to endpoint with no gaps or overlaps

Measure lengths of objects by laying non-standard units correctly

Compare lengths measured in different non-standard units

Count to measure lengths of objects in centimeters

Measure lengths of objects aligned to a centimeter ruler

Align objects to a centimeter ruler to measure length

Draw a line segment of a given length

Measure side lengths of 2-D objects using a centimeter ruler

Topic B: Measure and Estimate Length Using Different Measurement Tools
Students explore the ruler to relate millimeters to centimeters. They then convert among millimeters, centimeters, decimeters, and meters using real objects as a frame of reference.
Count to measure lengths of objects in meters

Learn about the relationship between meters and centimeters, and compare the two units of length

Use the greater than, less than, or equal to signs to compare measurements in centimeters and meters. Then, decide which unit fits a situation best

Match estimated lengths and units to objects

Measure approximate lengths of objects aligned to a ruler

Measure the approximate lengths of objects using a meter stick

Topic C: Measure and Compare Lengths Using Different Length Units
Students apply their understanding of measurement to add and subtract lengths using a ruler. They solve the problems of measuring objects that aren't aligned to 0 on the ruler as well as objects that exceed the length of the ruler by using addition and subtraction.
Measure objects that exceed the length of the ruler

Subtract to compare lengths of measured objects

Add or subtract lengths of measured objects

Subtract lengths of measured objects to solve word problems

Topic D: Relate Addition and Subtraction to Length
Students use real objects and abstract objects to determine lengths using addition and subtraction. They subtract to determine length when objects are not aligned to zero on a ruler. Students learn to use tape diagrams to represent and solve addition and subtraction word problems, including those with a missing addend or subtrahend.
Represent change in length as addition or subtraction

Add three measurements to find the total length of a path

Count to determine length of an object that isn't aligned to 0 on a ruler

Subtract to determine length of an object that isn't aligned to 0 on a ruler

Use the difference between two numbers to measure a given object

Use a tape diagram to solve a +/- word problem involving length

Show the question/solution element of a word problem on a tape diagram and solve

MODULE 3. Place Value, Counting, and Comparison of Numbers to 1000
Topic A: Forming Base Ten Units of Ten and Hundred
Students reinforce their counting and place value skills to three-digit numbers to 200. They will use base ten blocks to practice finding place values less than 200.
Count by tens up to one hundred

Use base ten blocks to determine the number

Build the number using base ten blocks

Topic B: Understanding Place Value Units of One, Ten, and a Hundred
Students will apply their counting, reading, and place value skills to three-digit numbers. They will use the base-ten block model to identify and build three-digit numbers. They strengthen their conceptual understanding of counting patterns and practice skip counting by ones, fives, tens, and hundreds.
Counting by hundreds

Build three-digit numbers with base ten blocks

Skip counting by ones and tens

Skip counting by fives and hundreds

Identify and continue the pattern

Topic C: Three-Digit Numbers in Unit, Standard, Expanded, and Word Forms
Students learn to represent the same number in different ways, including standard, unit, word, and expanded forms. They will apply their knowledge of place value to understand how numbers are converted between forms.
Represent numbers using a place value chart

Explore numbers in standard form

Explore numbers in unit form

Explore numbers in word form

Explore numbers in expanded form

Identify the value of numerals in 3-digit numbers

Rewrite numbers in expanded form

Review unit form

Review standard, unit, and word forms

Represent numbers in different forms

Topic D: Modeling Numbers Within 1,000 with Place Value Disks
Students are introduced to the thousand cube base-10 block as they build their concept of a thousand. They also explore the relationships between ones, tens, hundreds, and thousands as well as the count sequence using familiar representations.
Recognize and represent 2-digit numbers as tens and ones (Part 1)

Recognize and represent 2-digit numbers as tens and ones (Part 2)

Recognize and represent 3-digit numbers as hundreds, tens, and ones

Recognize and represent 3-digit numbers with placeholder zeros as hundreds, tens, and ones

Determine how many more ones, tens, or hundreds to reach the next ten, hundred, or thousand using a number line (Level 1)

Convert among ones, tens, hundreds, and thousands using number and unit notation

Convert among ones, tens, hundreds, and thousands using unit notation

Review the concept of 1s, 10s, and 100s to build understanding of 1000

Convert among ones, tens, hundreds, and one thousand using base-10 blocks

Review conversion values among ones, tens, hundreds, and one thousand

Topic E: Comparing Two Three-Digit Numbers
Students develop their deep understanding of place value to compare and order three-digit numbers. They master common pitfalls, such as placeholder zeros and transposed numbers. Students move from using base-10 models and place value cards to visual recognition of number order and place value.
Use >, =, and < to compare a two-digit number with a three-digit numberUse >, =, and < to compare a two-digit number with a three-digit number

Use >, =, and < to compare at the hundreds place based on a model of base-10 blocks

Use >, =, and < to compare at the hundreds place with and without place value cards

Use >, =, and < to compare at the tens place based on a model of base-10 blocks

Use >, =, and < to compare at the tens and ones place based on place value cards

Use >, =, and < to compare at the hundreds and tens place

Use >, =, and < to compare numbers with placeholder zeros

Use >, =, and < to compare numbers with placeholder zeros based on a model of base-10 blocks

Use >, =, and < to compare numbers with similar digits

Arrange three-digit numbers in ascending order (Level 1)

Arrange three-digit numbers in ascending order (Level 2)

Arrange three-digit numbers in ascending order (Level 3)

Topic F: Finding 1, 10, and 100 More or Less Than a Number
Students build number sense by working with 1, 10, and 100 more or less than 2- and 3-digit numbers. They begin with the support of a disk model using a place value chart. Students explore counting patterns up and down.
Determine 10 or 100 more with and without a place value chart

Determine 10 or 100 less with and without a place value chart

Determine 1/10/100 more or less (Part 1)

Determine 1/10/100 more or less (Part 2)

Determine 1/10/100 more or less (Part 3)

Compare using 1, 10, or 100 more or less

Determine 1 or 10 more across place values

Determine 1 or 10 less across place values

Count up and back by 1s (3-digit numbers)

Count up and back by 10s or 100s (3-digit numbers)

Counting patterns (Level 1)

Count up by 10s

Count up by 1s and 100s

Counting patterns (Level 2)

MODULE 4. Addition and Subtraction Within 200 with Word Problems to 100
Topic A: Sums and Differences Within 100
Students practice strategies for solving 2-digit +/- problems with and without exchanging. They use familiar representations (base-10 blocks and place value cards) and new strategies (decomposing numbers and making tens) to solve equations.
Use base-10 blocks to add a 2-digit number to a tens number

Add a 2-digit number to a tens number, without a model

Use base-10 blocks to add 2-digit numbers

Use understanding of place value to solve addition equations

Solve addition equations with 2-digit numbers

Solve more addition equations with 2-digit numbers

Use base-10 blocks to solve addition equations requiring exchanges

Use place value cards to solve addition equations requiring exchanges

Solve 2-digit addition problems without a model

Use base-10 models to solve subtraction equations

Solve 2-digit subtraction equations

Decompose 2-digit numbers

Decompose numbers as a strategy to solve 2-digit subtraction equations

Solve more 2-digit subtraction equations by decomposing numbers

Use making tens as a strategy to solve 2-digit subtraction equations

Use number bonds to solve 2-digit subtraction equations

Topic B: Column Addition with Exchanging into the Tens
Students use familiar manipulatives to guide them into using column addition with understanding. They begin by using the strategy of adding all tens and all ones and then combining the two. Then, they move into 2- and 3-digit column addition with and without exchanging ones for a ten.
Identify and build numbers using 10s and 1s on a place value chart

Use a place value chart to add 2-digit numbers

Solve 2-digit column addition without exchanging using a place value chart model

Add 2-digit numbers without exchanging (Part 1)

Add 2-digit numbers without exchanging (Part 2)

Exchange 1s for 10s on a place value chart when necessary

Solve 2-digit column addition with regrouping with the support of a place value chart model

Solve 2-digit column addition with regrouping using the standard algorithm

Add 2-digit numbers with exchanging (Part 1)

Add 2-digit numbers with exchanging (Part 2)

Practice the standard algorithm for addition with regrouping with step by step support (Part 1)

Practice the standard algorithm for addition with regrouping with step by step support (Part 2)

Practice column addition with one 3-digit and one 2-digit addend

Practice the standard algorithm of 2-digit column addition with regrouping (Part 1)

Practice the standard algorithm of 2-digit column addition with regrouping (Part 2)

Topic C: Column Subtraction with Exchanging into the Tens
Students use familiar manipulatives to guide them into using column subtraction with understanding. Students learn to determine whether or not an exchange is needed and, if so, how to do so with understanding. Then, they move into 2- and 3-digit column subtraction with and without exchanging a ten for ones.
Solve subtraction problems using disk models

Use disk models to support solving column subtraction

Solve column subtraction with scaffolding

Use disk models to practice exchanging into the tens

Solve subtraction problems with regrouping (Level 1)

Solve subtraction problems with regrouping (Level 2)

Solve subtraction problems with regrouping (Level 3)

Solve subtraction problems with regrouping (Level 4)

Solve subtraction problems with regrouping (Level 5)
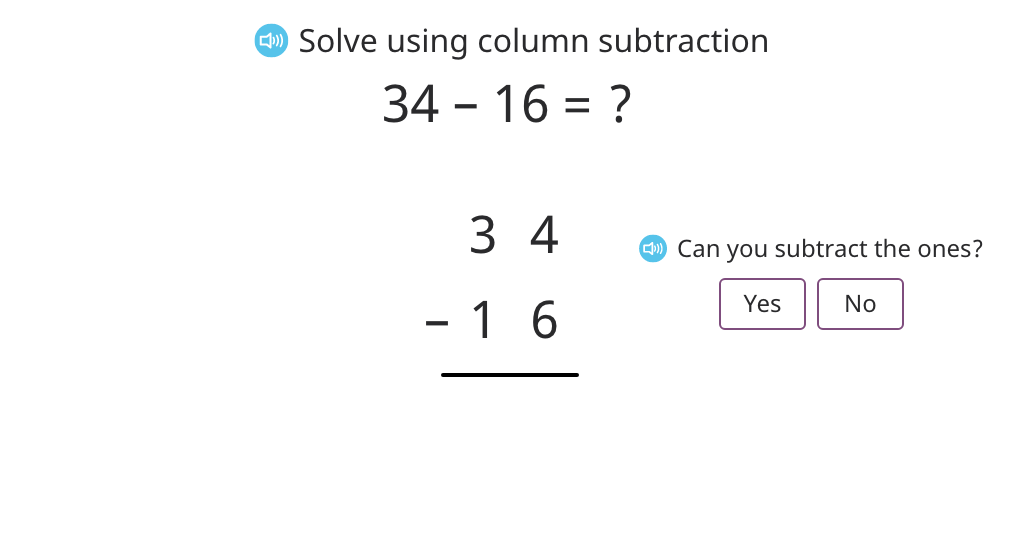
Solve column subtraction, making decisions about exchanging into the tens

Practice solving column subtraction problems independently (Part 1)

Practice solving column subtraction problems independently (Part 2)

Solve column subtraction problems with 2- and 3-digit components (Level 1)

Solve column subtraction problems with 2- and 3-digit components (Level 2)

Solve column subtraction problems with 2- and 3-digit components (Level 3)

Topic D: Column Addition with Exchanging into the Hundreds
Students build on their understanding of column addition and exchanging to move into the hundreds place. Disk models and step-by step prompting help ensure conceptual understanding and procedural fluency. A gradual release model helps students become independent with these multi-step problems.
Exchange 1s for 10s and 10s for hundreds on a place value chart. Write the corresponding number

Solve addition problems involving exchanging 1s and 10s using a place value chart for support

Practice column addition with exchanging alongside a place value chart

Use the standard algorithm of 2-digit column addition with regrouping into the hundreds (Part 1)

Use the standard algorithm of 2-digit column addition with regrouping into the hundreds (Part 2)

Use the standard algorithm to solve for various combinations of addends of 2 or 3 digits and with or without regrouping into the hundreds

Topic E: Column Subtraction with Exchanging into the Hundreds
Students build on their understanding of column subtraction and exchanging to move into the hundreds place. Step-by step prompting helps ensure conceptual understanding and procedural fluency. A gradual release model helps students become independent with these multi-step problems.
Solve 2- and 3-digit column subtraction equations by exchanging 100 for 10 tens to solve

Solve more 2- and 3-digit column subtraction equations by exchanging 100 for 10 tens with or without prompts

Solve 2- and 3- digit column subtraction equations with and without exchanging into the hundreds

Solve 2- and 3-digit column subtraction equations by exchanging into the 10s and 100s (Level 1)

Solve 2- and 3-digit column subtraction equations by exchanging into the 10s and 100s (Level 2)

Solve 2- and 3-digit column subtraction equations by exchanging into the 10s and 100s (Level 3)

Solve 2- and 3-digit column subtraction equations with and without exchanging into the hundreds and tens

MODULE 5. Addition and Subtraction Within 1,000 with Word Problems to 100
Topic A: Mental Strategies for Addition and Subtraction Within 1,000
Students work with 2- and 3-digit round numbers to develop strategies for mental addition and subtraction. The first strategy teaches them to add on/subtract to the nearest hundred and then add on/subtract what's left. The second strategy teaches students to add on/subtract all of the hundreds and then add on/subtract all of the tens. Both strategies are supported by manipulatives such as a disk model and number line.
Add and subtract 3-digit numbers with no tens or ones

Add 3-digit round numbers with and without using a disk model

Subtract 3-digit round numbers with and without using a disk model

Add a 2-digit round number to a 3-digit round number by adding hundreds, tens, then ones

Add up to the next hundred with and without using a number line model

Add a 2-digit number to a 3-digit number using the "Make the Next Hundred" strategy (Part 1)

Add a 2-digit number to a 3-digit number using the "Make the Next Hundred" strategy (Part 2)

Add a 2-digit round number to a 3-digit round number using mental math

Subtract a 2-digit round number from a 3-digit round number by subtracting hundreds, tens, then ones

Subtract to the next hundred with and without using a number line model

Subtract a 2-digit number from a 3-digit number using the "Make the Previous Hundred" strategy (Part 1)

Subtract a 2-digit number from a 3-digit number using the "Make the Previous Hundred" strategy (Part 2)

Subtract a 2-digit round number from a 3-digit round number using mental math

Break a 3-digit number into hundreds and a 2-digit number

Add 3-digit numbers by adding on the hundreds first

Add 3-digit numbers using mental math

Add 3-digit numbers with exchanging by adding on the hundreds first
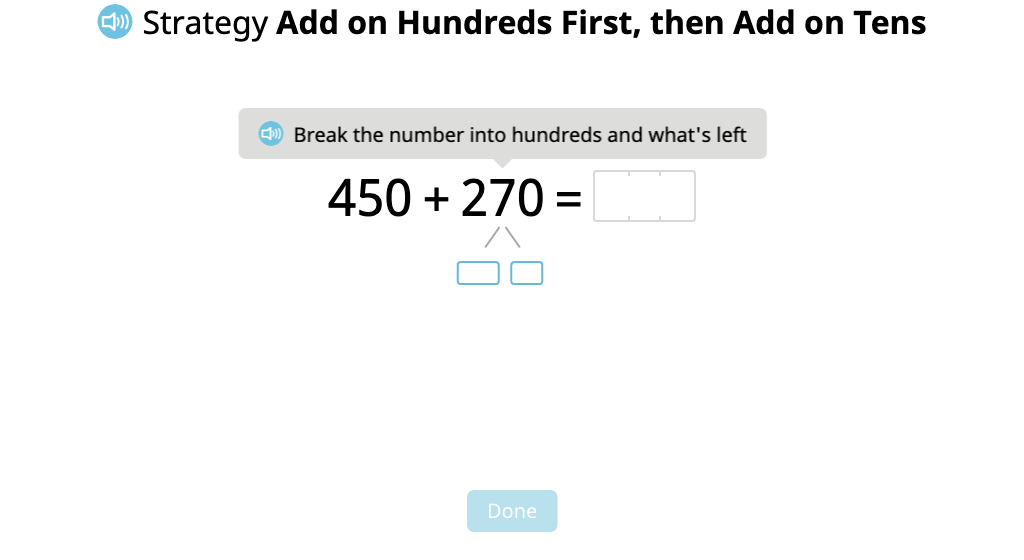
Add 3-digit numbers with exchanging using mental math

Subtract 3-digit numbers by subtracting the hundreds first

Subtract 3-digit numbers using mental math

Subtract 3-digit numbers with exchanging by subtracting the hundreds first

Subtract 3-digit numbers with exchanging using mental math

Topic B: 3-Digit Column Addition
Students use column addition to add 3-digit numbers with one or more exchanges. A gradual release model helps students become independent with these multi-step problems.
Solve 3-digit column addition with exchanging ones using a disk model

Solve 3-digit column addition with exchanging ones or tens

Solve 3-digit column addition with multiple exchanges (Level 1)

Solve 3-digit column addition with multiple exchanges (Level 2)

Topic C: 3-Digit Column Subtraction
Students use column subtraction to subtract 3-digit numbers with one or more exchanges. A gradual release model helps students become independent with these multi-step problems.
Solve 3-digit column subtraction with exchanging with and without using a disk model

Solve 3-digit column subtraction with multiple exchanges

Model 2-step exchanges in subtraction problems using a disk model

Solve 3-digit column subtraction with 2-step exchanges with and without using a disk model

Solve 3-digit column subtraction with 2-step exchanges

MODULE 6. Foundations of Multiplication and Division
Topic A: Formation of Equal Groups
Students work with identical real-world objects to form equal groups given either the number of groups or the number of objects to put in each group. They also determine the number of groups, the number of objects in each group, and the total number of objects. Students relate repeated addition number sentences to visual representations of equal groups.
Counting real-world objects and equal groups (Part 1)

Counting real-world objects and equal groups (Part 2)

Using sets of real-world objects as models for repetitive addition equations

Making two equal groups (Part 1)

Making equal groups (Part 2)

Making sets of a particular number (Part 1)

Making sets of a particular number (Part 2)

More practice counting real-world objects and equal groups

Using sets of equal groups to solve repetitive addition equations

Representing sets of equal groups as a repetitive addition equation

Topic B: Arrays and Equal Groups
Students explore the concepts of rows and columns using objects. They begin to learn to describe arrays in terms of their columns and rows, as well as through repeated addition.
Explore the concept of rows

Explore the concept of columns

Identify arrays by the number of columns

Identify the number of columns and the objects within them

Identify arrays by the number of rows

Identify the number of rows and the objects within them

Label arrays with the number of rows and columns

Compose a repeated addition sentence based on an array's rows

Compose a repeated addition sentence based on an array's columns

Represent arrays as their number of rows and objects and as repeated addition sentences

Describe arrays in terms of their columns and rows

Topic C: Rectangular Arrays as a Foundation for Multiplication and Division
Students begin to work with arrays composed of a grid of squares. As in the previous topic, they determine the number of objects in each column/row and the total number of objects, then use repeated addition to represent the array.
Find the total for an array model in terms of rows

Find the total for an array model in terms of columns

Find the total for the same array model in terms of rows and columns

Compose a repeated addition equation for an array in terms of rows

Compose a repeated addition equation for an array in terms of columns

Given the number of rows and squares, create an array and solve for the total

Given the number of columns and squares, create an array and solve for the total

Topic D: The Meaning of Even and Odd Numbers
Students explore the concept of even and odd in multiple ways. They determine that the sum of two equal addends is even. They use pairing, addition patterns, and number line patterns to determine even and odd. They also use ending digits to determine even or odd in numbers up to three digits.
Add two equal addends to get an even number sum

Pair objects to determine whether the total is even

Determine whether a set of objects is even or odd

Identify how addition pattern of +1 or +2 relates to even and odd

Determine whether a hidden number on a number line is even or odd

Identify even numbers as ones ending in 0, 2, 4, 6, or 8

Identify odd numbers as ones ending in 1, 3, 5, 7, or 9

Identify several digit numbers as even or odd

Determine if a given number is even or odd based on the final digit

Identify 3-digit numbers as odd or even

MODULE 7. Problem Solving with Length, Money, and Data
Topic A: Displaying and Interpreting Categorical Data
Students create bar graphs to represent and interpret categorical data. They solve problems like finding the number of objects in each category, identifying the least/greatest or equal categories, and finding the total amount represented.
Create picture and bar graphs to represent data

Use bar graphs to represent and interpet data

Calculate the total number of objects represented by a bar graph

Identify the largest and smallest categories and their amounts on a bar graph

Interpret data to answer questions about a bar graph (Level 1)

Interpret data to answer questions about a bar graph (Level 2)

Topic B: Coins and Their Values
Students explore the heads and tails sides of the penny, nickel, dime, and quarter. They learn the value of each coin, how to count a collection of them, and how to count a mixed collection of coins. Students match coin image, name, and value.
Identify a penny and its value

Identify a dime and its value

Match a penny or dime to its name, appearance, and value

Identify the total value of a collection of dimes and pennies

Exchange between one dime and ten pennies

Identify a nickel and its value

Match a penny, nickel, or dime to its name, appearance, and value (Part 1)

Match a penny, nickel, or dime to its name, appearance, and value (Part 2)

Identify a penny, nickel, or dime based on color or size

Exchange between pennies, nickels, and dimes

Show a given total using nickels and pennies

Identify a quarter and its value

Topic C: Creating an inch ruler
Students refine their ruler-using skills as they measure various objects using different units of length. In addition, they compare different lengths and units of measurement including centimeters, inches, and feet.
Compare different units of length and measure objects using centimeters and inches

Align 0 on the ruler with the endpoint of objects being measured

Use a ruler to make approximate measurements by rounding up or down to the nearest inch

Measure the sides of rectangles and compare their lengths

Students learn about feet as a unit of measurement

Topic D: Displaying and Interpreting Measurement Data
Students picture graphs and line plots based on measurements of length. They interpret the data from these representations, including how many objects, their lengths, and the total.
Build a picture graph based on measurement data

Answer questions based on a picture graph

Create and interpret data from a line plot

Answer questions based on a line plot (Level 1)

Answer questions based on a line plot (Level 2)

Identify the shortest objects on a line plot and their length

Identify the longest objects on a line plot and their length

Identify the column on a line plot representing the minimum measurment

Identify the column on a line plot representing the maximum measurment

MODULE 8. Time, Shapes, and Fractions as Equal Parts of Shapes
Topic A: Attributes of Geometric Shapes
Students build on their prior knowledge of a shape's defining attributes to recognize and draw categories of polygons with specified attributes: the number of sides, corners, and angles. For example, students see that a rectangle has four straight sides, four right angles, and opposite sides with equal length. Students then relate the square, a special rectangle, to the cube by building a cube from six congruent squares. They describe the cube in terms of its attributes, counting the number of edges, faces, and corners.
Discover that every geometric shape is made up of sides and angles

Discover the attributes of a quadrilateral

Determine if a given shape is or is not a quadrilateral

Draw triangles and quadrilaterals
Match a given label to the corresponding shape

Discover the attributes of a hexagon

Learn that triangles, quadrilaterals, and hexagons are all polygons

Discover the attributes of a pentagon

Identify pentagons based on their attributes

Identify different types of polygons

Answer questions that compare polygons

Discover the attributes of a cube

Topic B: Composite Shapes and Fraction Concepts
Working with triangles and squares, students rotate shapes to fill a pattern. They learn that the number of pieces in the whole are called halves, thirds, fourths, and sixths based on the total number.
Rotate and align two indentical triangles to fill a pattern

Rotate and align triangles and a square to fill a pattern

Rotate and align triangles that are halves, thirds, fourths, and sixths of a pattern

Create different shape patterns using the same three thirds or four fourths

Topic C: Halves, Thirds, and Fourths of Circles and Rectangles
Students build upon their knowledge of halves, thirds, and fourths to answer more complex questions about fractional parts of shapes. They split shapes into given fractions, identify the size of fractional parts, and tell how many parts make a whole.
Identify shapes that are split into halves

Split shapes in half and complete the missing half of shapes

Identify shapes that are split into thirds and split shapes into thirds

Identify shapes that are split into fourths and split shapes into fourths

Sort shapes that are split into halves, thirds, and fourths

Identify parts of a whole in shapes split into halves, thirds, and fourths

Identifying the number of pieces in a shape split in halves, thirds, and fourths

Topic D: Application of Fractions to Tell Time
Students begin with the basics of telling time - identifying the hour and minute hands on a clock, counting around the minutes on a clock, and telling time to the hour and half hour. They progress to telling time to 15 minutes and to 5 minutes, identifying noon and midnight, and using a.m. and p.m. Throughout, students use analog clocks, digital times, and words.
Read and write time to the hour

Identify a half hour as 30 minutes and an hour as 60 minutes

Tell time to the half hour and write time to the hour

Tell time to quarter past and quarter to the hour

Tell time to 15 minutes and show a given time on a clock

Tell time to 5 minutes

Identify midnight and noon

Use a.m. and p.m. in telling time
