Curriculum for Grade 1
Students look under the hood of addition and subtraction, applying place value understanding to 2-digit operations.
MODULE 1. Sums and Differences to 10
Topic A: Embedded Numbers and Decompositions
Students learn addition to 5 using concrete objects, abstract objects and equations. They learn the meaning and proper use of + and = signs, as well as the terms "addend" and "sum."
Count two addends and determine the total

Determine total number of objects and determine its two addends

Use the + and = signs in an equation

Identify addends and sum in an equation

Compose an addition equation based on a picture

Represent objects with cubes

Compose addition equations based on cubes, and solve equations with and without cubes

Solve addition equations

Topic B: Counting On from Embedded Numbers
Students learn addition to 10 using concrete objects, abstract objects, equations and number bonds. They solve for missing addend problems and begin to represent and solve word problems.
Add 0 to a number

Use the + sign in an equation and find the sum

Model and solve an addition equation

Record an addition equation based on a model to show more than one way to reach a given sum

Show more than one way to reach a given sum

Solve an addition equation (totals to 7)

Identify parts of an addition equation

Record an addition equation based on a model and create a model to show more than one way to reach a given sum

Solve addition equations to 10 with or without a model

Solve an addition equation (totals to 10)

Model and solve an addition word problem with objects

Model and solve an addition word problem with cubes

Write and solve an addition equation based on a word problem

Determine the missing addend based on a model of cubes

Determine the missing addend based on a cubes model

Counting on with cube models

Determine the missing addend in an equation (Part 1)

Determine the missing addend in an equation (Part 2)

Use a cube model to determine the missing addend

Determine the missing addend in an equation (Part 3)

Determine the missing addend in an equation

Choose two addends to reach a given total

Solve missing addend addition equations

Identify addends with a sum of 10

Identify a number bond

Build a number bond based on a model of cubes

Build a number bond based on a model of cubes and complete its addition equation

Build a model, number bond, and equation

Complete a number bond

Complete a number bond to show more than one way to reach a given total

Determine the missing addend in a number bond

Topic C: Development of Addition Fluency Within 10
Students reinforce their understanding of addition within 10 and its underlying concepts as they build more efficient strategies to solve problems. They use addition scenarios with objects, base-10 block patterns, the number line, and equations to reinforce the relationships among fact families. They build upon existing knowledge of composition of numbers 6-10 as they move from the concrete to the abstract.
Identify a missing addend in equations with a sum and their turnaround facts

Record a model of base-10 blocks as an addition equation

Identify the missing addend in equations paired as turnaround facts with sums of 4, 5, 6 and 7

Solve for a missing addend in an equation

Identify the missing addend in equations paired as turnaround facts with sums of 6, 7, 8 and 9

Choose the correct sum for an addition expression

Identify the missing addend in equations paired as turnaround facts with sums of 9 and 10

Topic D: The Commutative Property of Addition and the Equal Sign
Students learn about the commutative property of addition by comparing addition expressions with the same addends, but in a different order. In addition, students practice making expressions equal to each other by filling in the missing addend. Finally, students are introduced to the equal sign as a way to show that two expressions are equal or the same.
Solve simple addition equations and observe that changing the order of the addends doesn't change the sum

Explore expressions and reinforce the commutative property of addition

Make equal expressions and solve equations with the same addends in a different order

Identify and create equal and non equal addition expressions

Use the equal sign to show and create equal expressions

Identify whether number sentences are true and false

Topic E: Subtraction as an Unknown Addend Problem
Students build their understanding of subtraction as its relate to addition. They move from the concrete to the abstract to solve problems. They use number bonds to relate addition and subtraction facts.
Explore the concept of "taking away" with concrete objects

Use minus and equal signs to rewrite "taking away" as subtraction

Complete subtraction number sentences using concrete objects

Match sets of cubes to real objects to model "taking away"

Complete subtraction number sentences using a cube model

Compose and solve subtraction equations

Take away cubes to match and solve a subtraction equation
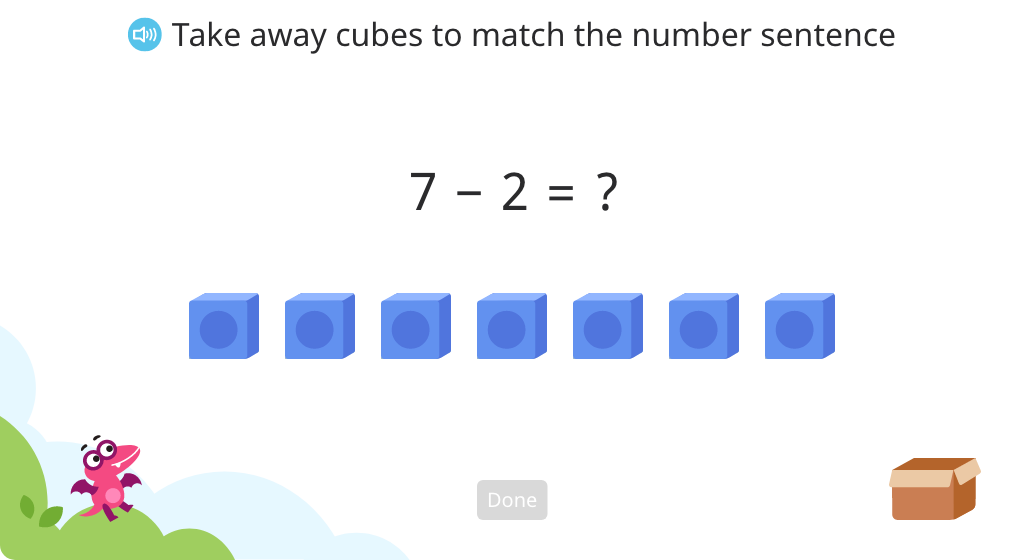
Solve subtraction equations within 7

Write a full subtraction equation to match a cube model

Use cubes to model subtraction from 8, 9, and 10

Solve subtraction equations from 8, 9, and 10

Solve subtraction equations within 10

Addition and subtraction as types of expressions

Sort expressions into addition and subtraction

Complete number bonds and relate them to subtraction number sentences

Explore how addition and subtraction equations are related through number bonds

Identify the missing parts of related addition and subtraction facts

Identify members of a fact family from a given set of equations

Topic F: Decomposition Strategies for Subtraction
Students reinforce their understanding of subtraction within 10 and its underlying concepts as they build more efficient strategies to solve problems. They explore the relationship between addition and subtraction and work increasingly with 0 as a subtrahend and difference. They use subtraction scenarios with objects, base-10 block patterns, the number line, and equations to reinforce the relationships among fact families. They build upon existing knowledge of composition of numbers 6-10 as they move from the concrete to the abstract.
Record a scenario based on objects as a subtraction equation with a difference of 0 (Part 1)

Record a number line scenario as a -0 subtraction equation

Record a number line scenario as a subtraction equation with a difference of 0

Identify missing numbers in subtraction equations with a difference of 0

Subtract by moving an object backward on a number line and solve a related equation that shows subtraction from 3, 4, or 5

Record a number line scenario as an equation that shows subtraction from 3, 4, or 5

Record a scenario based on objects as a subtraction equation with a difference of 0 (Part 2)

Use base-10 blocks to represent subtraction scenarios with objects within 5 and identify base-10 block patterns that represent subtraction scenarios with objects within 5

Solve equations based on a model of base-10 blocks to subtract 1 or all but 1

Record a model of base-10 blocks as two related equations that show subtraction from 6

Record a model of base-10 blocks as two related equations that show subtraction from 7 or 8

Subtract by moving an object backward on a number line and solve a related equation that shows subtraction within 7

Record a model of base-10 blocks as two related equations that show subtraction from 9 or 10

Identify missing numbers in subtraction equations from 9

Topic G: Development of Subtraction Fluency Within 10
Students reinforce the relationship between addition and subtraction and the relationships among fact families. They use familiar objects, base-10 blocks, the number line, and equations to explore the composition of numbers 3-10. They build speed and accuracy with all +/- facts within 10.
Identify a number line model that represents a subtraction scenario given in words

Identify missing numbers in subtraction equations from 4, 5, and 6

Identify missing numbers in subtraction equations from 6 and 7

Choose matching subtraction expression and difference

Identify missing numbers in subtraction equations from 7 and 8

Identify missing numbers in subtraction equations from 8 and 9
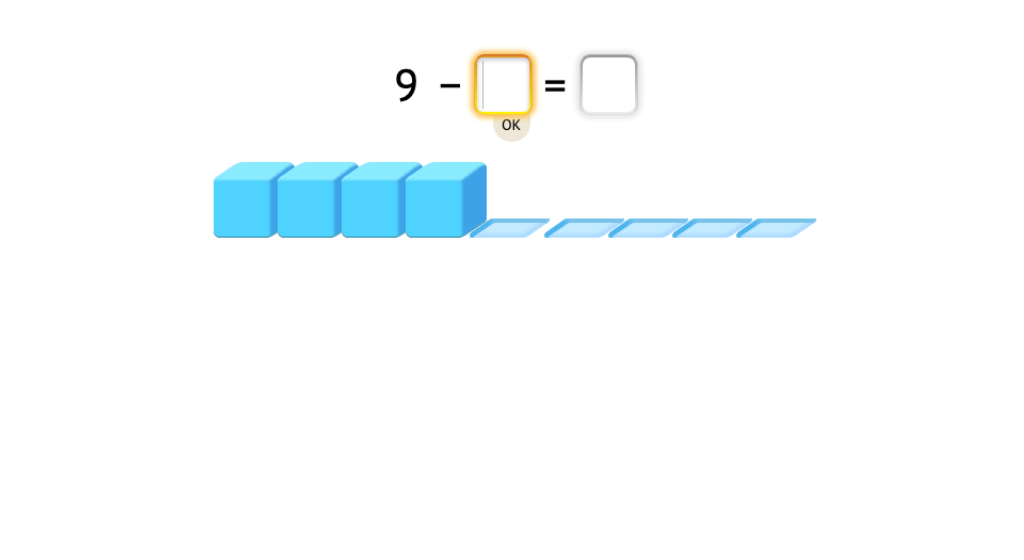
Determine the missing element in a subtraction equation

Identify missing numbers in subtraction equations from 9 and 10

MODULE 2. Introduction to Place Value Through Addition and Subtraction Within 20
Topic A: Counting On or Making Ten to Solve Result Unknown and Total Unknown Problems
Students reinforce their understanding of "tens" and "ones" while sorting, counting, adding, and subtracting. They use objects, base-10 blocks, the number line, and a ten-frame. They practice various strategies to add across 10 and increase fluency with +/- facts within 20.
Reinforce knowledge of numbers 11-20 by adding a single digit to the number ten

Discover the addends to make ten

Determine the missing addend

Practice with ten frames

Use ten frames to explore equations and determine the sum

Use base ten blocks to make ten then find the sum

Use base ten blocks to determine the sum

Introduction to equations with three addends

Making 10 to solve three-addend equations

Decomposing addends in order to make ten then adding to find the sum

Continued practice decomposing addends to solve an equation

Demonstrate knowledge of missing addend to make ten

Use the strategy of making ten to solve addition equations

Solving using a number bond

Using number bonds to solve addition equations

Continued practice using number bonds to solve addition equations

Demonstrate proficiency or practice with assistance

Solve the addition equations with sums of 11-16 to combine objects

Solve the addition equations with sums of 11-16

Solve the addition equations with regrouping

Topic B: Counting On or Taking from Ten to Solve Result Unknown and Total Unknown Problems
Students will use the strategy of making 10 to solve subtraction problems. They will use number bonds to break elements of subtraction equations into useful parts. Then, students will adapt these strategies to solving subtraction problems mentally.
Solve subtraction problems taking from 10

Subtract single digits from numbers 11-19 to make 10

Subtract the digit in the ones place from numbers 11-19 to make 10

Find the unknown number in subtraction problems to make 10

Solve subtraction problems beginning with a number from 11-15 and crossing 10

Use the strategy of making 10 to solve subtraction equations

Introduce subtraction across 10 using base-ten blocks

Model subtraction across 10 using base-ten blocks and knowledge of number bonds

More practice subtracting across 10 with base-ten blocks

Use number bonds to break down components of subtraction equations; use two equations to solve

Use number bonds to break down components of subtraction equations; use one equation to solve

Solve subtraction equations by using the strategy of making 10

Solve subtraction equations that cross 10

Topic C: Varied Problems with Decompositions of Teen Numbers as 1 Ten and Some Ones
Students explore place value as they add and subtract across 10. They use multiple representations (objects, ten-frame, number line, base-10 blocks, and equations) to move from the concrete to the abstract. Students build their fluency with +/- facts within by reinforcing the underlying concept of exchanging and using the strategy of "resting" on 10. They also solve +/- problems in which all ones or all tens are added or subtracted.
Solve substraction equations that include the number 10

Complete equations that add or subtract all tens or all ones with and without a model of base-10 blocks

Add ones to numbers in the second ten using base-10 blocks

Subtract from numbers 11-20 using base-10 blocks

Solve +/- equations that use numbers in the second ten and a single-digit number (Part 1)

MODULE 3. Ordering and Comparing Length Measurements as Numbers
Topic A: Indirect Comparison in Length Measurement
Students use familiar, real objects to build their sense of length comparison. They determine the longest, shortest, longer, and shorter among objects, even when not aligned.
Identify the longer or shorter of two objects and align objects to compare length

Identify the statement that correctly compares the length of two objects

Identify the shortest or longest object in an unaligned set of three objects

Arrange a set of aligned objects according to length

Topic B: Non-Standard Length Units
Students use paper clips as a non-standard unit of length to measure objects. They learn that units must measure from endpoint to endpoint with no gaps or overlaps.
Count to measure lengths of objects

Measure lengths of objects from endpoint to endpoint with no gaps or overlaps

Identify which of two objects is measured correctly

Measure lengths of objects by laying units correctly

Topic C: Data Interpretation
Students count real objects and use tally marks or bar graphs to represent them. They interpret data presented in tables and graphs, and use it to find total, how many more, and how many fewer.
Make tally marks to count up to 5 objects

Identify totals of tally marks (Part 1)

Identify totals of tally marks (Part 2)

Interpret data in a table using tally marks (Level 1)

Interpret data in a table using tally marks (Level 2)

Interpret data in a 1-category bar graph

Create a 2-category bar graph and use it to interpret data

Interpret data in 2-category bar graphs

Interpret horizontal bar graphs and find the difference between 2 categories

Interpret vertical bar graphs and find the difference between 2 categories

Interpret vertical bar graphs to find "how many fewer" between 2 categories

Write and solve subtraction equations to find the difference between 2 categories

Interpret data in a 3-category bar graph (Part 1)

Interpret data in a 3-category bar graph (Part 2)

MODULE 4. Place Value, Comparison, Addition and Subtraction to 40
Topic A: Tens and Ones
Students will explore the concept of 2-digit numbers and place value. Students will begin to understand that 2-digit numbers represent a value of tens and some ones. They will have the support of base-10 blocks, number lines, and 10-frames.
Decompose numbers 11-19 into a group of 10 and some ones

Practice with number words 0-50

Practice with number lines showing 10-100

More practice with number lines showing 0-50

Review the difference between letters and digits. Learn about 1- and 2-digit numbers

Learn about the concept of 10-frames

Represent groups of ten as 2-digit numbers

Review the concept of tens written as a 2-digit number

Represent 2-digit numbers as groups of ten and some ones

More practice making equivalencies between groups of ten and some ones and 2-digit numbers

Write a 2-digit number to represent tens and ones

Identify place value within a 2-digit number

More practice identifying place value within 2-digit numbers

Complete number sentences breaking 2-digit numbers into tens plus some ones

Topic B: Comparison of Pairs of Two-Digit Numbers
Students compare and order numbers, reinforcing their understanding of place value and sequence. They use familiar base-10 blocks, number line, and begin using inequality signs.
Count and compare sets of objects

Explore with > and < signs when counting and comparing objects

Use >, =, and < to compare two single-digit numbers

Use >, =, and < to compare at the ones and tens place, using base-10 blocks for support

Use >, =, and < to compare one- and two-digit numbers, without additional supports

Use >, =, and < to compare two-digit numbers (Part 1)

Use >, =, and < to compare two-digit numbers (Part 2)

Use >, =, and < to compare two-digit numbers, without additional supports

Select the correct < or > sign to compare a pair of two-digit numbers

Select the number from a set that is the least or greatest

Order a set of one- and two-digit numbers from least to greatest

Topic C: Addition and Subtraction of Tens
Students work with round numbers to reinforce place value understanding of 10 more and 10 less. They use equations and the number line to solve addition problems and counting patterns.
Solve addition equations that add round numbers to 40

Count backward by 10 on a number line (Part 1)

Count backward by 10 on a number line (Part 2)

Topic D: Addition of Tens or Ones to a Two-Digit Number
Students begin to develop strategies to add ones or tens to a 2-digit number. They utilize base-10 models, making ten, and number bonds to solve addition equations.
Use base-10 models to add ones to a 2-digit number

Add ones to a 2-digit number

Use base-10 blocks to add a tens to a 2-digit number

Solve addition equations adding tens or ones to a 2-digit number

Identify tens numbers from a set

Given a number along a number line, identify the next ten

Identify the next ten from a given number, without models

Use base-10 blocks to practice adding to make a next ten
Identify the next ten and find the missing addend

Find the missing addend to make the next ten from a given number

Use base-10 blocks to solve addition equations with exchanging

Use number bonds to solve addition equations with exchanging (Level 1)

Use number bonds to solve addition equations with exchanging (Level 2)

Solve addition equations with exchanging, using a number bond if needed

Add ones to a 2-digit number

Add ones to a 2-digit number, with and without exchanging

Topic E: Addition of Tens and Ones to a Two-Digit Number
Students synthesize their learning from the previous topic to add tens and ones to a 2-digit number. They are supported by the familiar model of base-10 blocks, place value charts, and step-by-step guidance.
Review adding ones to 2-digit numbers

Review adding tens to 2-digit numbers

Identify tens from a group of numbers and label place value of 2-digit numbers

Break down 2-digit numbers into tens and ones

Use place value charts with base-10 blocks to add two 2-digit numbers

Solve 2-digit addition equations by adding tens and ones separately

Mentally solve 2-digit addition problems

Use place value charts with base-10 blocks to add 2-digit numbers, including regrouping

Review adding 1- and 2-digit numbers

MODULE 5. Identifying, Composing, and Partitioning Shapes
Topic A: Attributes of Shapes
Students learn the basic attributes of shapes: lines, closed figures, sides, and corners. They learn to identify triangles, rectangles, squares, trapezoids, and hexagons.
Identify the lines

Identify curved lines

Identify closed shapes

Identify shapes with a given number of sides

Count the number of sides and corners of shapes

Identify hexagons

Identify triangles, rectangles, squares, and hexagons

Identify a trapezoid

Draw given shapes

Identify given shapes

Identify shapes of everyday objects

Topic B: Halves and Quarters of Rectangles and Circles
Students learn to identify and count equal parts in a partitioned shape. They learn the names for halves and quarters, and use these names in identifying shapes partitioned as such.
Identify a shape that is partitioned into halves (Level 1)

Identify a shape that is partitioned into halves (Level 2)

Determine the number of equal parts in a partitioned shape

Identify a shape that is partitioned into quarters

Topic C: Application of Halves to Tell Time
Students explore digital and analog clocks to understand the passage and identification of time. They learn parts of the clock and different types of time notation: X:XX, X o'clock, X-thirty, and half past X.
Identify clock parts and time to the hour on a clock

Identify daily and hourly passage of time

Identify time to the hour on a digital and analog clock

Determine time to the hour on an analog clock

Identify passage of minutes on an analog clock

Identify time to the half hour on an analog clock and use associated language (Part 1)

Identify time to the half hour on an analog clock and use associated language (Part 2)

Identify time to the half hour on a digital and analog clock

Identify time on a clock

MODULE 6. Place Value, Comparison, Addition and Subtraction to 100
Topic A: Numbers to 120
Students use familiar representations such as base-10 blocks, place value charts, numeric form, word form, and addition equations to extend place value understanding of numbers up to 120.
Review tens numbers to 100

Identify the missing tens numbers

Show 2-digit numbers in unit form

Express the same values as a 2-digit number and tens and ones

Label the place value of a number

Identify the 2-digit number represented

Match whole numbers to the corresponding unit form

Use addition to show that a number is composed of a tens number and some ones

Find one more or one less than a number

Find ten more or ten less than a number

Count forward and backward by ones from a number

Identify the rule and continue the pattern

Use <, =, and > to compare numbers

Explore representations of numbers to 120

Write the numeric and word form for numbers to 120

Represent numbers to 120 in numeric and word form

Count from 100-120

Count forward and backward by ones from 100-120

Add 1- and 2-digit numbers to 100 to compose numbers to 120

Identify the rule and continue the pattern up to 120

Topic B: Addition to 100 Using Place Value Understanding
Students use place value charts and base-10 blocks to solve 2-digit addition and subtraction equations. They also practice solving these problems mentally. Students begin to learn when to regroup in equations with 2-digit numbers.
Add tens numbers (Level 1)

Add tens numbers (Level 2)

Subtract tens numbers (Level 1)

Subtract tens numbers (Level 2)

Solve addition problems with 2-digit numbers and tens numbers (Level 1)

Solve addition problems with 2-digit numbers and tens numbers (Level 2)

Solve addition problems with two 2-digit numbers (Level 1)

Solve addition problems with two 2-digit numbers (Level 2)

Solve addition problems with two 2-digit numbers (Level 3)

Solve addition problems with two 2-digit numbers, including regrouping
