Curriculum for Grade 4
As students develop a more abstract understanding of numbers, we stretch their skills in both directions - with multi-digit whole numbers as well as decimals and fractions. Students learn traditional algorithms as well as other approaches that build math flexibility and fluency. In addition to performing operations with these numbers, students learn new ways to measure, convert units, round numbers, and compare numbers. A firm understanding of place value is the common thread running through all topics.
MODULE 1. Place Value, Rounding, and Algorithms for Addition and Subtraction
Topic A: Place Value of Multi-Digit Whole Numbers
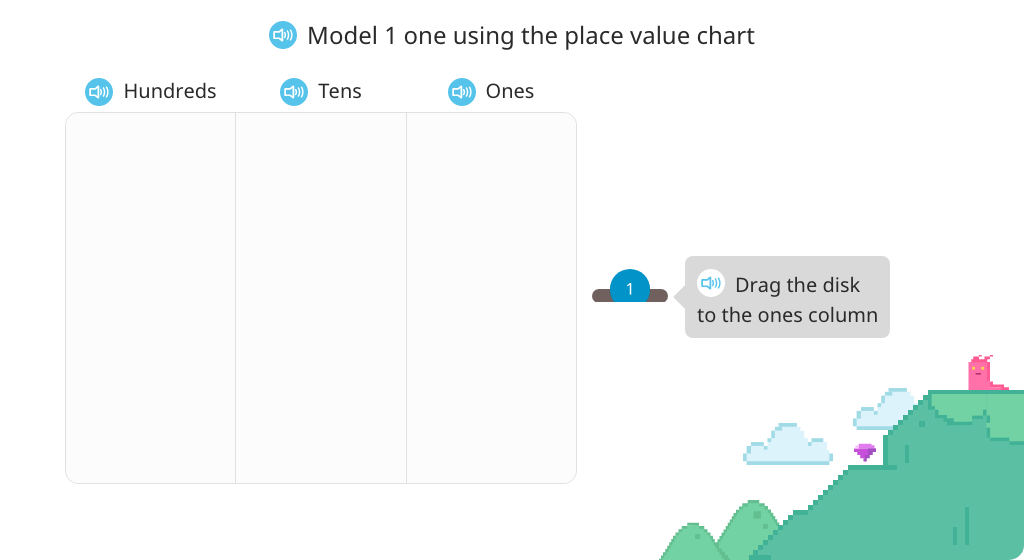
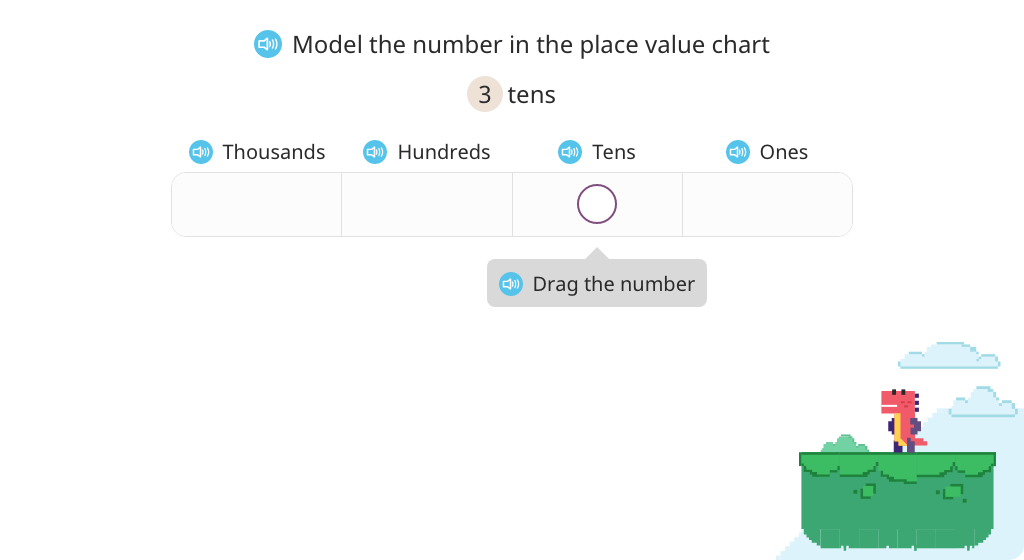
Students work with whole numbers to the thousands place using number disks and the place value chart. They develop understanding of magnitudes of 10, as well as how multiplication and division relate to place value.
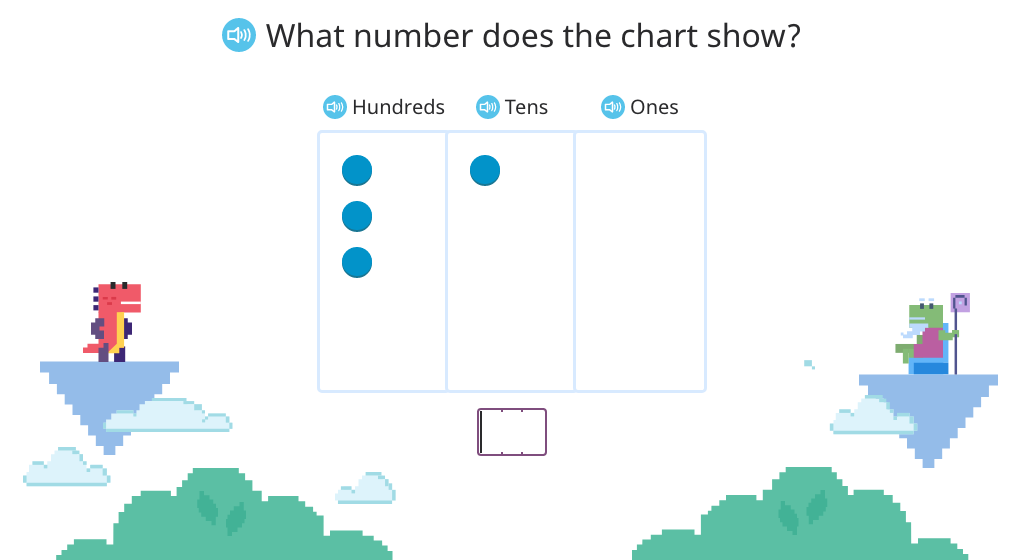
Convert between 3-digit numbers and unit form

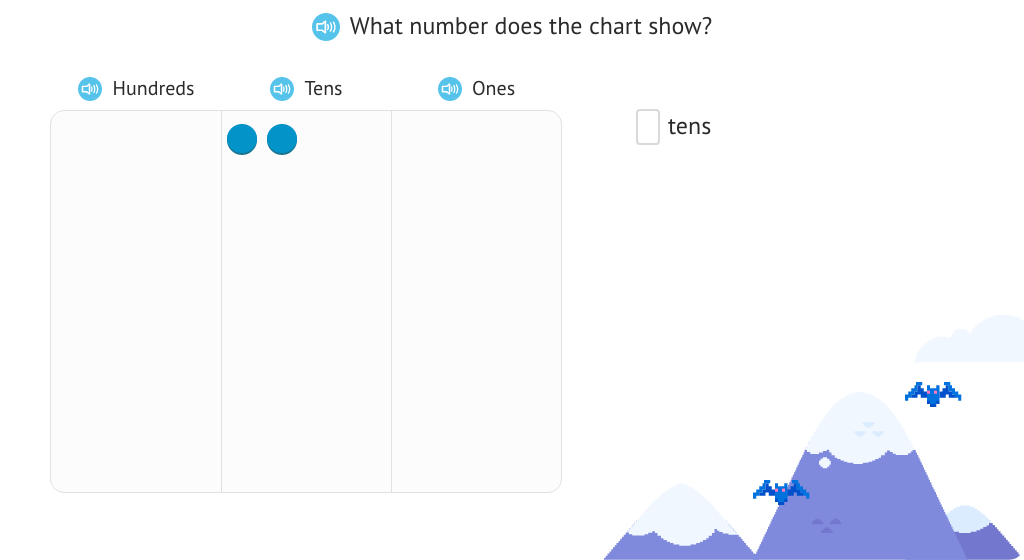
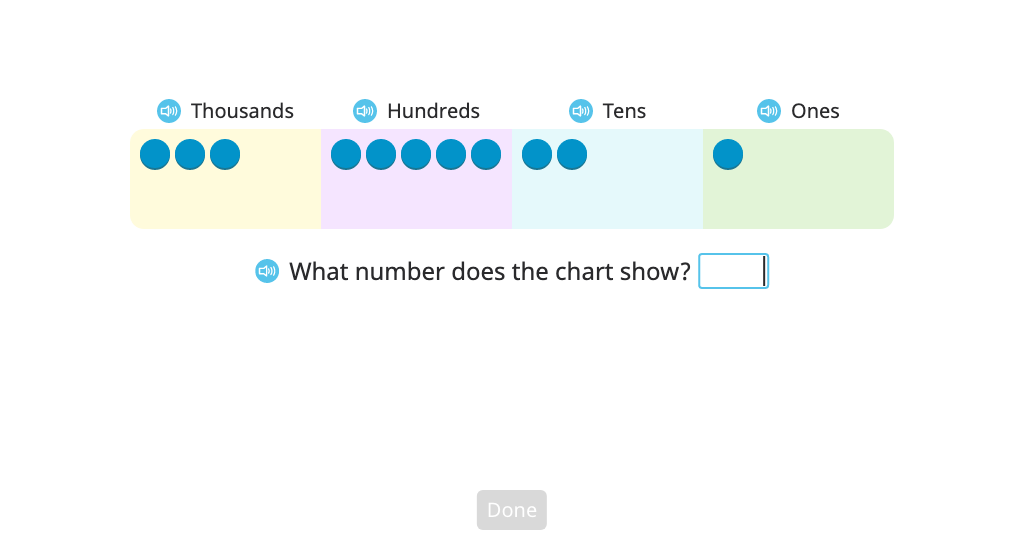
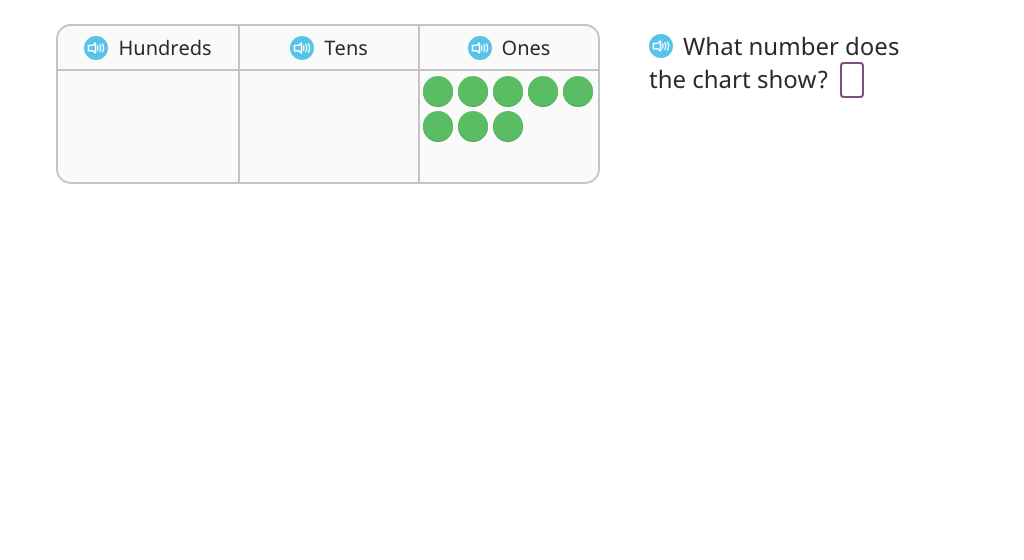
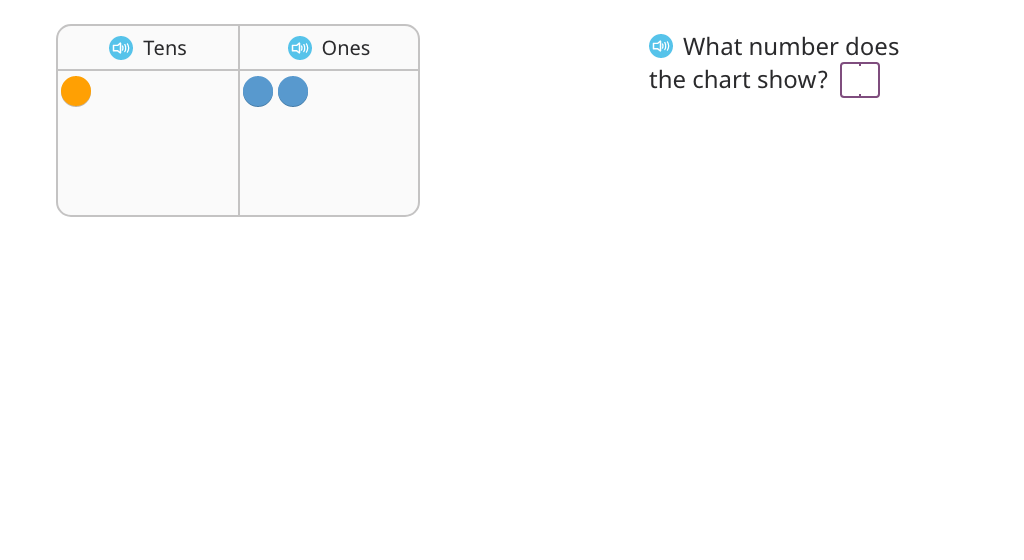
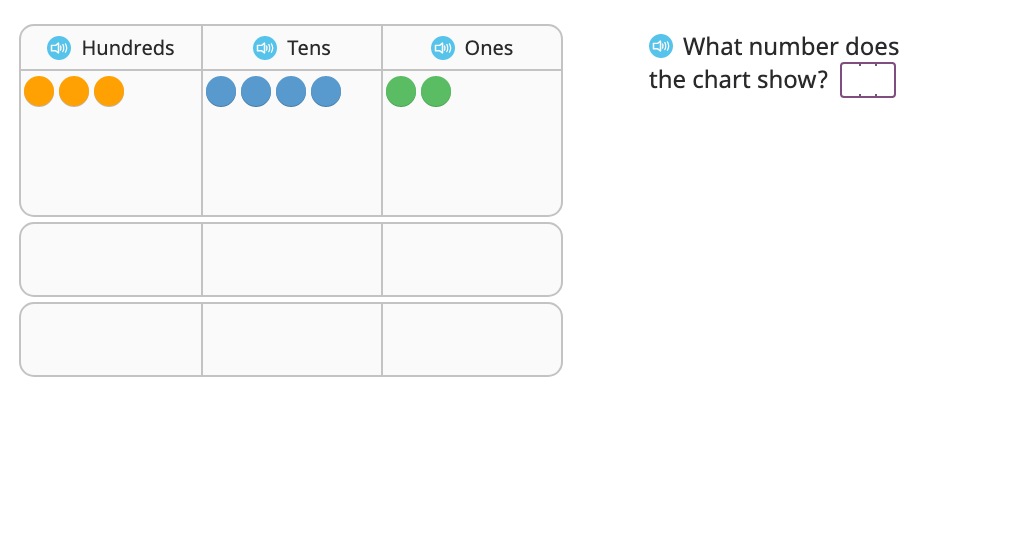
Represent a place value chart as a 2-or 3-digit number
Solve multiplication by 10 in unit form and number form
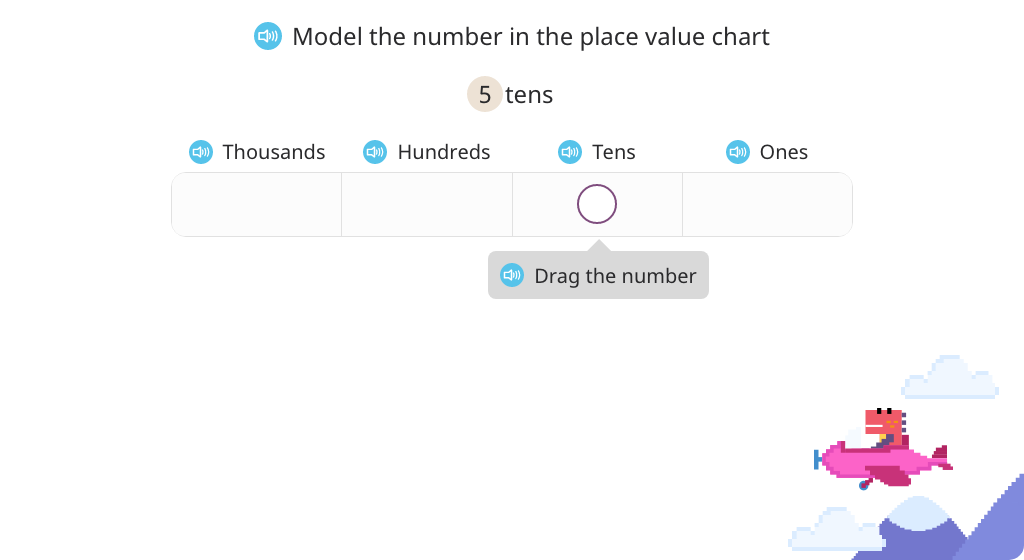
Solve multiplication by 10 in unit form and number form and model on a place value chart
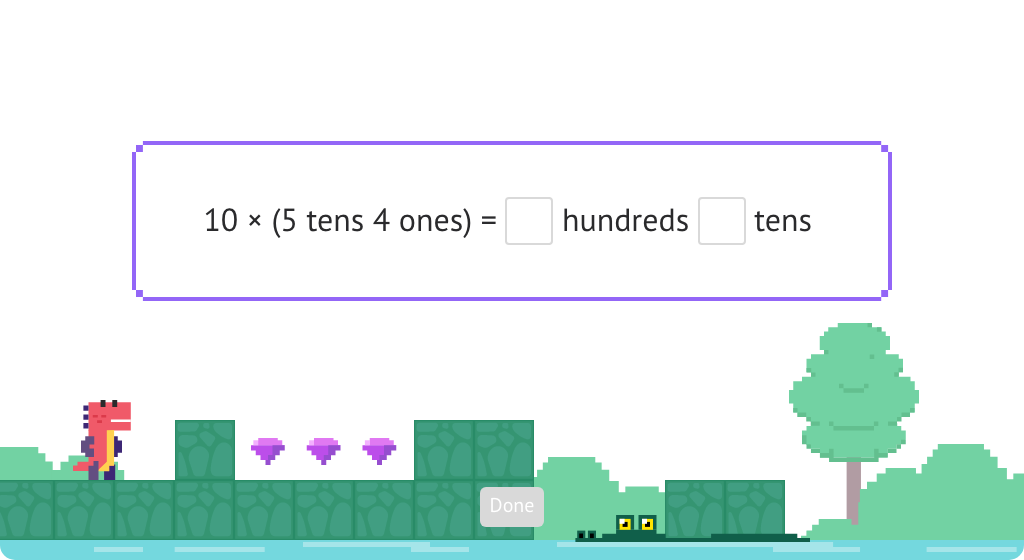
Solve multiplication by 10 in unit form and number form
Model division by 10 using a disk model (Level 1)
Model division by 10 using a disk model (Level 2)
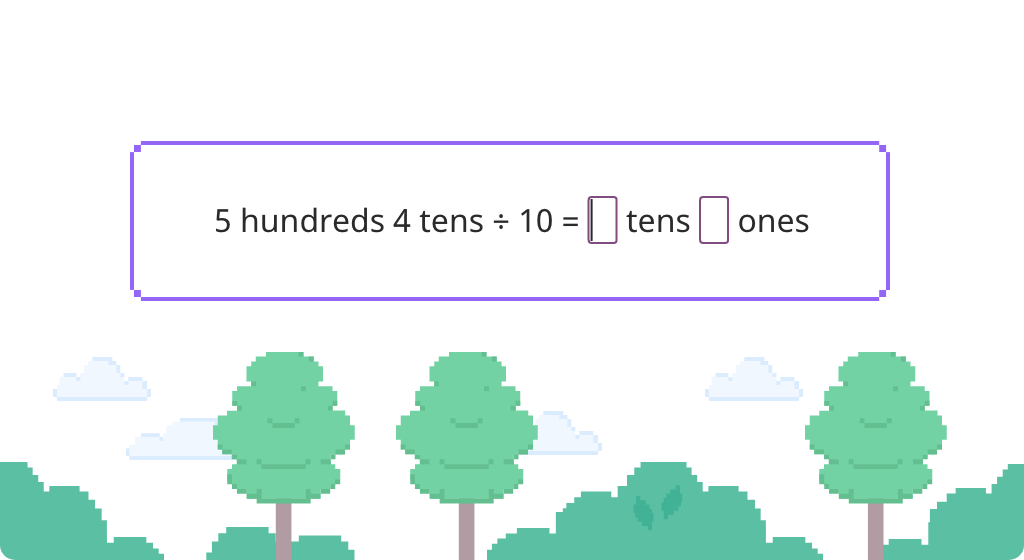
Solve division by 10 in unit form and number form
Topic B: Comparing Multi-Digit Whole Numbers
Students work with numbers in the thousands, ten thousands, and hundred thousands. Building upon previous knowledge, such as use of inequality symbols, they deepen their understanding of how to compare large numbers to several place values or numbers of different place value. As part of this understanding, they build their fluency in the base-10 system by finding 1,000, 10,000 and 100,000 more or less than a number.
Compare numbers in a place value chart (at their highest place value)
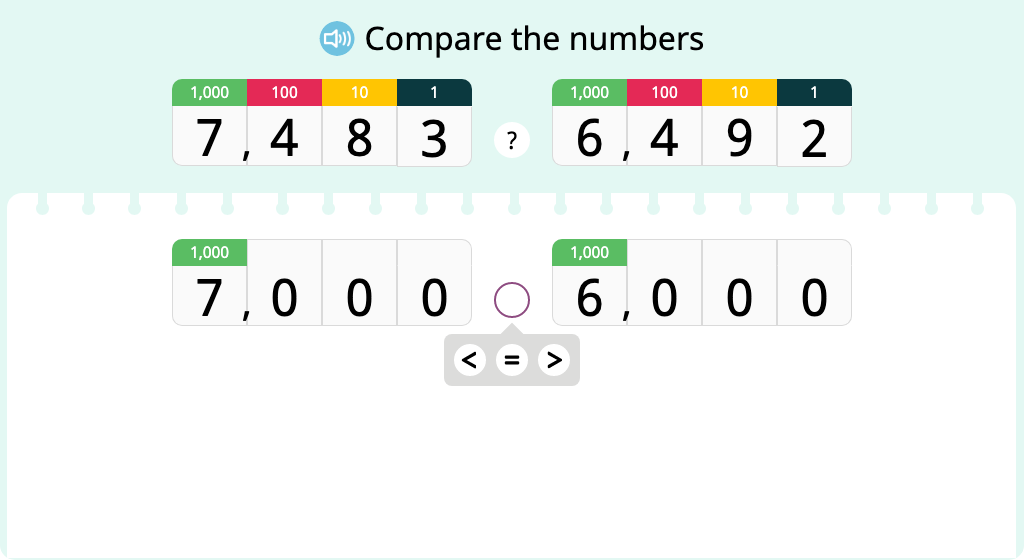
Compare numbers in a place value chart (at a place value other than their highest)
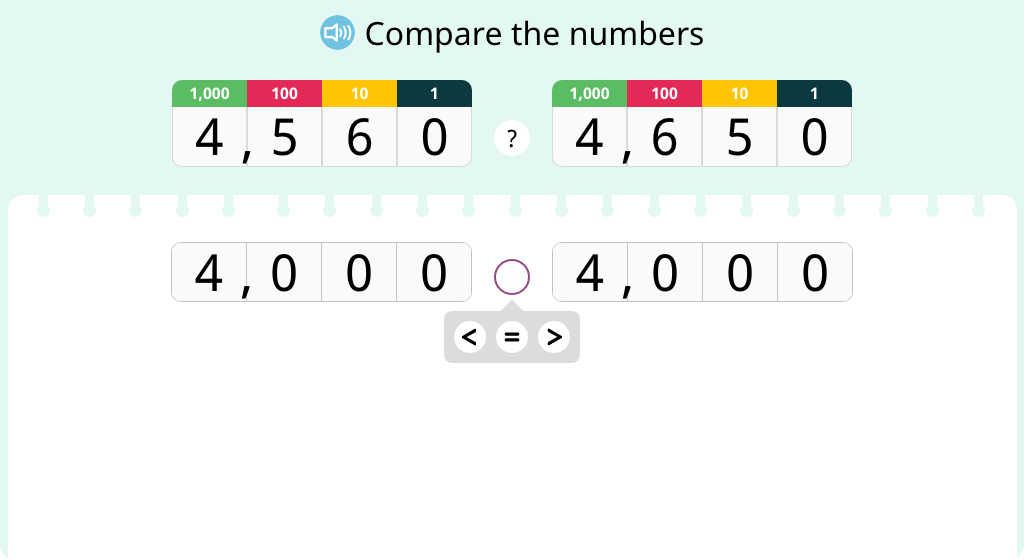
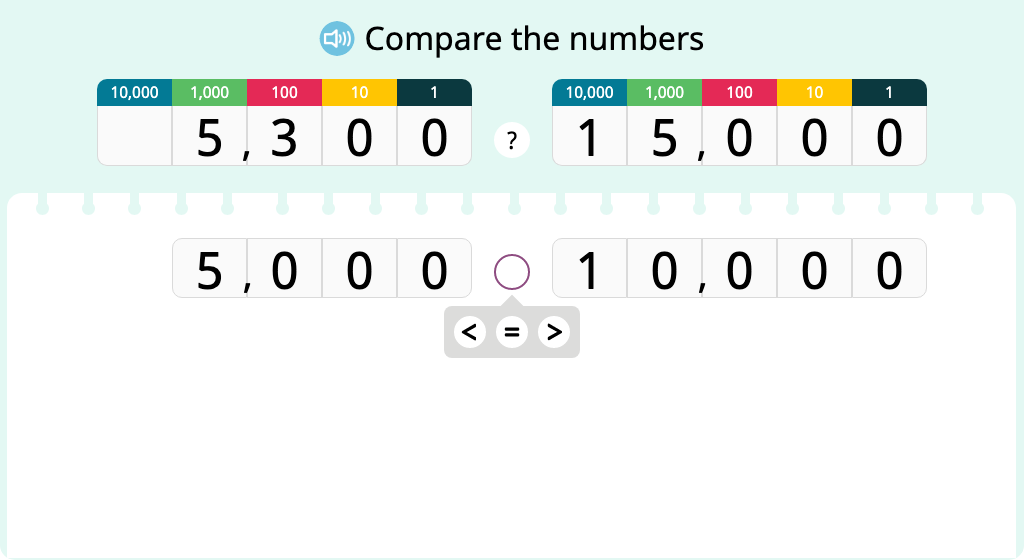
Compare numbers in a place value chart (at different place values)
Complete inequalities comparing multi-digit numbers

Order numbers in ascending and descending order using < and > (Part 1)

Order numbers in ascending and descending order using < and > (Part 2)
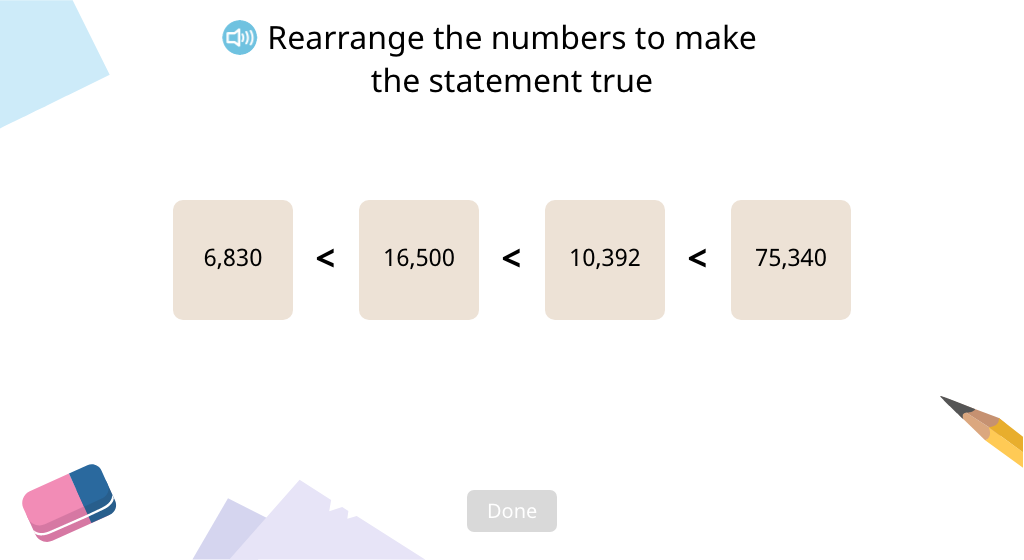
Order numbers in ascending and descending order using < and > (Part 3)
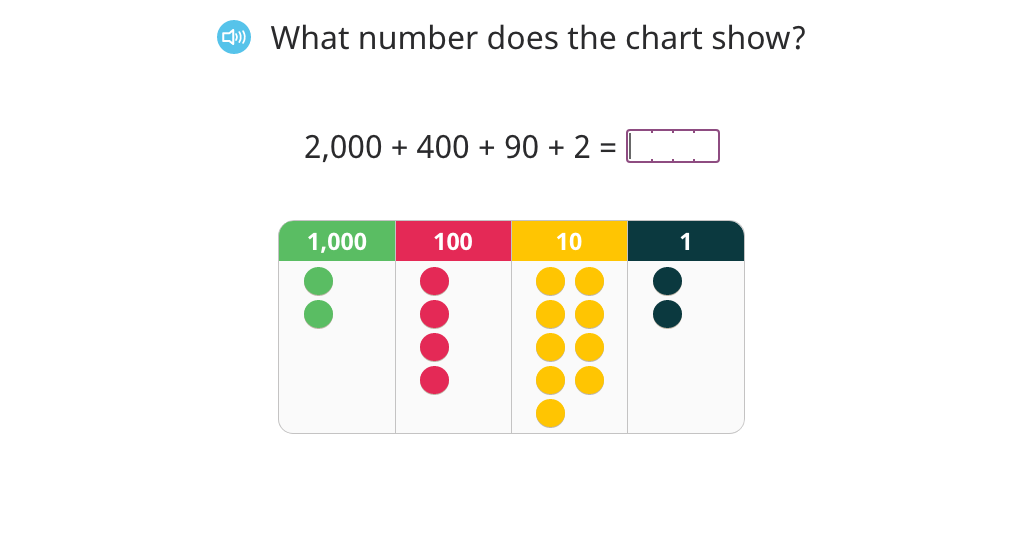
Determine 1,000 more or less than a number using a place value chart
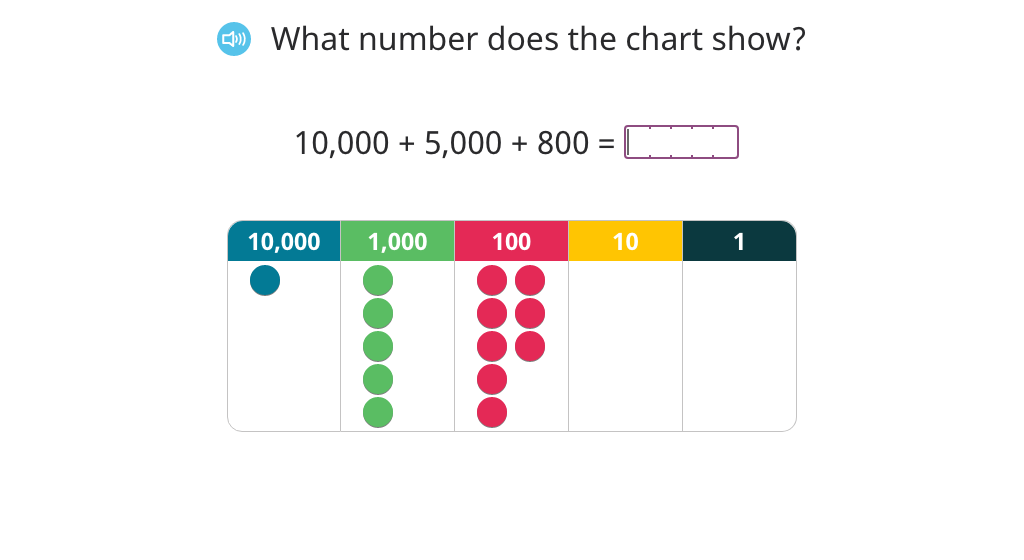
Determine 10,000 more or less than a number using a place value chart
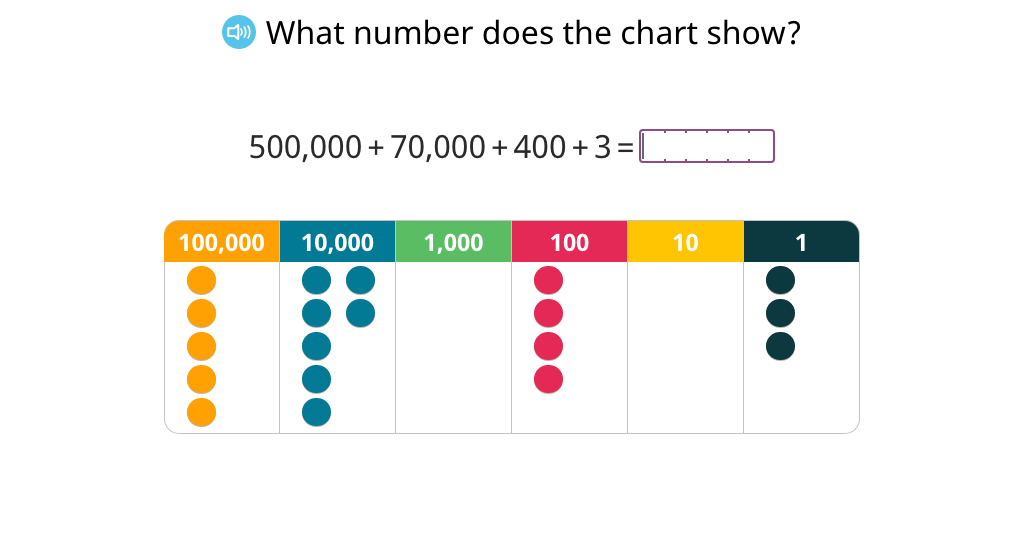
Determine 100,000 more or less than a number using a place value chart
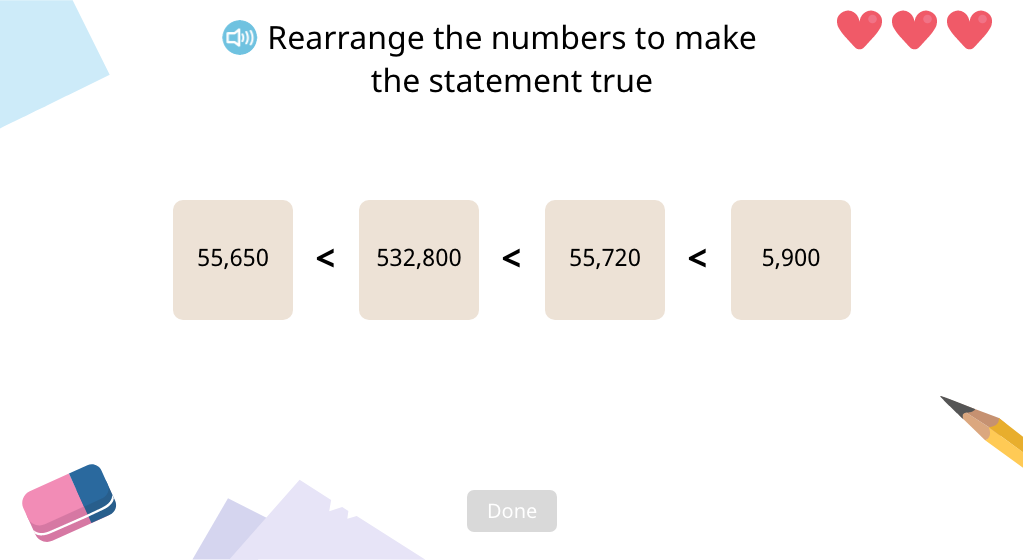
Complete a statement comparing numbers with and without a place value chart (1,000 or 10,000 more or less)
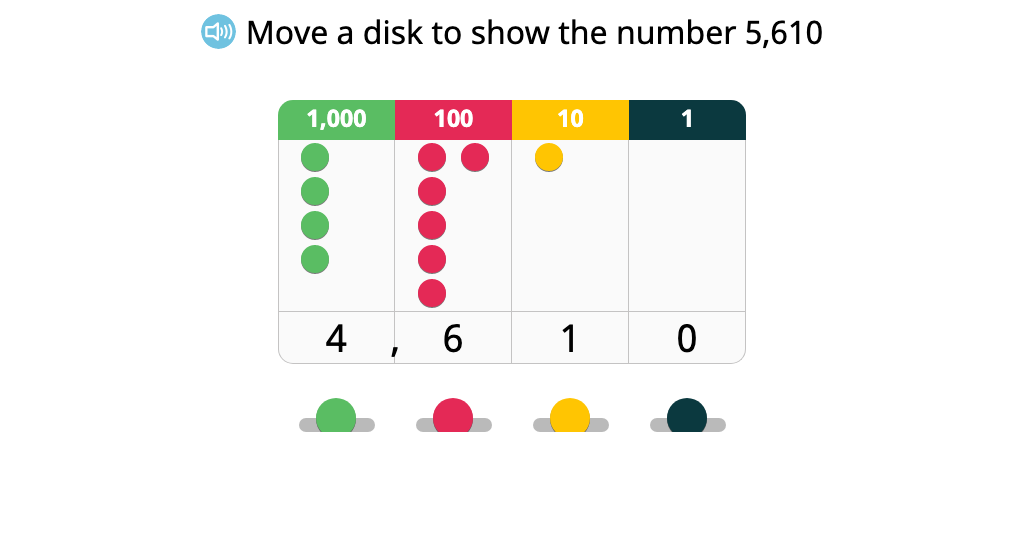
Determine 1,000/10,000/100,000 more or less than a given number

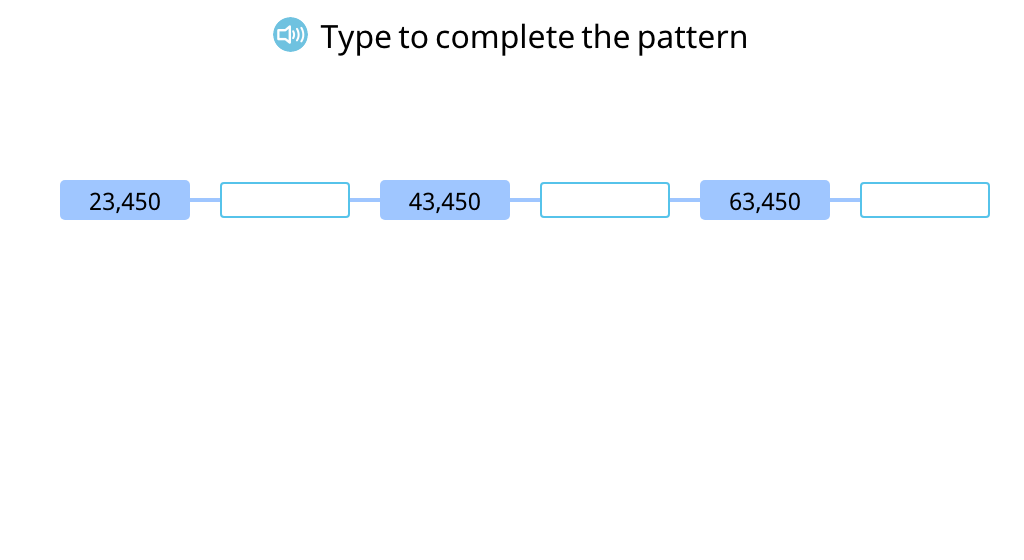
Order numbers in a pattern increasing or decreasing by 1,000 or 10,000 (Level 1)
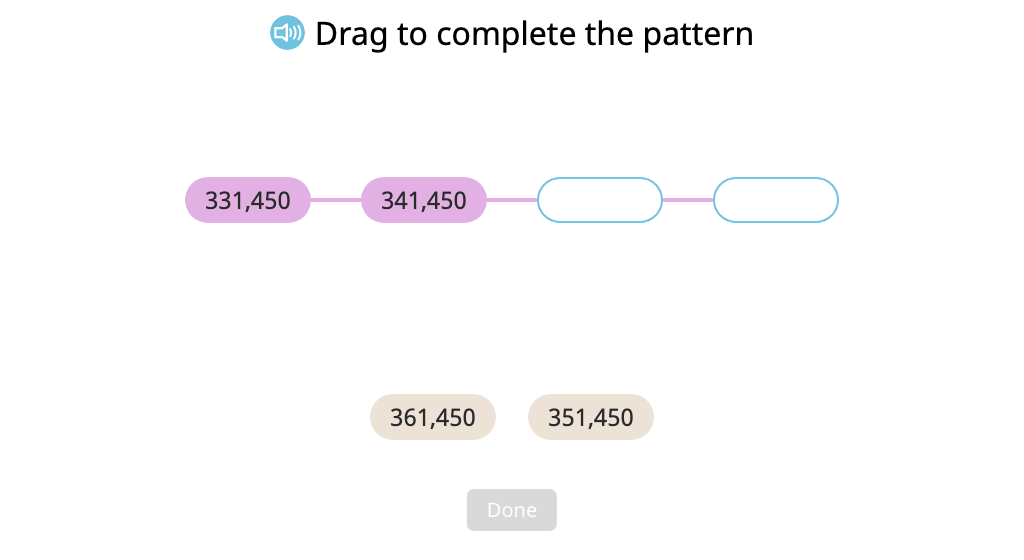
Order numbers in a pattern increasing or decreasing by 1,000 or 10,000 (Level 2)
Topic C: Rounding Multi-Digit Whole Numbers
Using a number line to provide context, students master finding neighboring thousands and choose the nearest one. Then they learn the rule for rounding up or down to the nearest thousand and ten thousand. Finally, students round 4-,5- and 6-digit numbers to any given place value and practice their rounding skills using real-world facts.
Identify place values up to ten thousand

Rounding to the nearest ten or hundreds

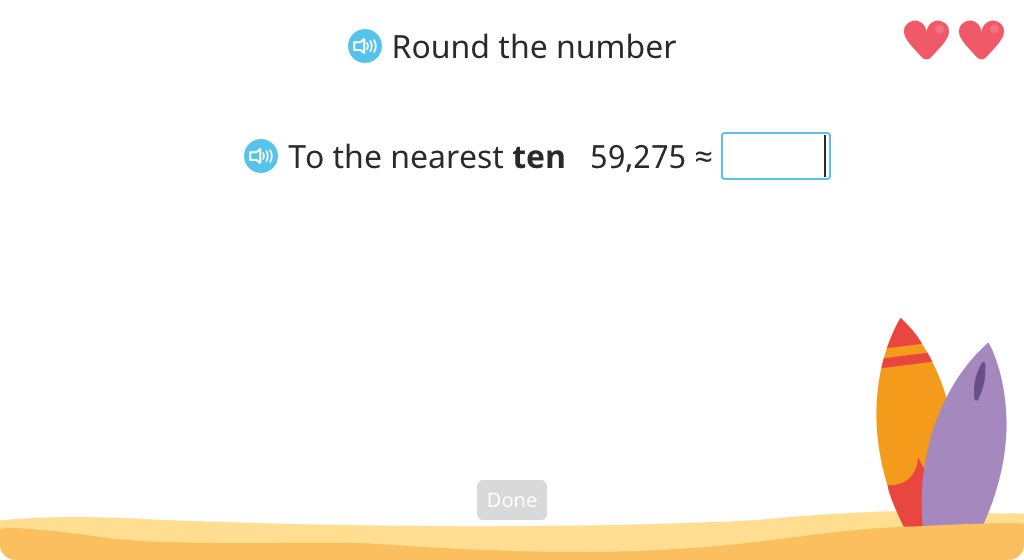
Round to the nearest ten

Identify the nearest thousands of a given number
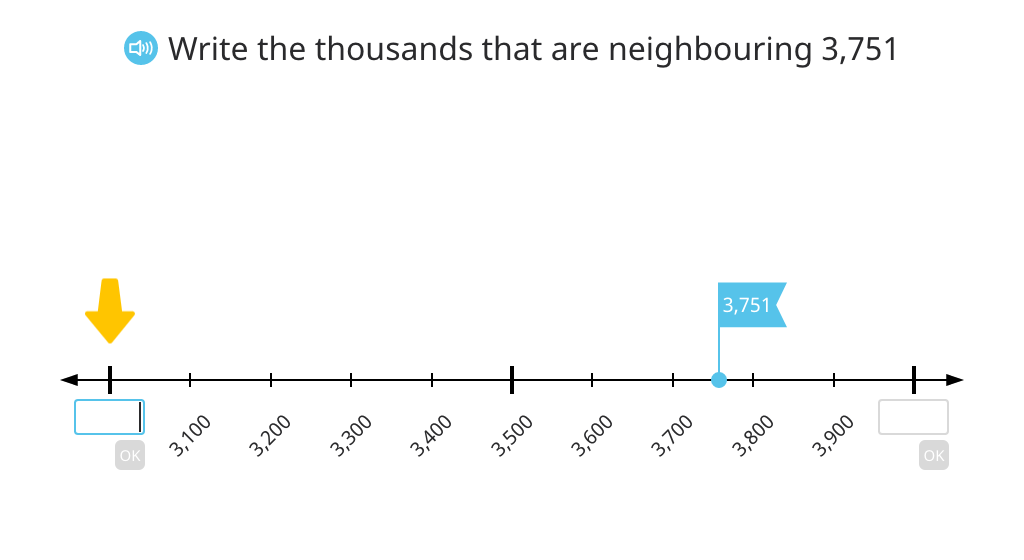
Rounding to the nearest thousand and practical application
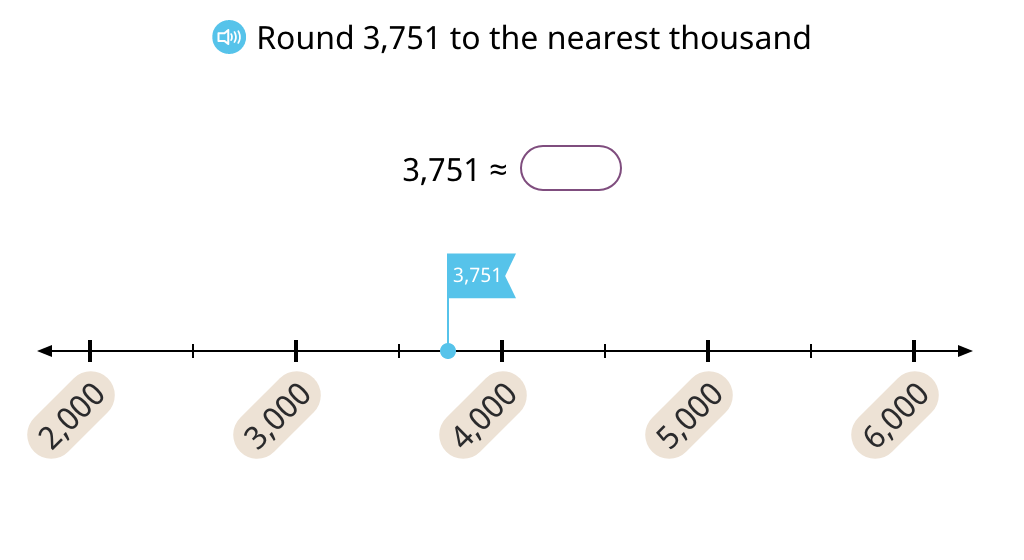
Use the approximation symbol when rounding to the nearest thousand using a number line for reference
Learn the rule for rounding numbers that are exactly in the middle of two thousands

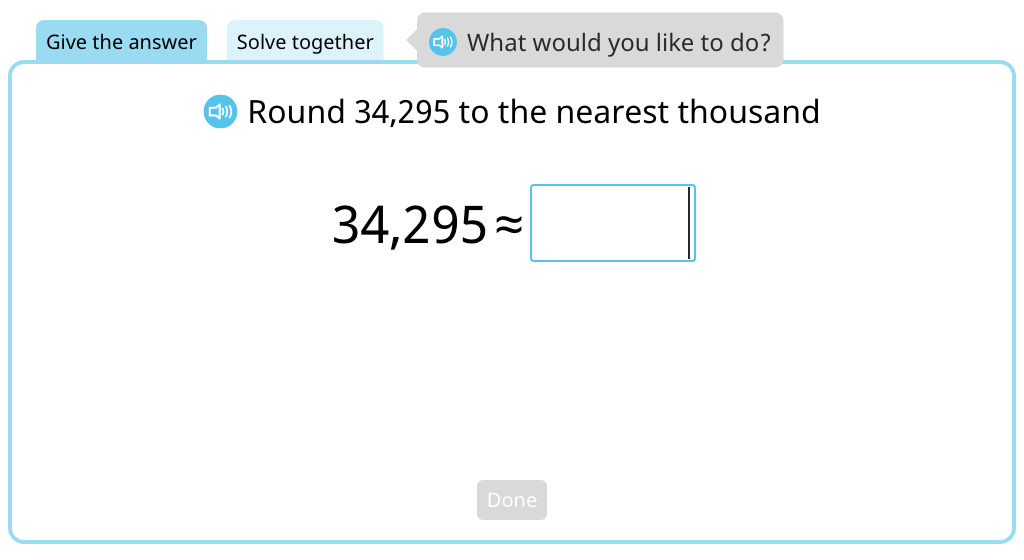
Round a given number to the nearest thousand

Rounding to the nearest thousand using five-digit numbers continued
Round a given number to the nearest ten thousand using the rule of rounding (Part 1)
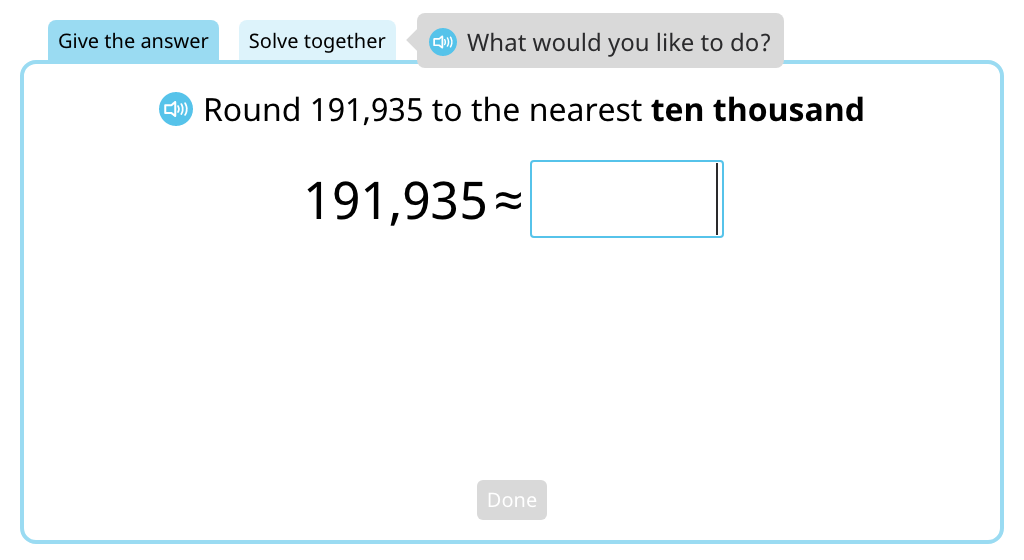
Round a given number to the nearest ten thousand using the rule of rounding (Part 2)
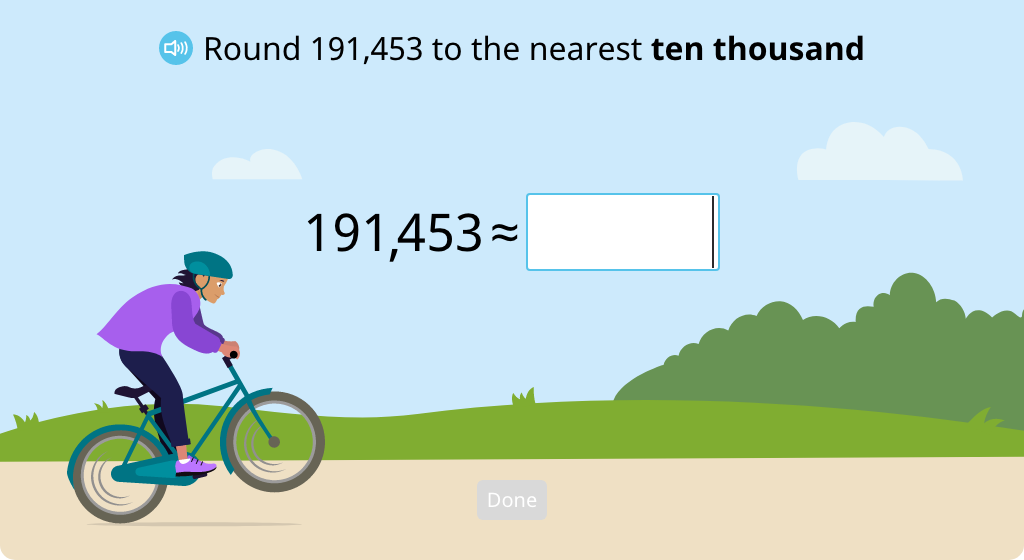
Round a given number to the nearest thousand up or down
Round a given number to the nearest thousand or ten thousand up or down

Rounding to the tens, hundreds, thousands, and ten thousands place
Topic D: Multi-Digit Whole Number Addition
Students use column addition to add multi-digit numbers. They begin with the support of a disk model to illustrate the underlying concepts. They learn to record addition problems as column addition, how to regroup and record this action, how to line up numbers of varying length, and how to regroup to a place value higher than the original numbers.
Add two 4-digit numbers with and without regrouping in one place using a disk model
Add two 4-digit numbers with and without regrouping in two places using column addition and a disk model
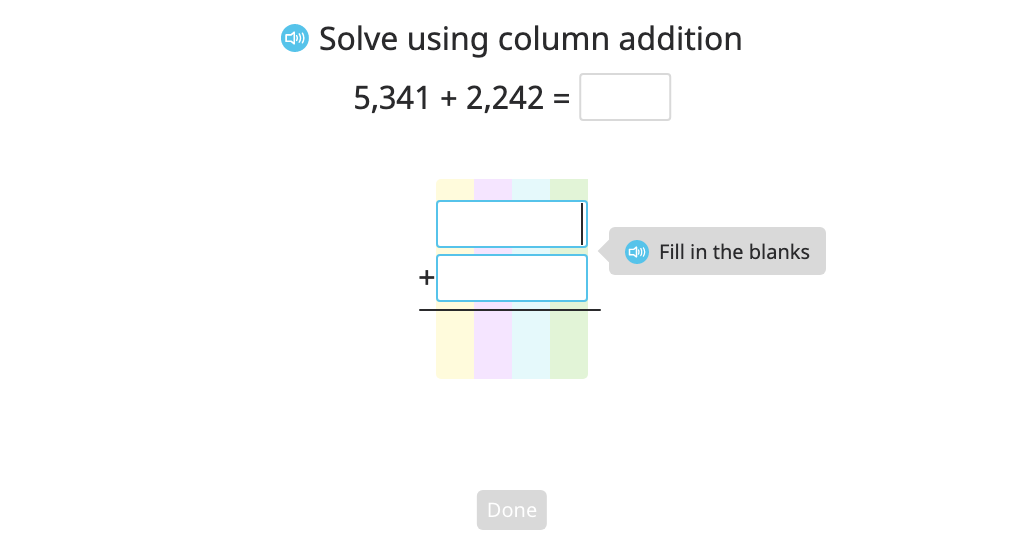
Add two 4-digit numbers with and without regrouping in one place using a disk model part II
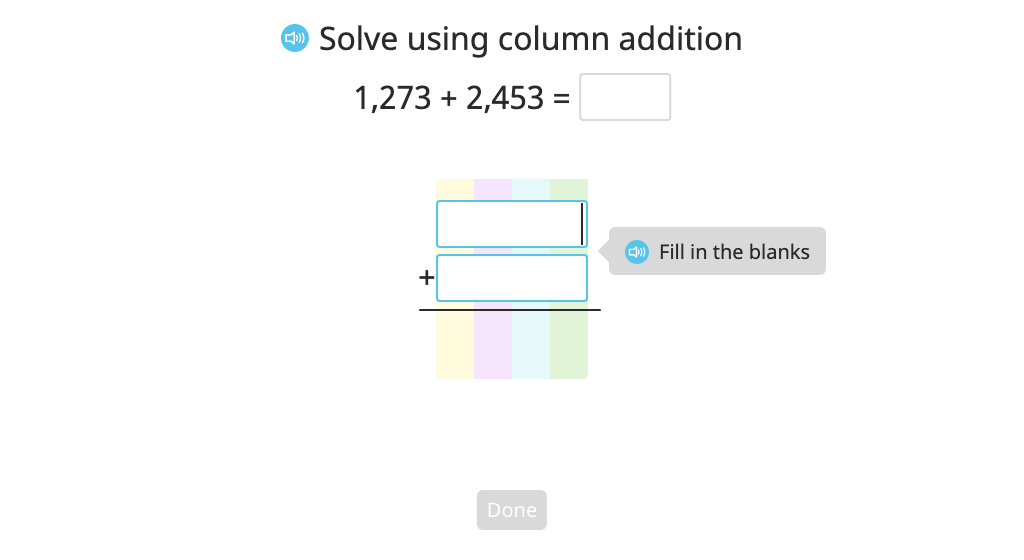
Add multi-digit numbers with regrouping in multiple places using column addition and disk models
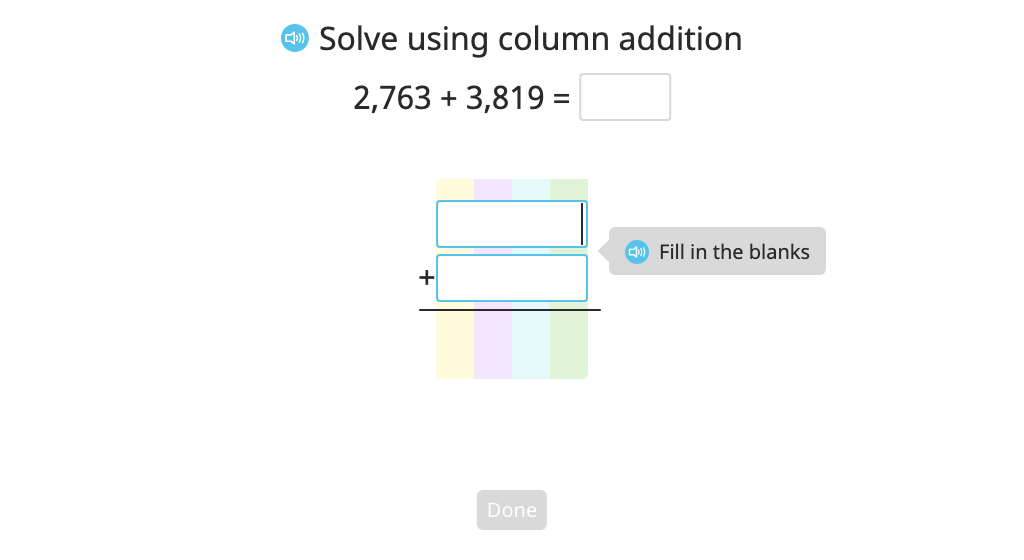
Add multi-digit numbers with regrouping in multiple places using column addition
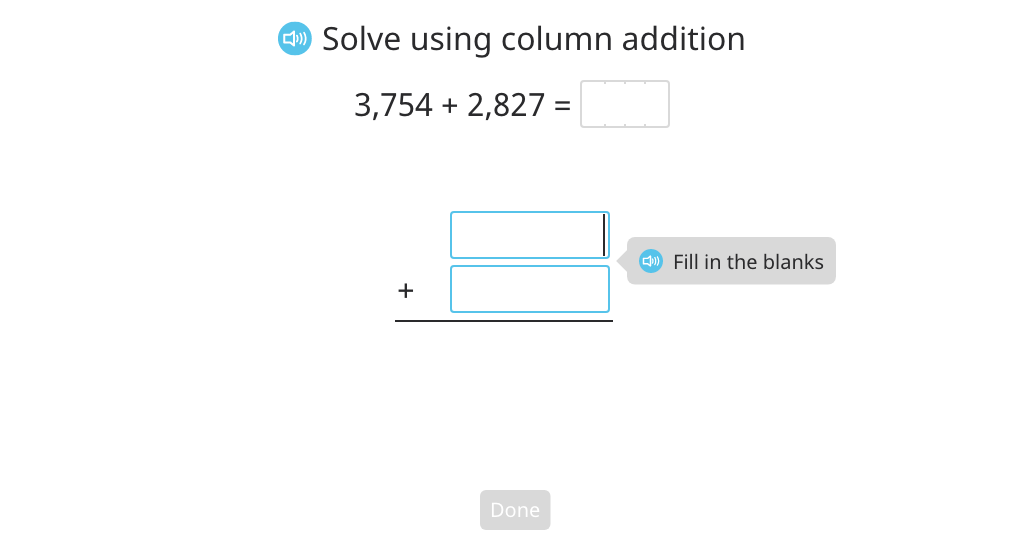
Add multi-digit numbers using the standard algorithm
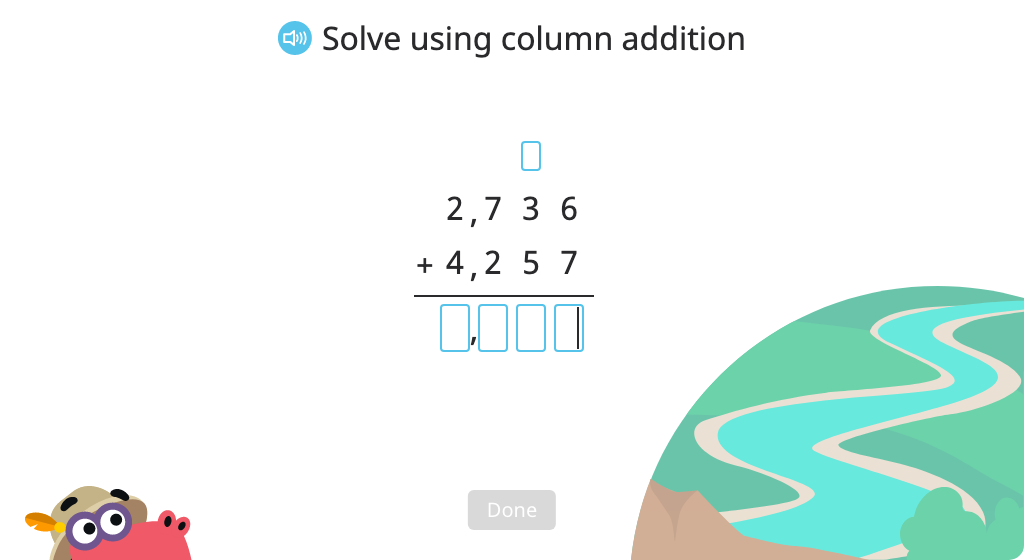
Topic E: Multi-Digit Whole Number Subtraction
Students use column subtraction to subtract multi-digit numbers. They learn to rewrite subtraction problems as column subtraction, regroup when necessary, and regroup across zeroes using disk models for support.
Use column subtraction with multi-digit numbers
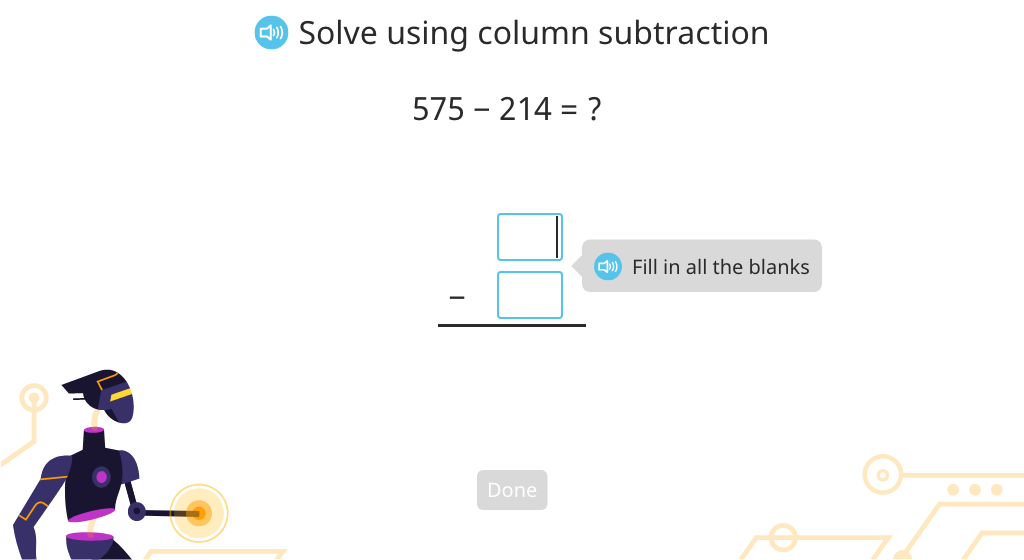
Solve 4-digit column subtraction with regrouping (Level 1)
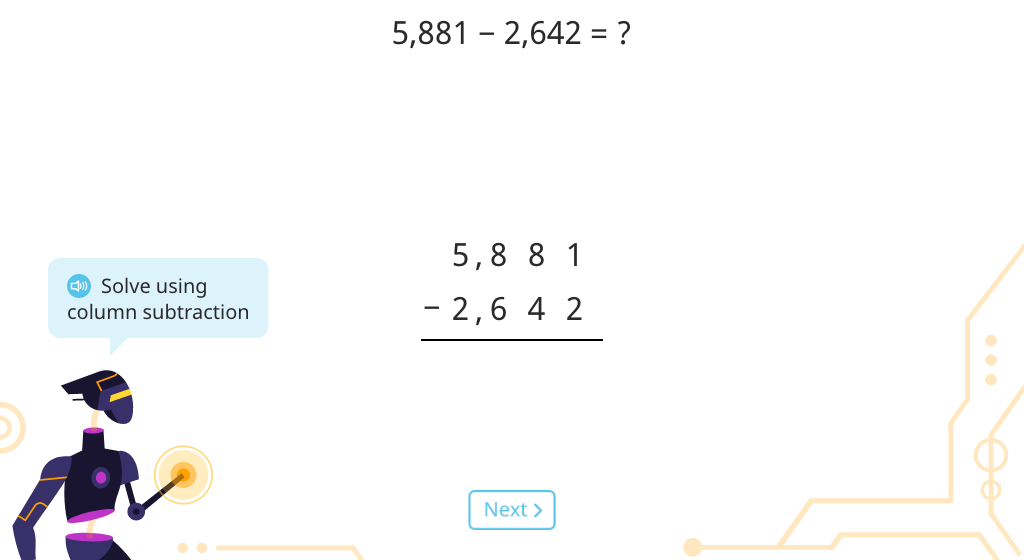
Solve 4-digit column subtraction with regrouping (Level 2)
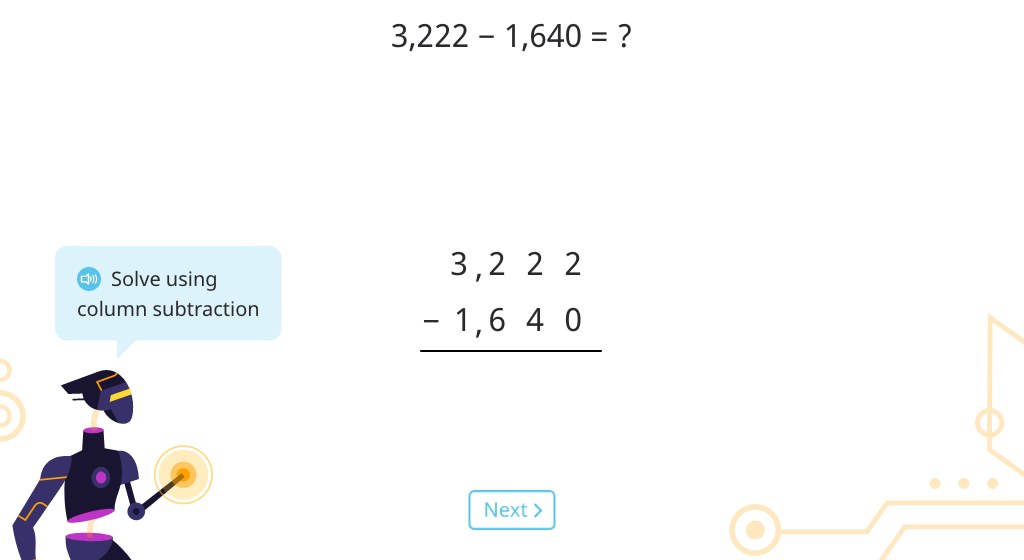
Write and solve multi-digit column subtraction
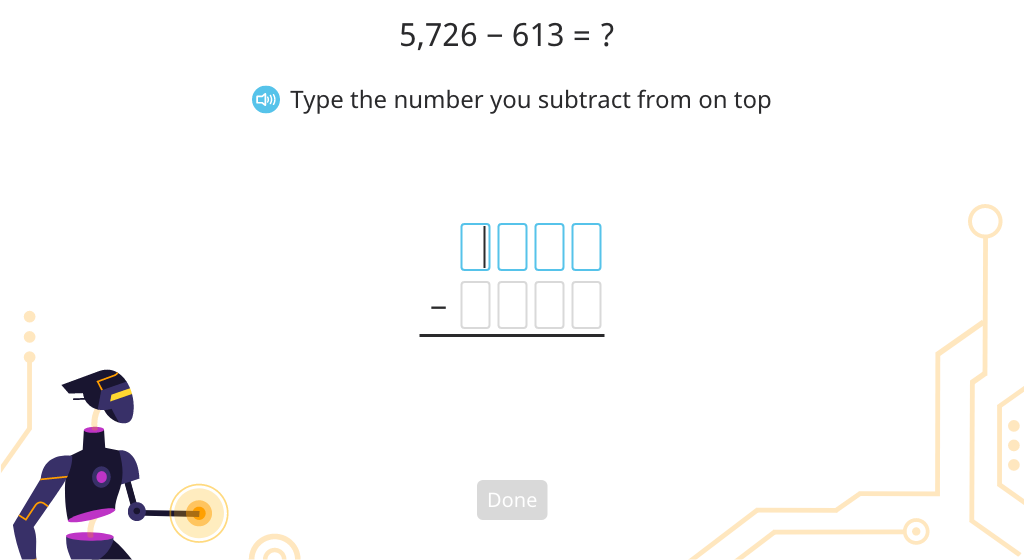
Write and solve multi-digit column subtraction with regrouping
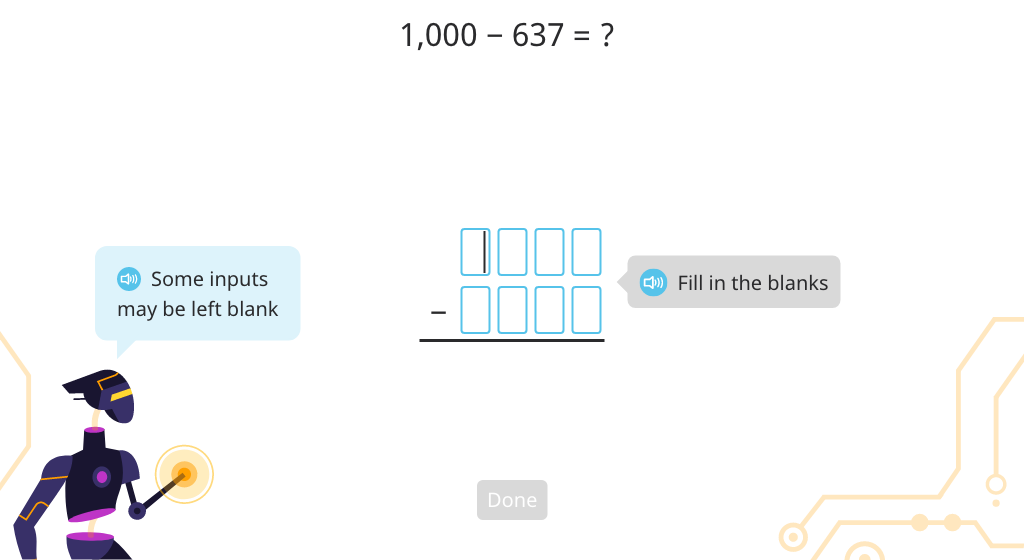
Solve 5-digit column subtraction with regrouping
MODULE 2. Unit Conversions and Problem Solving with Metric Measurement
Topic A: Conversions and Problem-Solving with Metric Units
Students explore metric units of length, liquid volume, and mass and their conversions. They use their understanding of these units to estimate measurements and solve word problems.
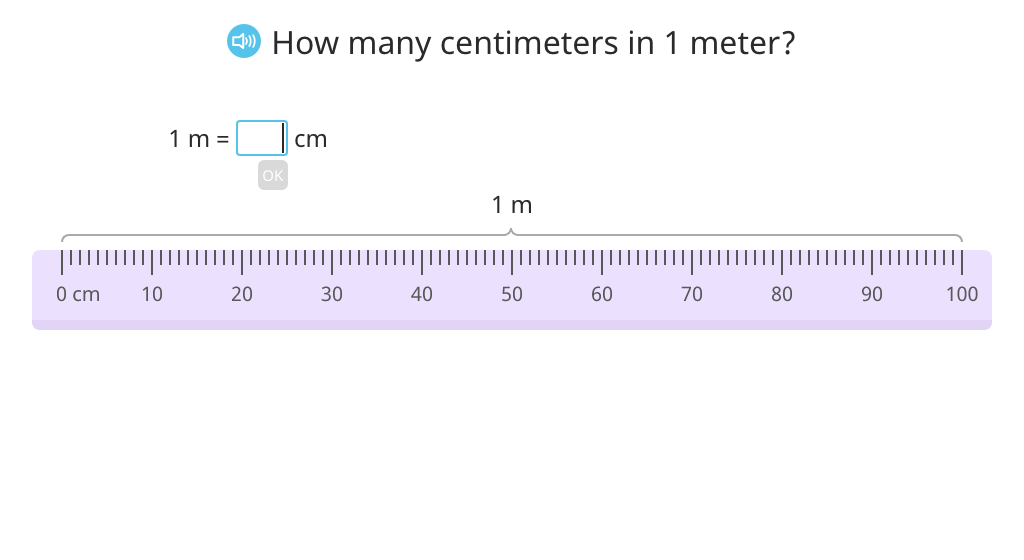
Measure items in centimeters
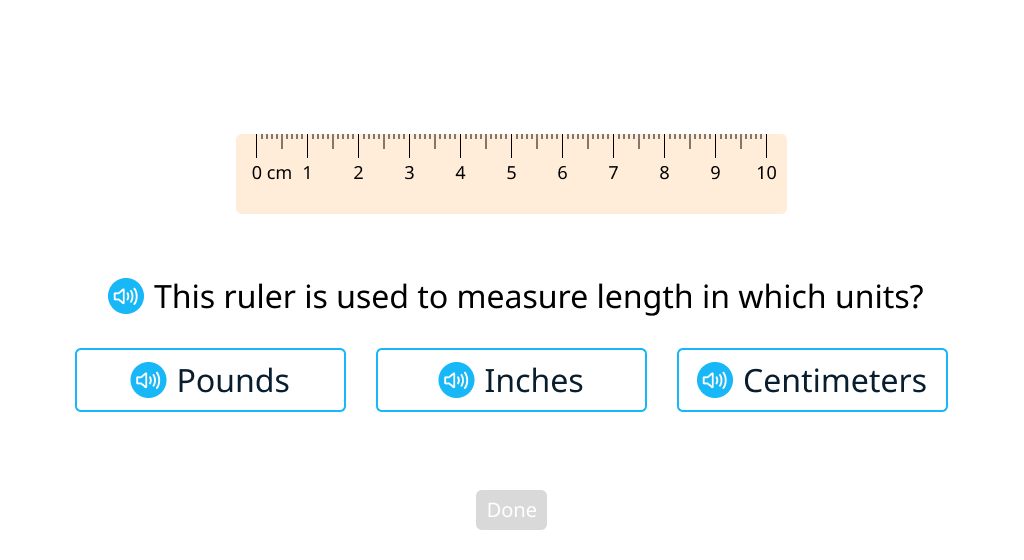
Measure items with a meter stick
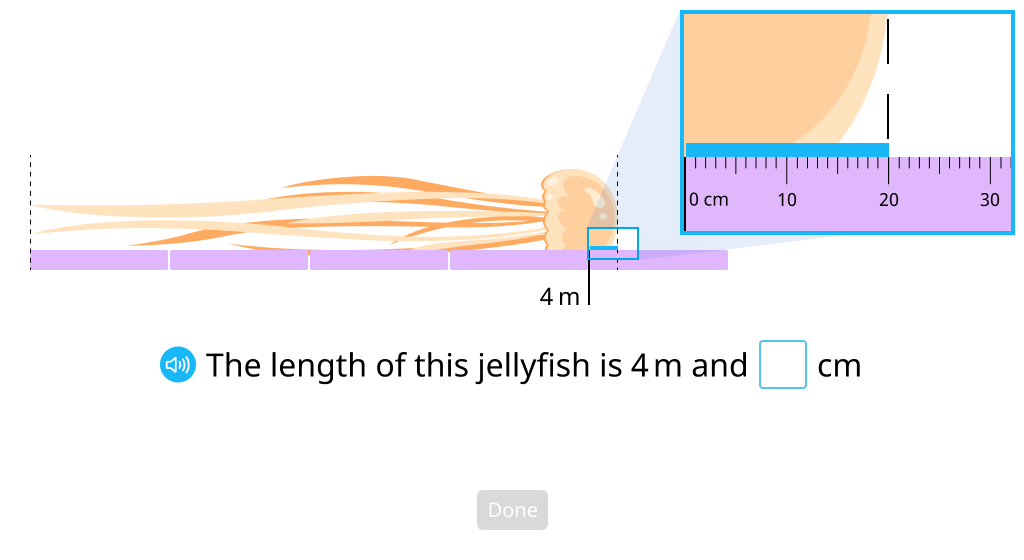
Convert meters to centimeters

Convert measurements to centimeters (Level 1)

Convert measurements to centimeters (Level 2)
Solve a word problem comparing lengths in centimeters
Estimate the length of real-world objects
Explore kilometers
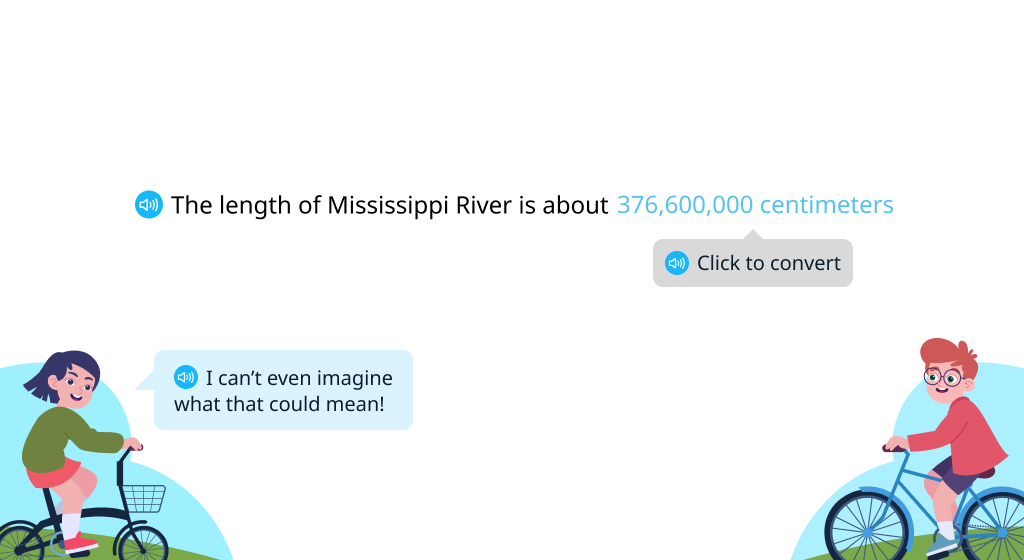
Convert measurements to meters (Level 1)

Convert measurements to meters (Level 2)
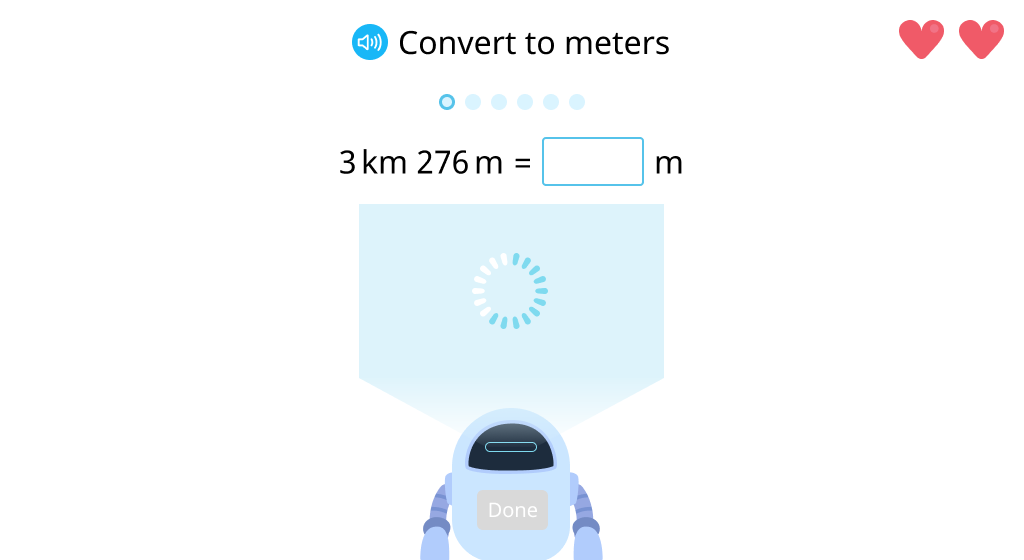
Solve a word problem comparing lengths in meters

Estimate the length of real-world objects or distances

Explore liquid volume in liters

Explore liquid volume in milliliters

Measure liquid volume in milliliters
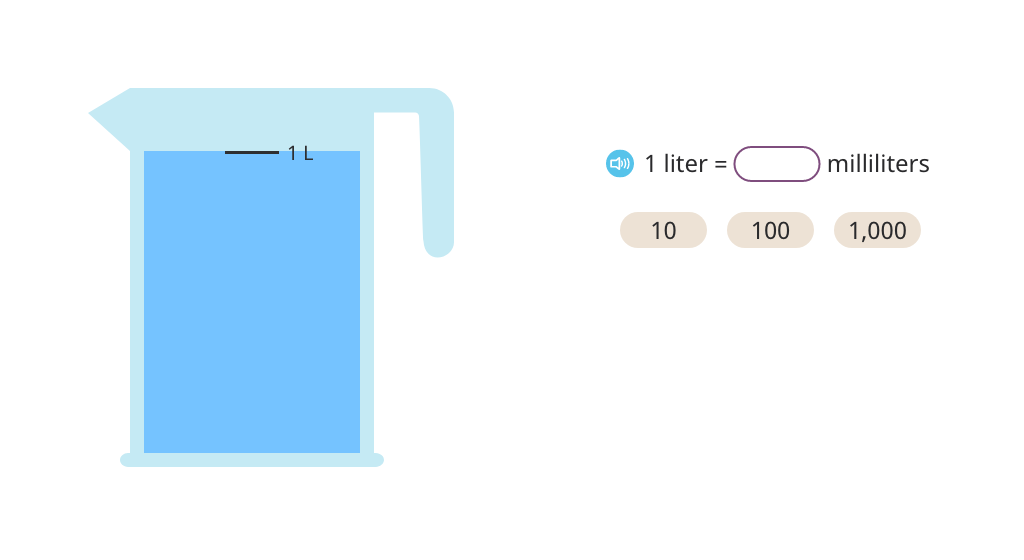
Explore real liquid volumes

Convert liters to milliliters (Level 1)

Convert liters to milliliters (Level 2)
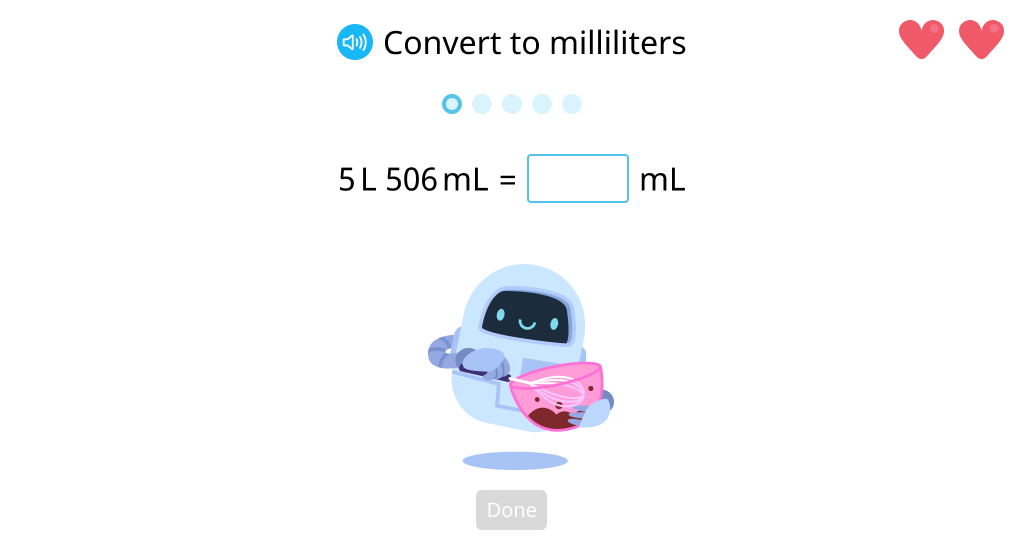
Find the sum of two volumes
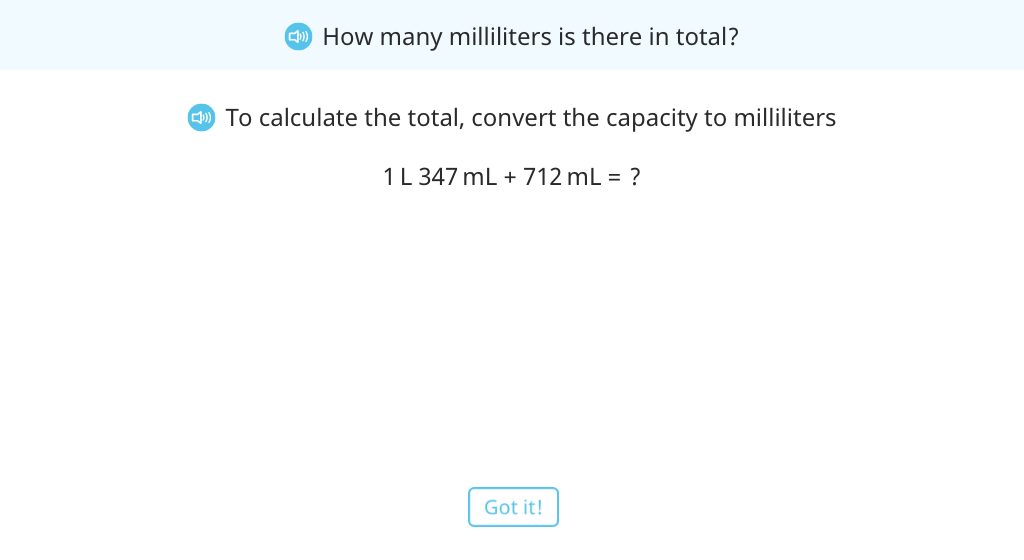
Solve a word problem by adding liquid volumes

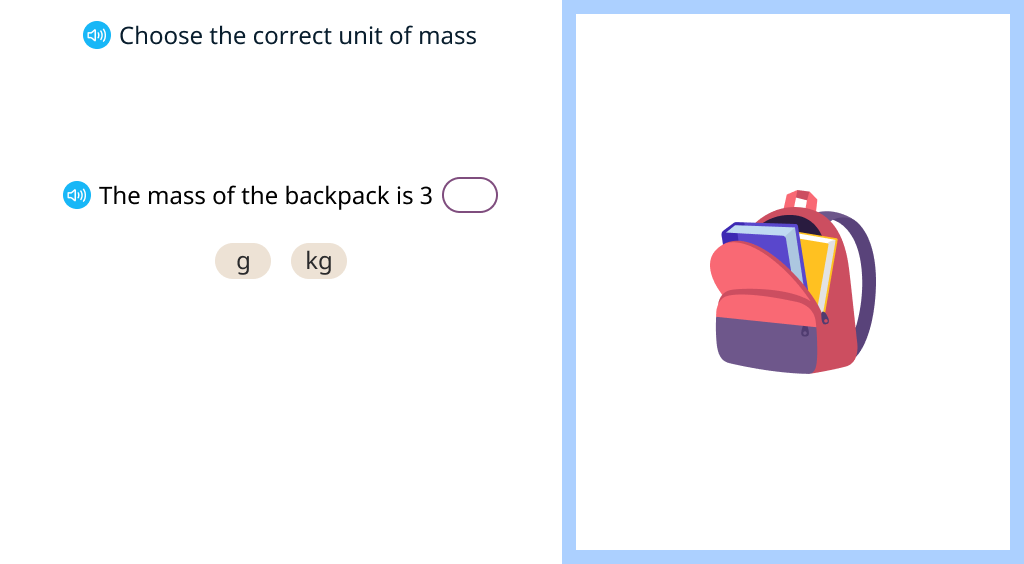
Explore units of mass

Explore the relationship between grams and kilograms

Estimate the mass of real objects
Convert kilograms to grams
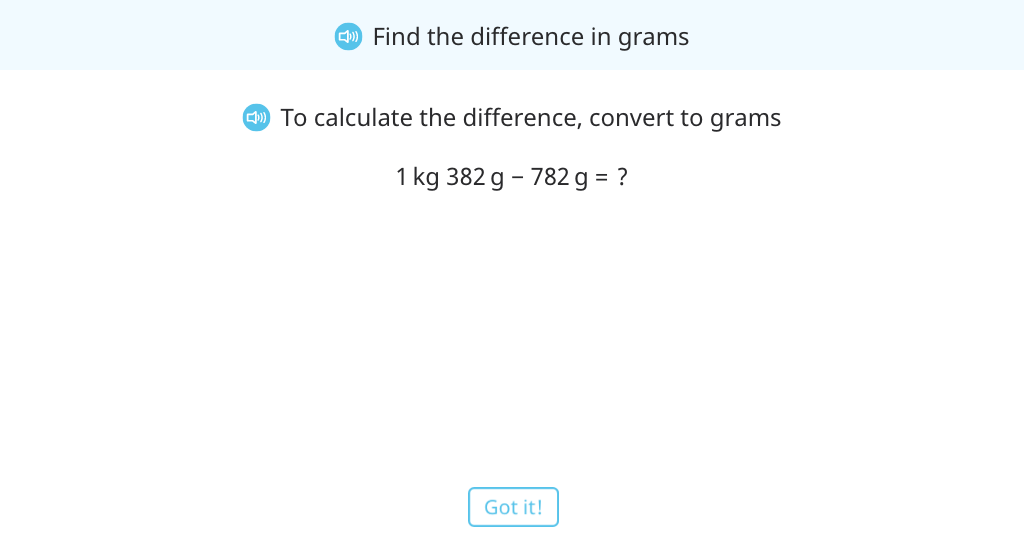
Find the difference of two masses
Solve a word problem by comparing mass
MODULE 3. Multi-Digit Multiplication and Division
Topic A: Finding Area and Perimeter of a Rectangle
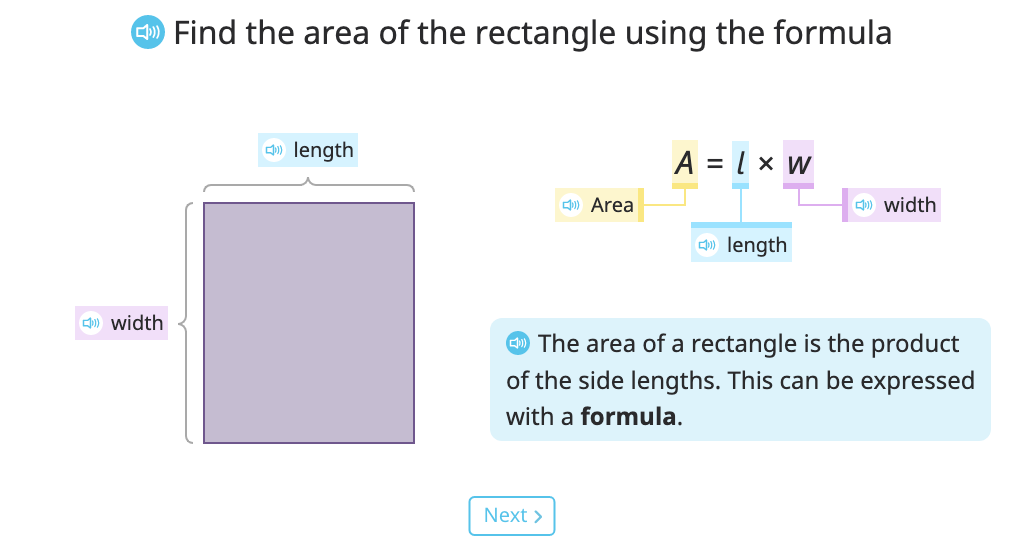
Students apply their understanding of measurement and area models to use the formulas for area and perimeter of a rectangle. They use the area model to find both the area and a missing side length. Students identify different ways of writing the same formula for both area and perimeter.
Determine the area of a rectangle by multiplying the lengths of its sides
Identify the formula for area of a rectangle and use it to solve a problem
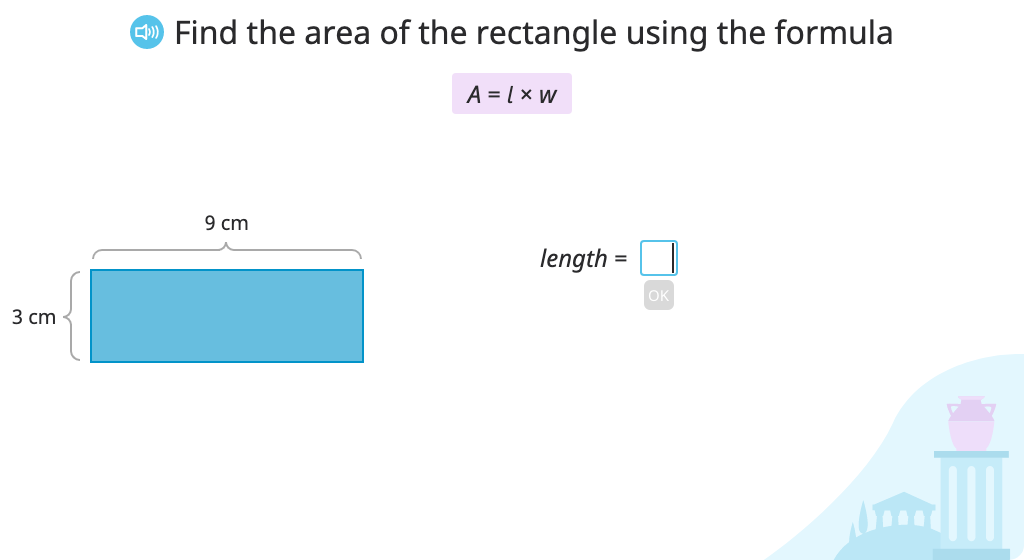
Determine the area of a rectangle using the formula A = l x w
Determine the side length of a rectangle based on its area and width using the formula
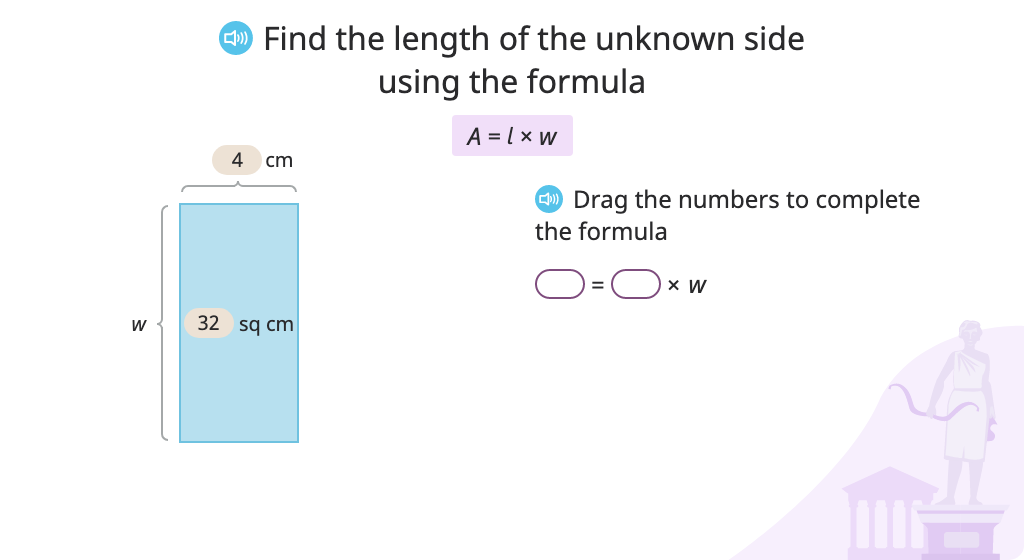
Identify the formula for perimeter of a rectangle and use it to solve a problem
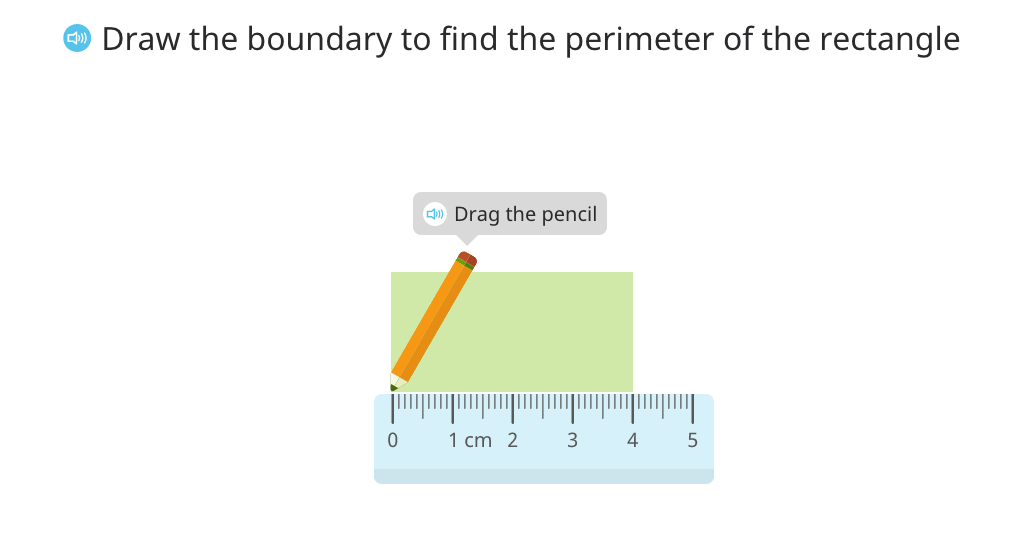
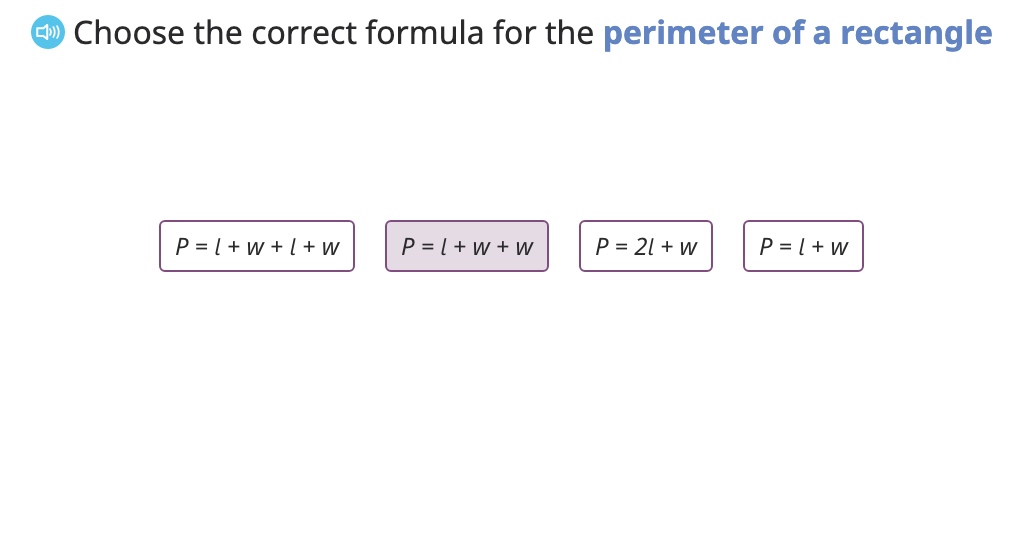
Identify the formula for perimeter of a rectangle
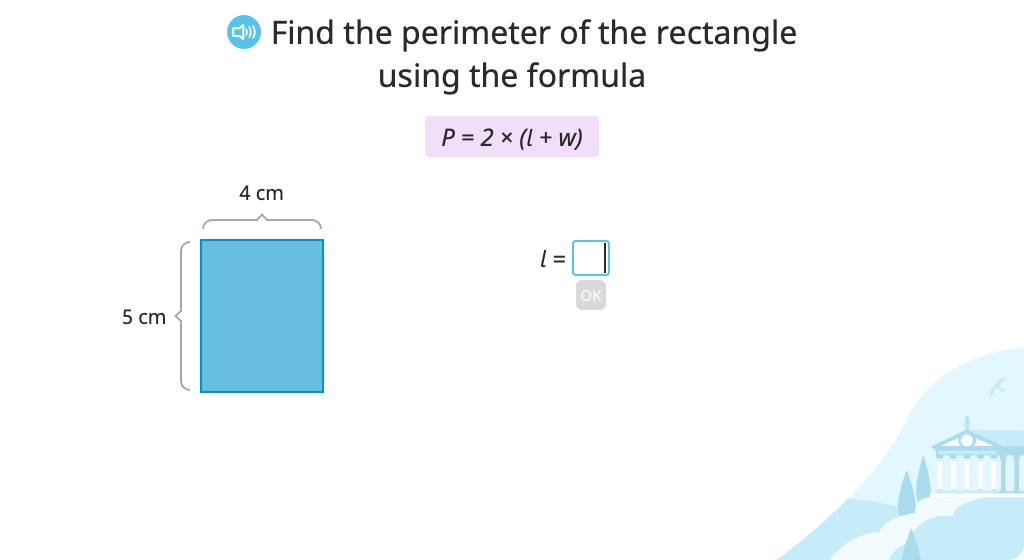
Determine the perimeter of a rectangle using the formula P = 2 x (l + w)
Determine the area and perimeter of the same rectangle
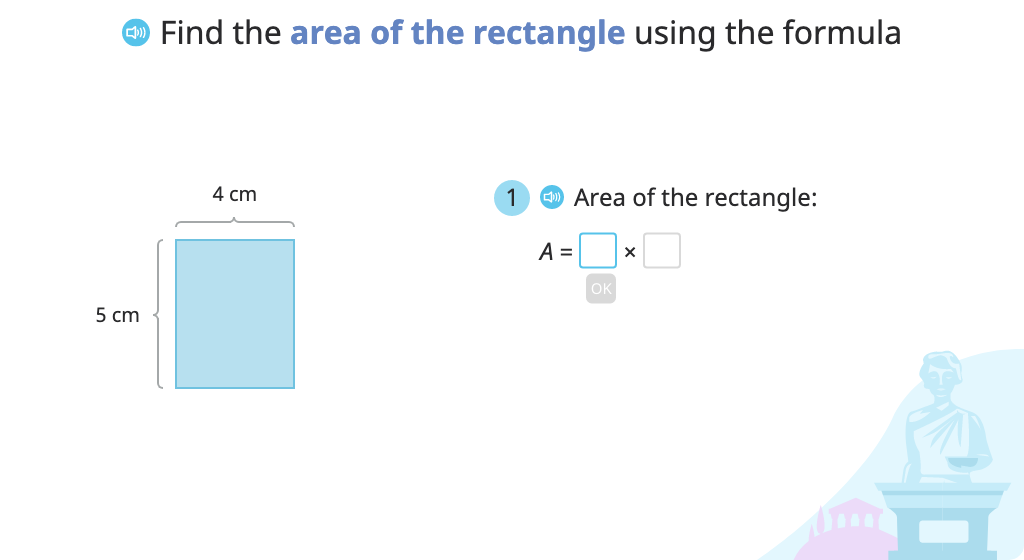
Topic B: Multiplication by 10, 100, and 1,000
Students extend their understanding of multiplication to include powers and multiples of 10. They initially use place value charts, then build fluency and learn to solve by regrouping factors.
Use a place value chart to model multiplying by 10
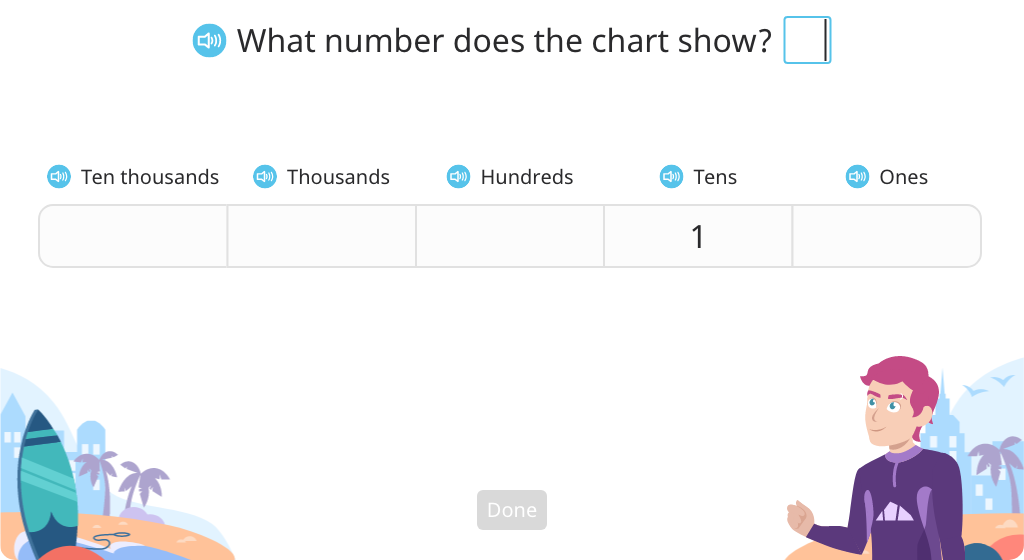
Use a place value chart to model multiplying by 100
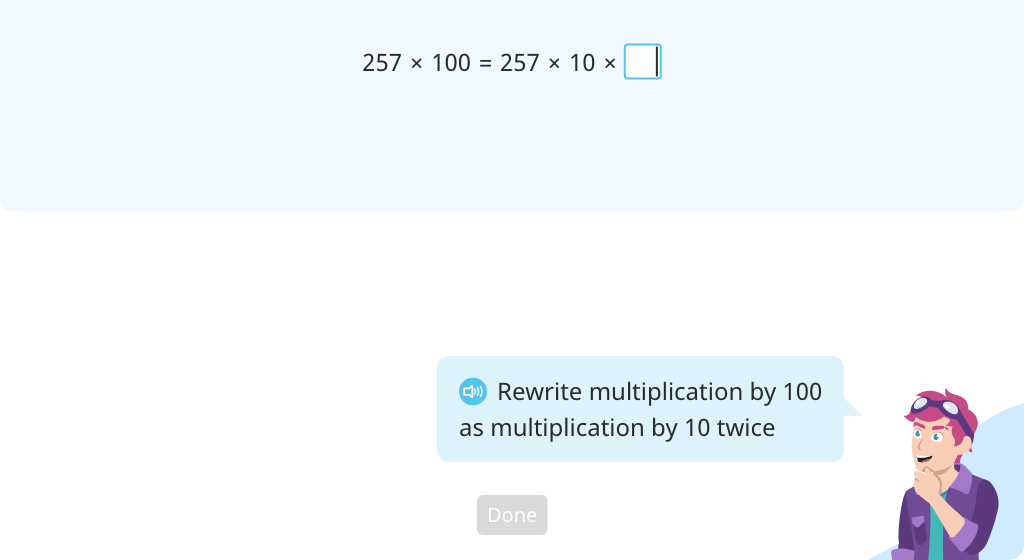
Multiply whole numbers by powers of 10 to notice the pattern

Multiply whole numbers by powers of 10 (Level 1)
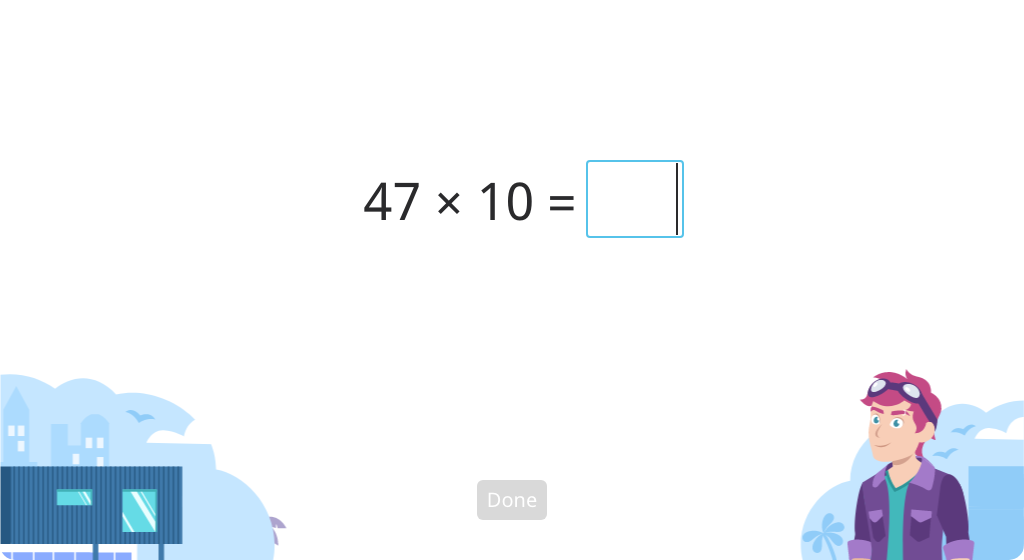
Multiply whole numbers by powers of 10 (Level 2)
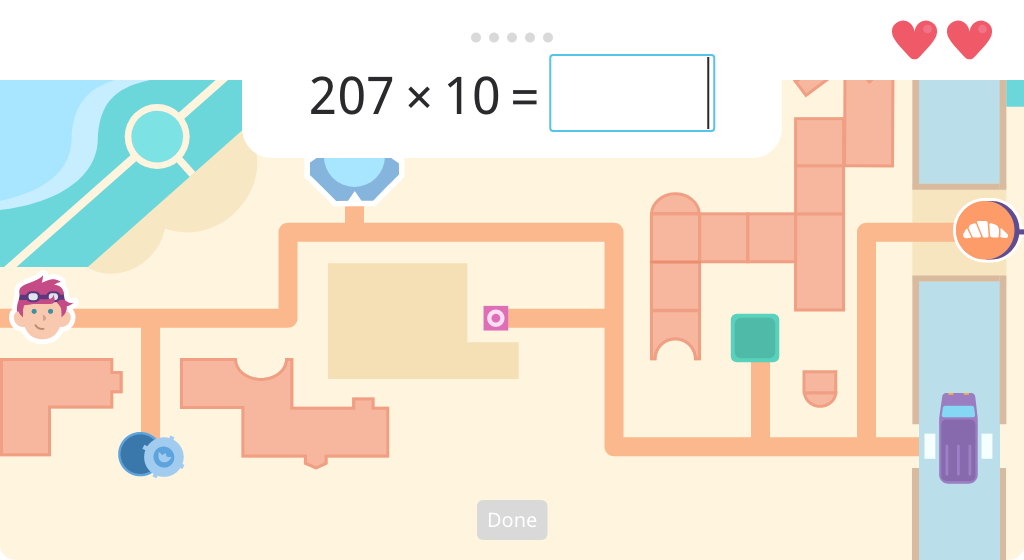
Solve 3-factor multiplication equations in two ways
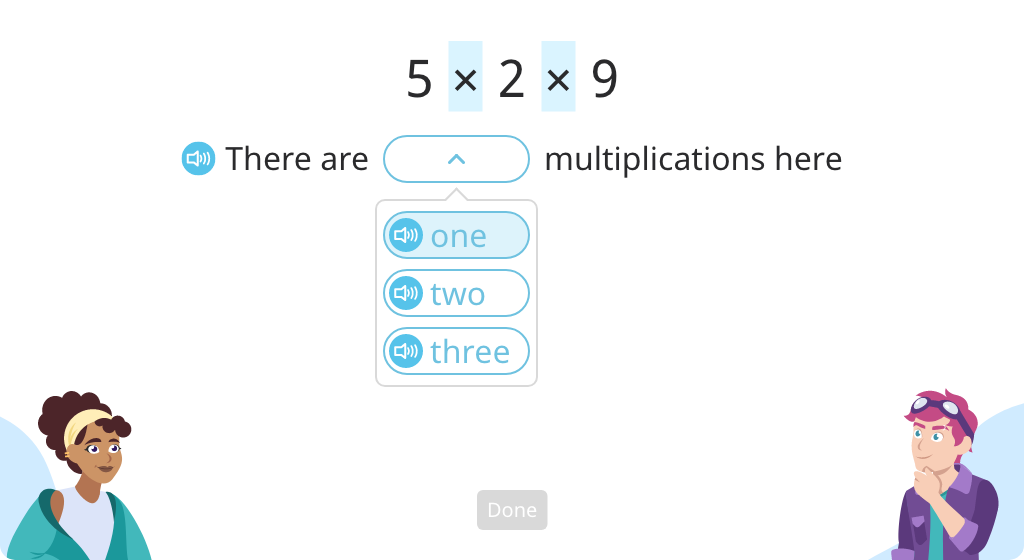
Multiply a single-digit number and tens number (Level 1)
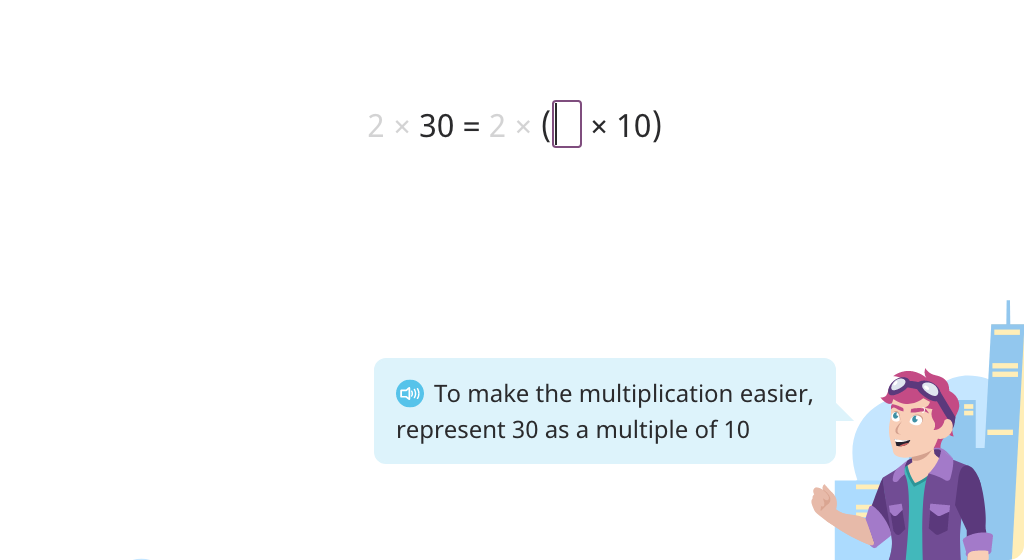
Multiply a single-digit number and tens number (Level 2)

Multiply a single-digit number and tens number (Level 3)
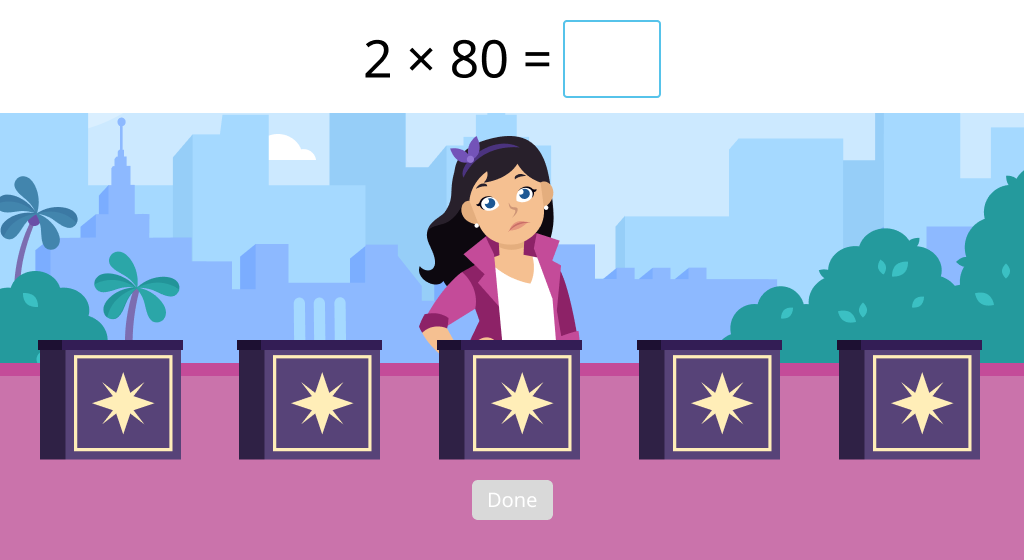
Multiply a single-digit number by a multiple of 100 or 1000 (Level 1)

Multiply a single-digit number by a multiple of 100 or 1000 (Level 2)

Multiply a single-digit number by a multiple of 100 or 1000 (Level 3)
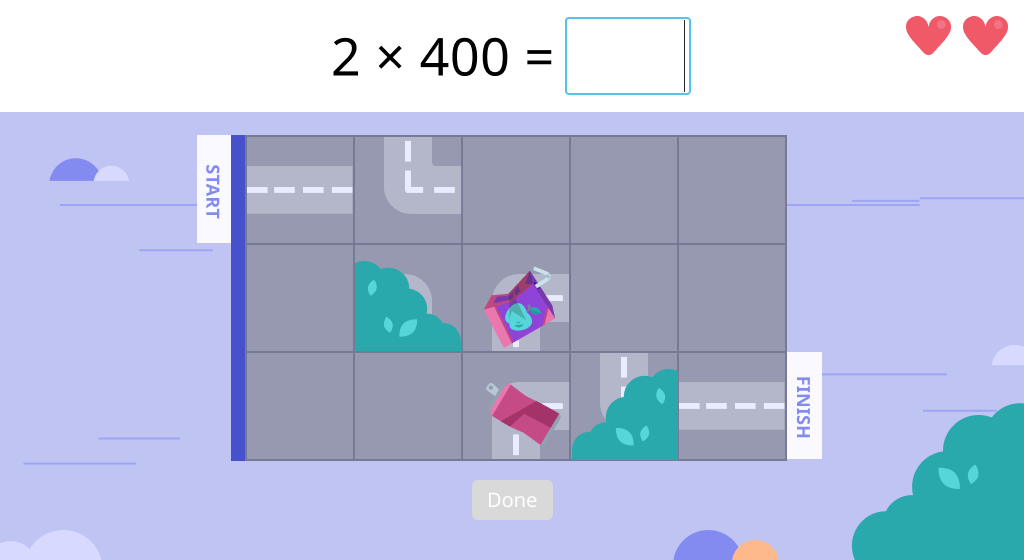
Topic C: Multiplication of up to Four Digits by Single-Digit Numbers
Students are gradually scaffolded through the steps of multiplying a multi-digit number by a single-digit number using the standard algorithm. They begin using a concrete disk model and a partial products method of recording. As they begin to work with the standard algorithm, they become more skilled and independent by regrouping, using zeros, using larger numbers, and receiving fewer prompts.
Solve a multiplication equation using partial products with and without a disk model

Solve a multiplication equation with regrouping using partial products with and without a disk model
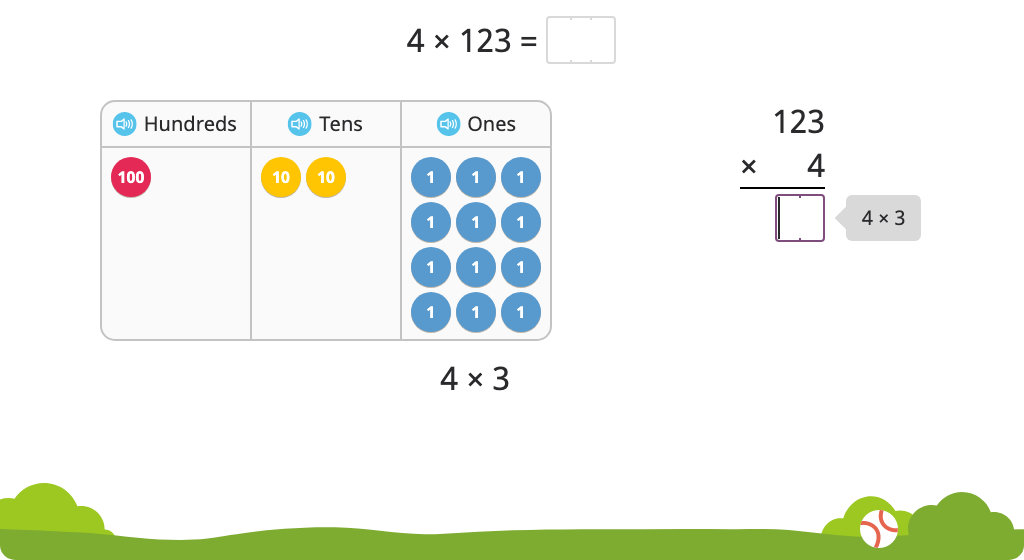
Solve a multiplication equation including a zero using partial products with and without a disk model
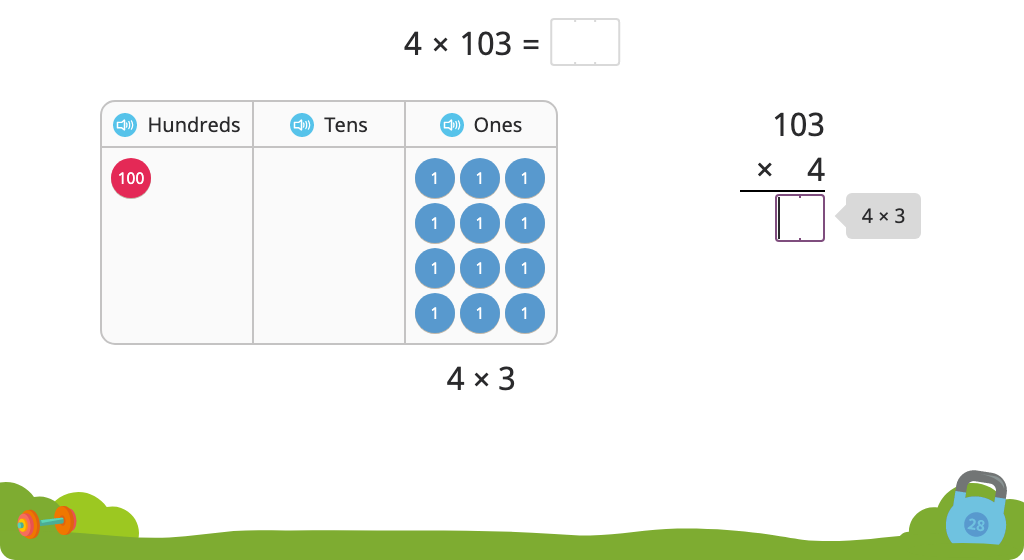
Solve a multiplication equation using the standard algorithm with and without a disk model
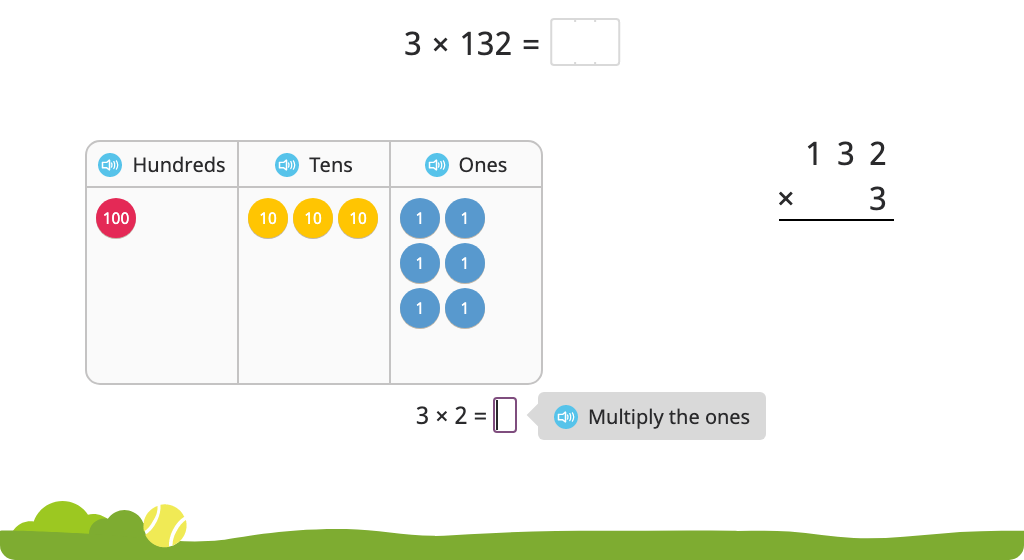
Solve a multiplication equation with regrouping using the standard algorithm using a disk model
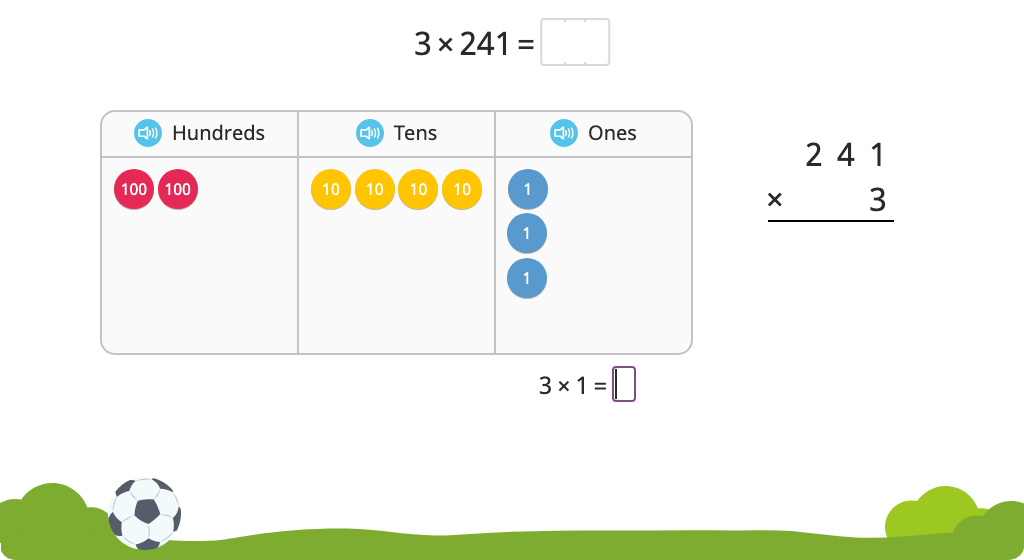
Solve a multiplication equation with regrouping using the standard algorithm (Level 1)
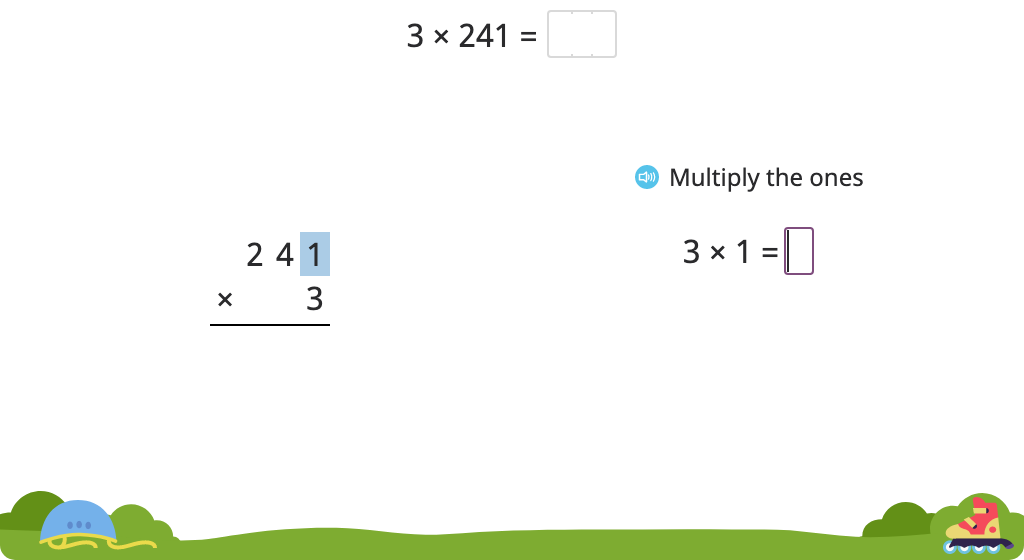
Solve a multiplication equation with regrouping using the standard algorithm (Level 2)
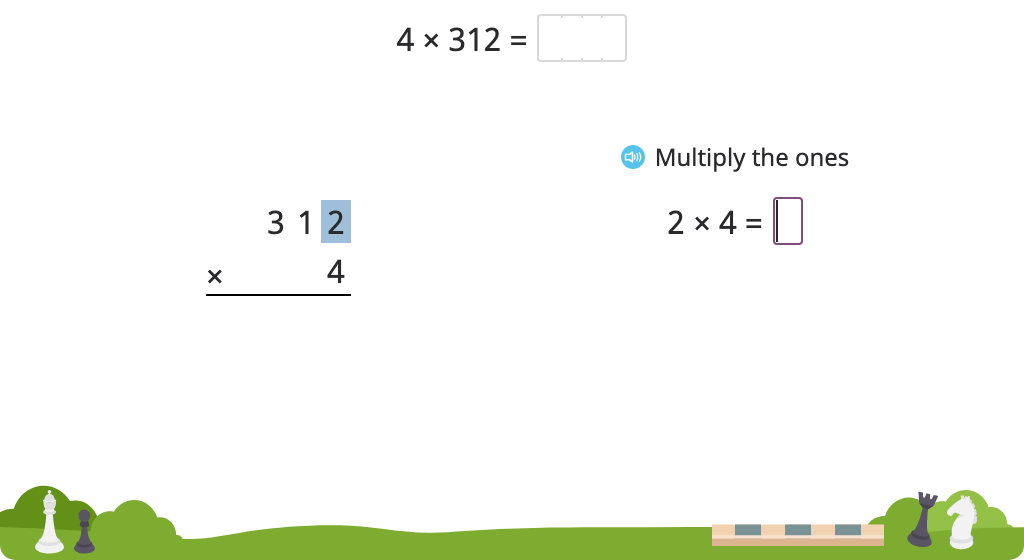
Solve a multiplication equation with regrouping using the standard algorithm (Level 3)
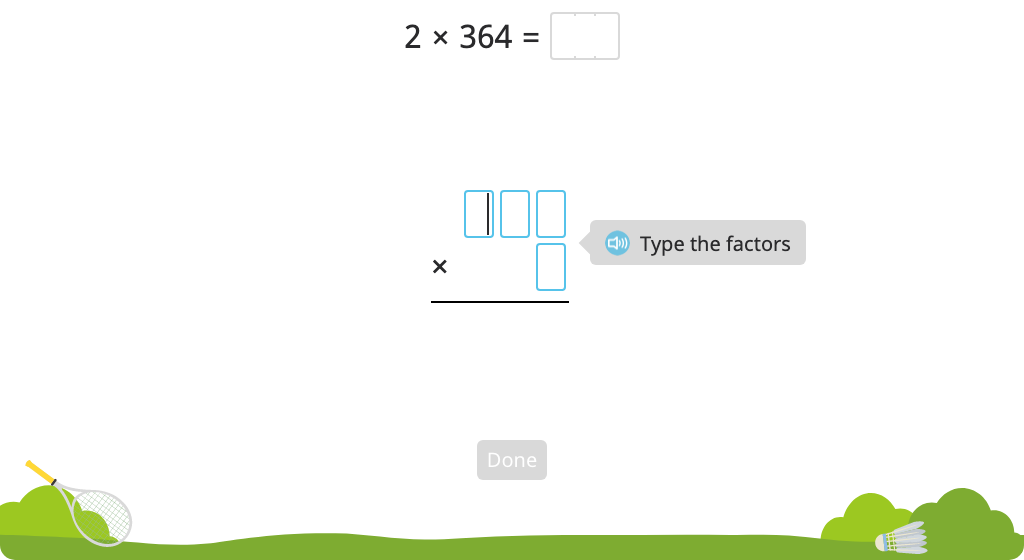
Solve a multiplication equation with regrouping using the standard algorithm (Level 4)
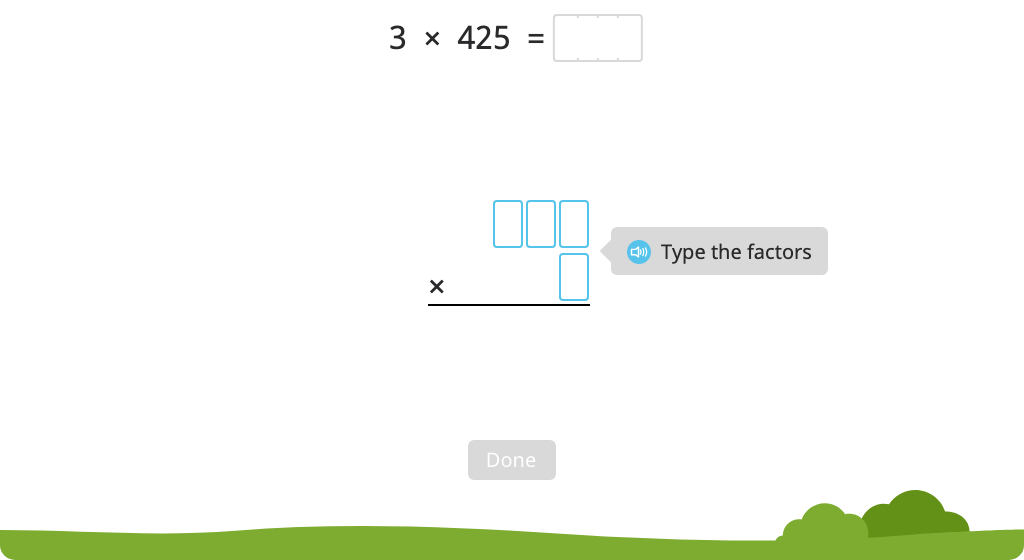
Solve a multiplication equation with regrouping while identifying steps of the standard algorithm
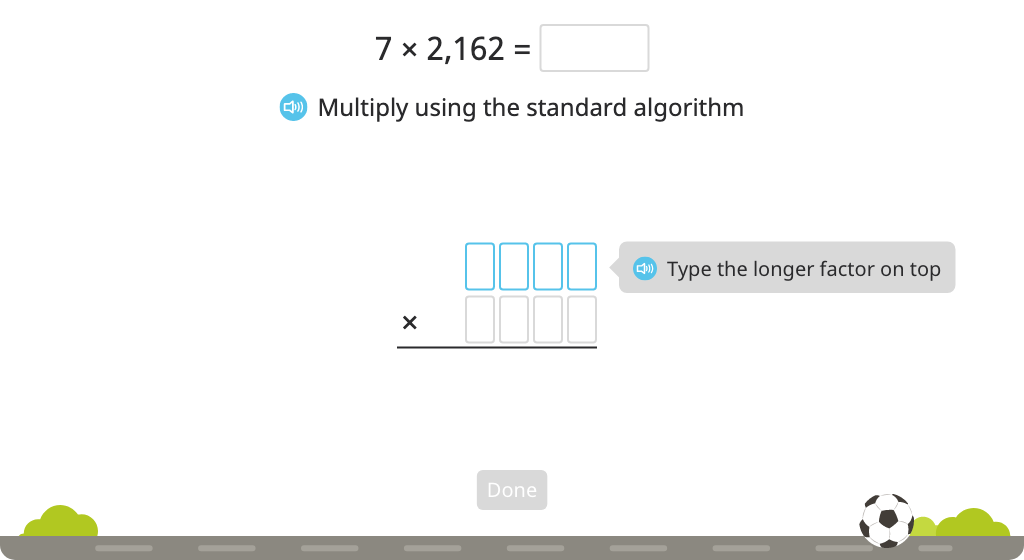
Solve a multiplication equation with regrouping using the standard algorithm (Level 5)
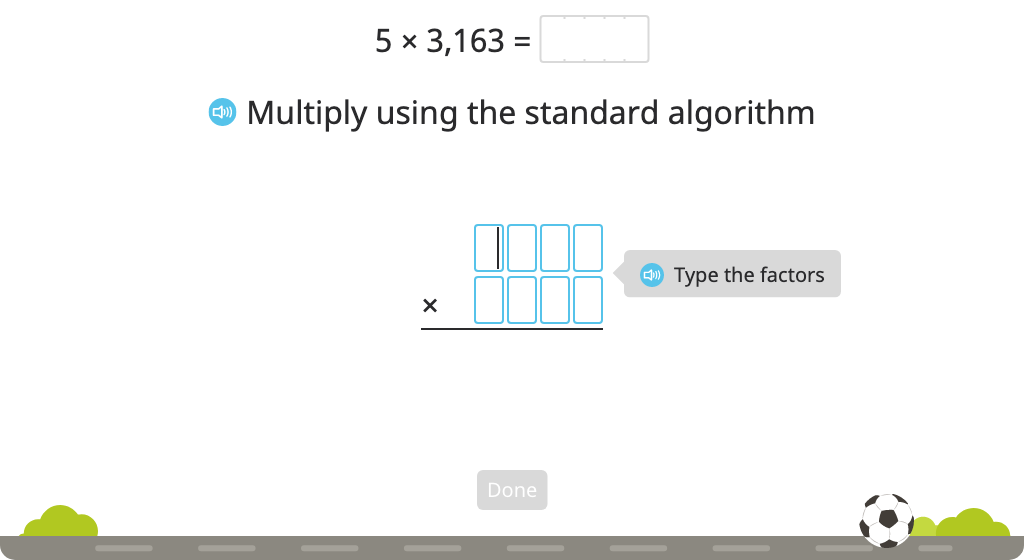
Solve a single multiplication equation using both partial products and the standard algorithm

Multiply to find the area of a rectangle
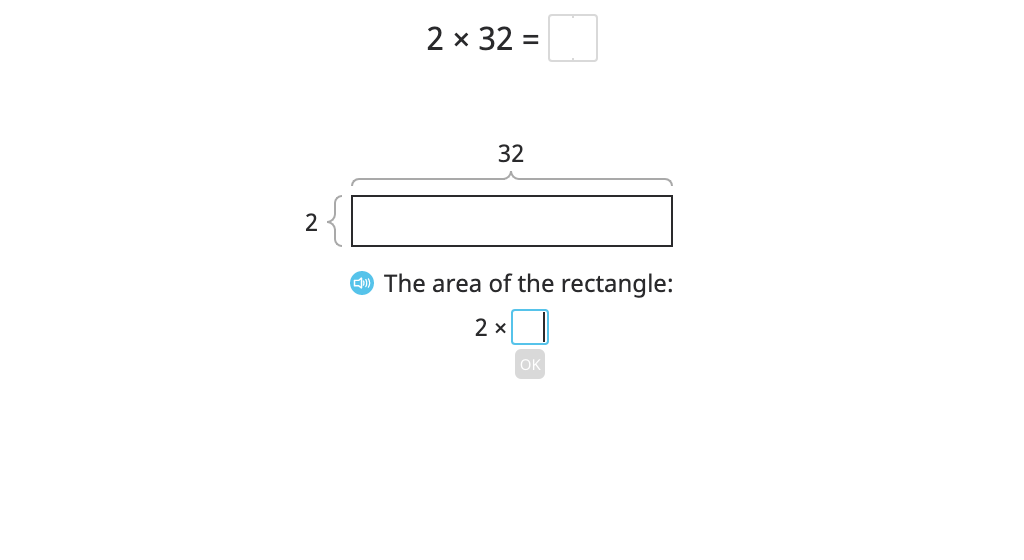
Multiply to find the area of a rectangle using partial products (Level 1)

Multiply to find the area of a rectangle using partial products (Level 2)

Topic D: Division of Tens and Ones with Successive Remainders
Students divide 1- and 2-digit numbers to determine the number in each group or the number of groups. They use models to illustrate a word problem and equations to record their work. Students are introduced to the term "quotient" and a method for checking their answer. Students move from simple division to division with a remainder in this topic, and they learn to use long division notation.
Solve a division problem (number in each group) with a remainder based on a model
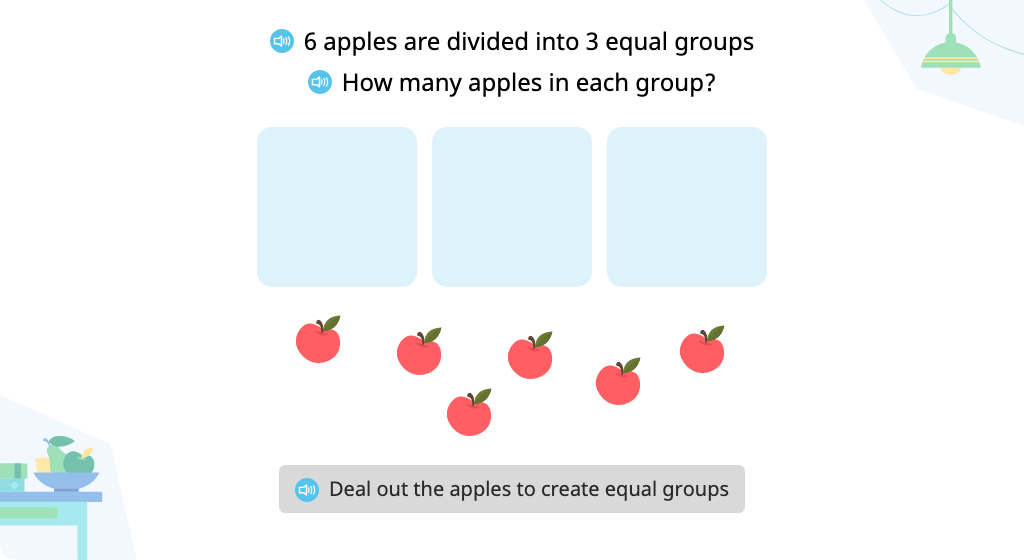
Solve a division problem (number of groups) with a remainder based on a model

Solve a division problem (number in each group) with a remainder using an array model
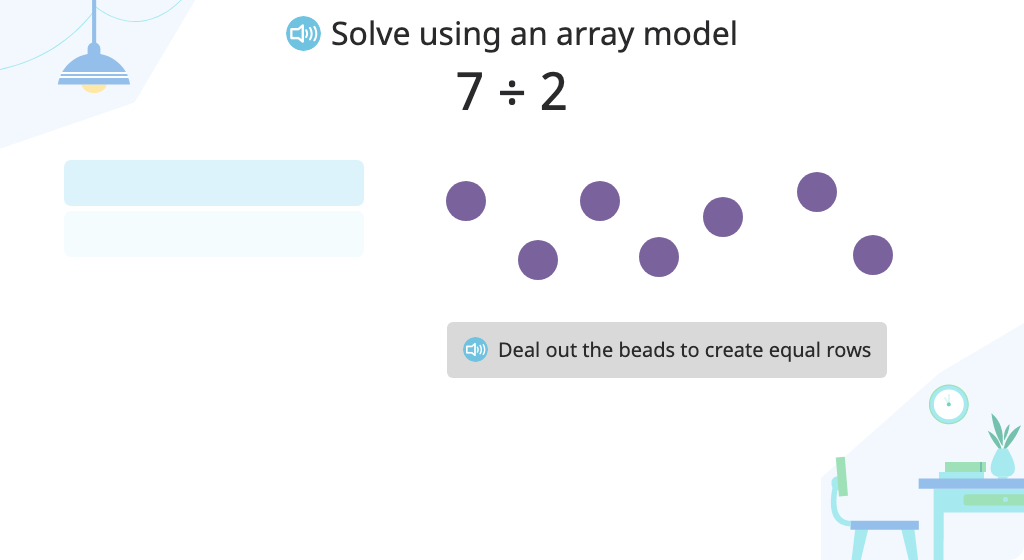
Solve a division problem (number of groups) with a remainder using an array model
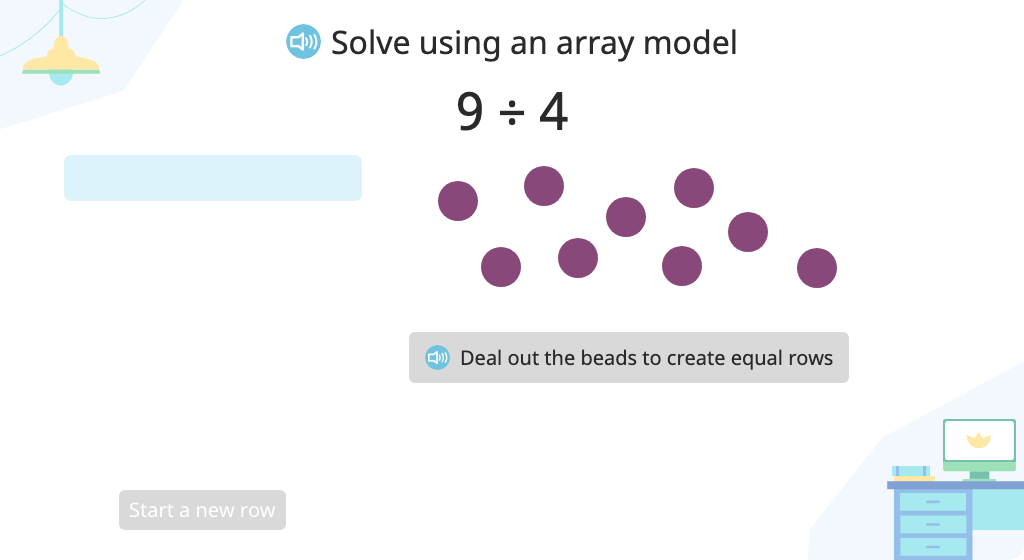
Multiply to find multiples of a given number

List and identify multiples of a given number

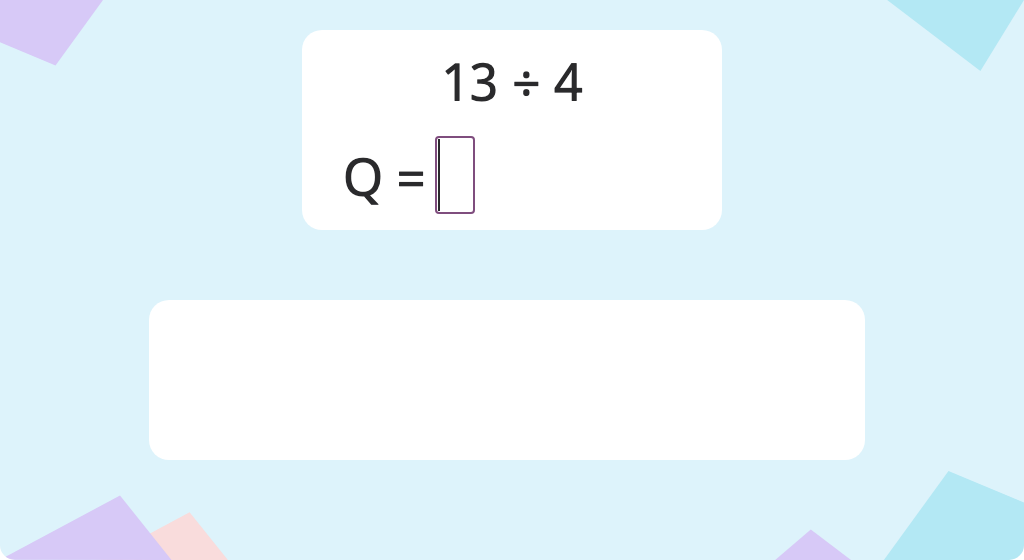
Use multiples to find the quotient and remainder of a division problem

Model division (number in each group) with a remainder using a tape diagram
Model division (number of groups) with a remainder using a tape diagram
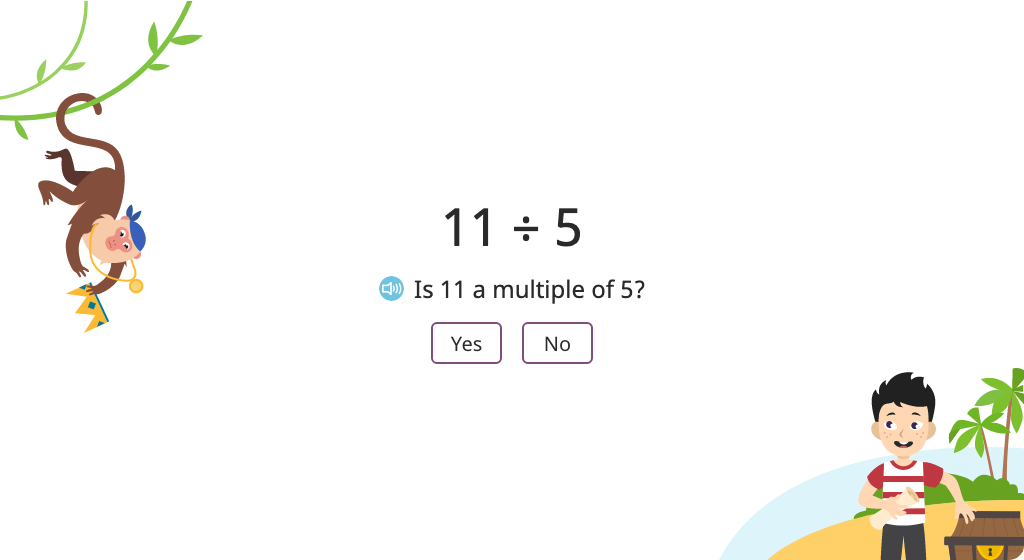
Solve a division problem with a remainder using the closest multiplication fact

Solve a division problem with a remainder

Solve a division word problem (number of groups) with a remainder using a tape diagram and an equation

Solve a division word problem (number in each group) with a remainder using a tape diagram and an equation

Model and solve a division problem, and identify the divisor
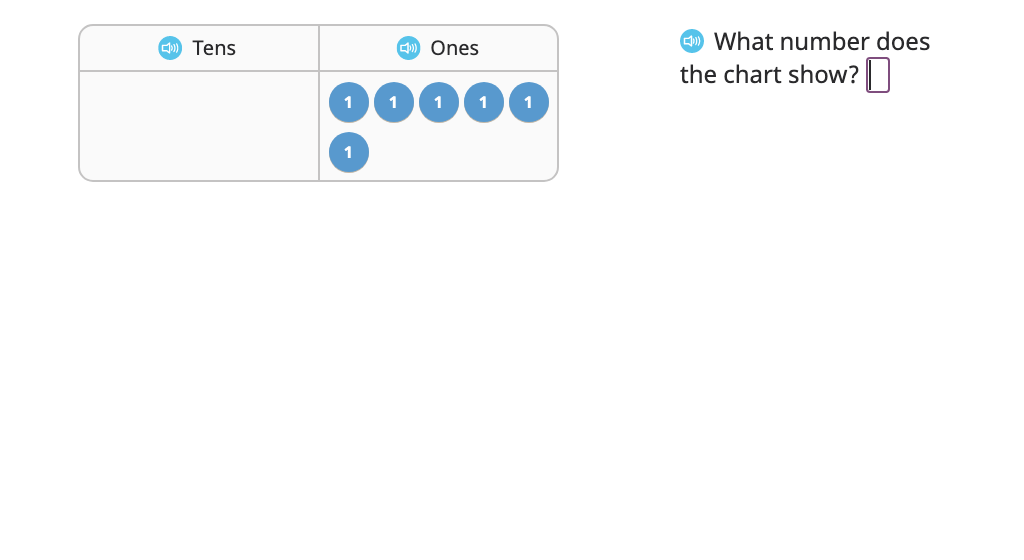
Model and solve a division problem using long division (single-digit quotient)
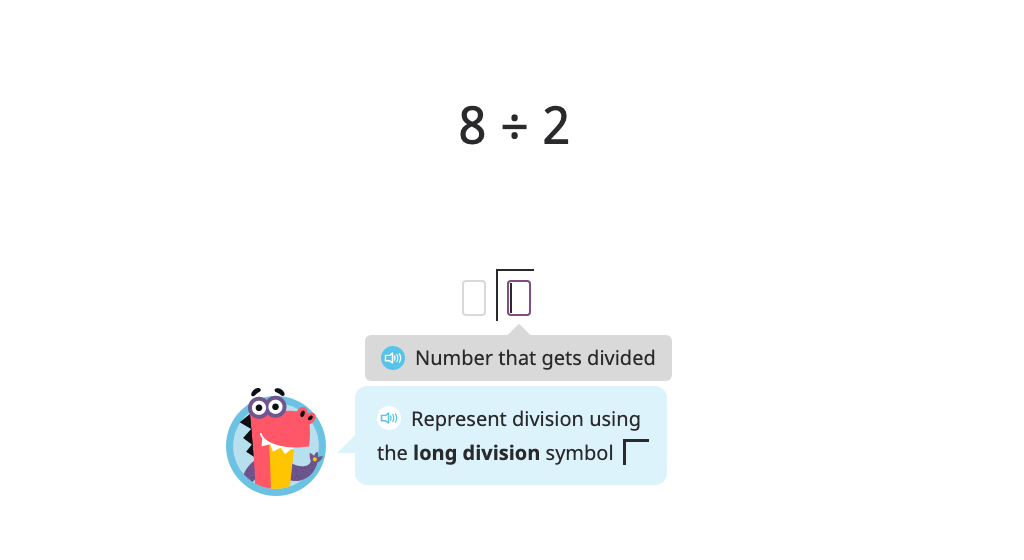
Solve a division problem (number in each group) with a remainder using a disk model
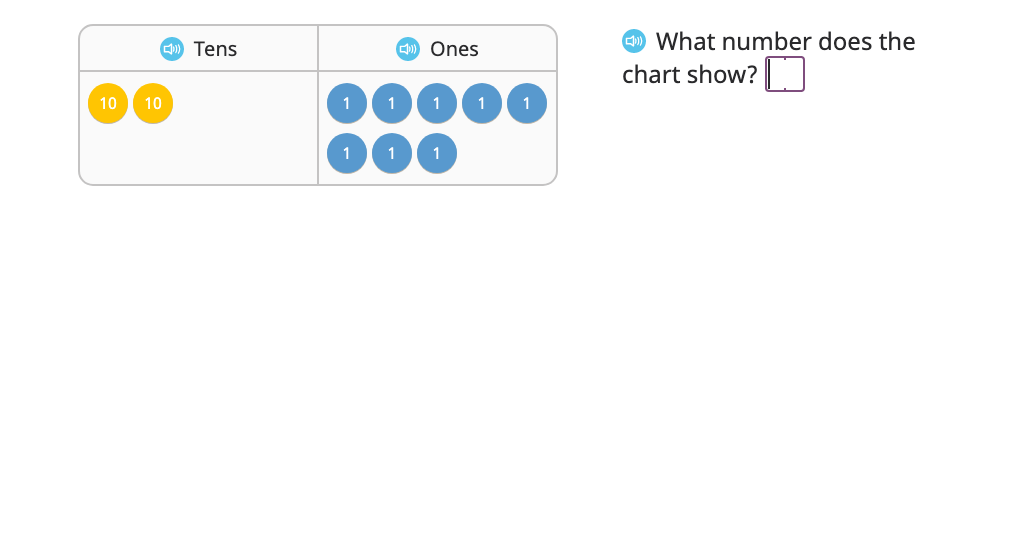
Model and solve a division problem using long division (two-digit quotient)
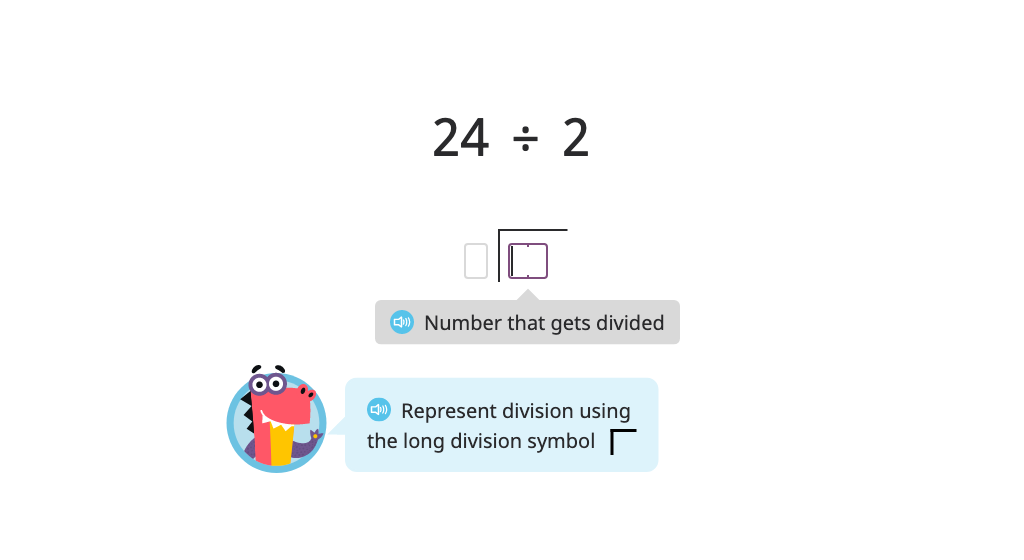
Model and solve a division problem that involves regrouping
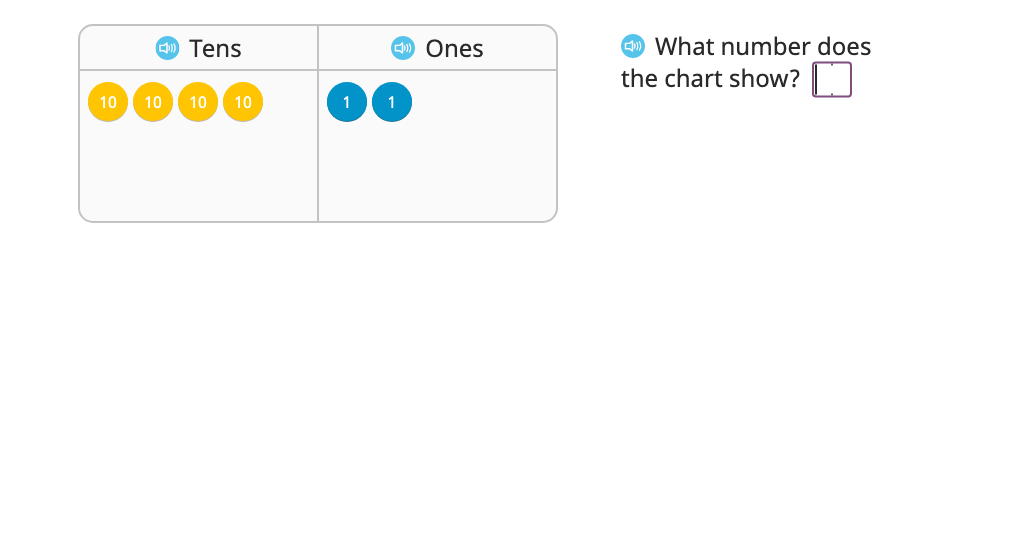
Model and solve a division problem that involves regrouping using long division (two-digit quotient)

Model and solve a division problem that involves regrouping using long division (two-digit quotient) (Level 2)

Model and solve a division problem using long division by recording partial quotients
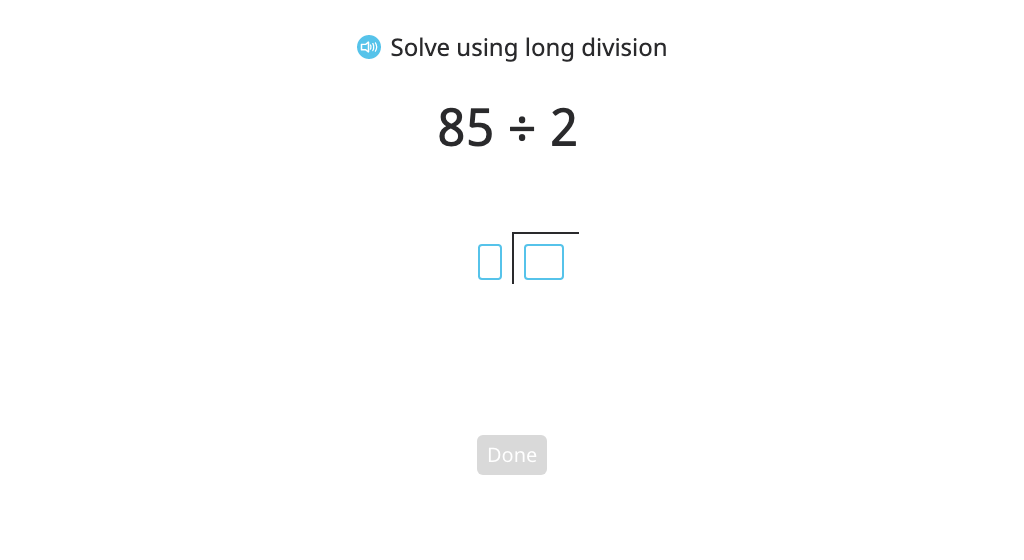
Use long division to solve problems with a 2-digit quotient
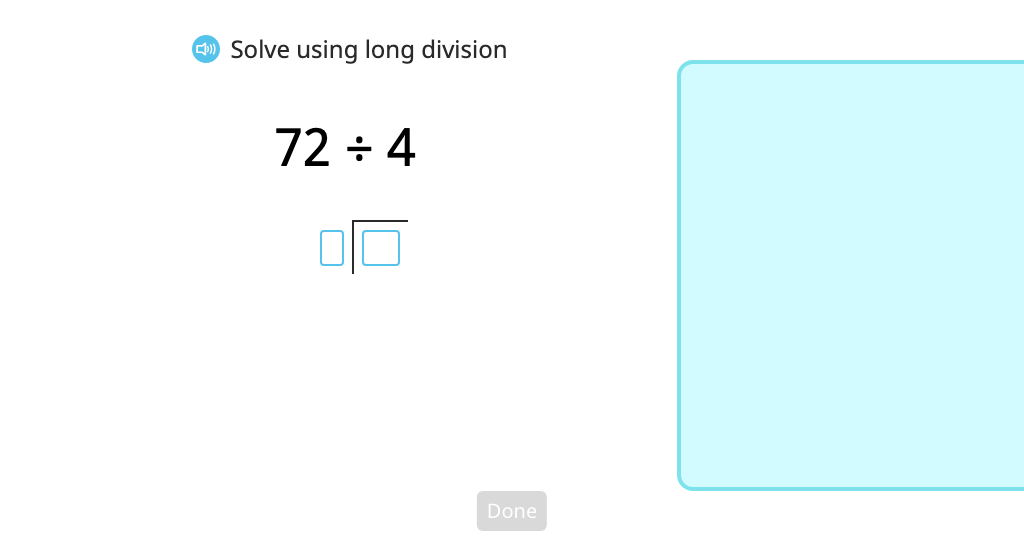
Topic E: Reasoning with Divisibility
Students build a firm understanding of the concepts of factor, multiple, and divisible by, as well as the relationship among those concepts. They explore divisibility patterns/rules for 2, 3, 5, 6, 9, and 10. To build this understanding, students use manipulatives, arrays, long division, and the hundred chart.
Solve single-digit multiplication problems

Find factors of a given number by labeling arrays (Level 1)

Find factors of a given number by labeling arrays (Level 2)

Find factors of a given number by building and labeling arrays
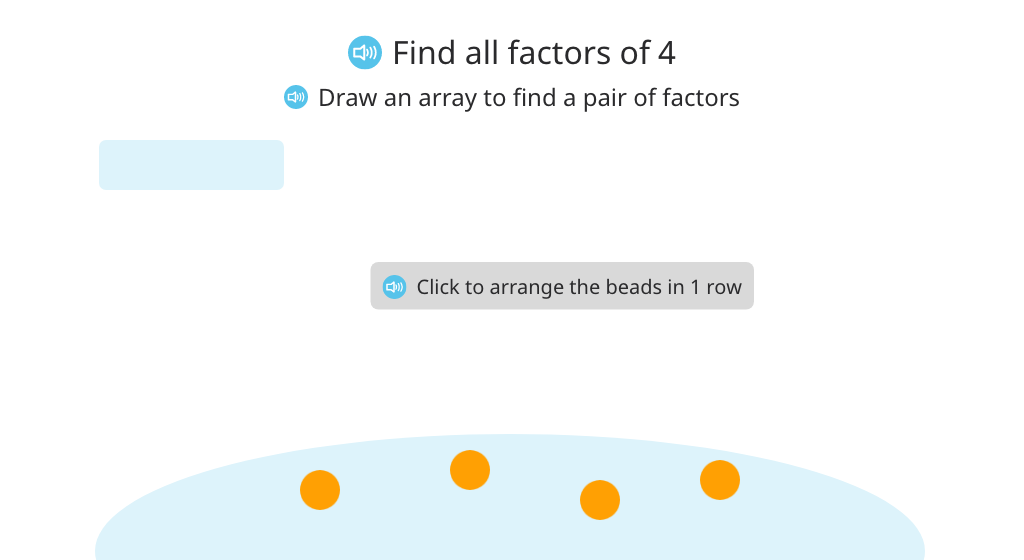
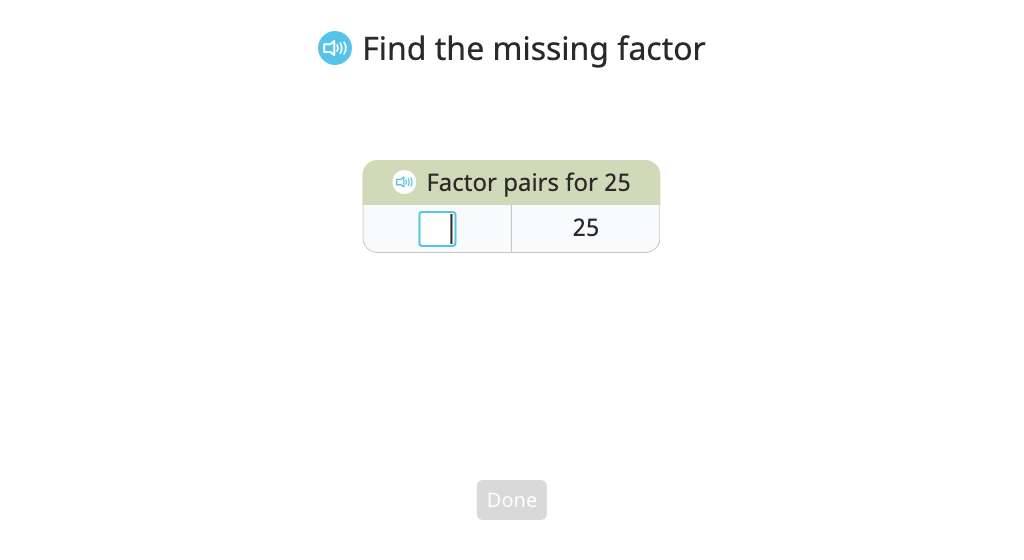
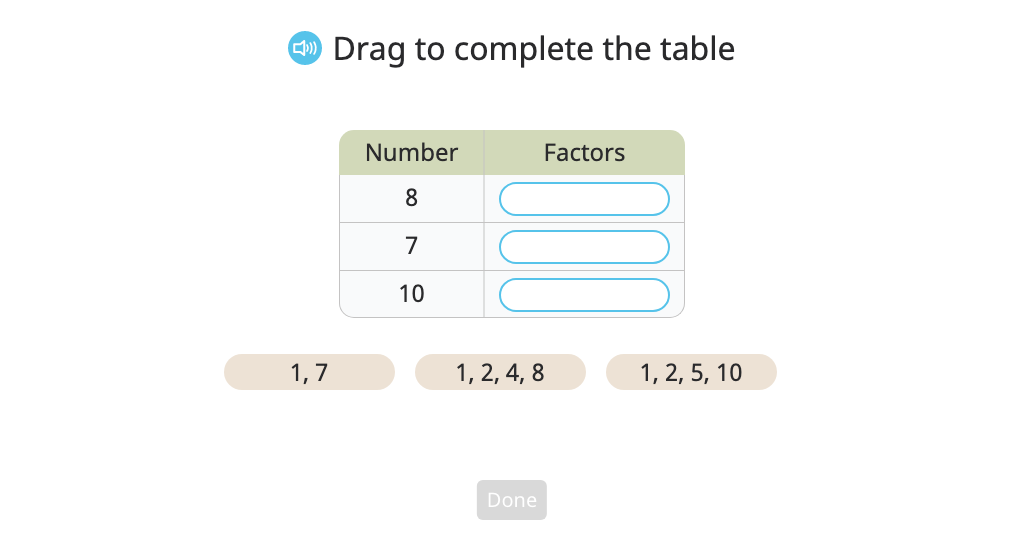
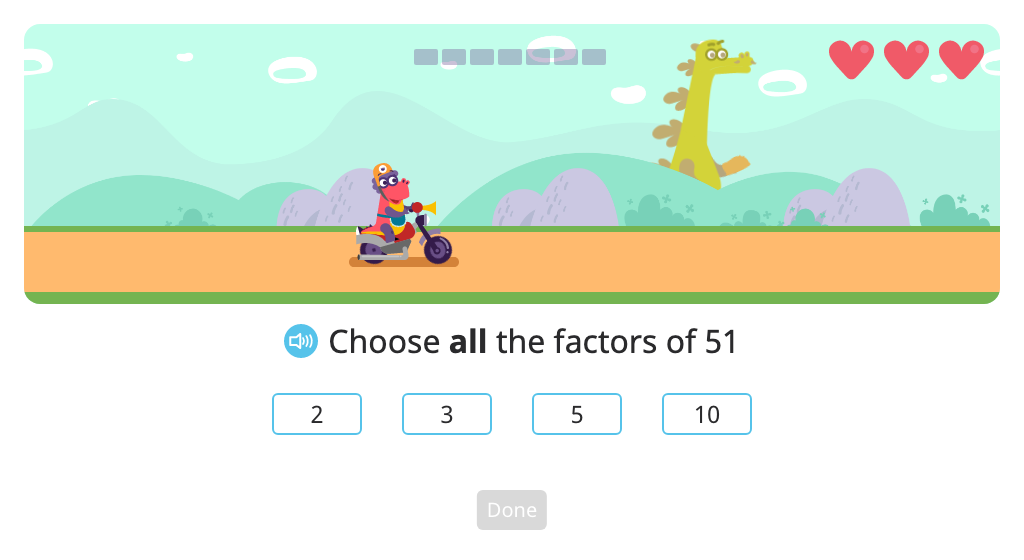
List factor pairs for a given number and identify the number as prime or composite
Determine whether a given number is a factor of another given number
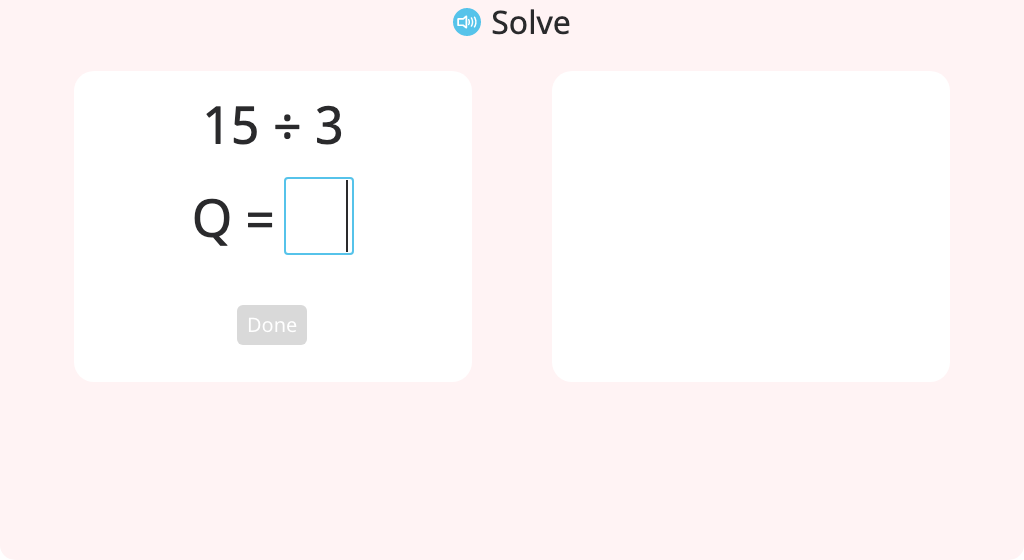
Use long division to determine whether a given number is a factor of another given number

Use long division to show that if a number is a factor of another number, its factors are also factors of that number

Use properties of multiplication to show that if a number is a factor of another number, its factors are also factors of that number

Determine multiples of a given factor
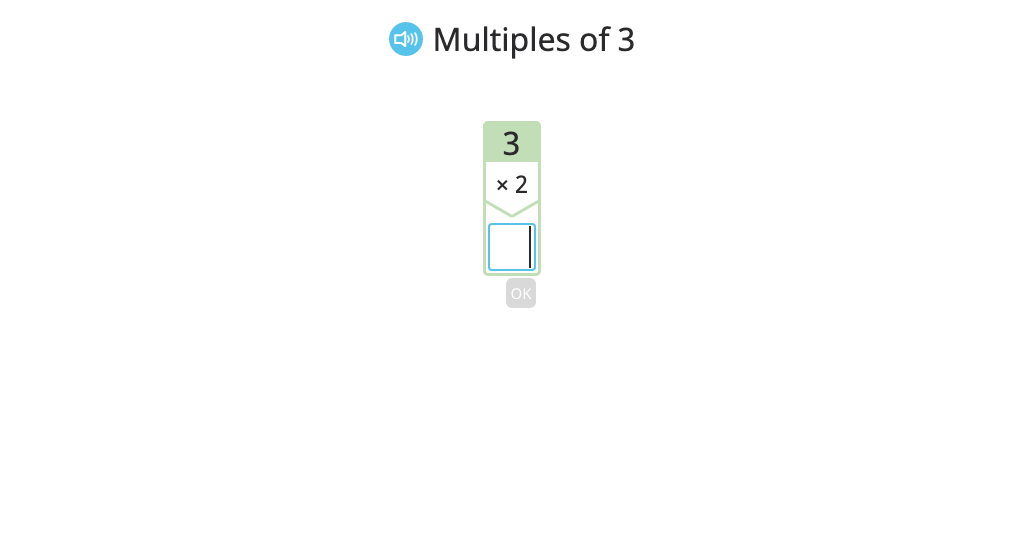
Identify the relationship between factors, multiples, and divisible by

Identify factors or multiples of a list of given numbers
Use long division to determine whether a given number is a multiple of another given number
Use long division to show that if a number is a multiple of another number, it is also a multiple of that number's factors

Use properties of multiplication to show that if a number is a multiple of another number, it is also a multiple of that number's factors

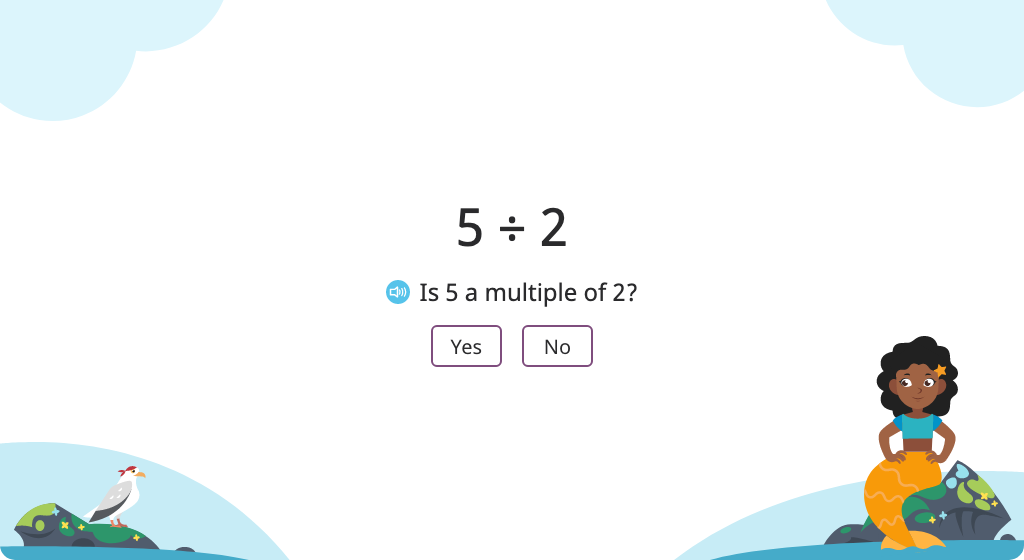
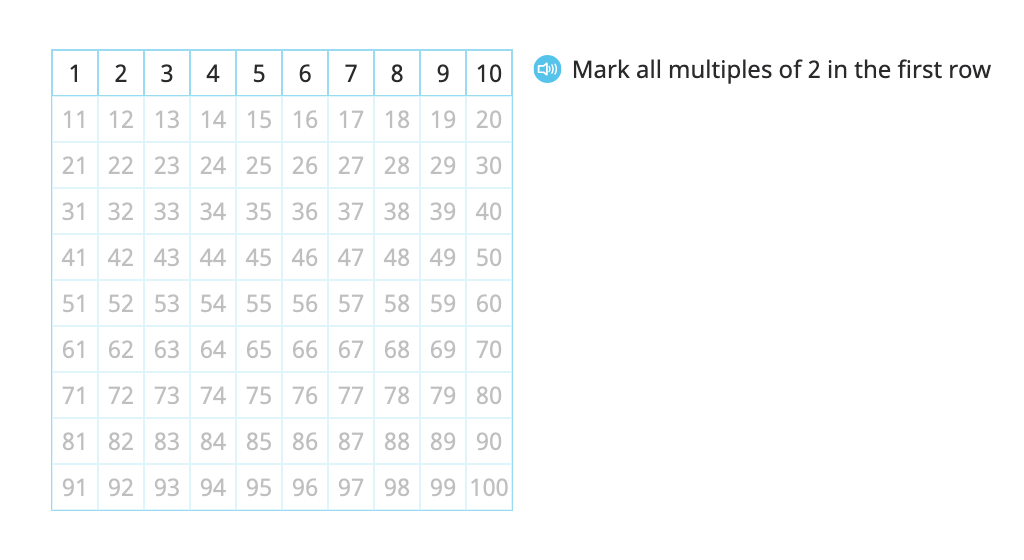
Identify multiples of 2, 5, and 10 on a hundred chart and identify patterns in the ones place of the multiples
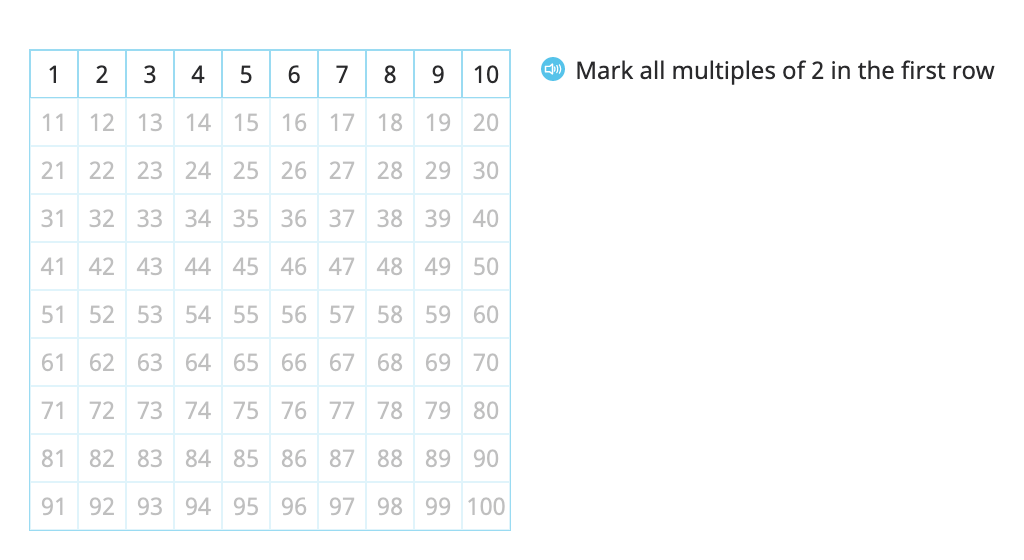
Determine whether a given number is a multiple of 2, 5, or 10
Determine whether a given number is even or odd

Identify multiples of 3 and 9 on a hundred chart and identify patterns in the multiples
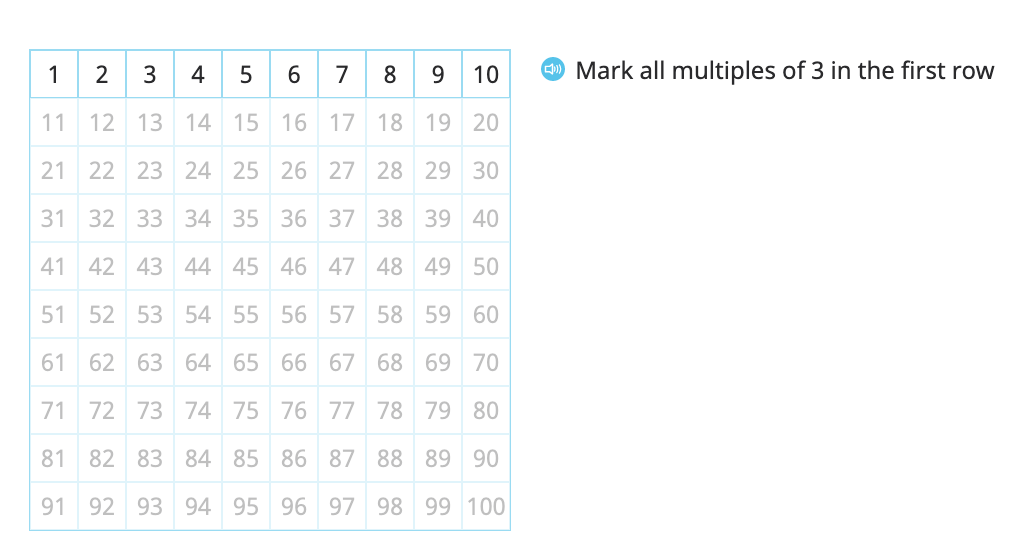
Determine whether a given number is a multiple of 3 or 9
Identify factors (2, 3, 5, 10) of a given multiple
Use a hundred chart to show that multiples of 2 and 3 are multiples of 6, and that multiples of 2 and 5 are multiples of 10
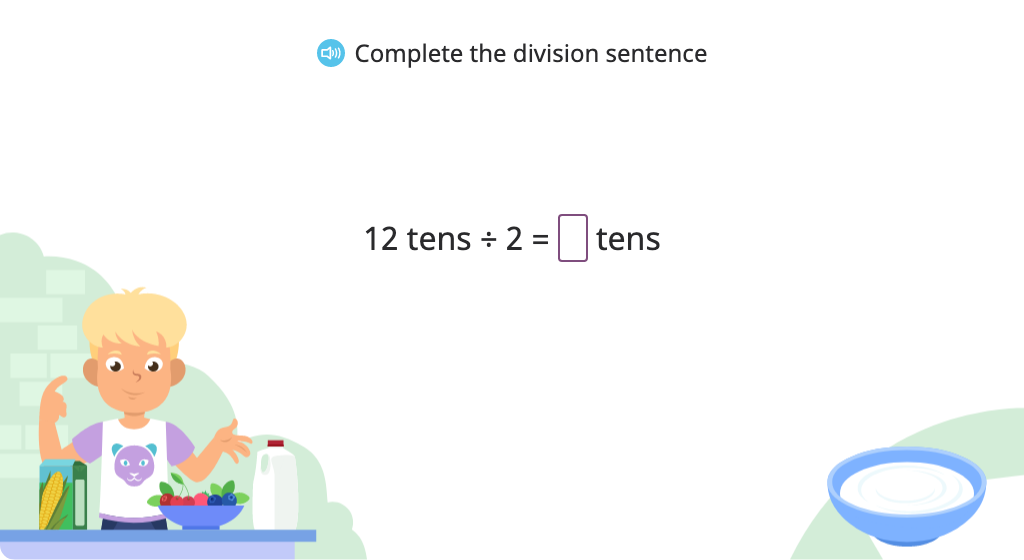
Topic F: Division of Thousands, Hundreds, Tens, and Ones
Students divide numbers in the hundreds and thousands by single-digit numbers. They move from unit notation to standard notation to help facilitate mental math with large numbers. Understanding of the standard algorithm is supported by familiar models - a disk model and tape diagrams. Students are supported in dealing with various division challenges from regrouping to remainders to working with zero.
Multiply using unit notation and standard notation

Divide using a disk model
Divide using a disk model (with regrouping) (Part 1)
Divide using unit notation and standard notation (Level 1)
Divide using unit notation and standard notation (Level 2)

Divide using standard notation

Divide using a disk model (with regrouping) (Part 2)
Divide using long division and a disk model (with regrouping and a remainder) (Part 1)

Divide using long division and a disk model (with regrouping and a remainder) (Part 2)

Divide using a disk model (with regrouping) (Part 3)
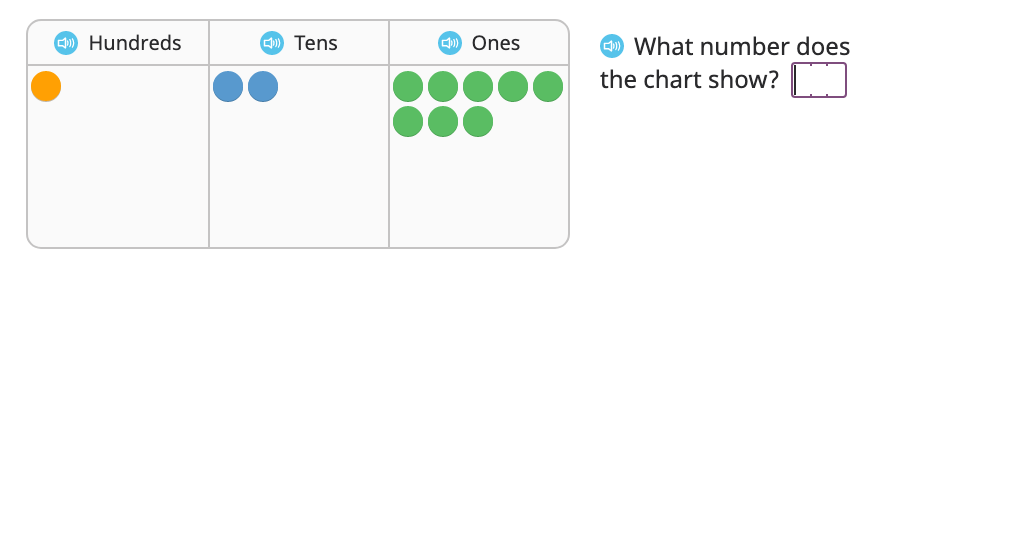
Divide using long division and a disk model (with regrouping and a remainder) (Part 3)

Divide using long division and a disk model (with regrouping and a remainder) (Part 4)

Divide using long division and a disk model (with regrouping and a remainder) (Part 5)

Divide using long division with partial quotients and a disk model
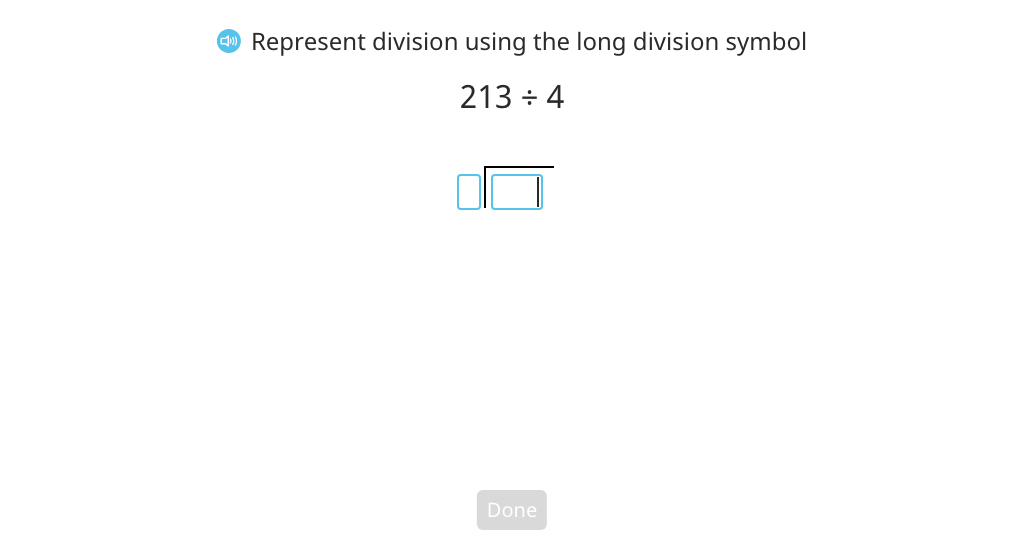
Divide using long division with partial quotients (Level 1)
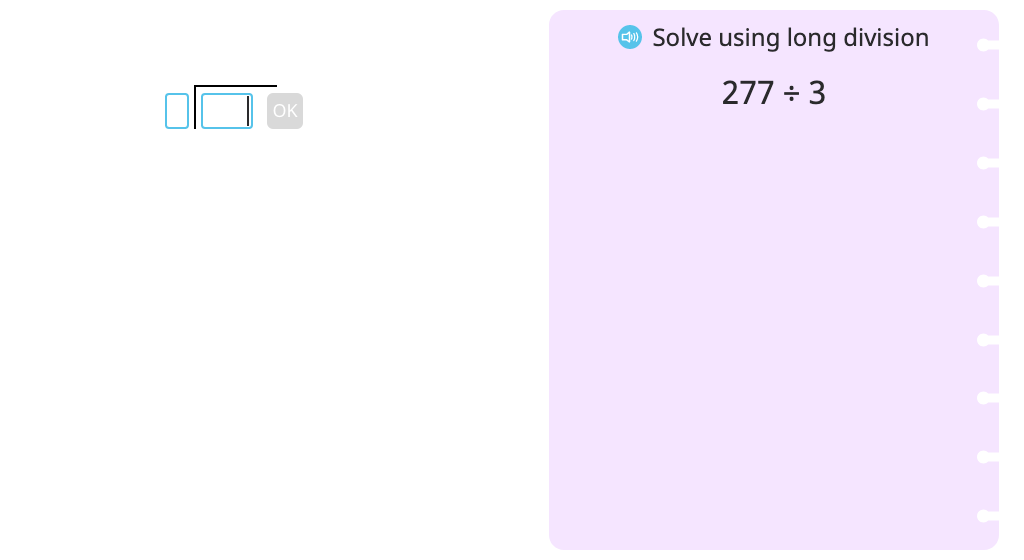
Divide using long division with partial quotients (Level 2)
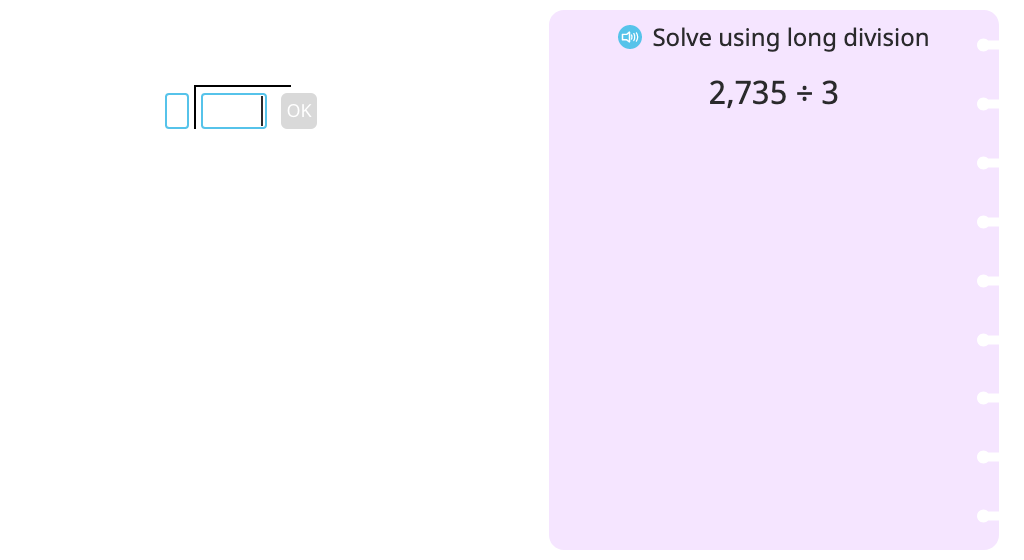
Divide across a zero using a disk model (with regrouping and a remainder)
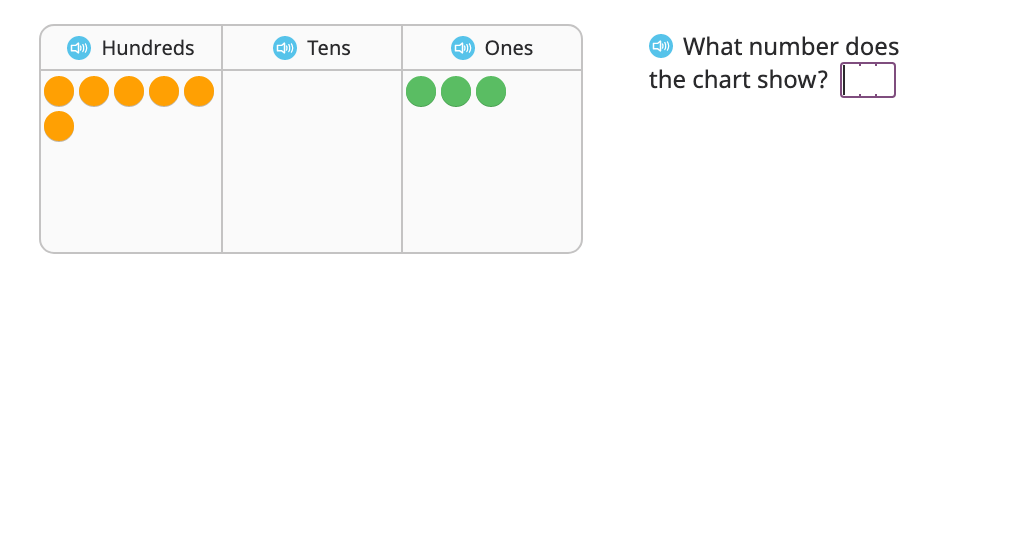
Divide across a zero using long division and a disk model (with regrouping and a remainder) (Part 1)

Divide using a disk model with zero in the quotient (with regrouping)
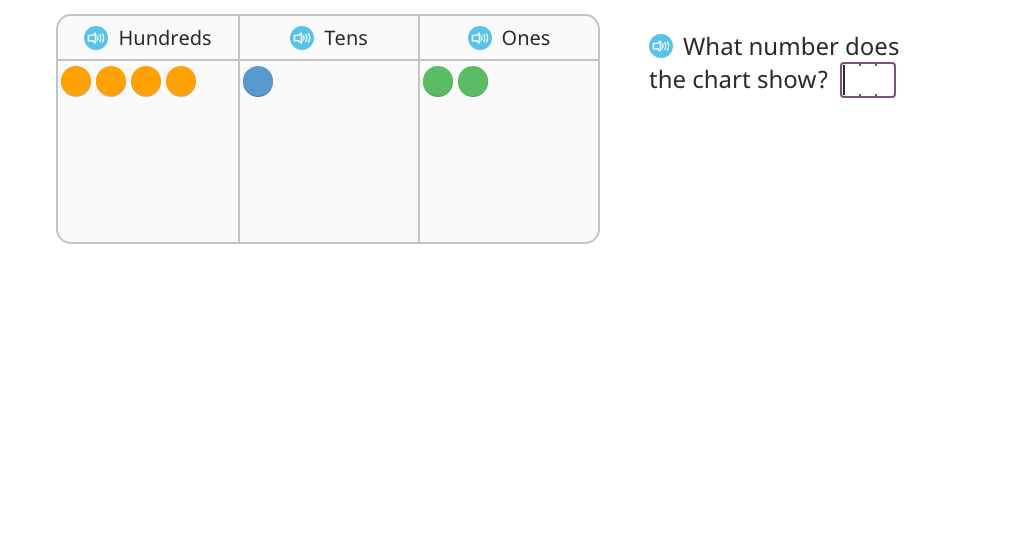
Divide using long division and a disk model with zero in the quotient (with regrouping)

Divide across a zero using long division and a disk model (with regrouping and a remainder) (Part 2)
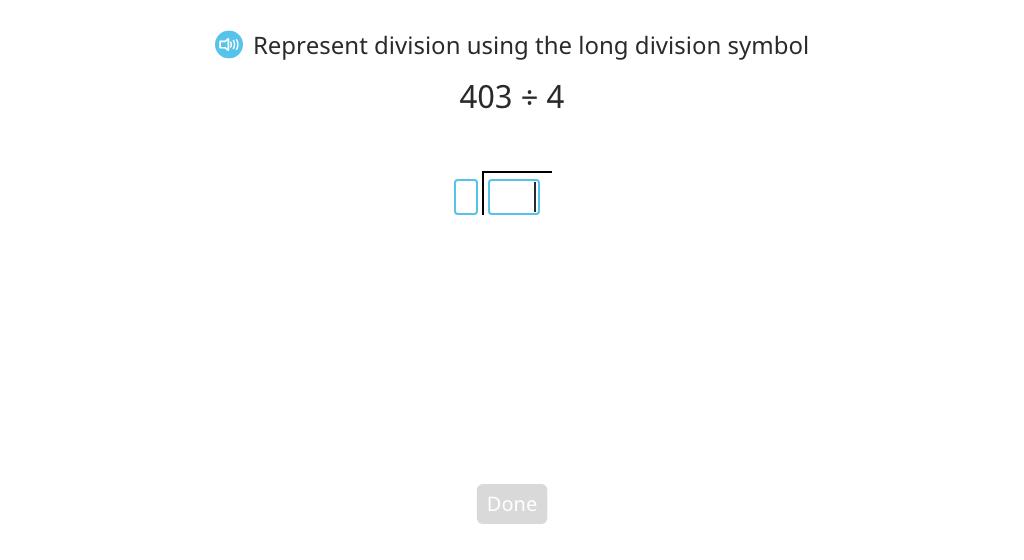
Solve division problems with a quotient of zero (with a remainder) (Level 1)
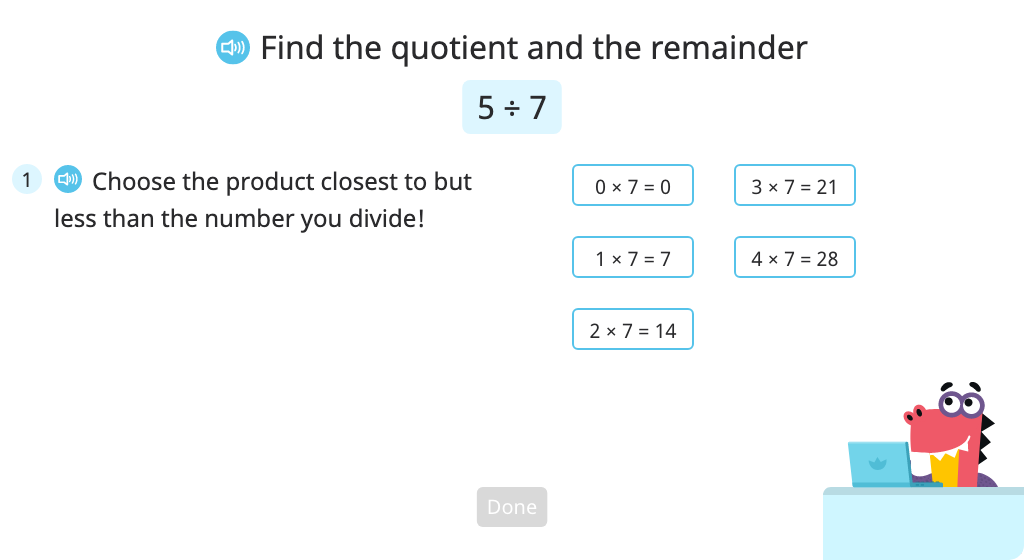
Solve division problems with a quotient of zero (with a remainder) (Level 2)

Divide across a zero using long division with partial quotients and a disk model (with regrouping and a remainder) (Part 1)
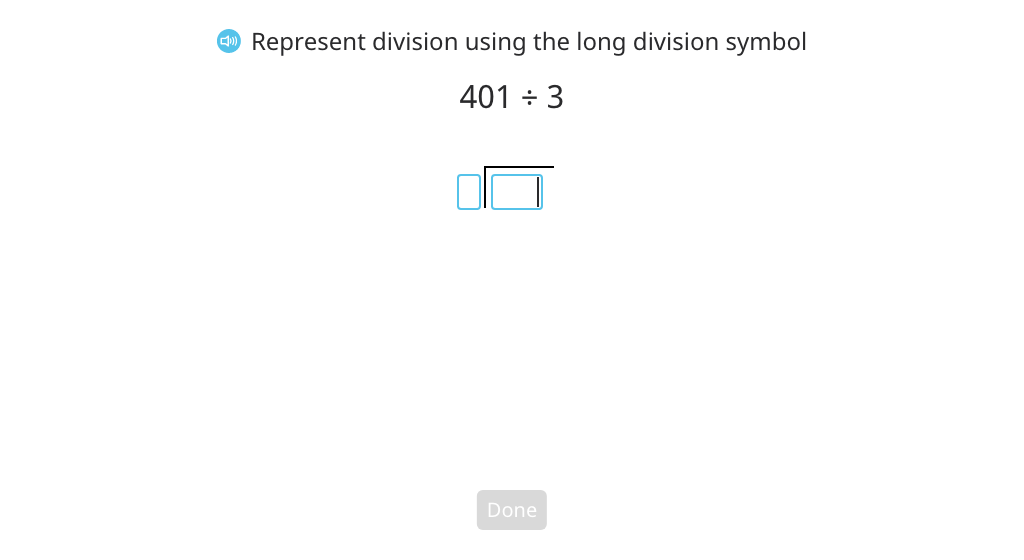
Divide across a zero using long division with partial quotients and a disk model (with regrouping and a remainder) (Part 2)

Divide across a zero using long division with partial quotients (with regrouping and a remainder) (Part 1)
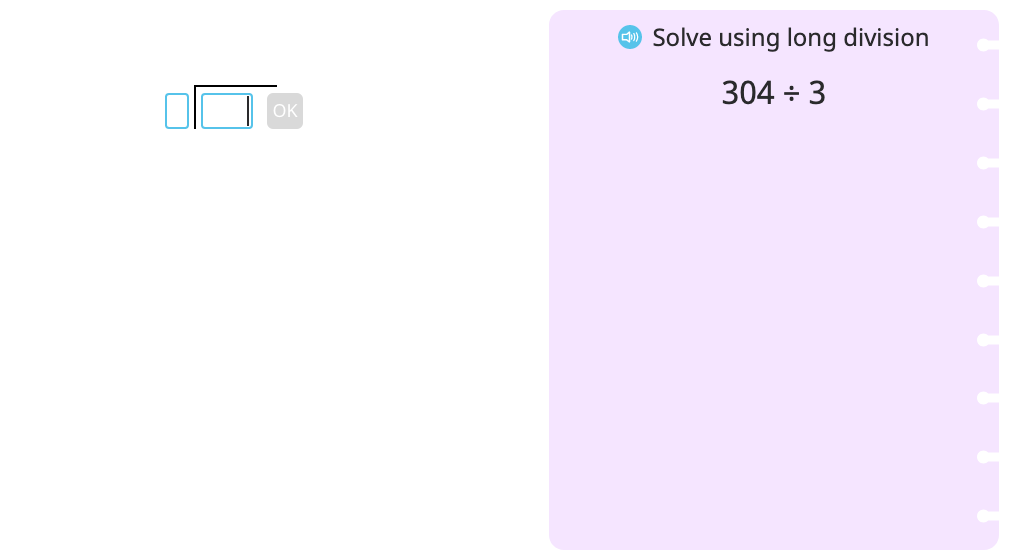
Divide across a zero using long division with partial quotients (with regrouping and a remainder) (Part 2)
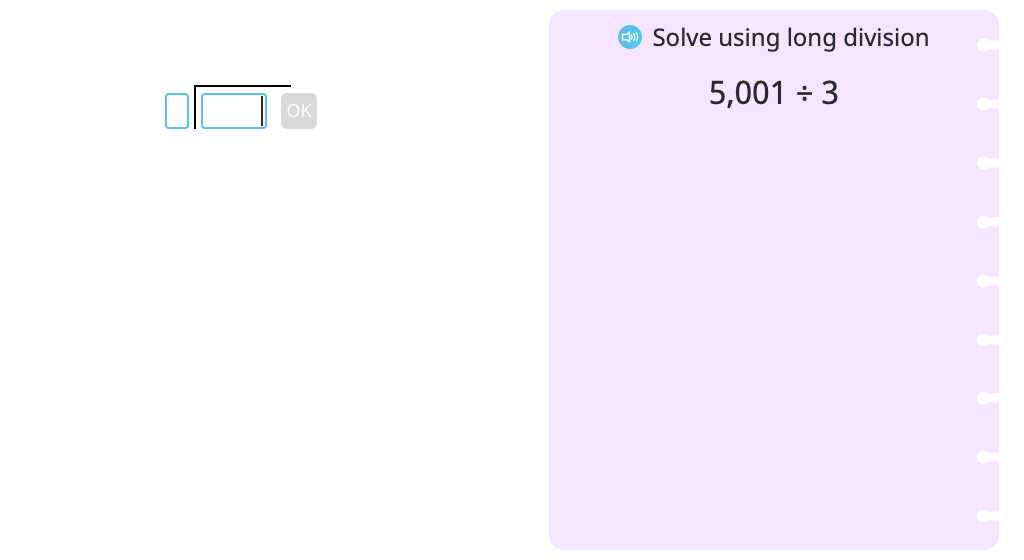
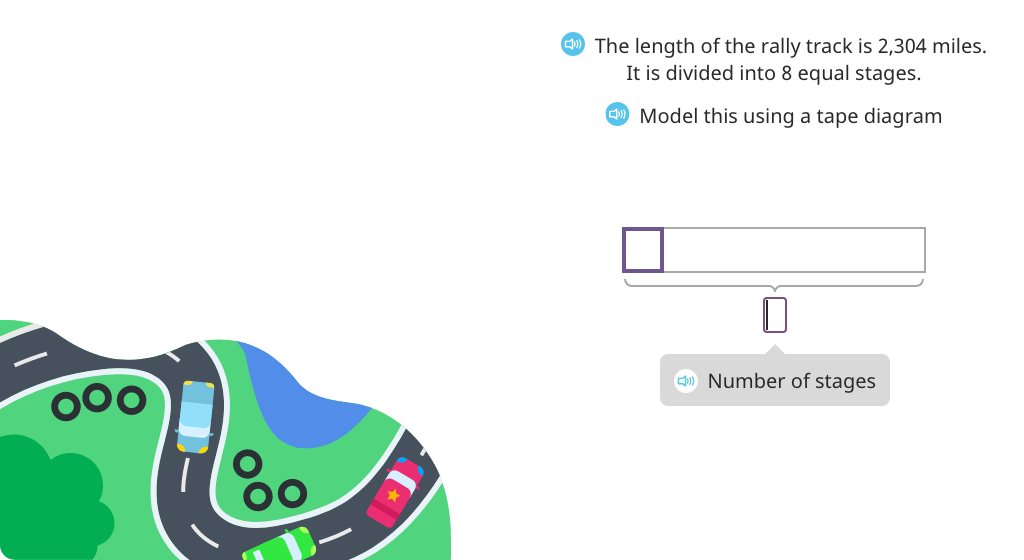
Solve division word problems using long division and a tape diagram (with regrouping and a remainder)
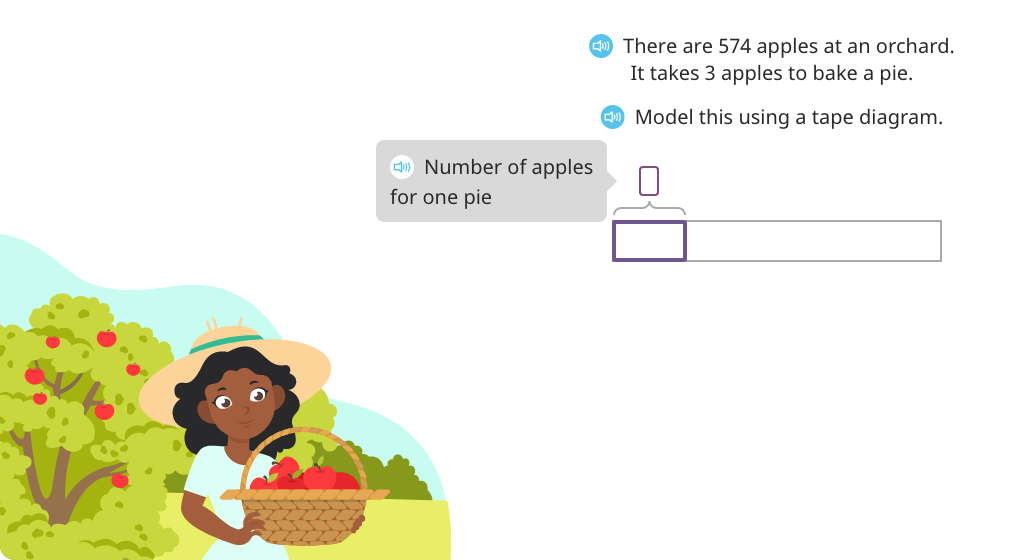
Solve division word problems using long division and a tape diagram (with regrouping)
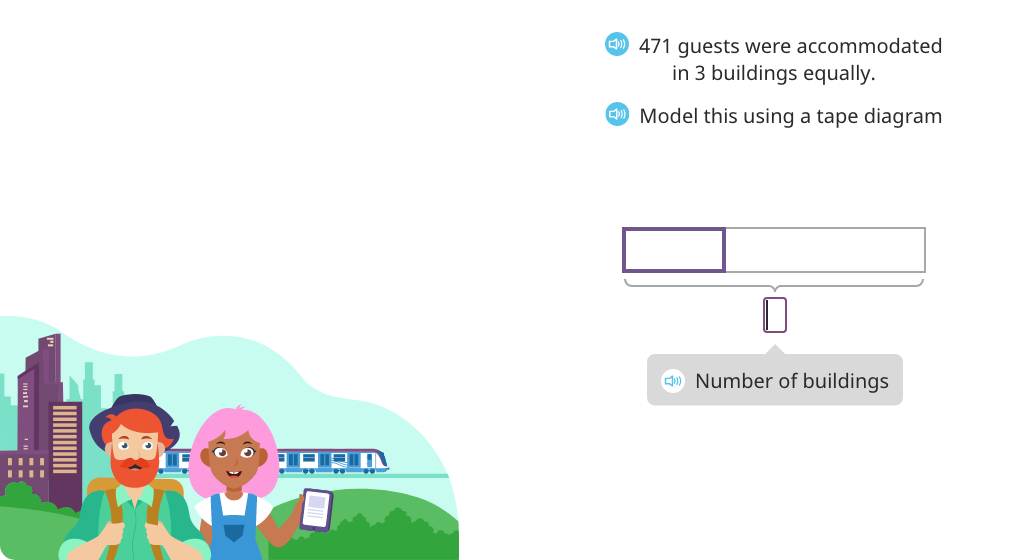
Divide using long division with partial quotients (Level 3)
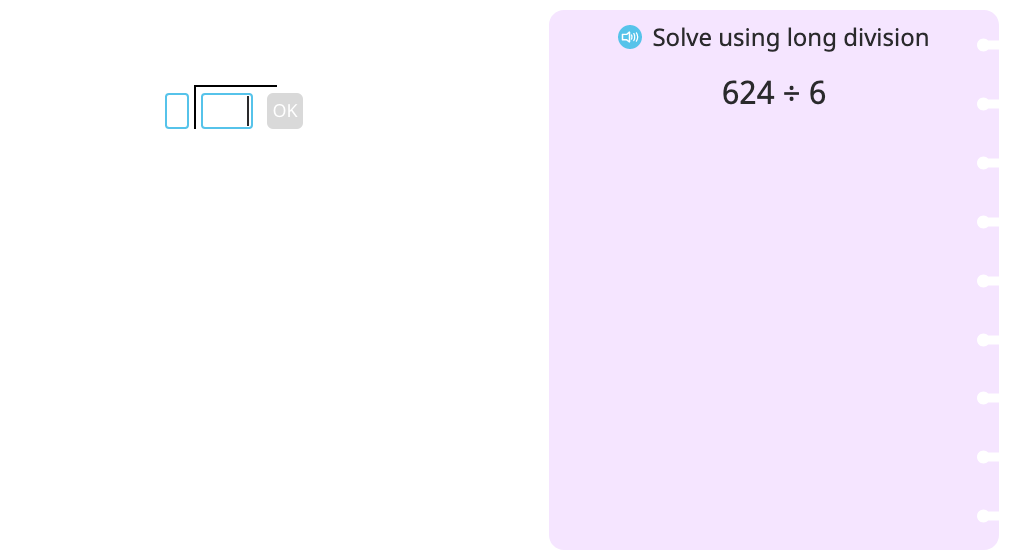
Solve division word problems across zero using long division and a tape diagram (with regrouping)
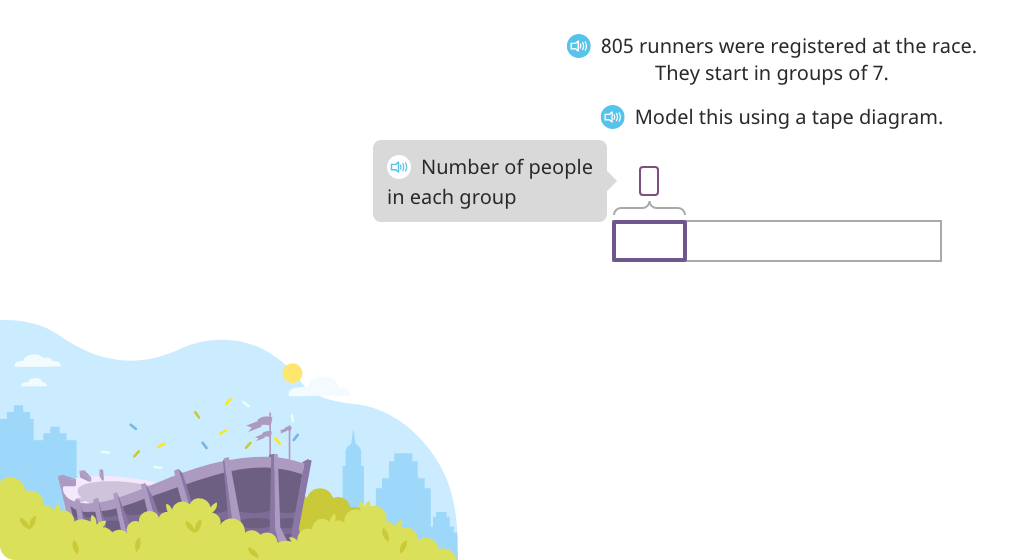
Solve division word problems using long division and a tape diagram (with a remainder)
Topic G: Multiplication of Two-Digit by Two-Digit Numbers
Students apply their prior knowledge of multiplication to multiply a 2-digit number by a 2-digit number. They use familiar tools and strategies, including a disk model, an area model, partial products, the distributive property, and the standard algorithm. To support their learning, students work extensively with multiples of 10.
Multiply a 2-digit number by 10
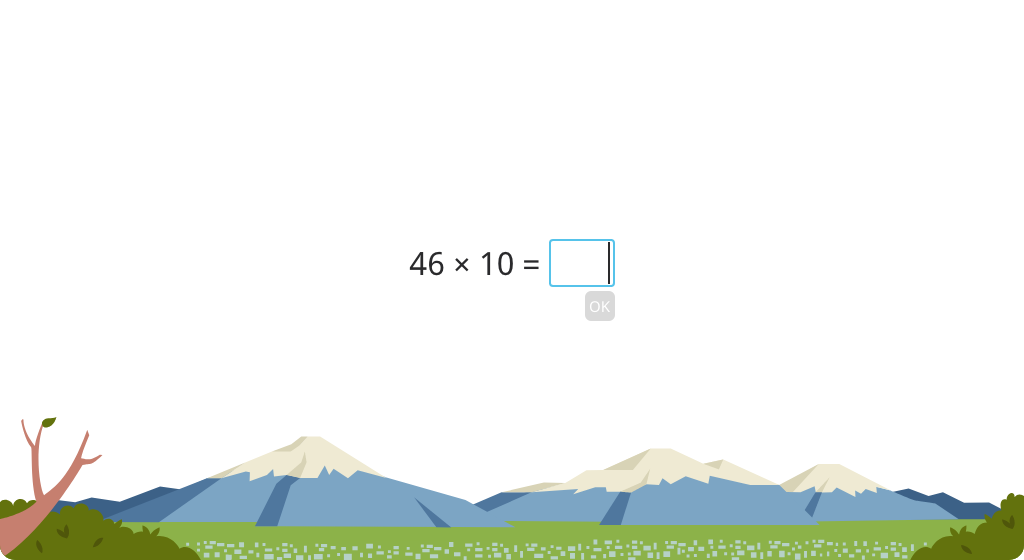
Identify a round number as a multiple of 10
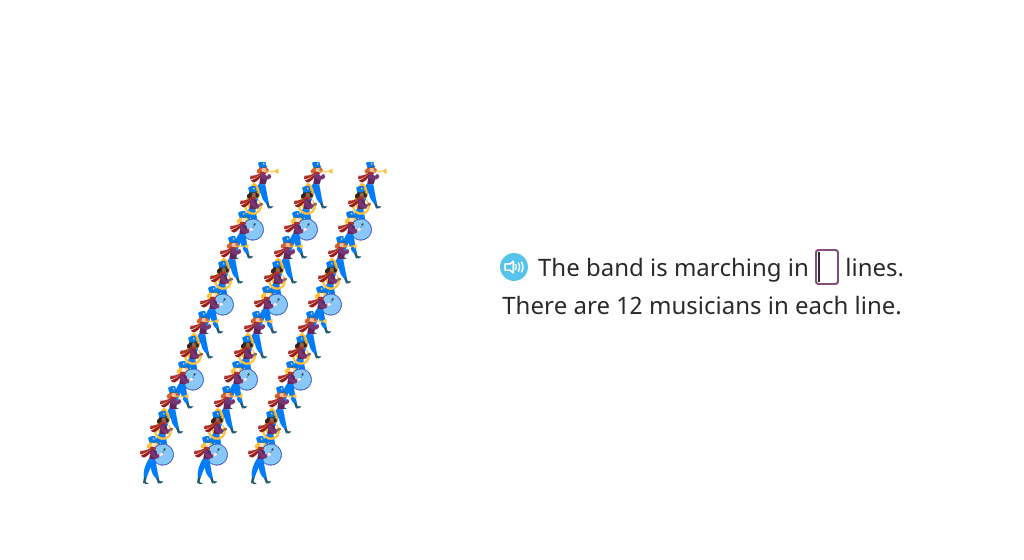
Solve a word problem two different ways by regrouping factors
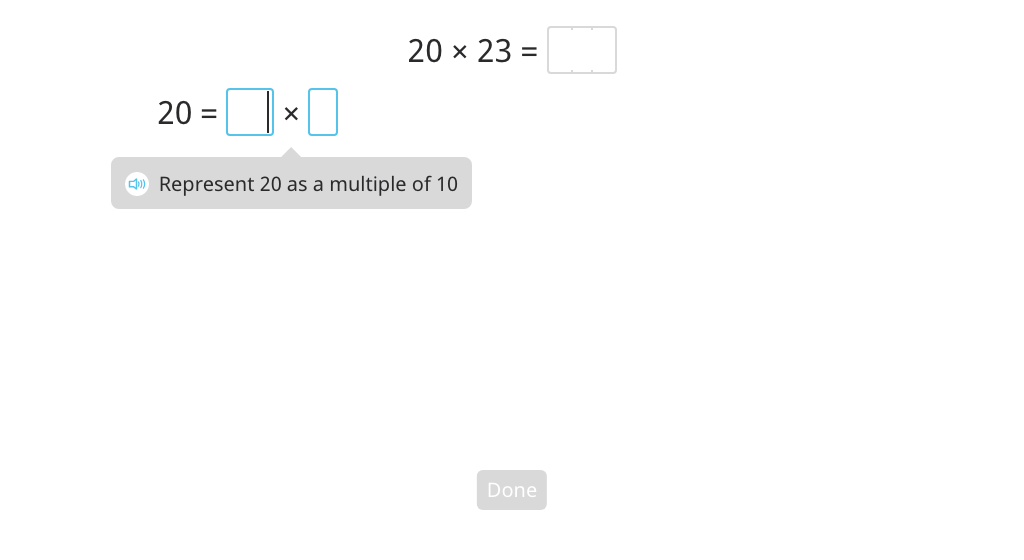
Multiply by splitting a round number into a multiple of 10 and regrouping factors based on a disk model (multiply by 10 last)
Multiply by splitting a round number into a multiple of 10 and regrouping factors based on a disk model (multiply by 10 first)
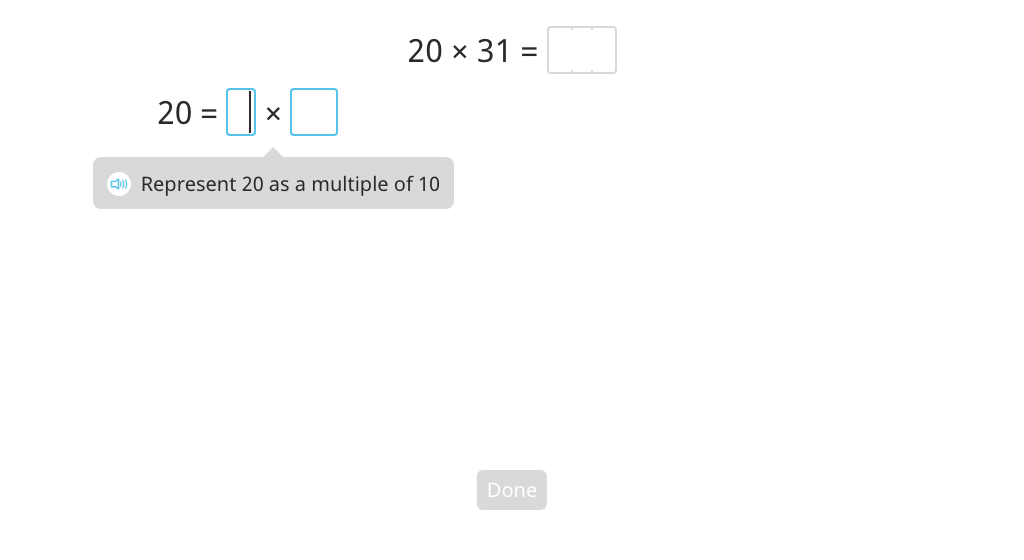
Multiply by splitting a round number into a multiple of 10 and regrouping factors (Level 1)

Multiply by splitting a round number into a multiple of 10 and regrouping factors (Level 2)

Rewrite an area model multiplication equation using the distributive property
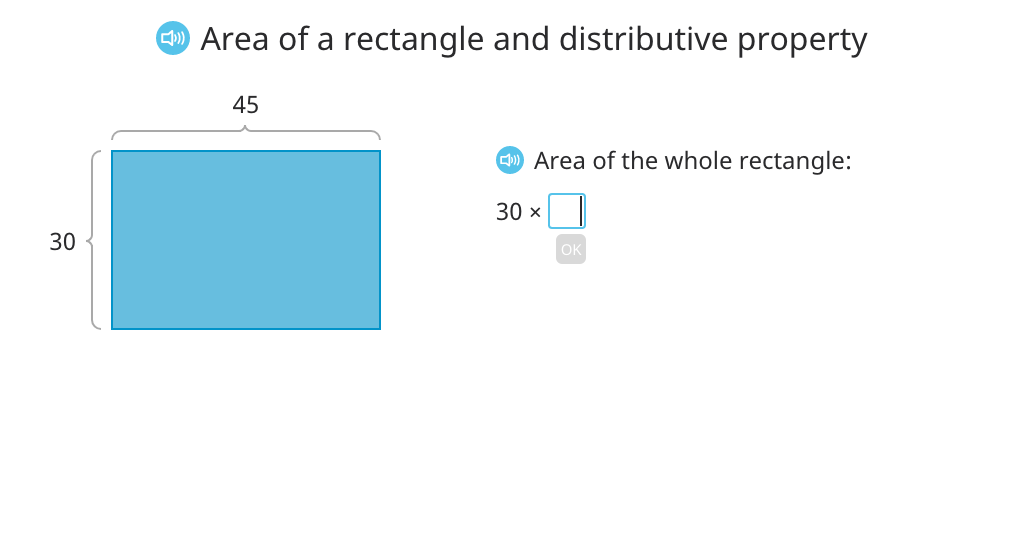
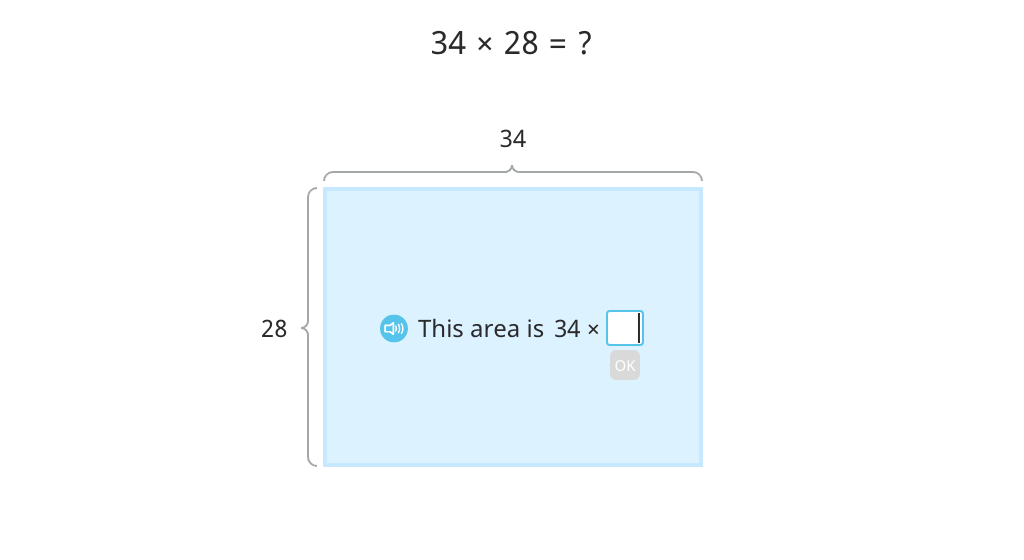
Multiply to find the area of a rectangle using the distributive property
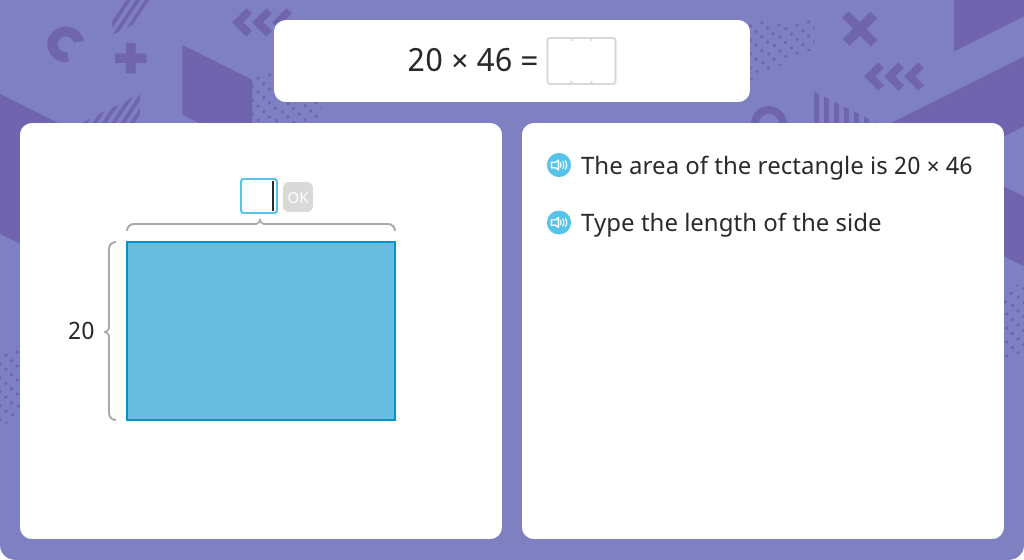
Multiply using partial products and the standard algorithm (one round number)

Multiply to find the area of a rectangle using the distributive property and the standard algorithm

Multiply using partial products and the standard algorithm

Multiply using the standard algorithm (one round number)
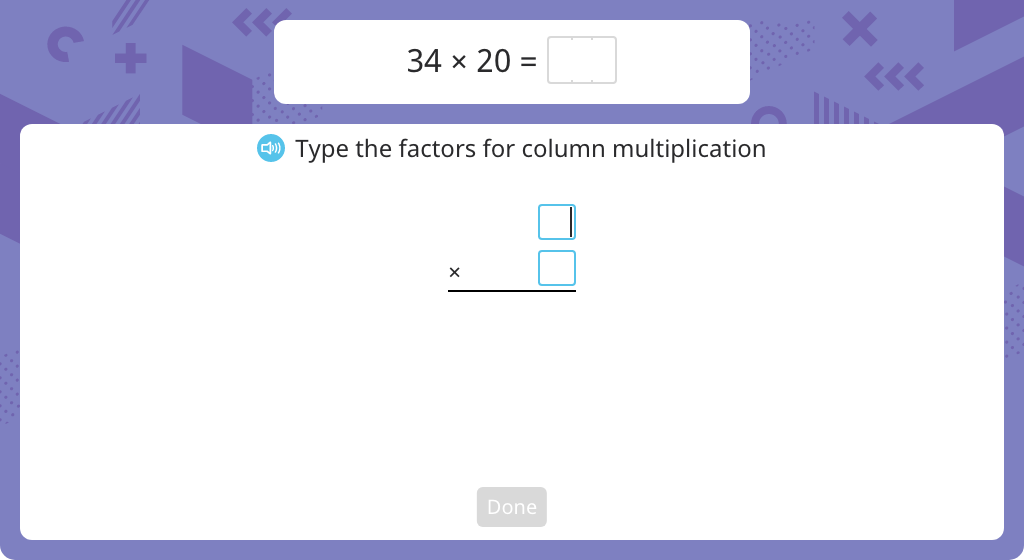
Multiply using the standard algorithm with regrouping (one round number)
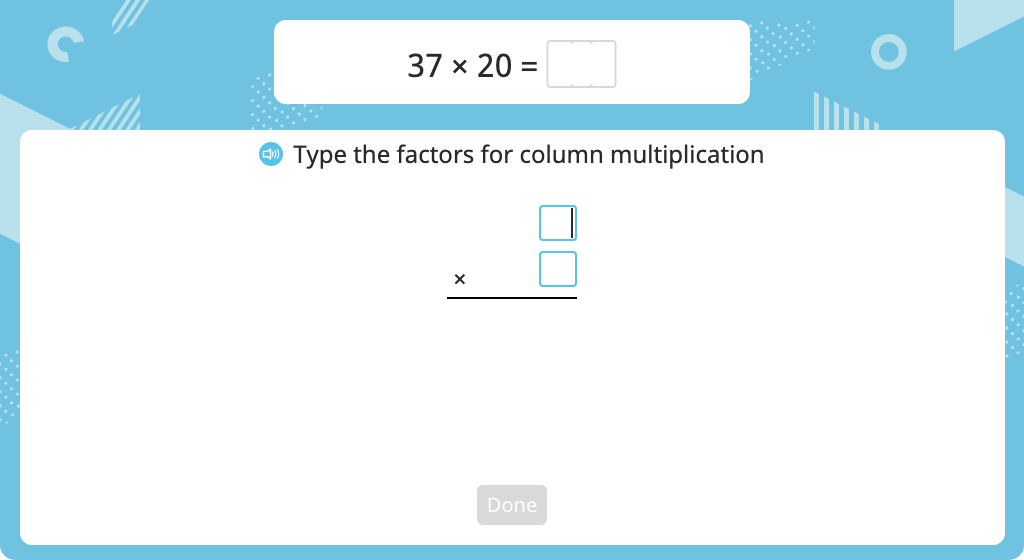
Multiply using partial products and the standard algorithm with regrouping (Part 1)
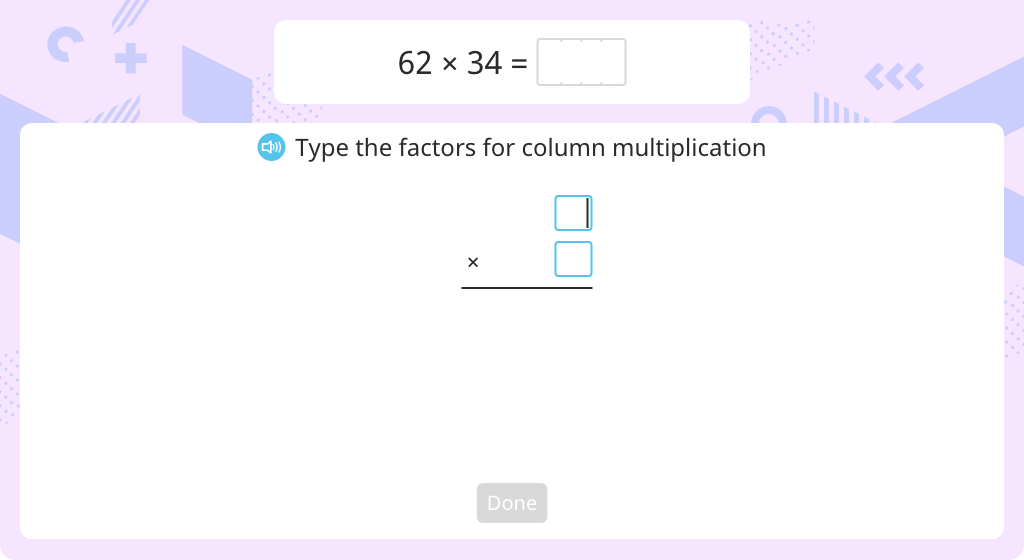
Multiply using partial products and the standard algorithm with regrouping (Part 2)
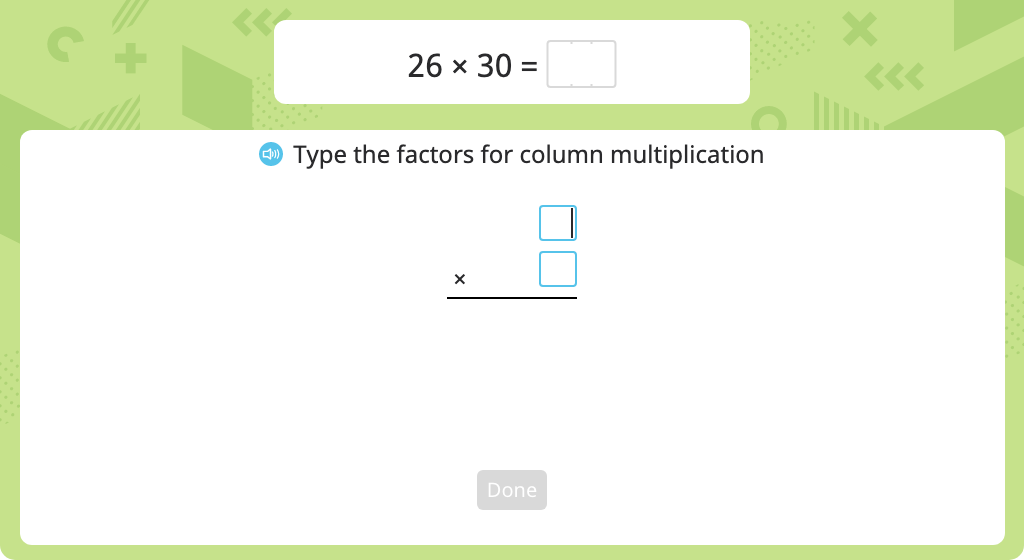
Multiply using the standard algorithm (one round number)
MODULE 4. Angle Measure and Plane Figures
Topic A: Lines and Angles
Students explore various figures, including line segments, lines, rays, and angles. They label different types of lines, including meeting, perpendicular, and parallel lines. They also identify different types of triangles.
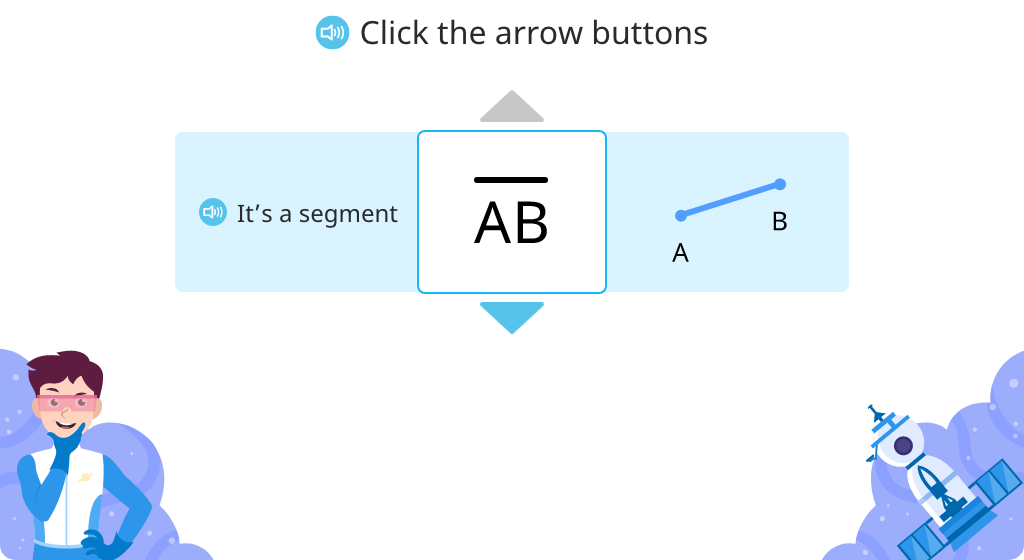
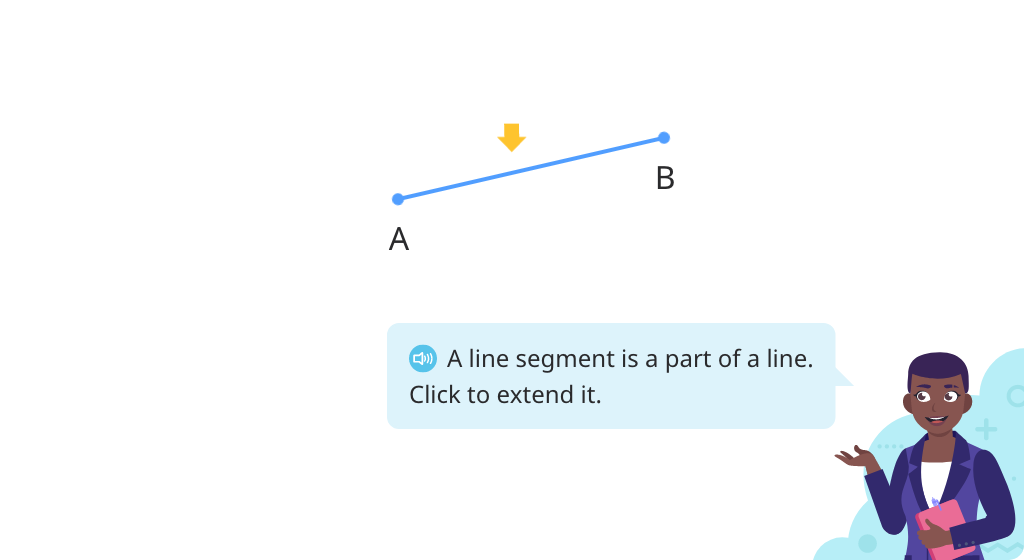
Identify and label points and line segments
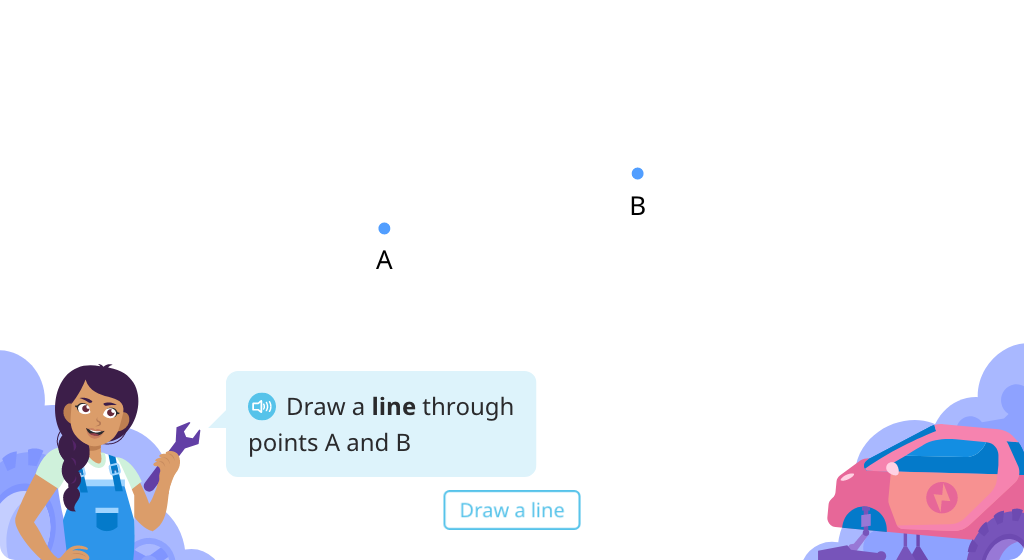
Identify and label lines
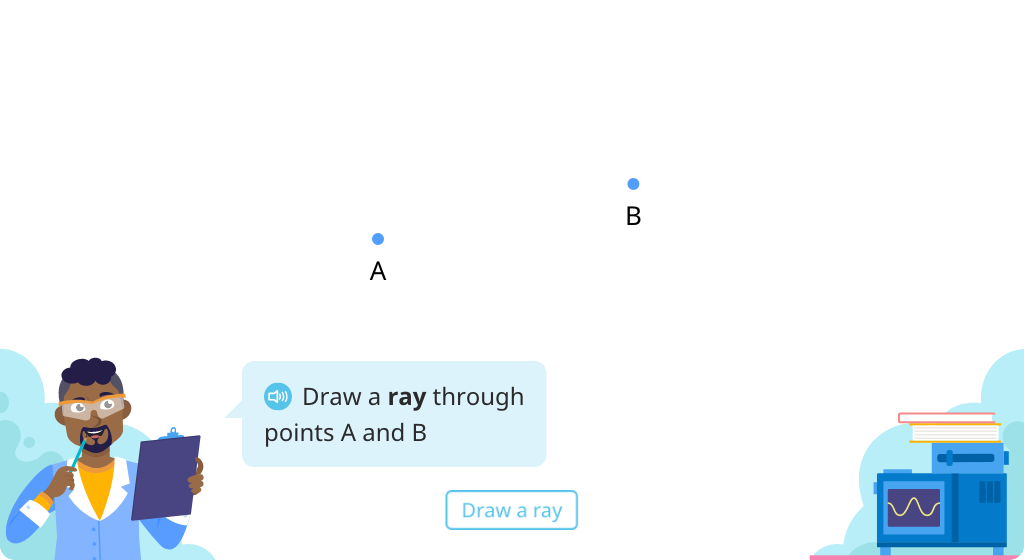
Identify and label rays
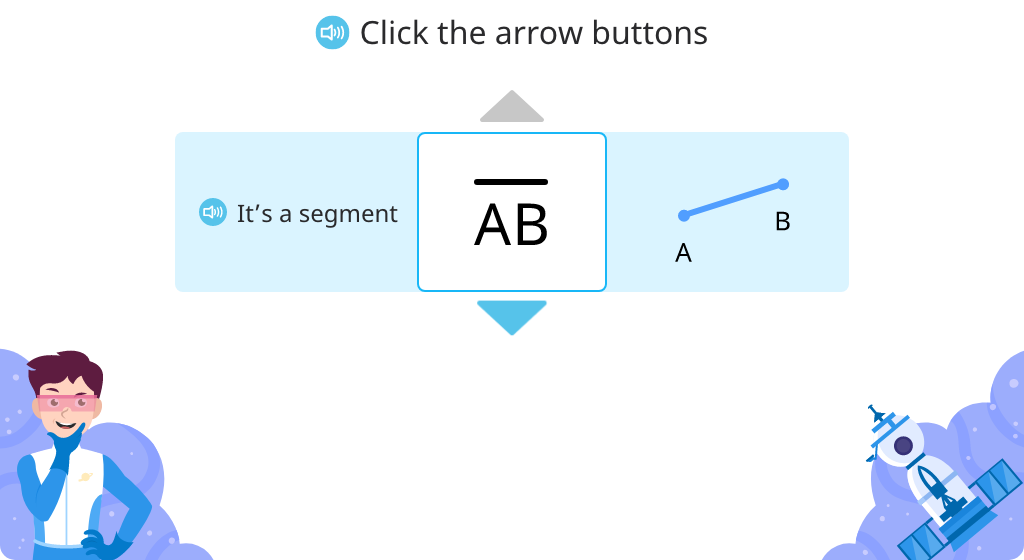
Review line segments, lines, and rays
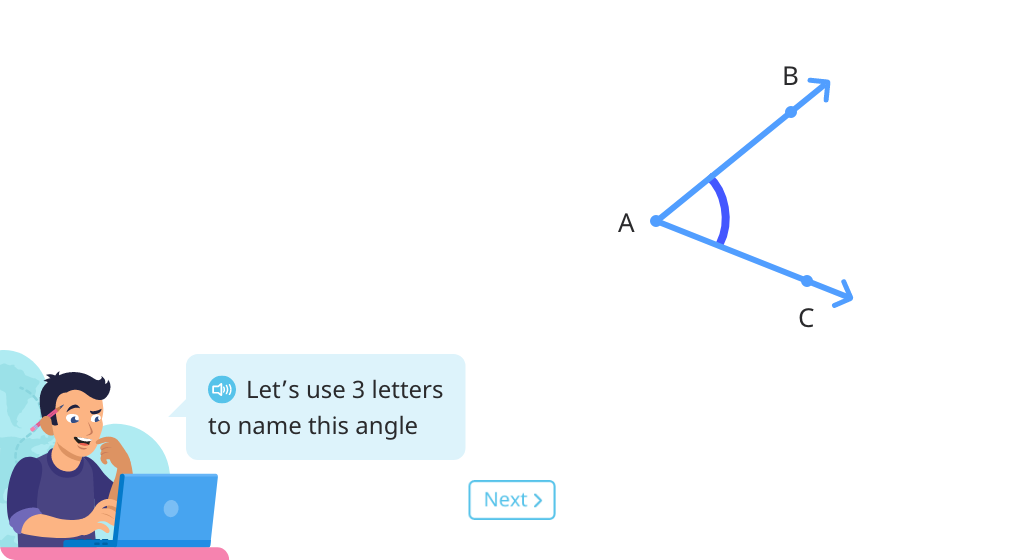
Identify and label parts of an angle

Name angles and their sides

Name the sides of angles, starting at the endpoint

Explore multiple ways to name the same angle
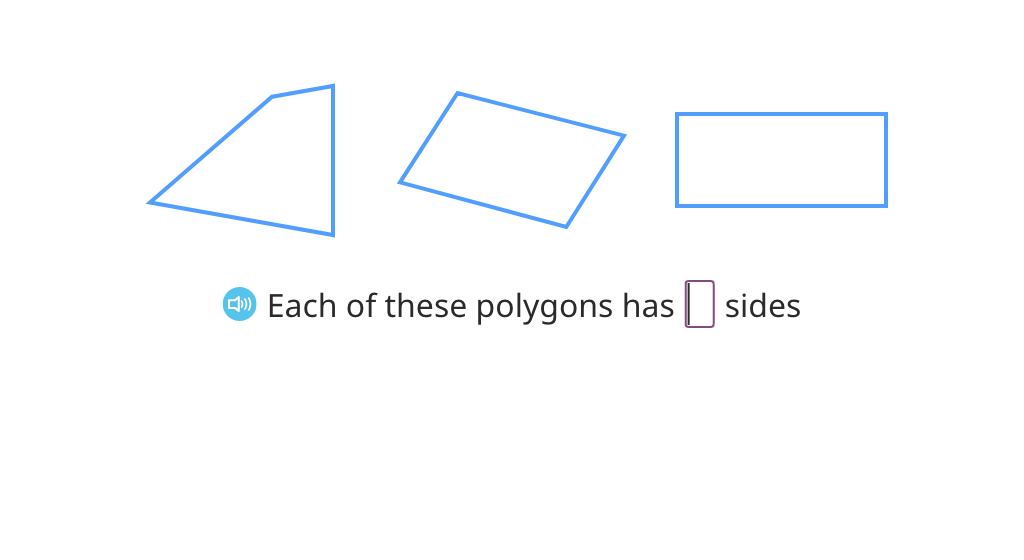
Identify the number of angles in polygons
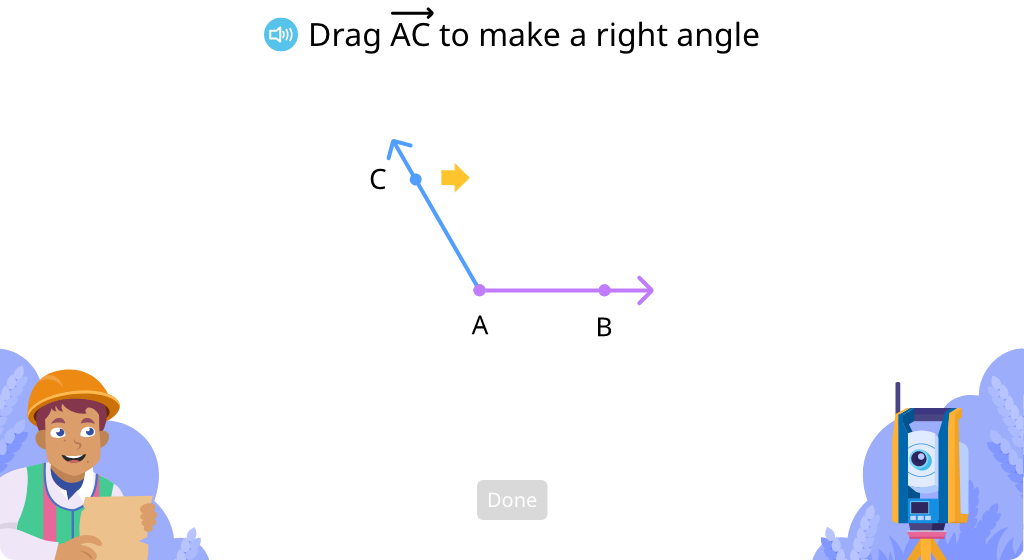
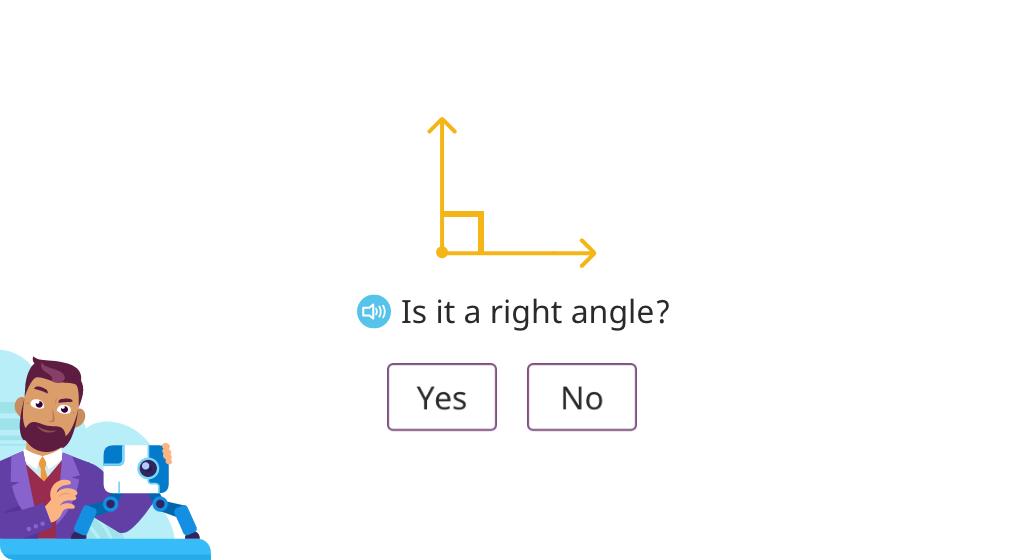
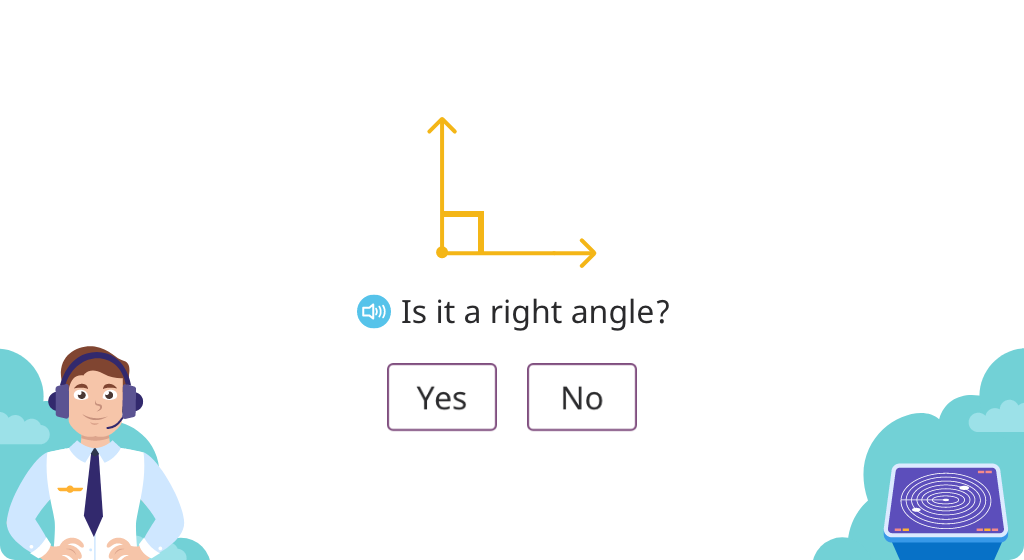
Explore right angles
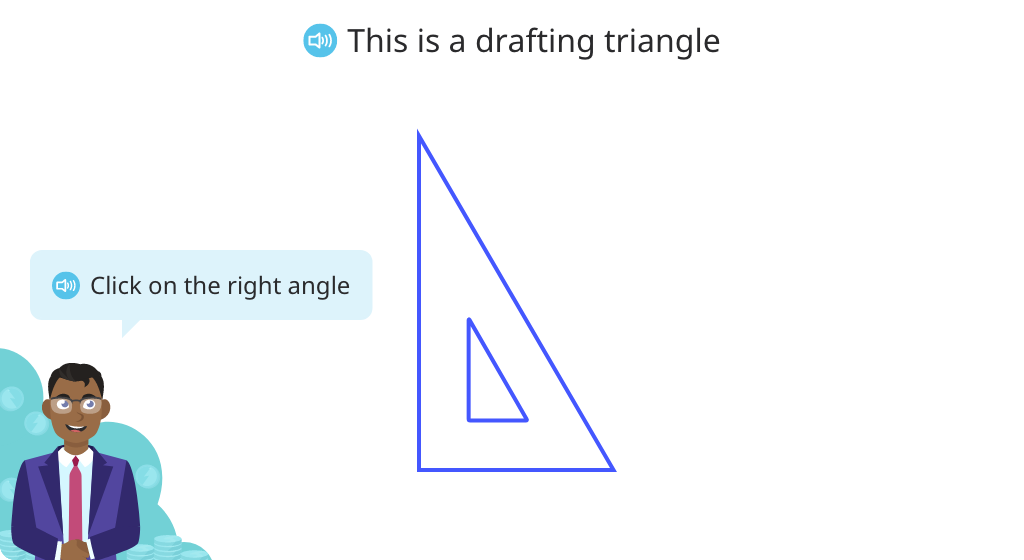
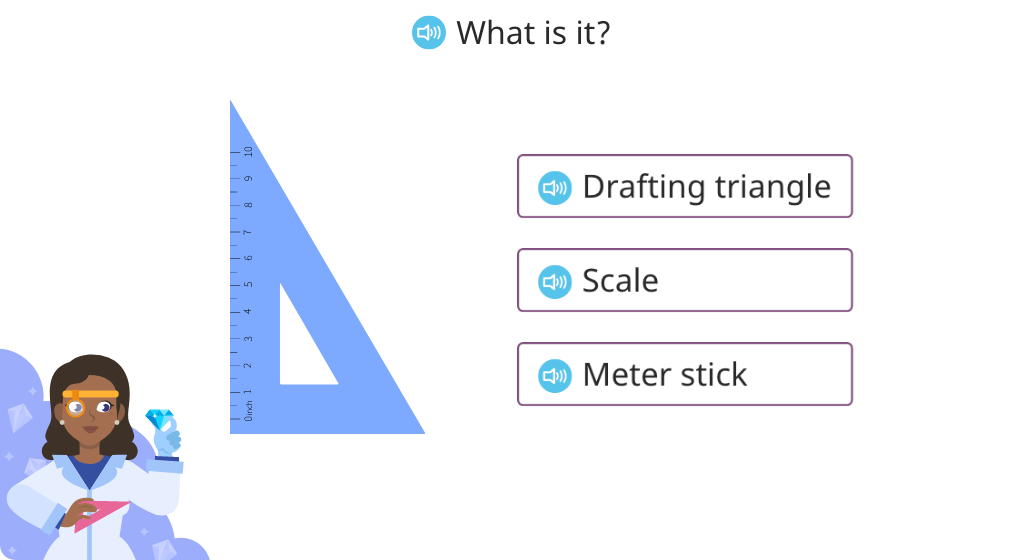
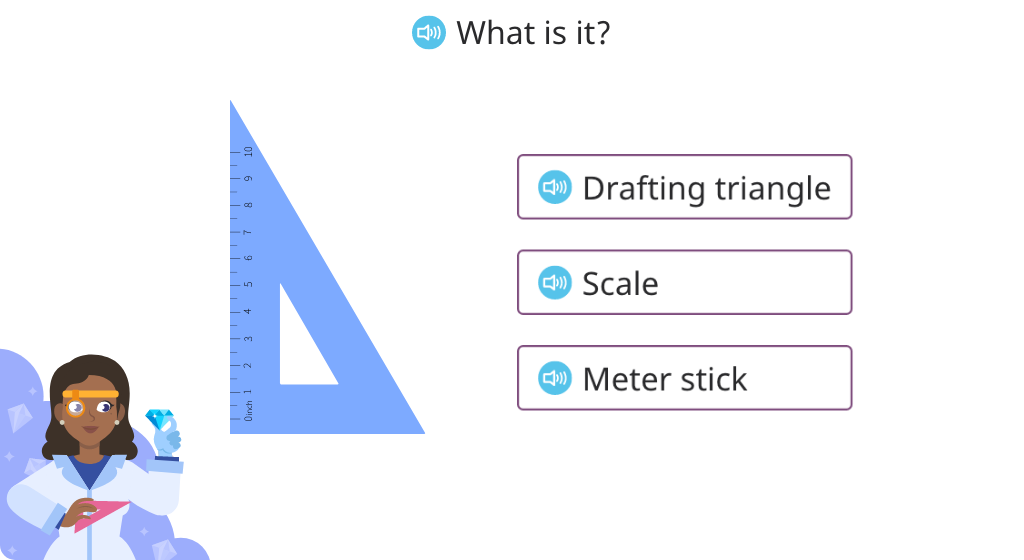
Use a drafting triangle to determine if an angle is right
Identify the number of right angles in a polygon
Explore acute angles
Explore obtuse angles
Use a drafting triangle to determine the type of angle (Level 1)
Use a drafting triangle to determine the type of angle (Level 2)
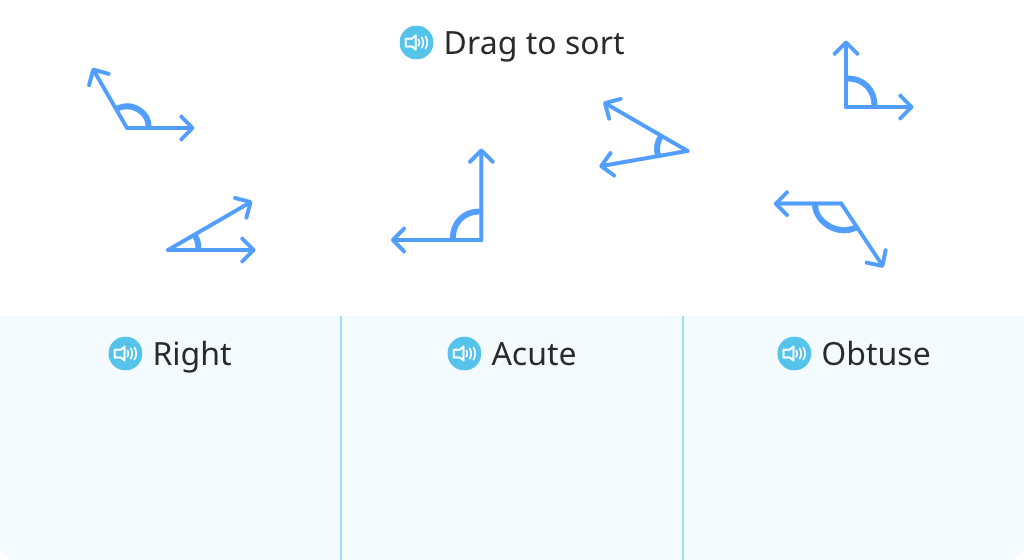
Classify angles
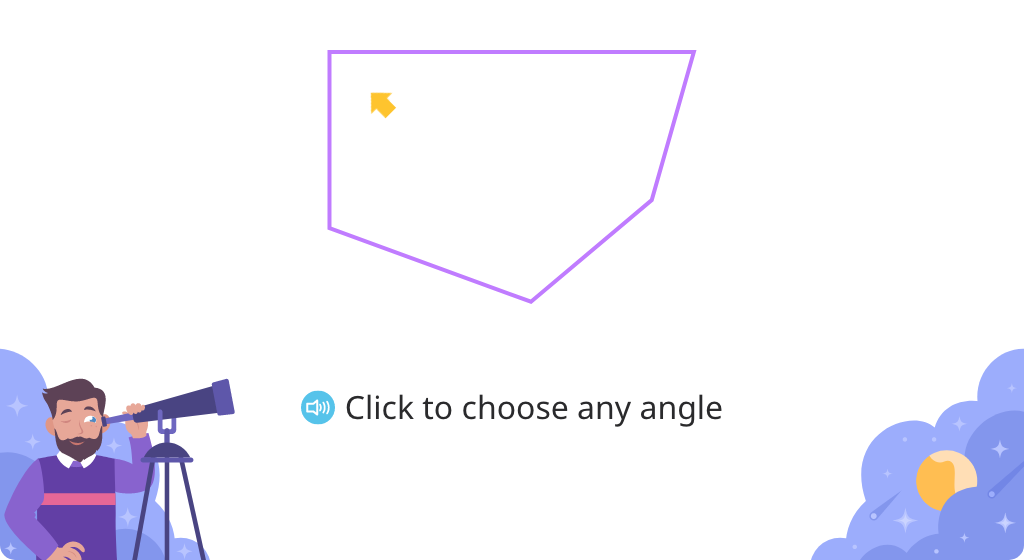
Classify the angles of a polygon
More practice with line segments, rays, and lines
Identify acute triangles

Identify obtuse triangles
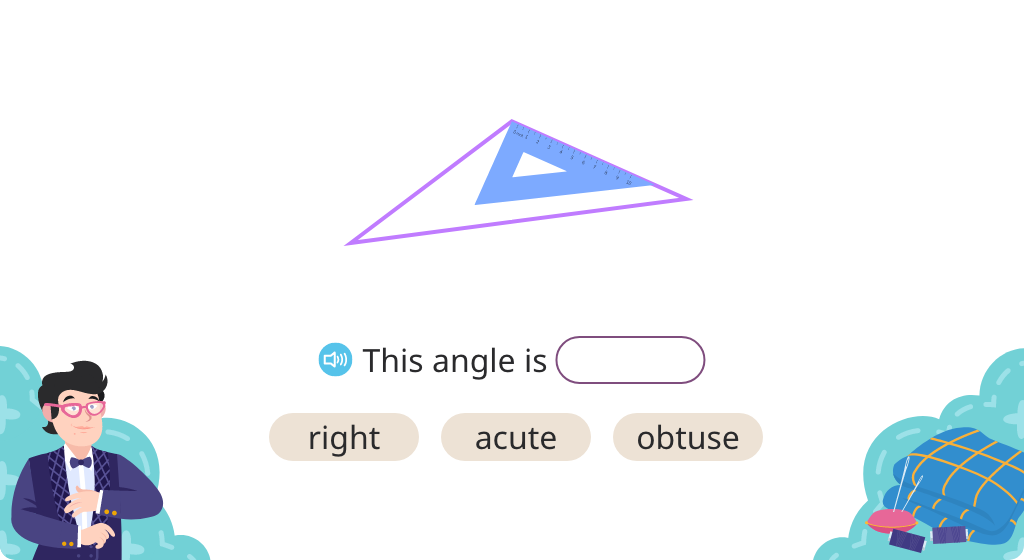
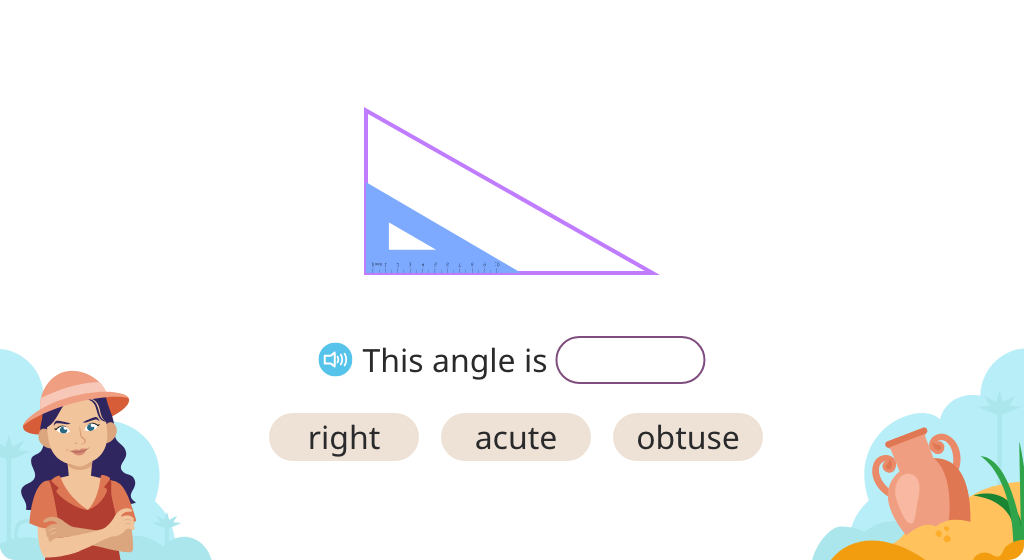
Identify acute and obtuse triangles

Identify right triangles
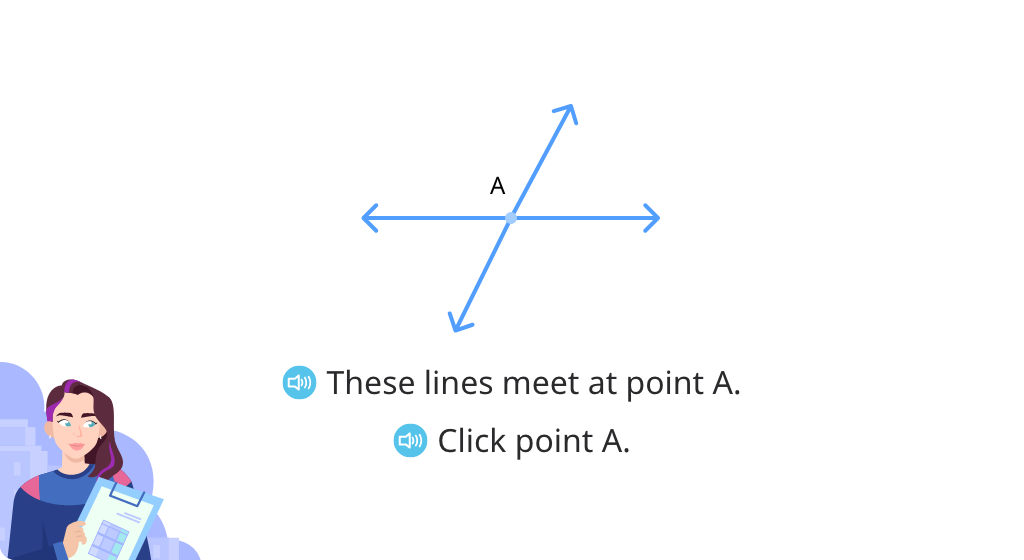
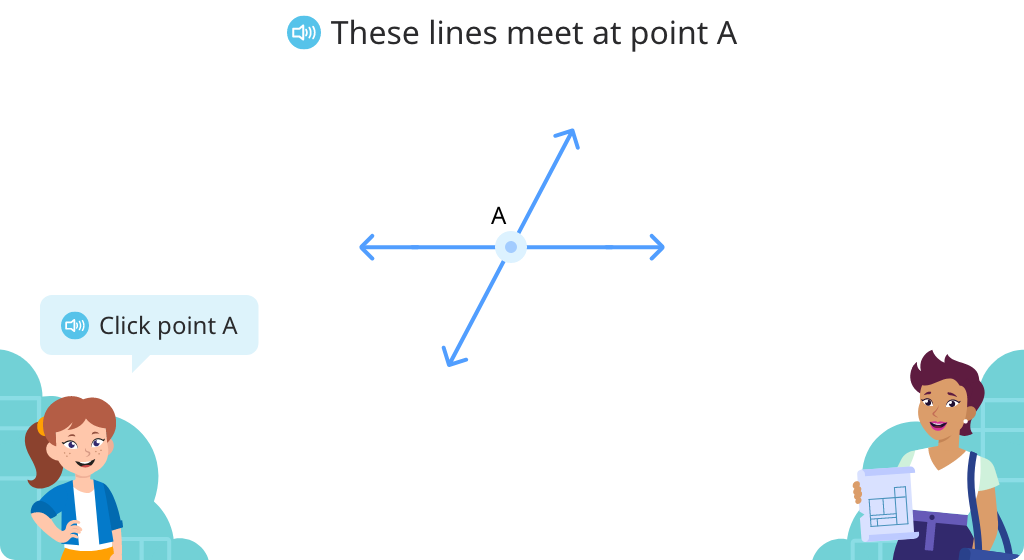
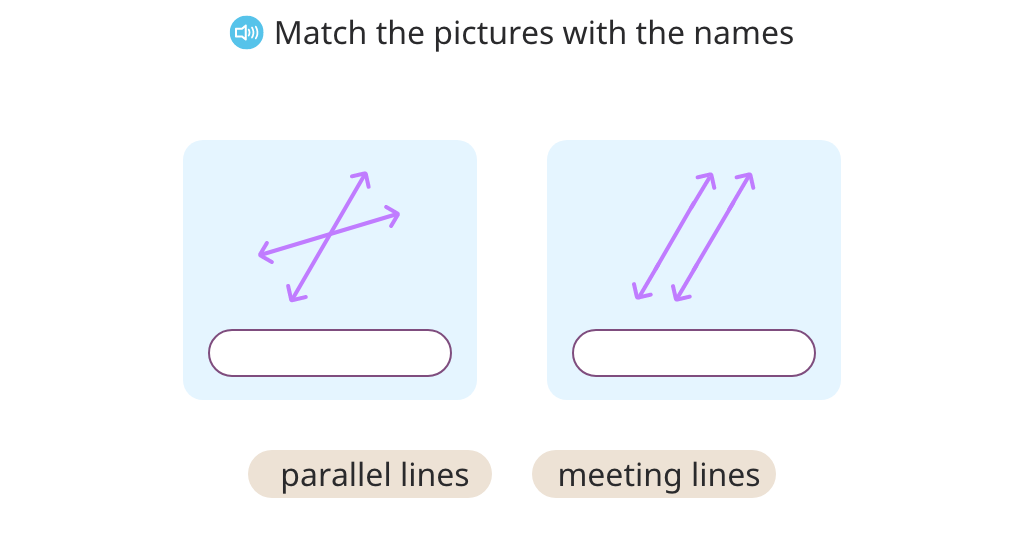
Identify perpendicular lines
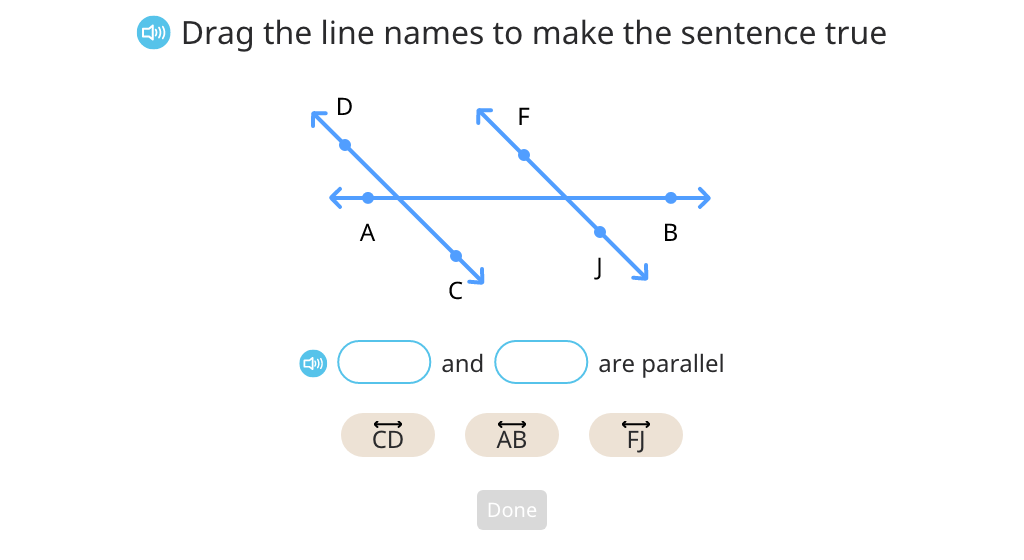
Identify parallel lines
Classify types of lines
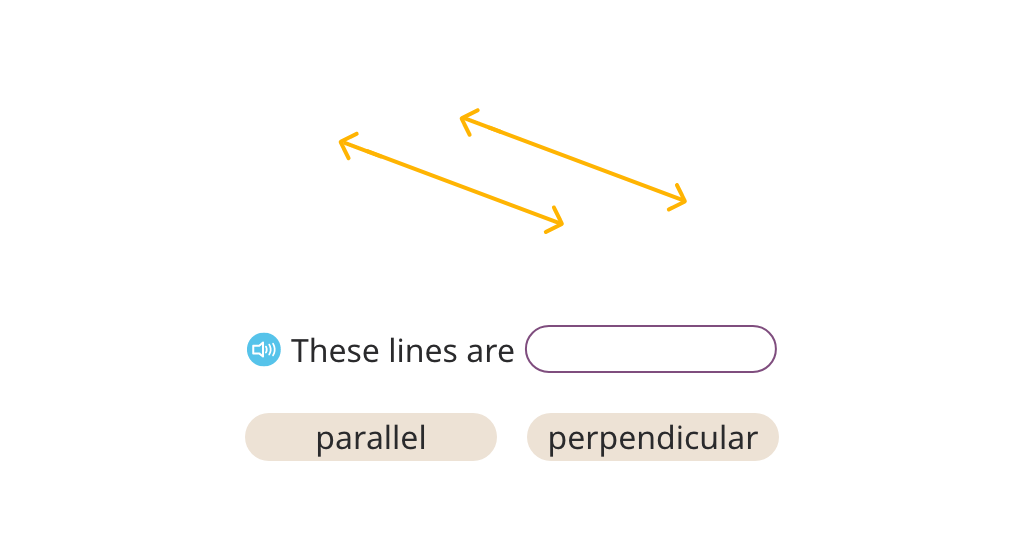
Identify perpendicular or parallel line segments in a figure (Level 1)
Identify perpendicular or parallel line segments in a figure (Level 2)
Classify lines (Level 1)
Review types of triangles
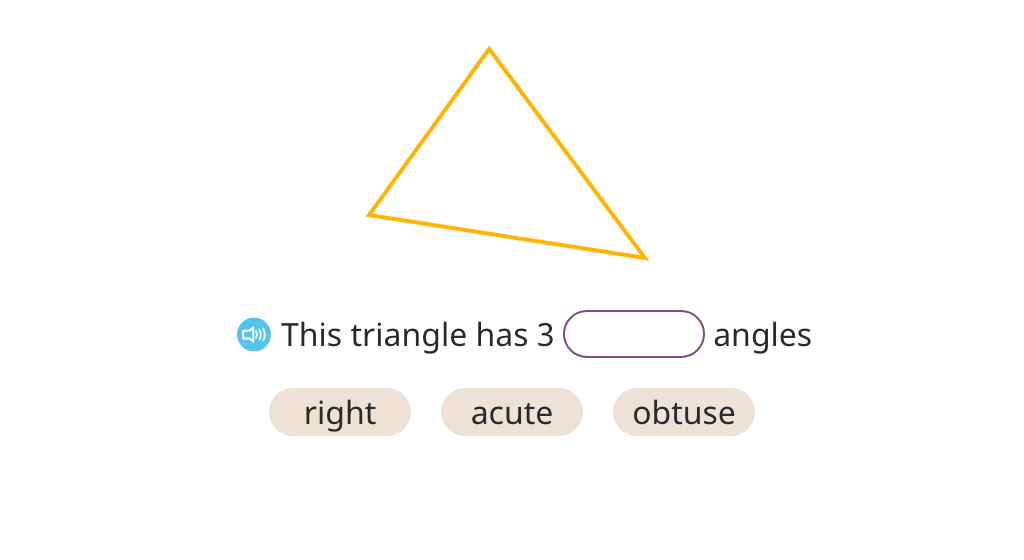
Classify lines (Level 2)
Topic B: Angle Measurement
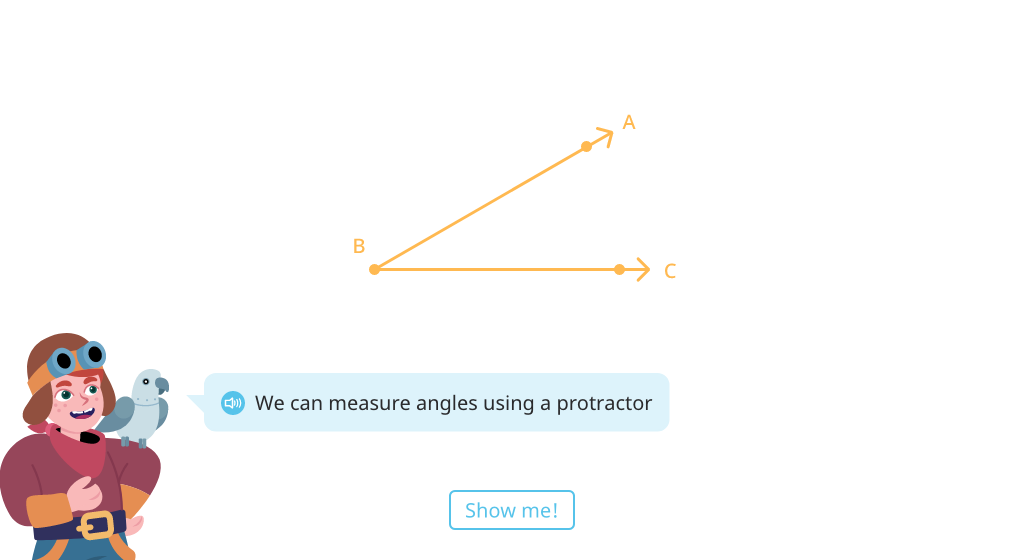
Students learn to use a protractor to draw angles and find their measurements in degrees. They explore the parts of a protractor and learn to work with 1- and 2-scale versions.
Explore degrees
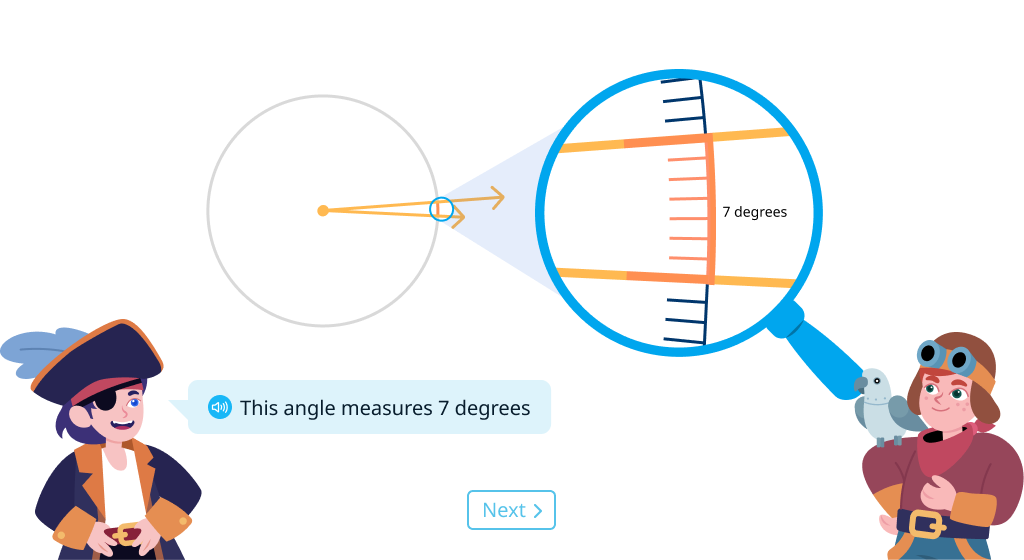
Measure and represent angles using degrees

Explore protractors
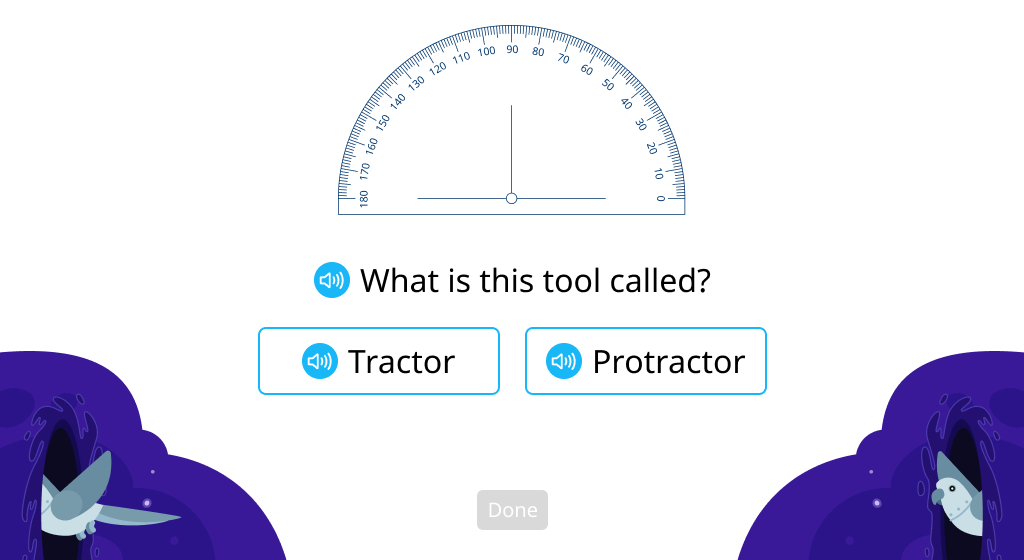
Identify the parts of a protractor
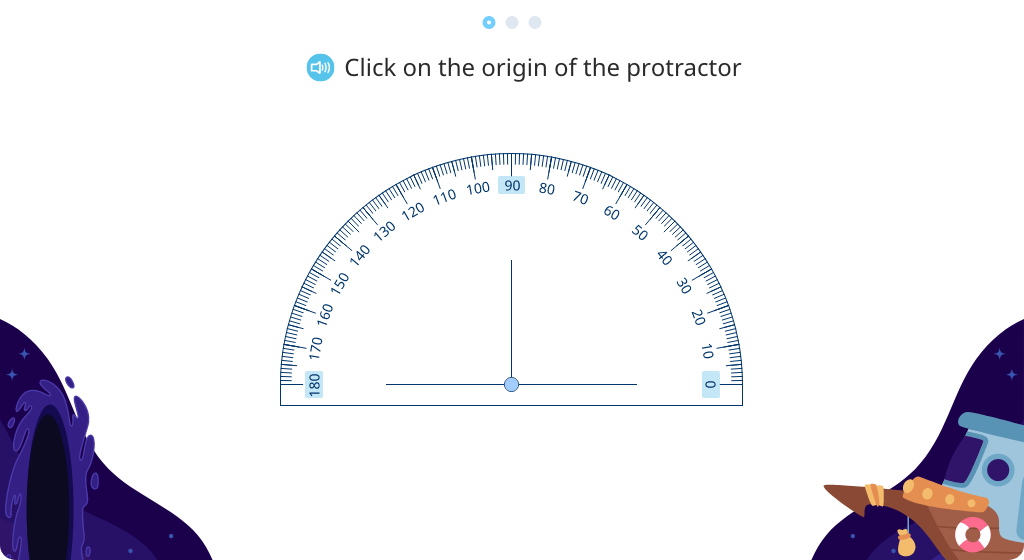
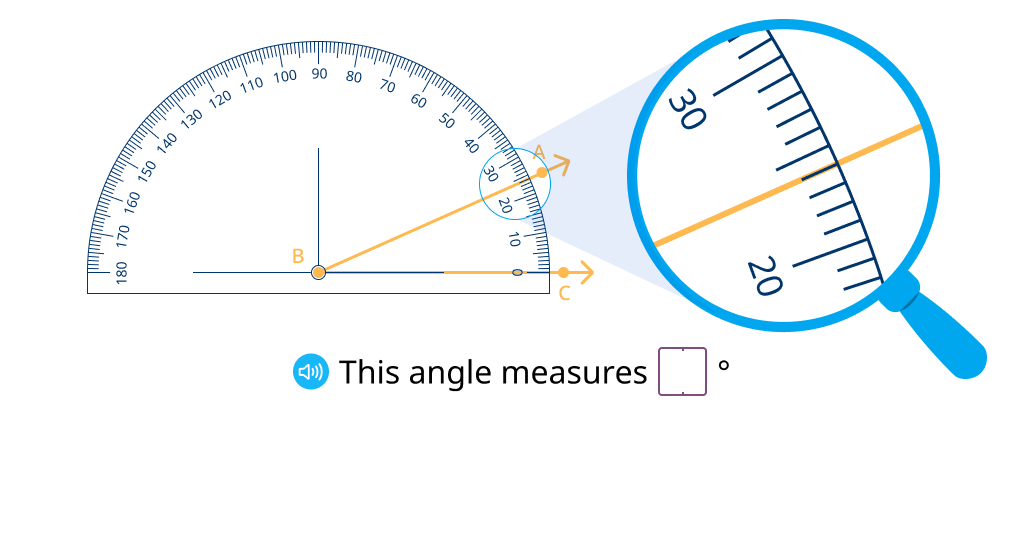
Measure angles with a 1-scale protractor (Level 1)
Measure angles with a 1-scale protractor (Level 2)
Measure angles with a 2-scale protractor (Level 1)

Measure angles with a 2-scale protractor (Level 2)
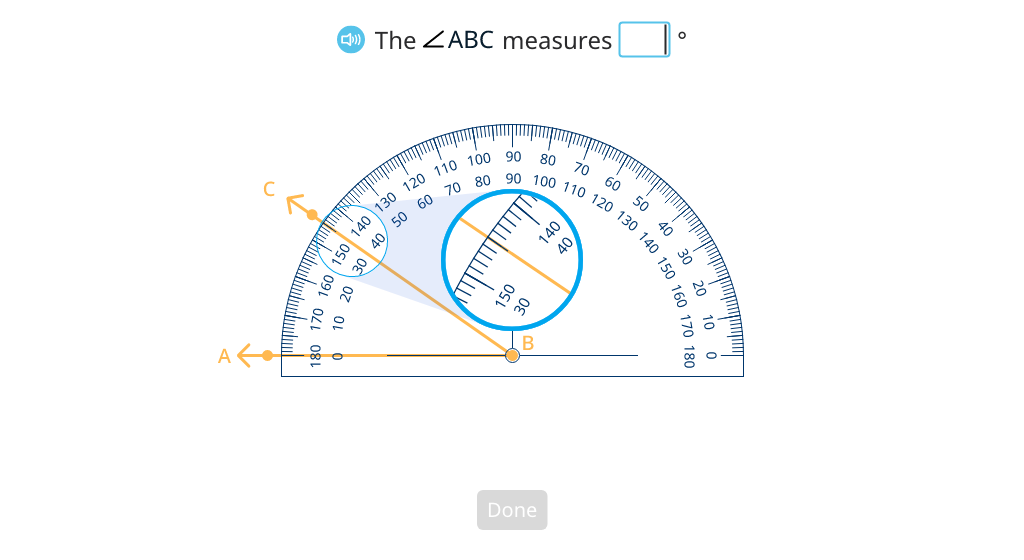
Measure angles with a 2-scale protractor (Level 3)
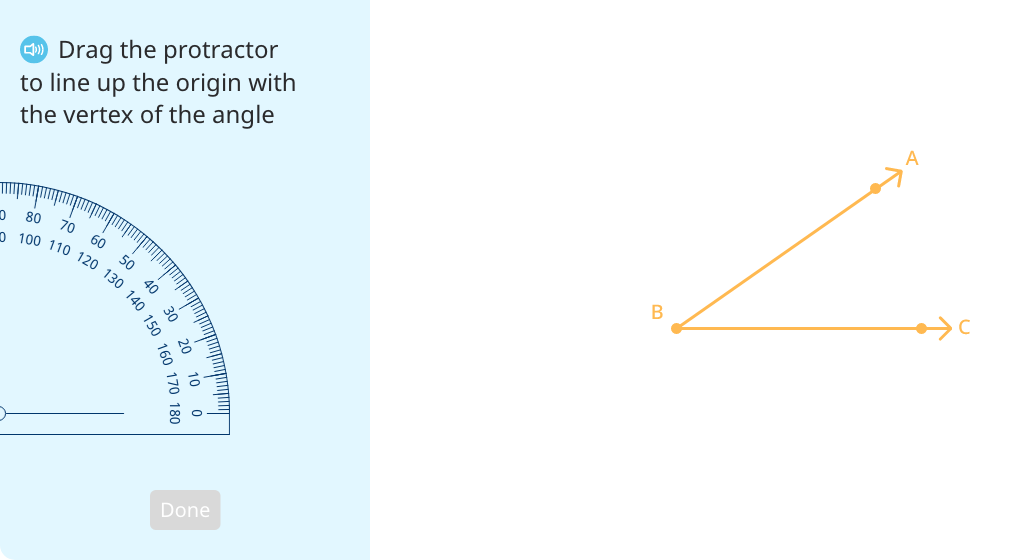
Correctly align a protractor to measure angles
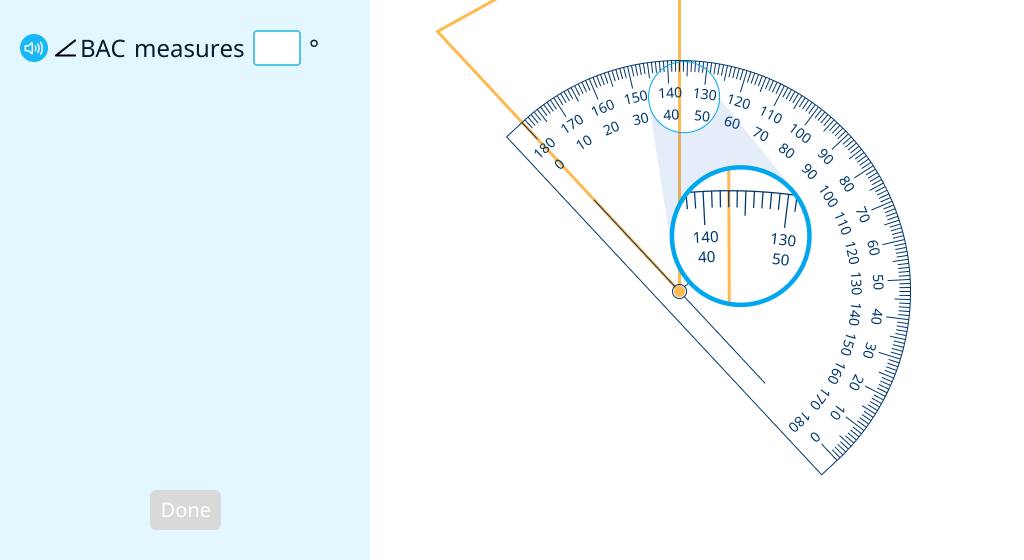
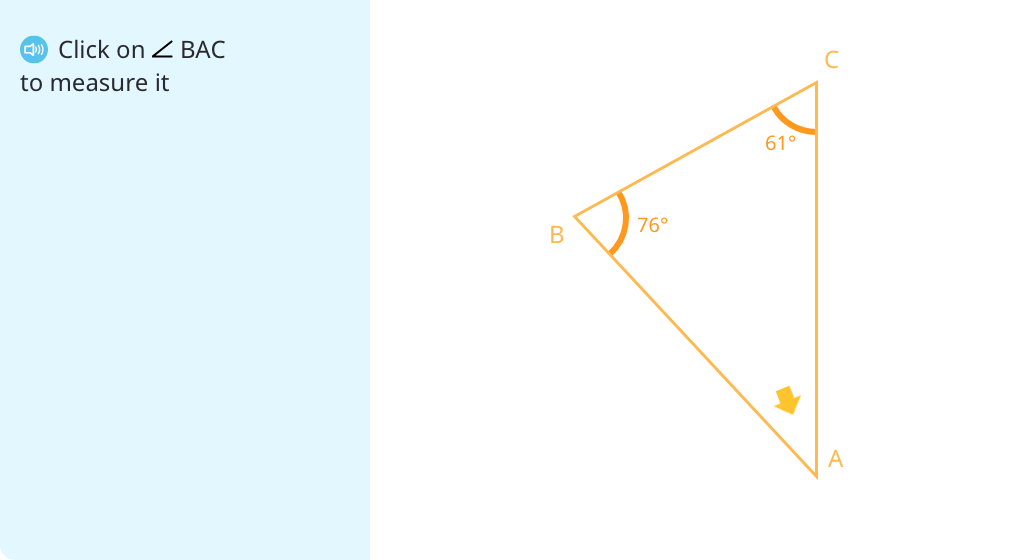
Measure all the angles of a triangle
Measure angles in triangles (Level 1)
Measure angles in triangles (Level 2)
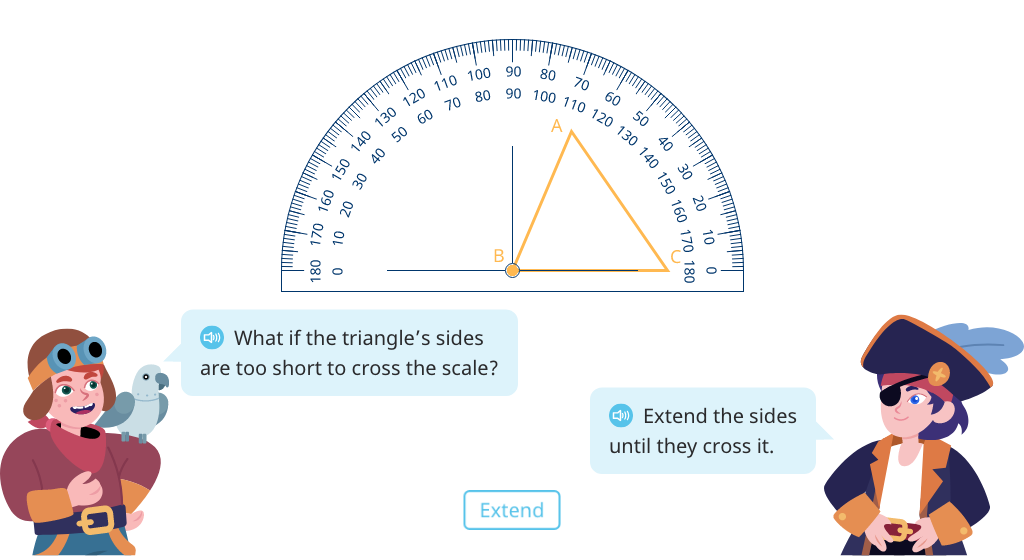
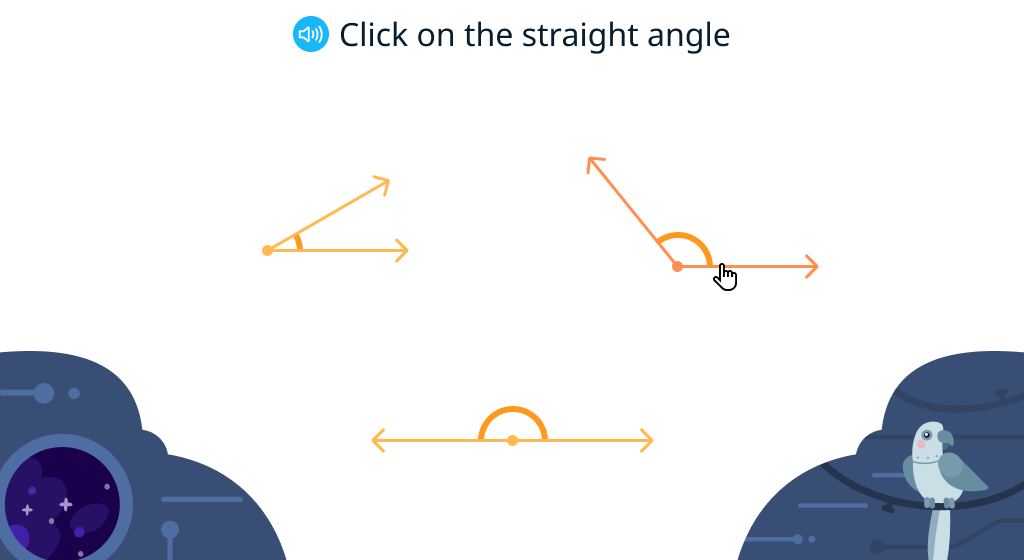
Identify 180 degree angles
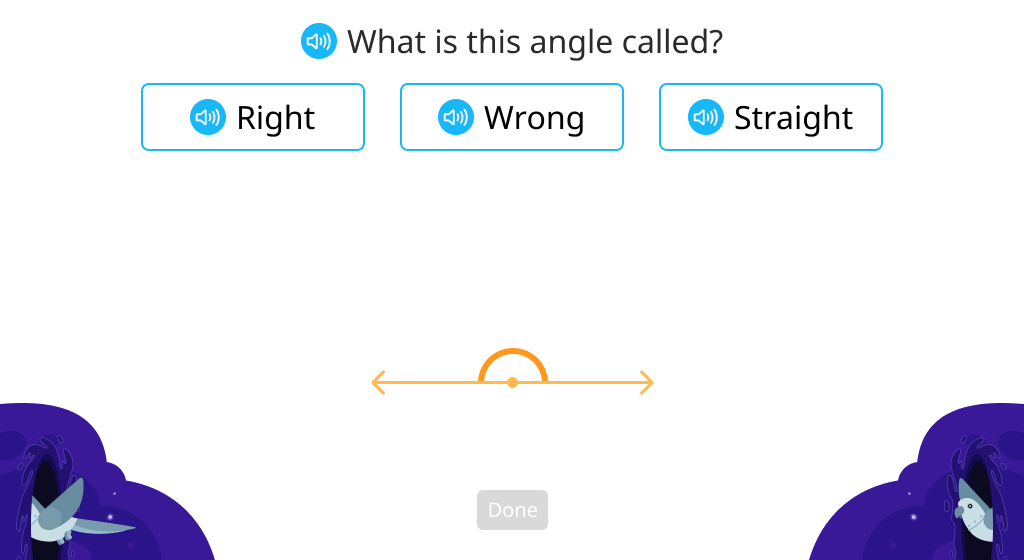
Measure 90 and 180 degree angles using a protractor
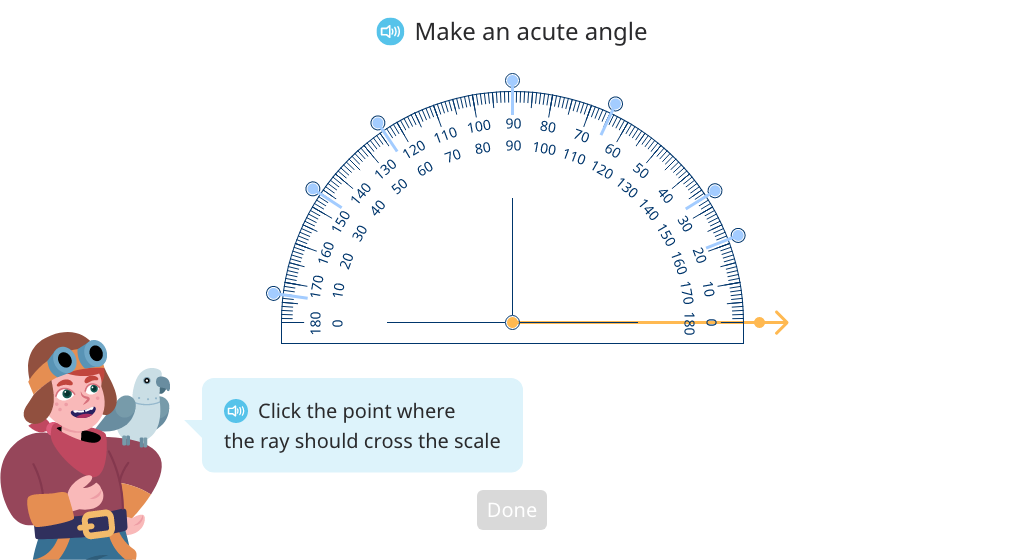
Use protractors to draw angles

Use protractors to draw acute and obtuse angles
Topic C: Problem-Solving with Angle Measure
Students are introduced to the additivity of angle measure. They use the property to solve one- and two-step problems and identify the measure of missing parts.
Explore the symbol for angle measure
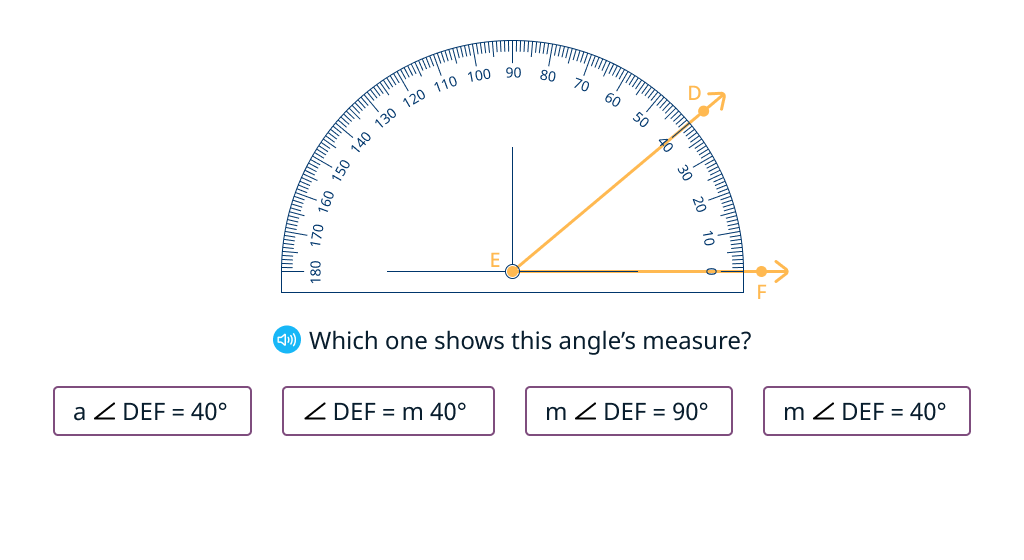
Explore the additivity of angle measure (Level 1)
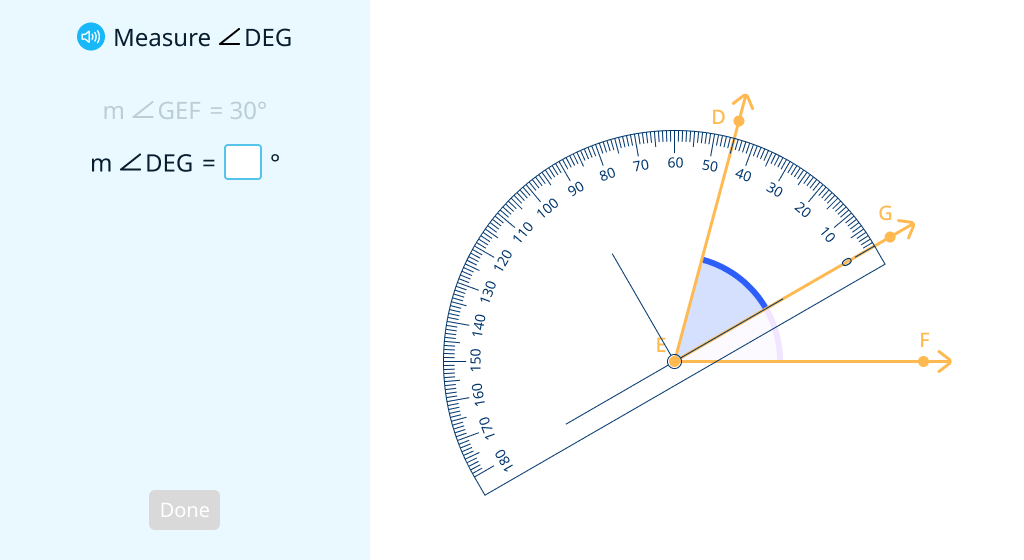
Explore the additivity of angle measure (Level 2)
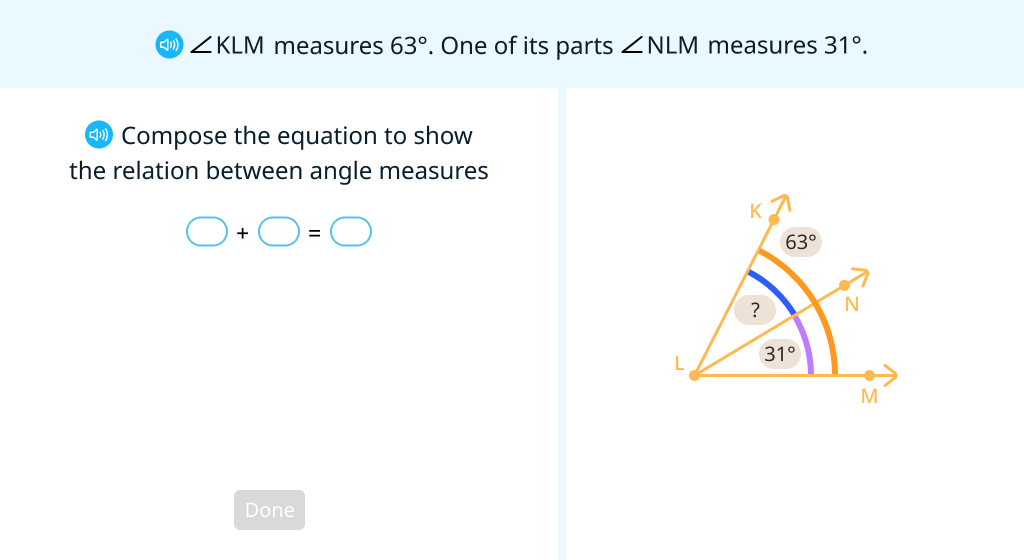
Solve problems with right angles
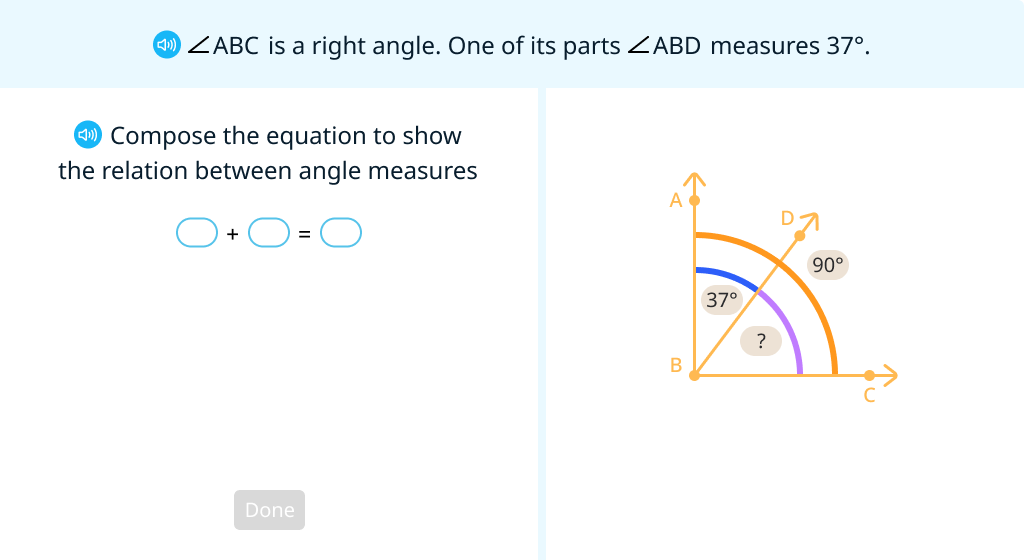
Solve problems with rectangles
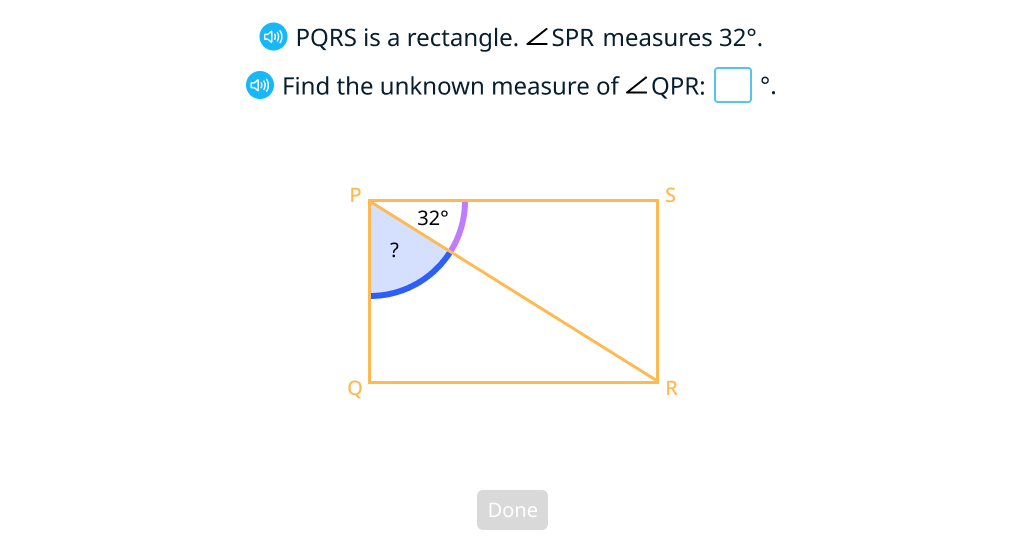
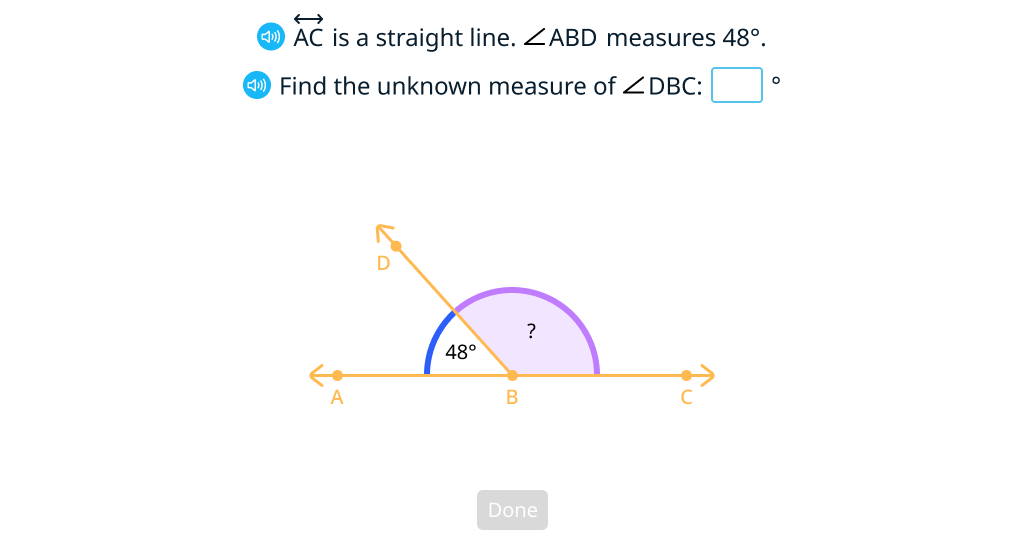
Solve problems with straight angles
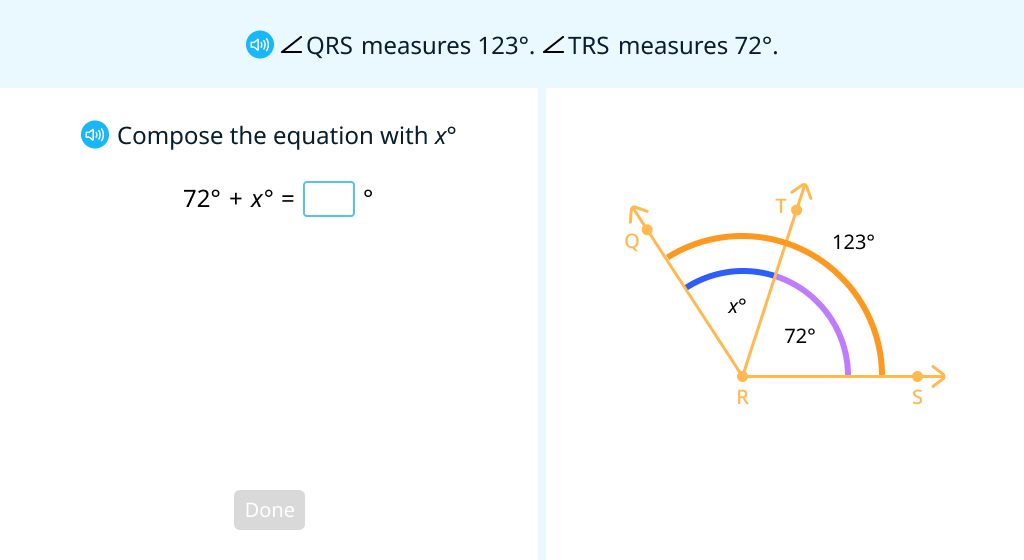
Use equations to solve angle measure problems
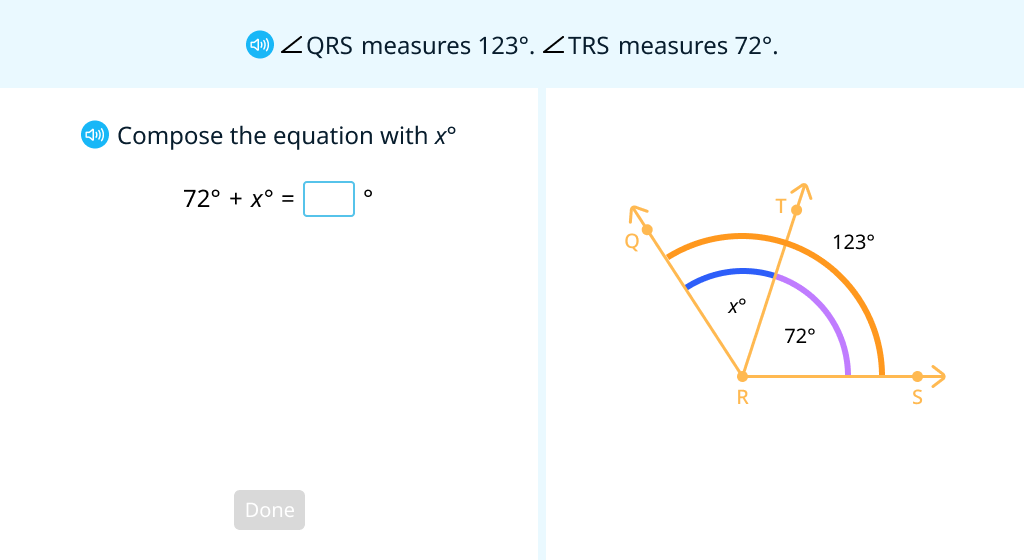
Use equations to solve 2-step angle measure problems
Topic D: Two-Dimensional Figures and Symmetry
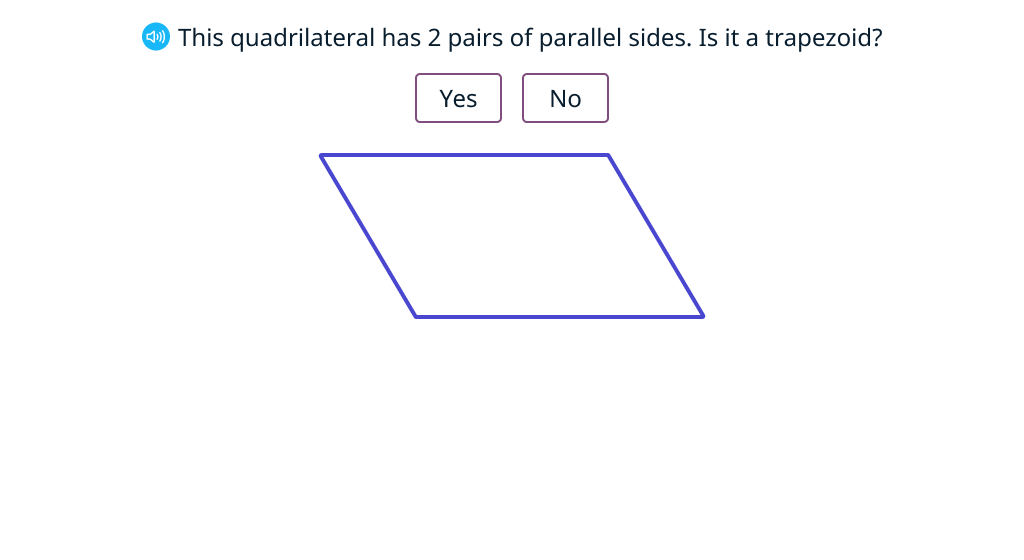
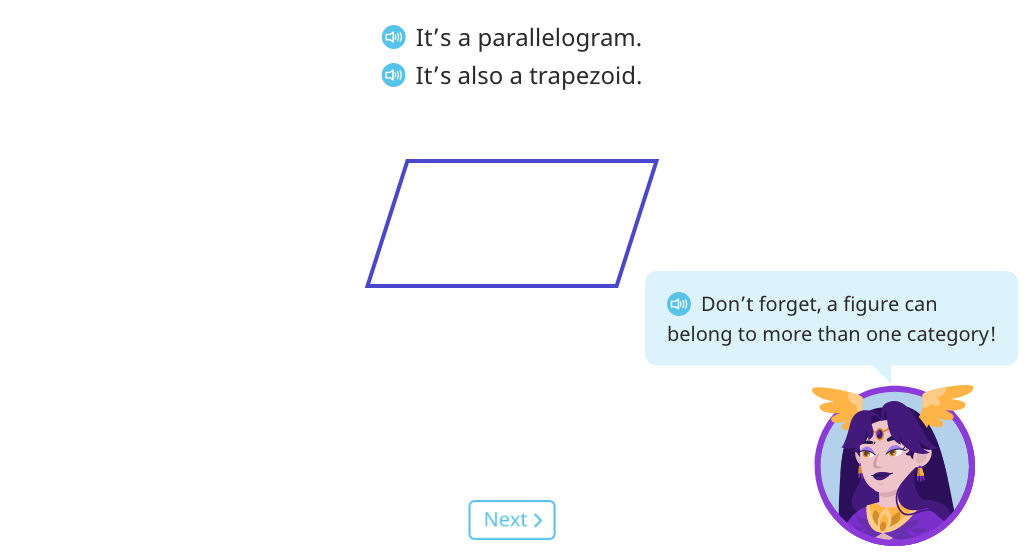
Students explore line-symmetric figures and learn to identify their lines of symmetry. They also learn the features of different quadrilaterals and discover that one figure may belong to multiple categories.
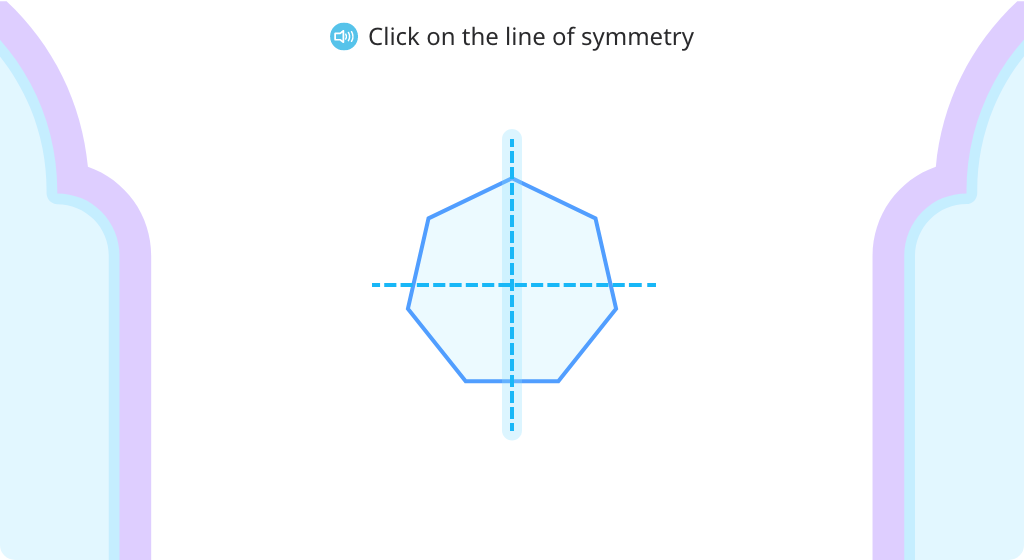
Explore line-symmetric figures
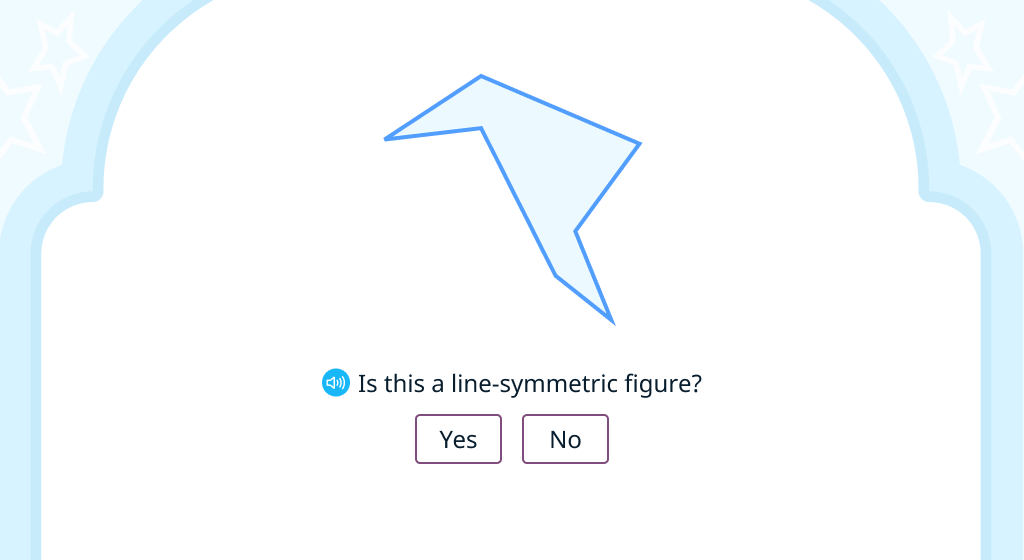
Identify the line of symmetry
Draw lines of symmetry

Identify figures with no or multiple lines of symmetry

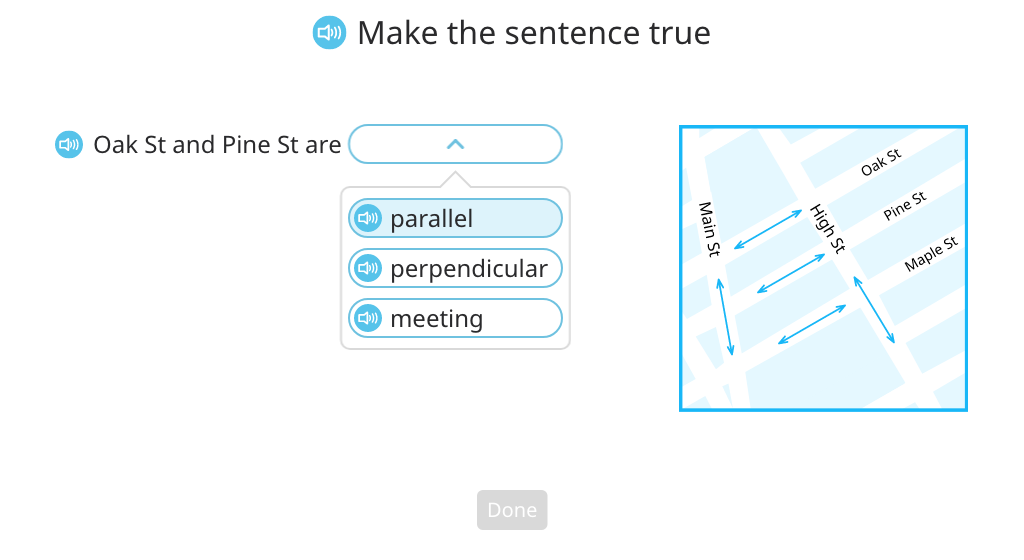
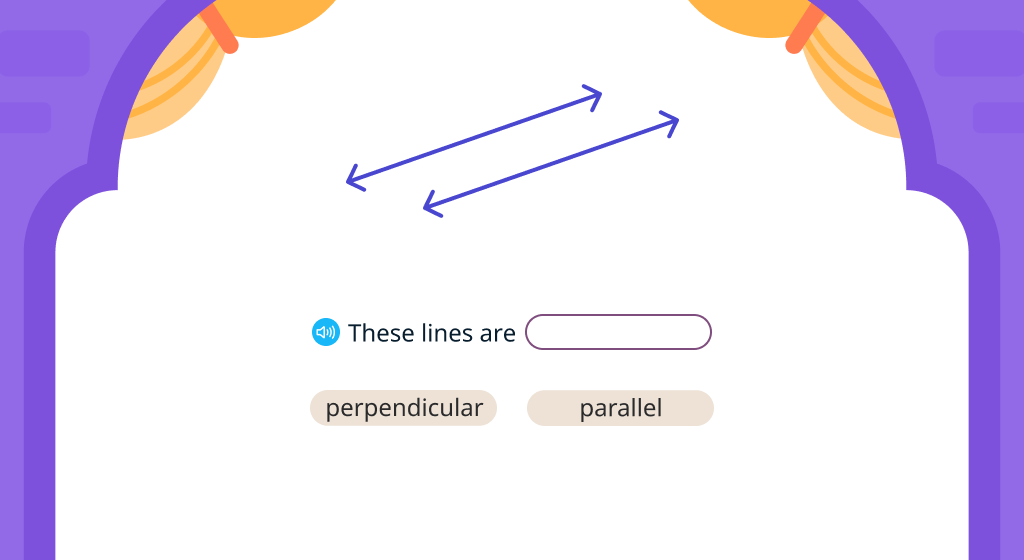
Identify parallel and perpendicular lines
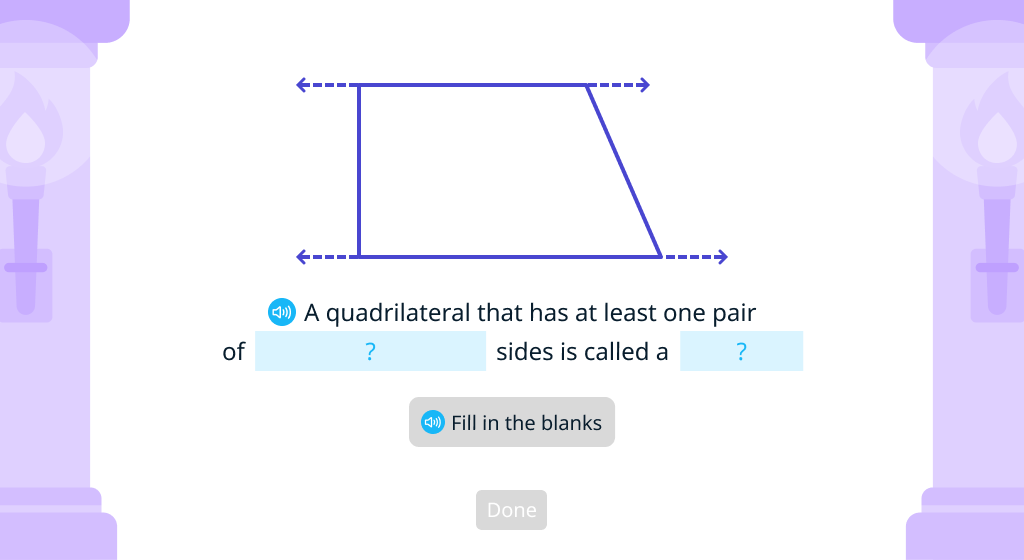
Identify trapezoids
Identify parallelograms
Name figures (Level 1)
Name figures (Level 2)
MODULE 5. Fraction Equivalence, Ordering, and Operations
Topic A: Decomposition and Fraction Equivalence
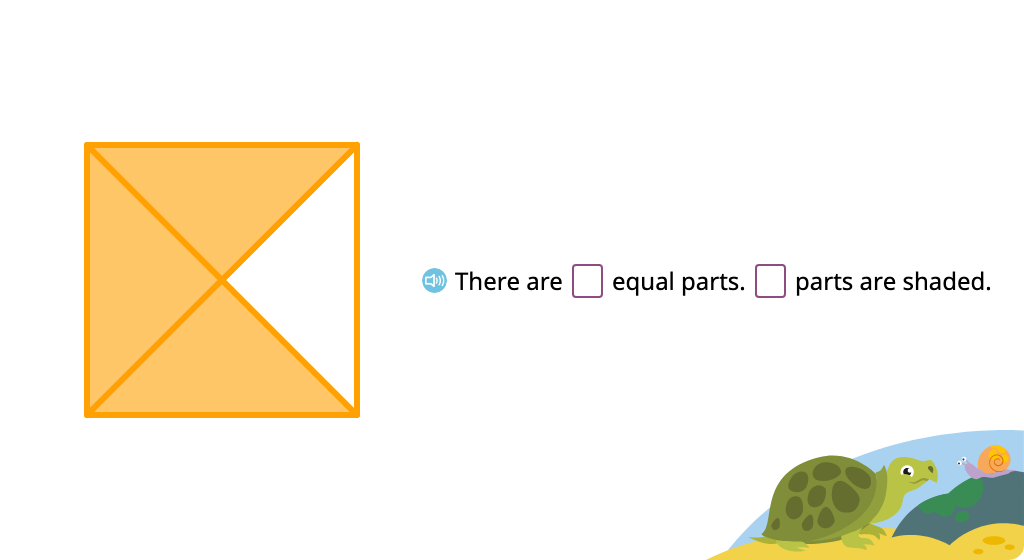
Students learn everything about what a fraction is, how it is written, what it represents, and what its parts are called. They work with fractions both less than and greater than 1 as they model, record, and rename fractions. They explore fractions as part of a whole and also as points on a number line.
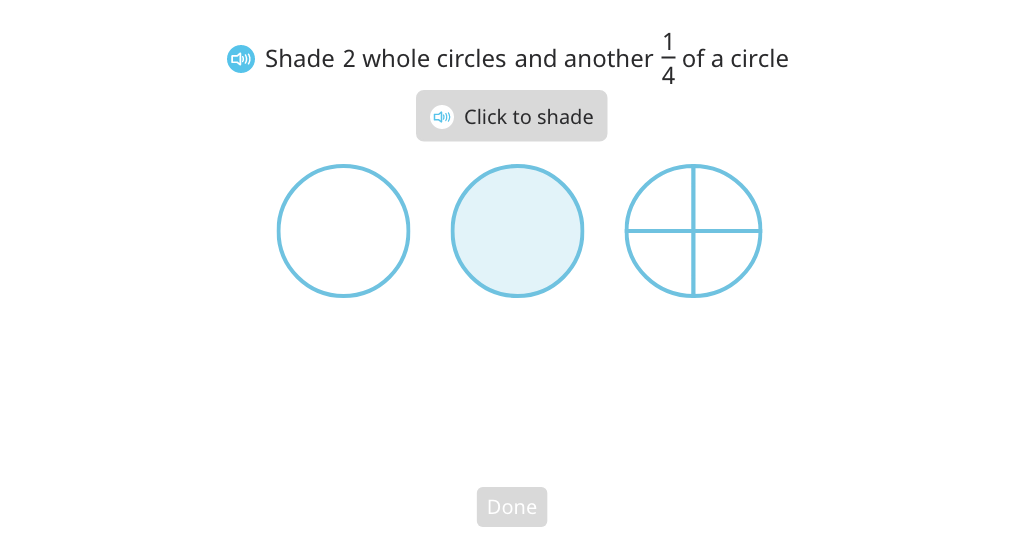
Label a shaded figure using fraction notation and shade a given fraction of a figure
Label a shaded figure using fraction notation and shade a given fraction of a figure (fractions greater than 1)
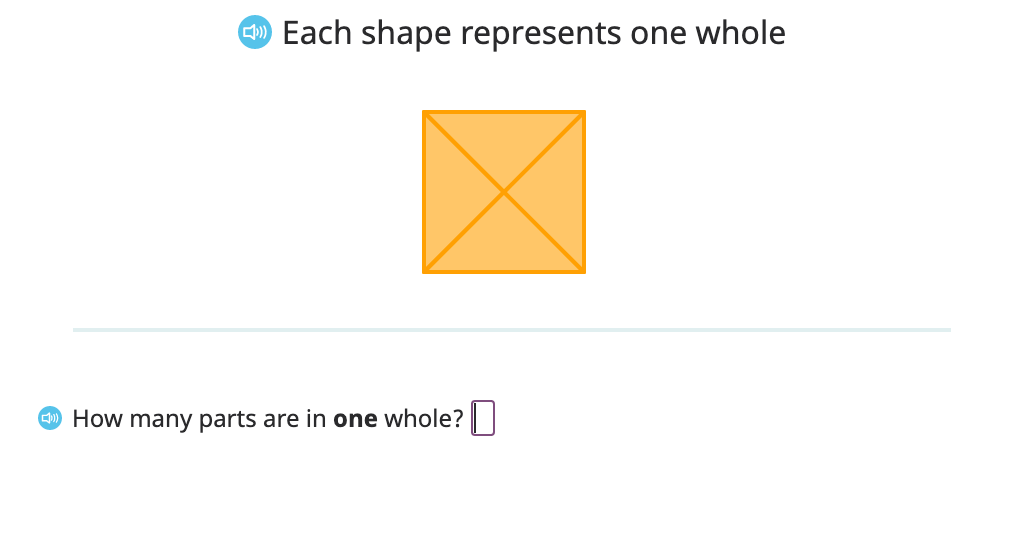
Label a missing fraction on a labeled number line
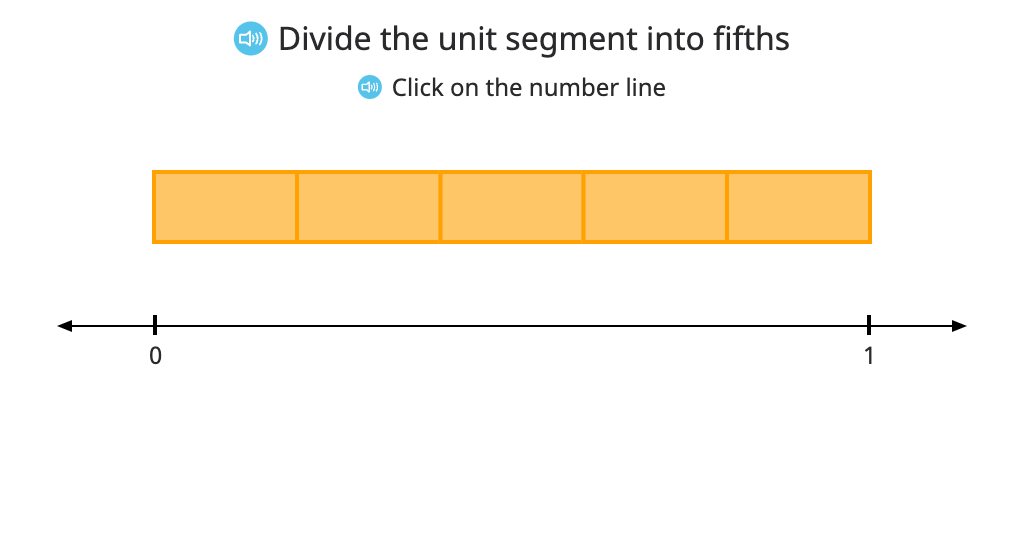
Place a fraction on a number line

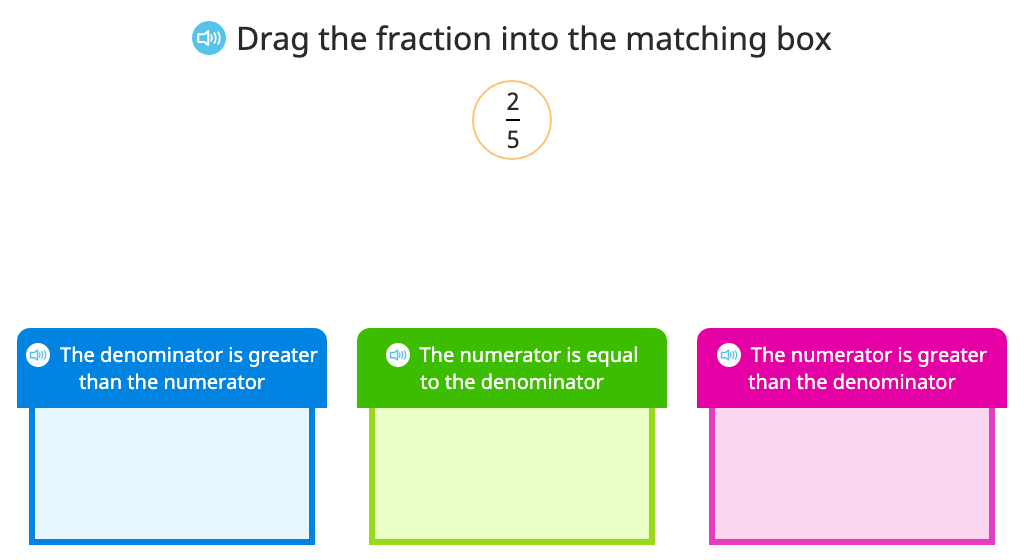
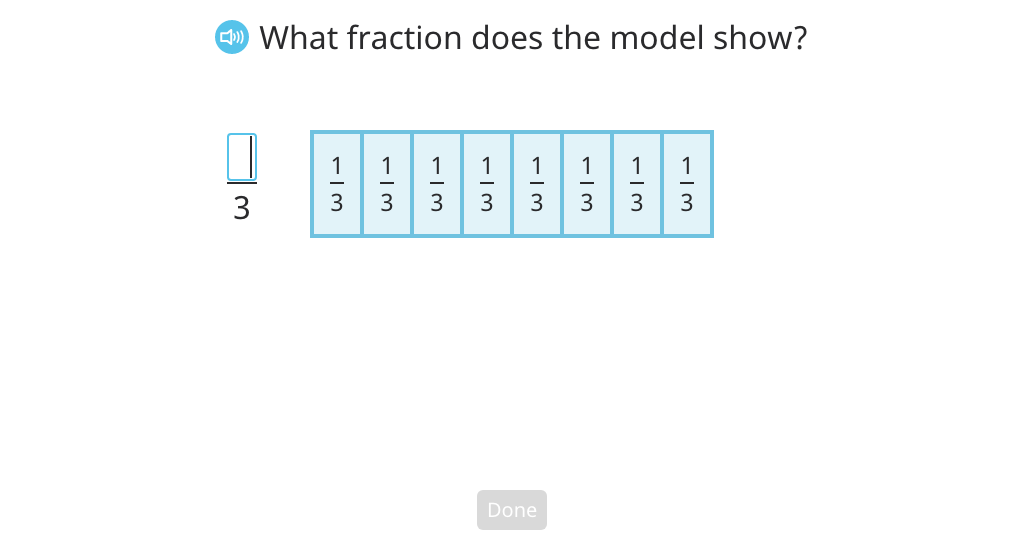
Identify numerator and denominator in a fraction
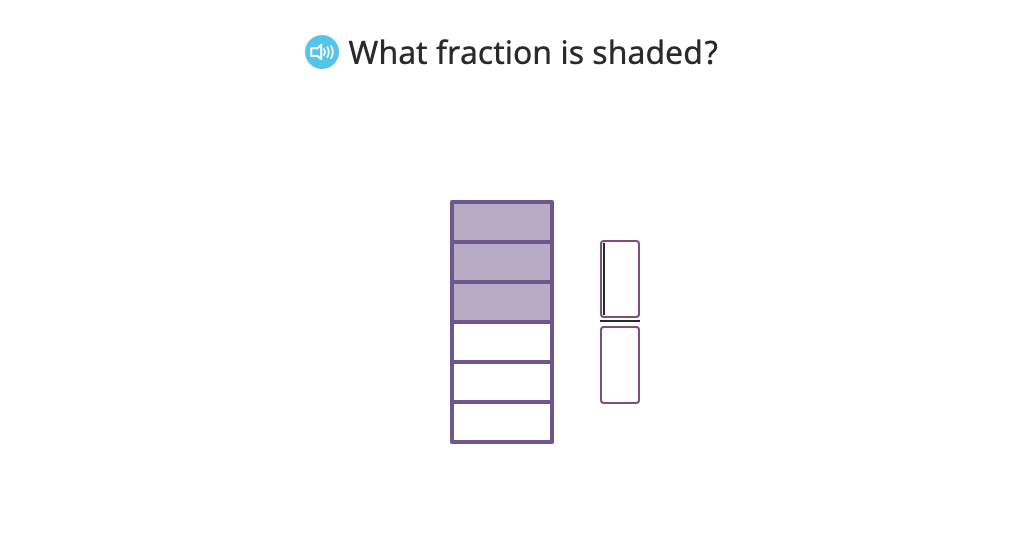
Identify fractions with a given numerator or denominator
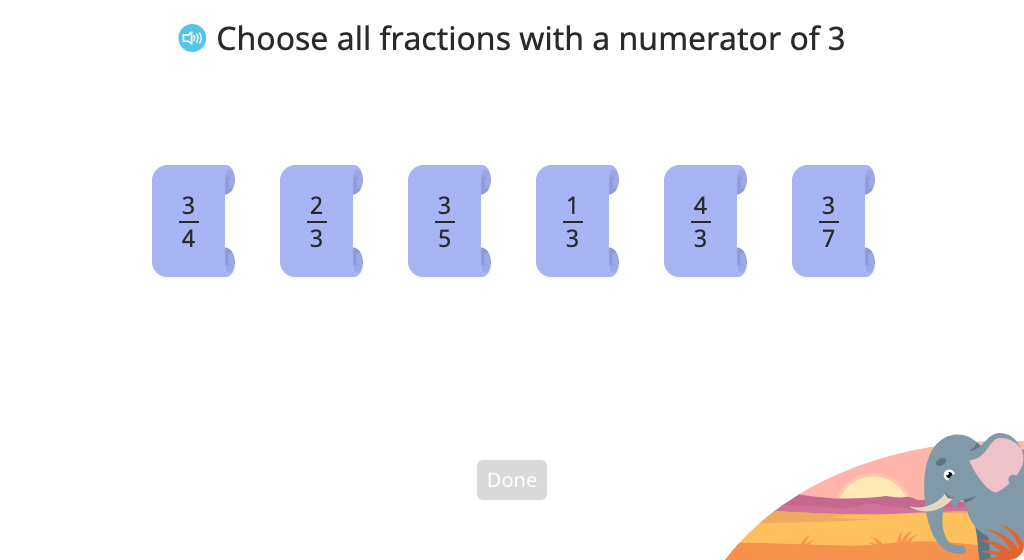
Model a fraction as the sum of its parts and record this as an equation
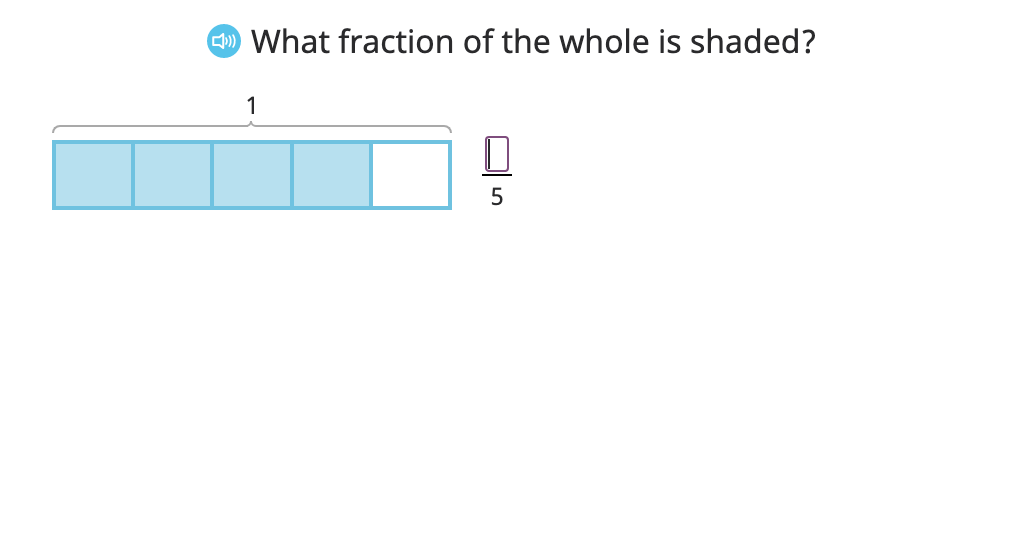
Model a fraction as the sum of its parts and record this as an equation (fractions greater than one)

Record a fraction as the sum of its parts
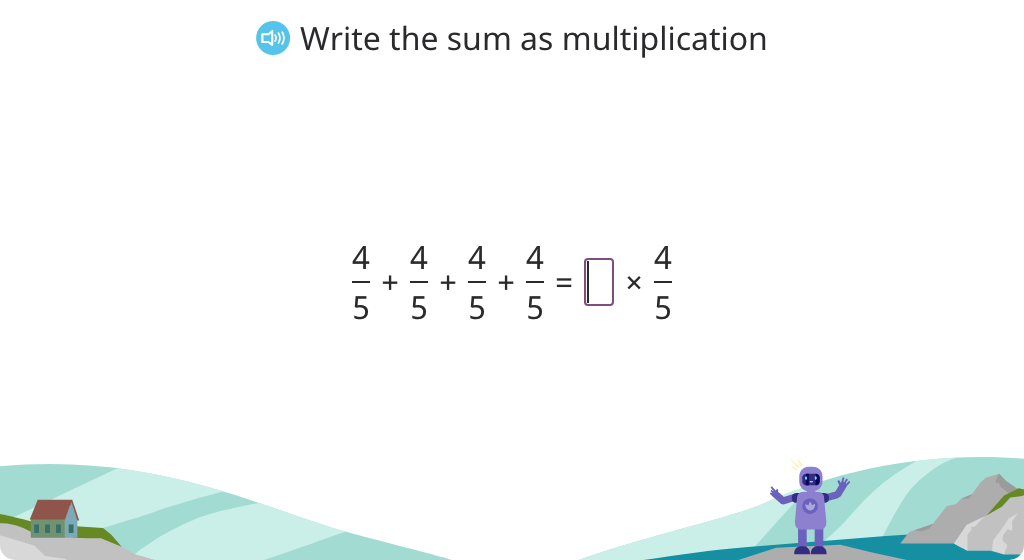
Record repeated addition of whole numbers as multiplication
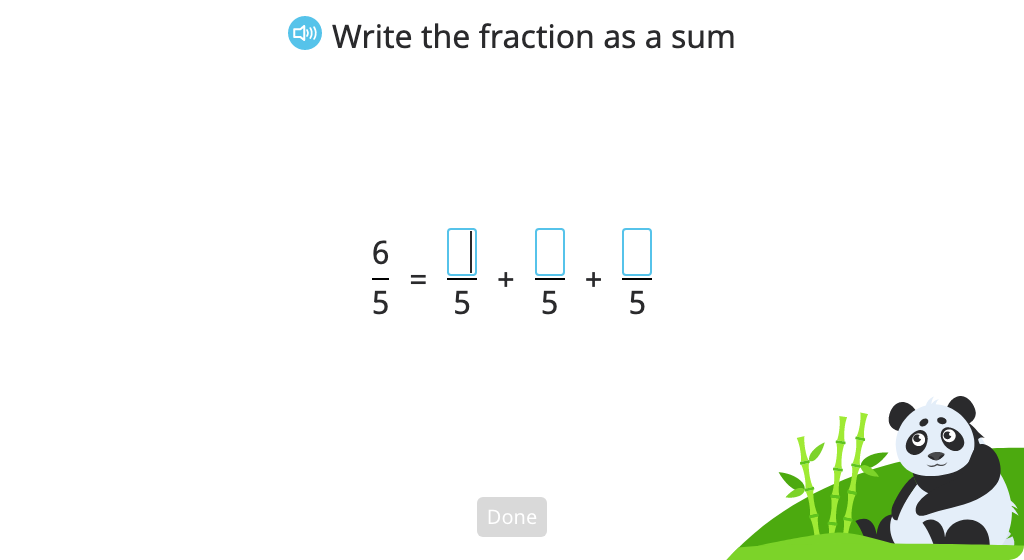
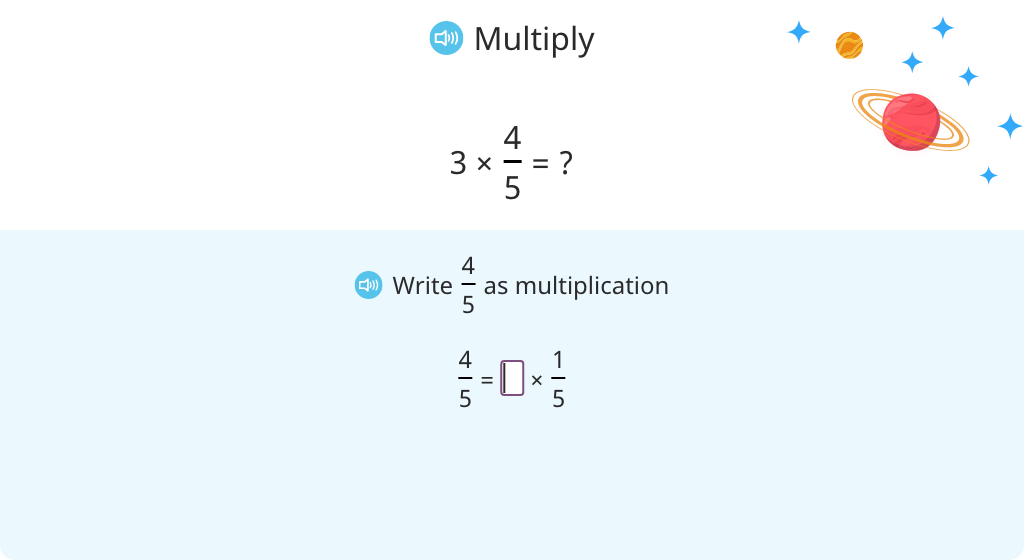
Record repeated addition of fractions as multiplication
Record repeated addition of fractions as multiplication (fractions greater than 1)
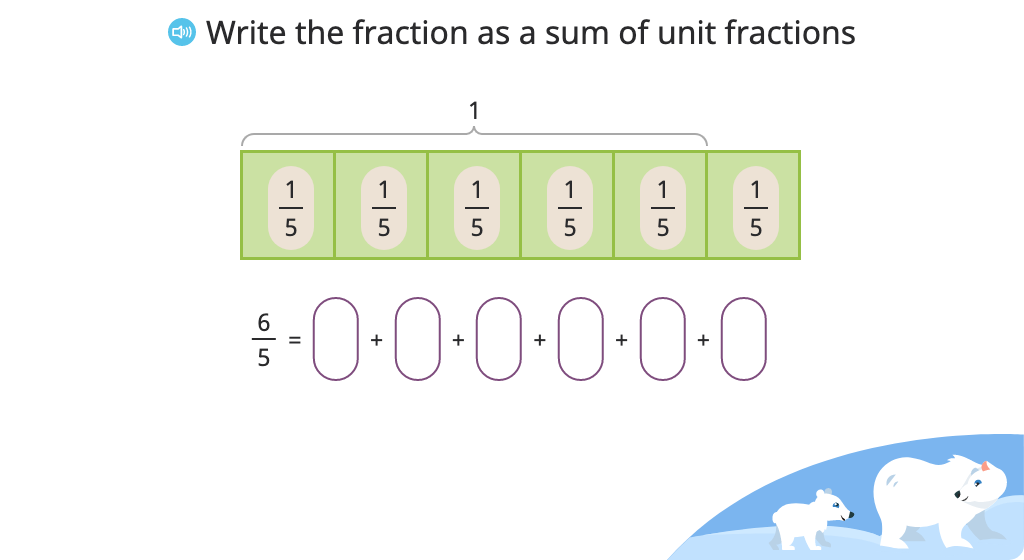
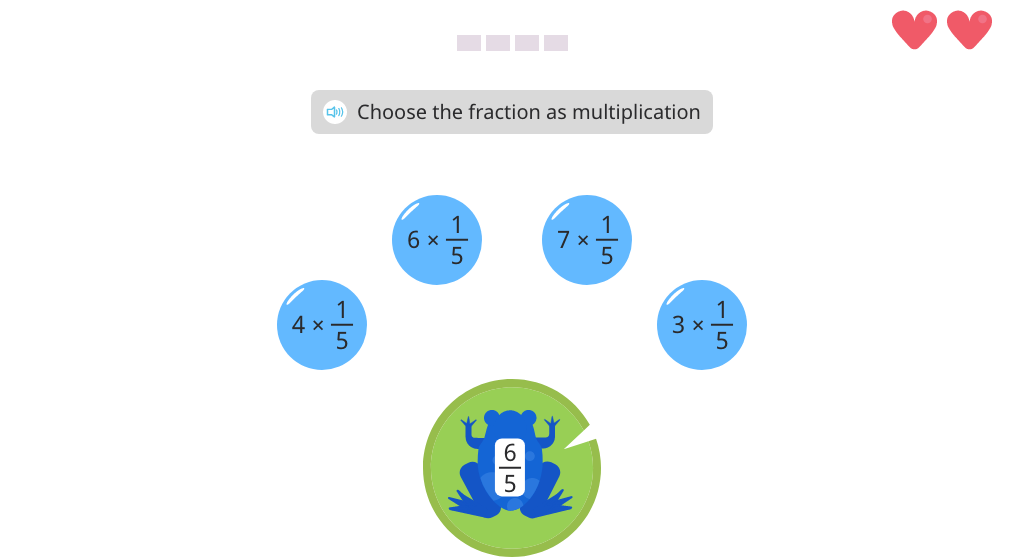
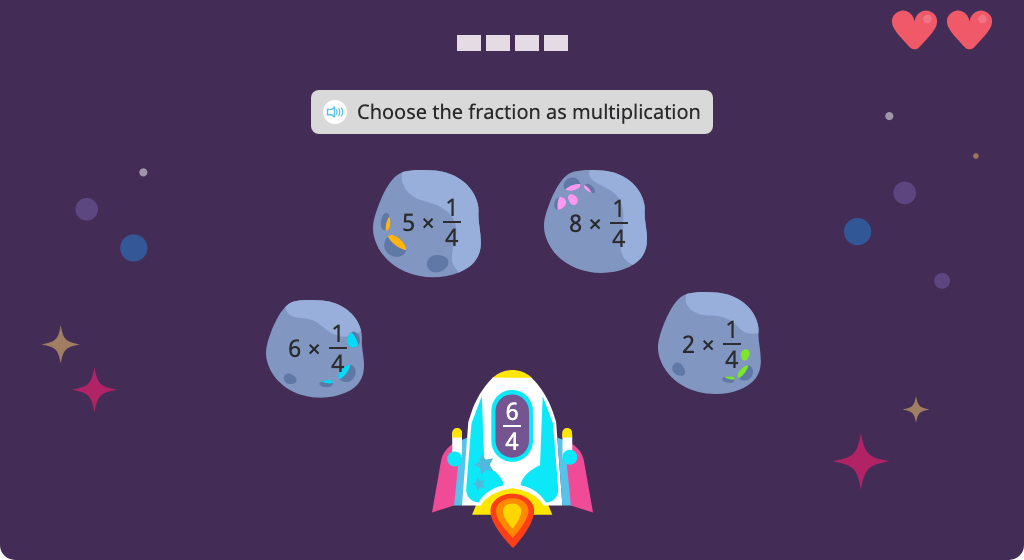
Identify the multiplication expression that matches a given fraction
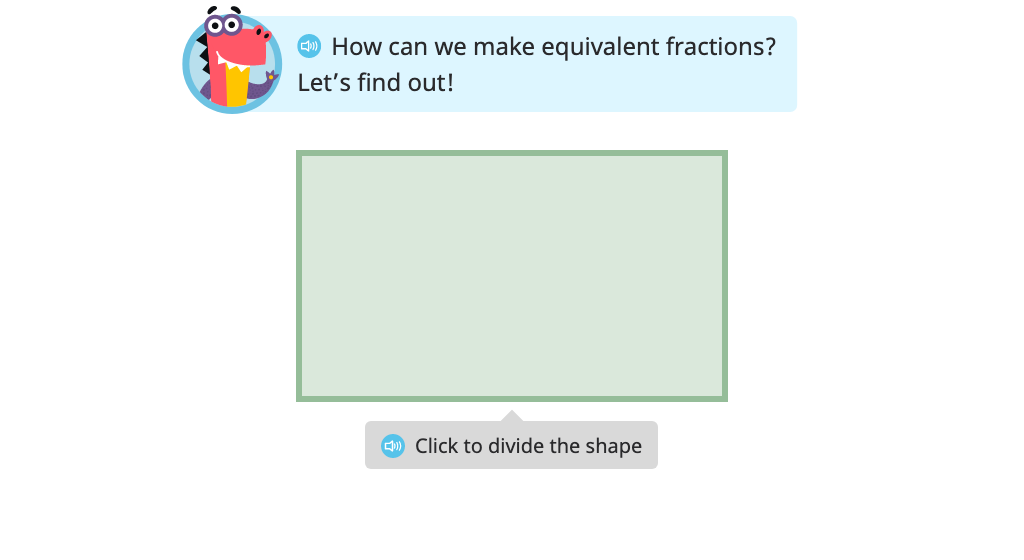
Topic B: Fraction Equivalence Using Multiplication and Division
Students compose equivalent fractions based on a model. They then label the fractions and identify the factor or divisor that relates one to the other.
Identify, label, and compare equivalent fractions
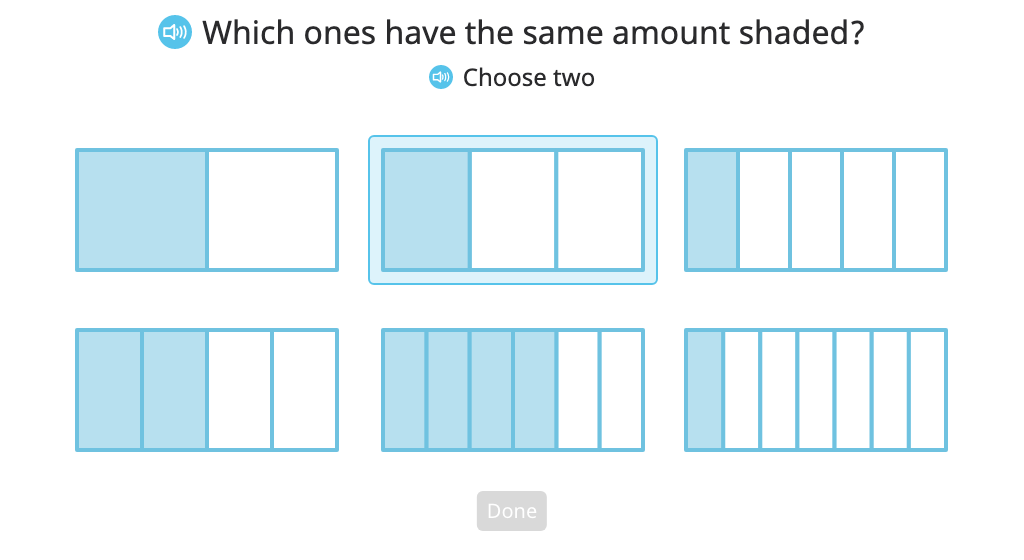
Divide a model in two different ways to show and label equivalent fractions
Multiply to find equivalent fractions based on a model
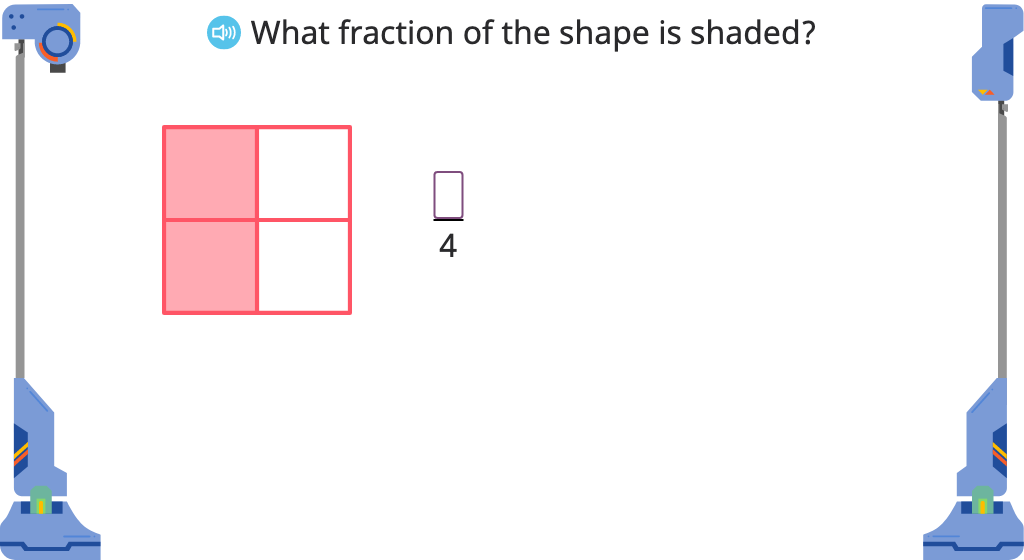
Multiply to find equivalent fractions with and without a model
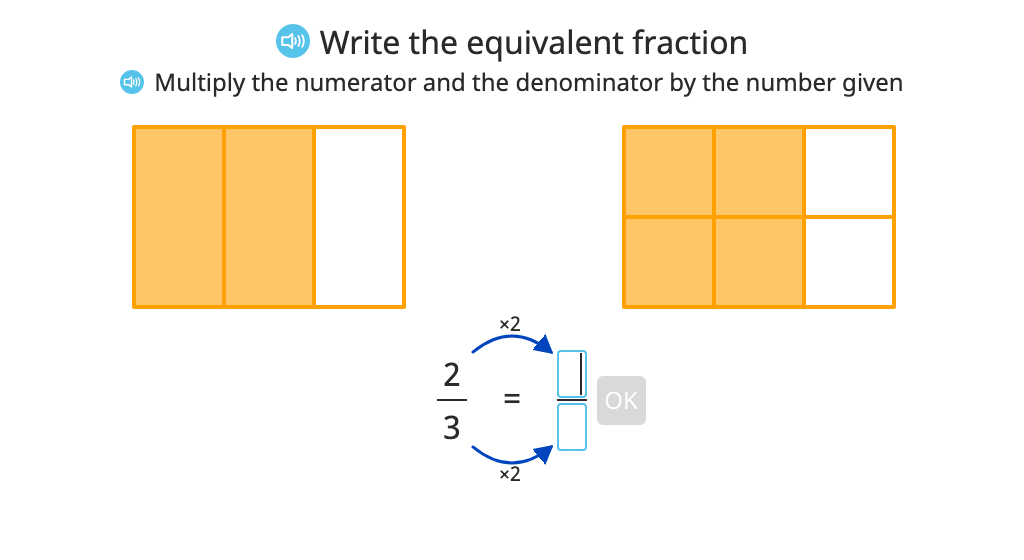
Complete the numerator or denominator in a larger equivalent fraction

Divide to find equivalent fractions based on a model
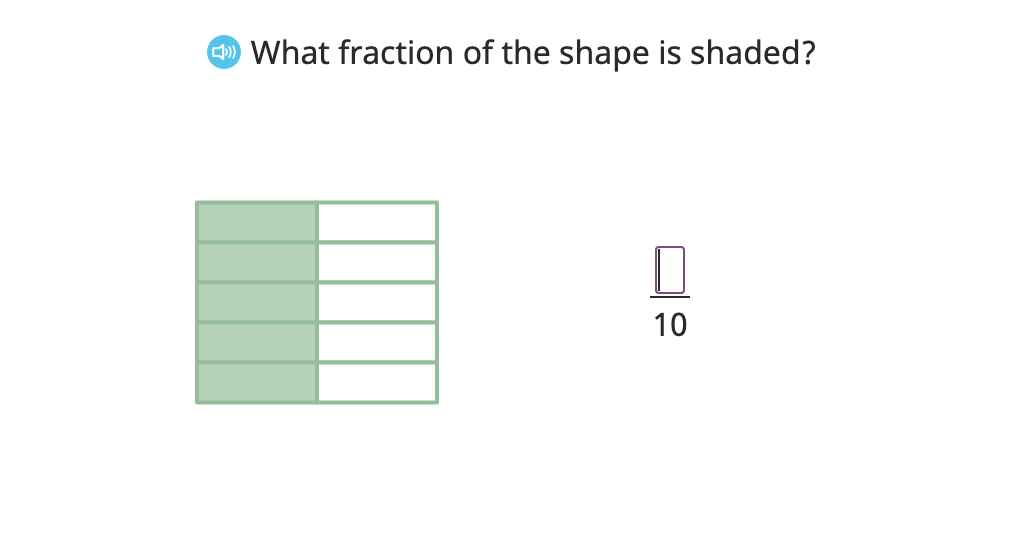
Divide to find equivalent fractions with and without a model
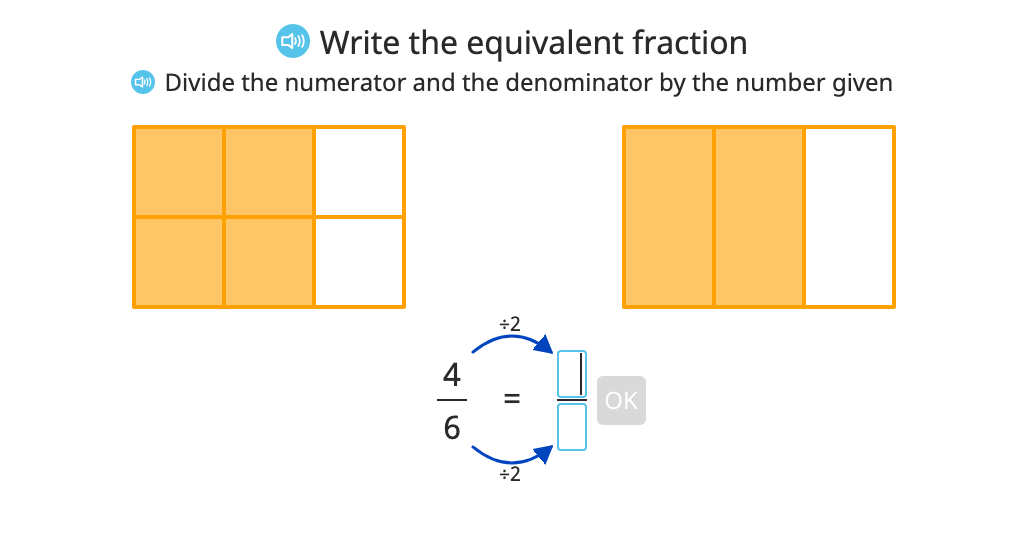
Complete the numerator or denominator in a smaller equivalent fraction

Solve problems related to equivalent fractions and multiplier

Topic C: Fraction Comparison
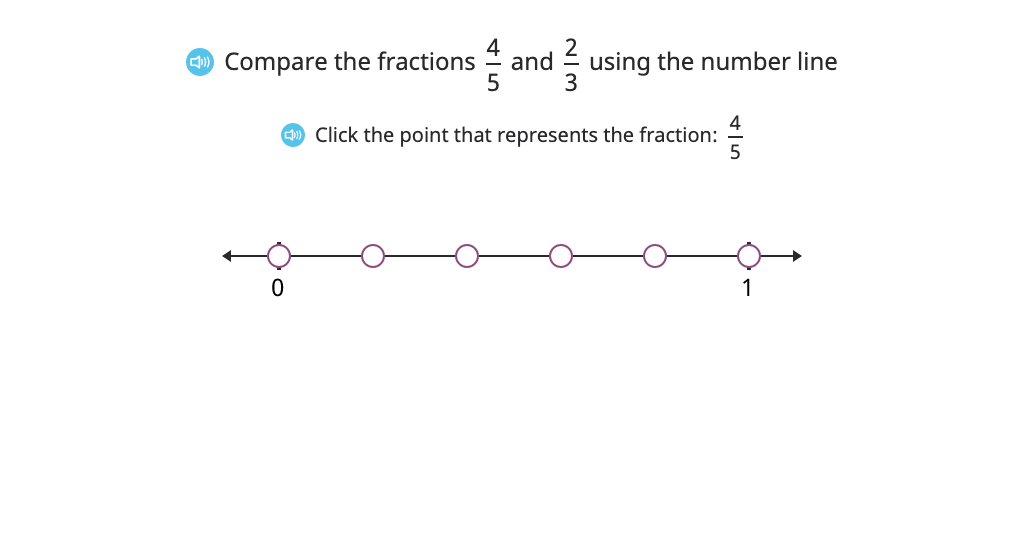
Using familiar models and the number line, along with their ability to find equivalent fractions, students compare fractions. They explore strategies to find a common numerator or denominator, or to compare to a benchmark. Students work with fractions greater than and less than one.
Label and compare fractions with like denominators or like numerators based on a model
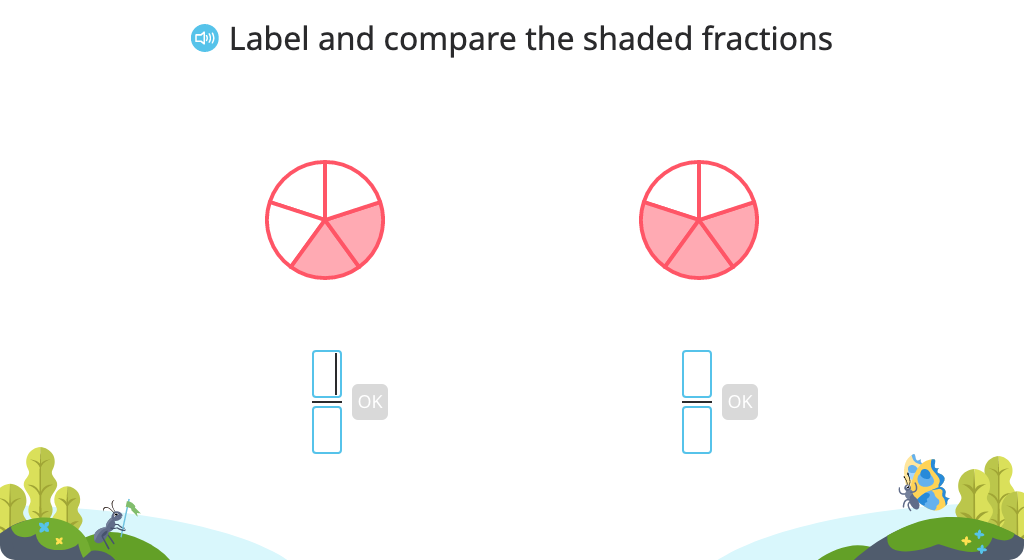
Place fractions with like denominators or like numerators on a number line and compare

Order four fractions with like denominators or like numerators based on a model
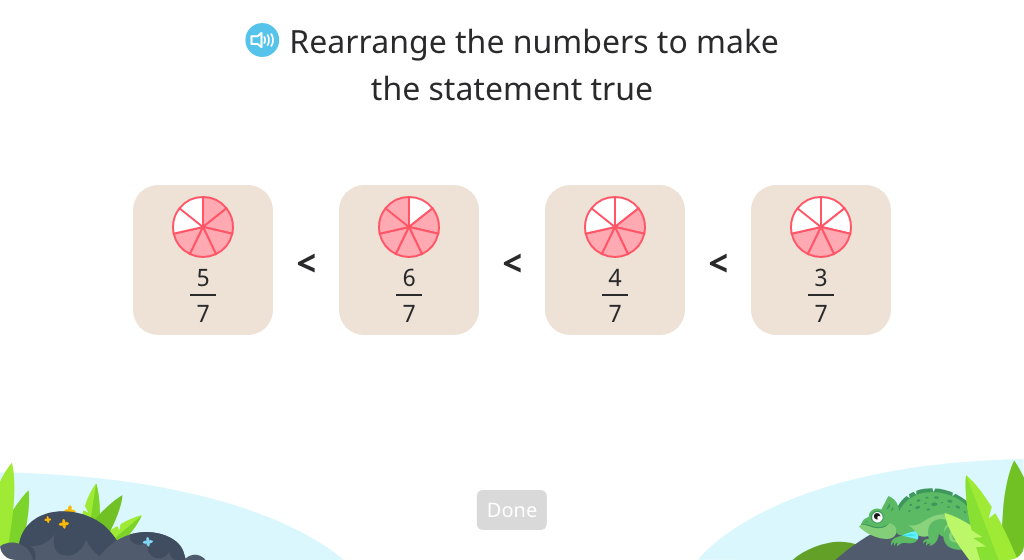
Compare fractions with like denominators or like numerators
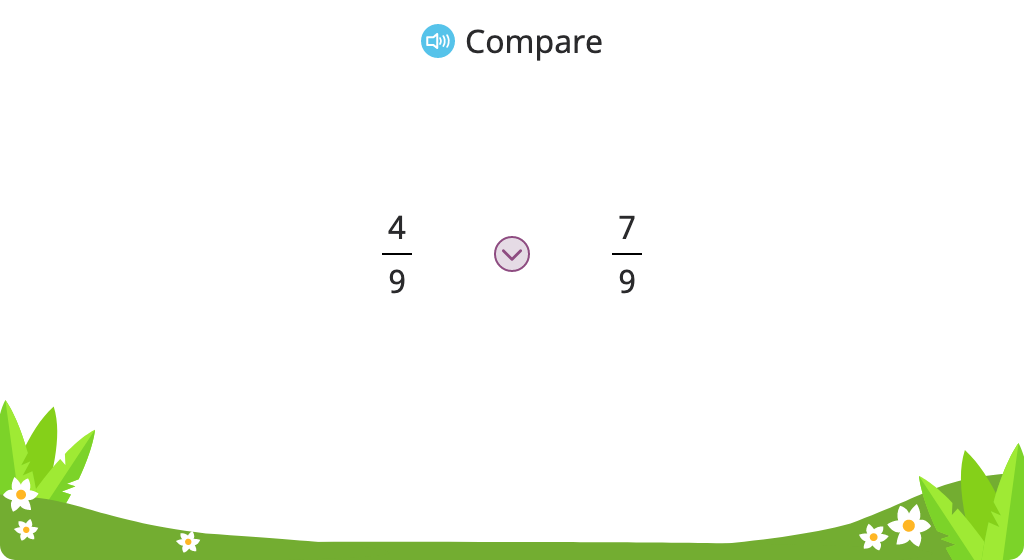
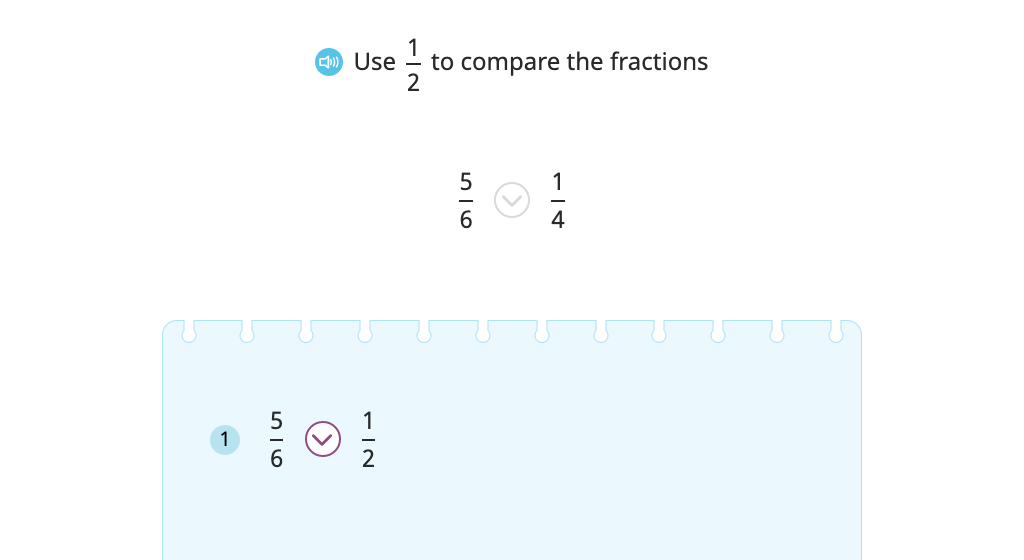
Compare fractions to 1/2 with and without a number line
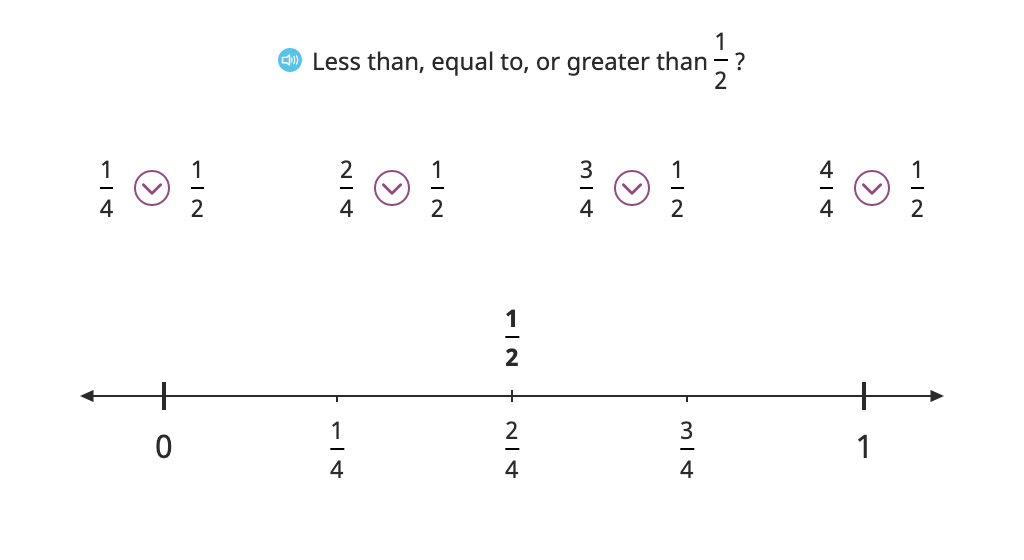
Solve word problems comparing a fraction to 1/2 using an equivalent fraction
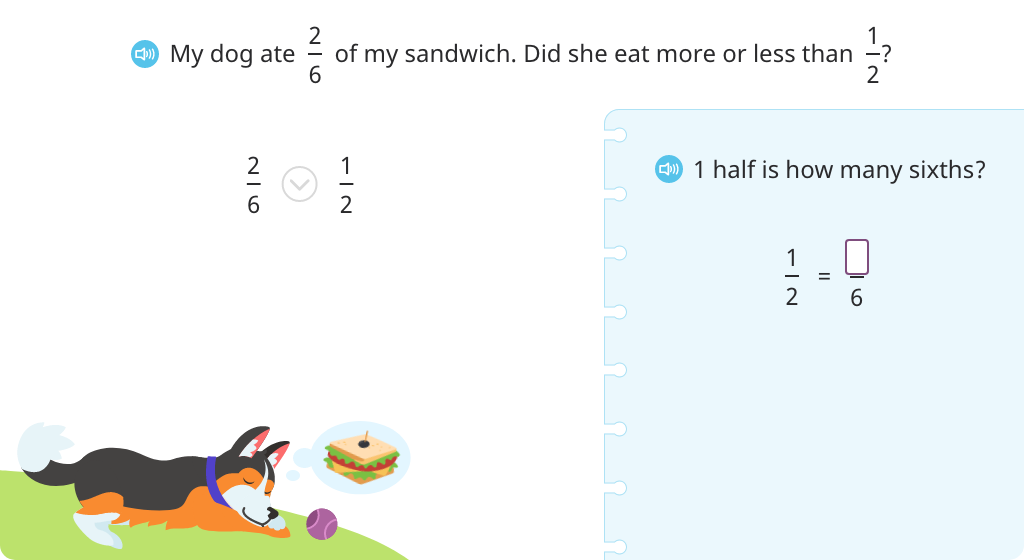
Compare fractions by comparing each one to 1/2
Compare fractions by comparing each one to 1

Choose a strategy and use it to compare fractions
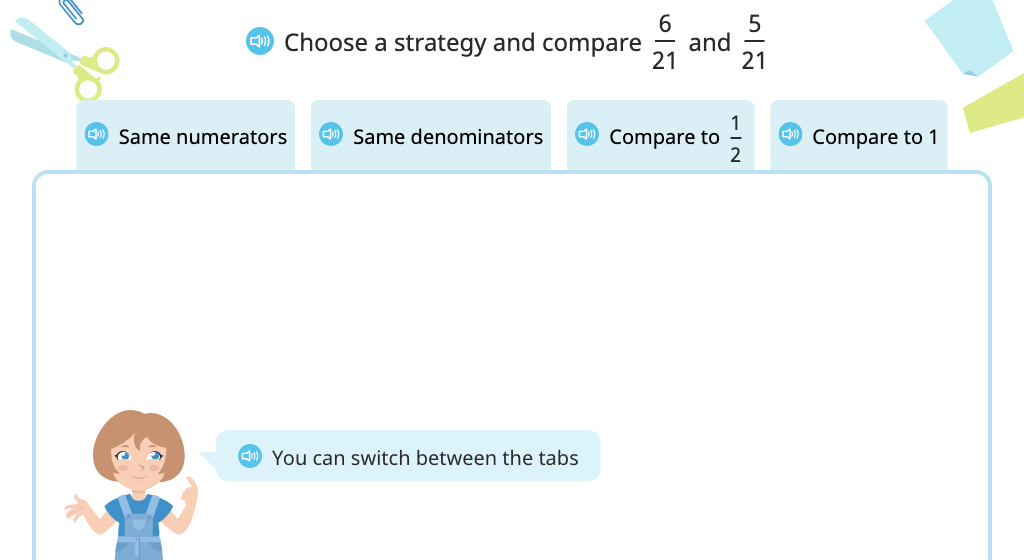
Compare fractions by comparing the remaining unit fraction using a number line and model
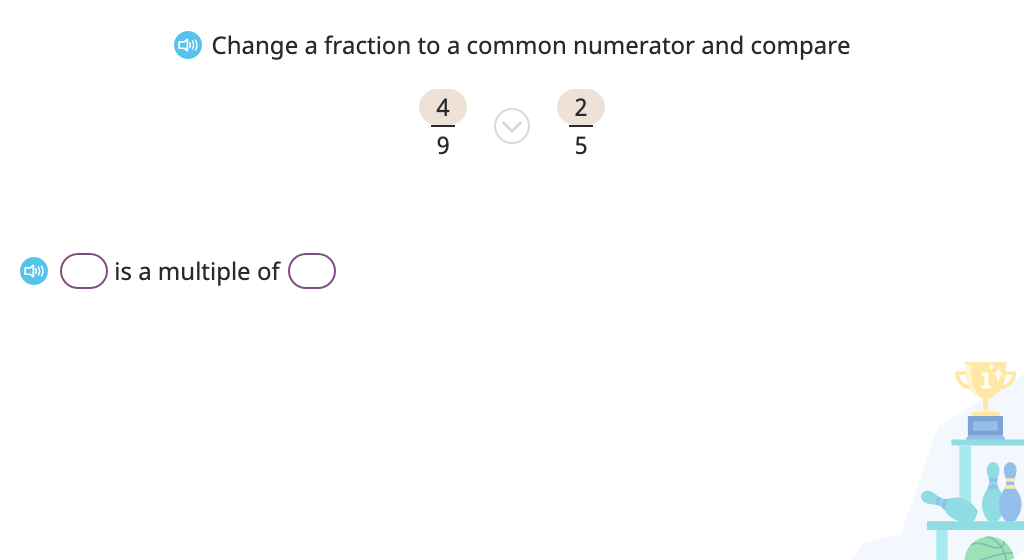
Compare fractions by finding a common numerator (when one numerator is a multiple of the other)
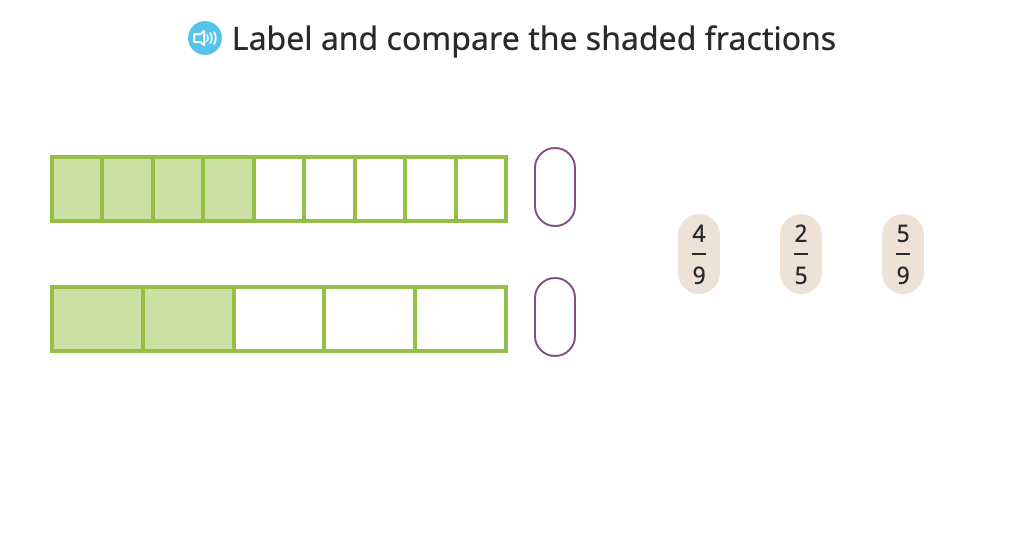
Compare fractions by finding a common denominator (when one denominator is a multiple of the other)
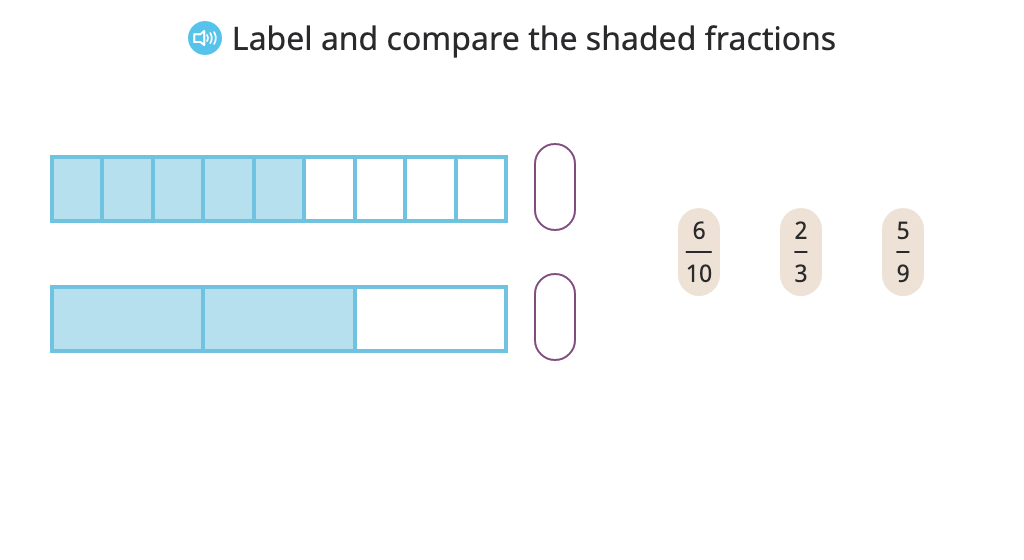
Compare fractions by finding a common denominator (when one denominator is not a multiple of the other)
Compare fractions by finding a common numerator or denominator (when one is a multiple of the other)
Topic D: Fraction Addition and Subtraction
Students apply their understanding of fraction basics to add and subtract fractions. They work with familiar models and the number line to build understanding of the concepts behind the operations. In solving addition and subtraction problems, students convert among equivalent fractions, mixed numbers, and improper fractions.
Identify and add fractions with a common denominator based on a model
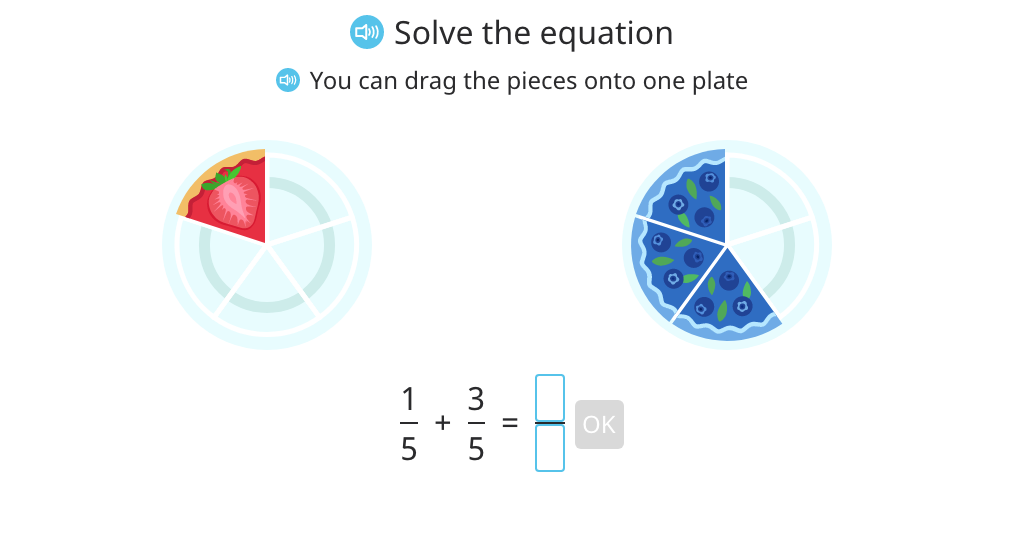
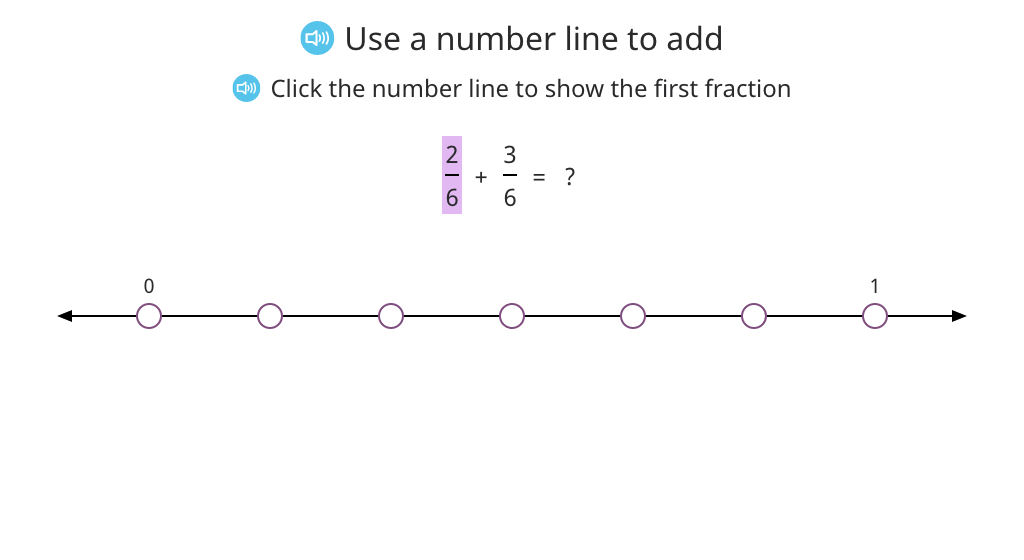
Add fractions with a common denominator with and without a number line
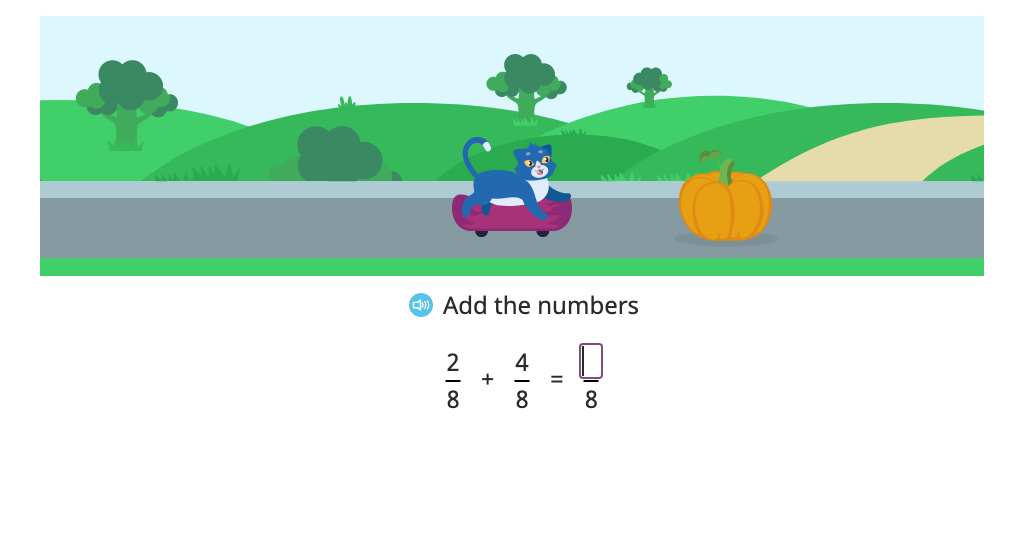
Add fractions with a common denominator
Add fractions with a common denominator and convert the sum to a mixed number (Level 1)
Subtract fractions with a common denominator with and without a number line
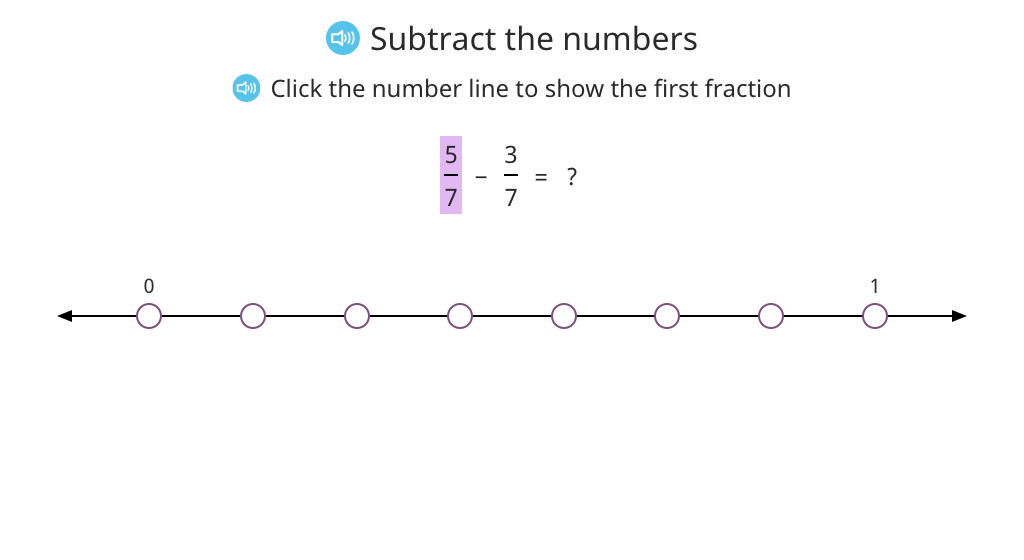
Rename a mixed number as a fraction to subtract a fraction

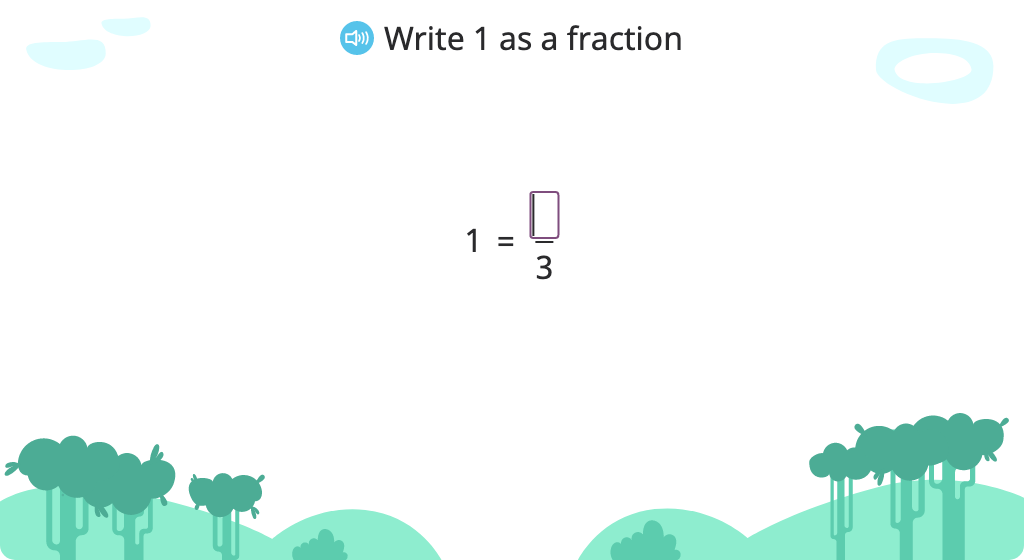
Rename a fraction as an equivalent fraction
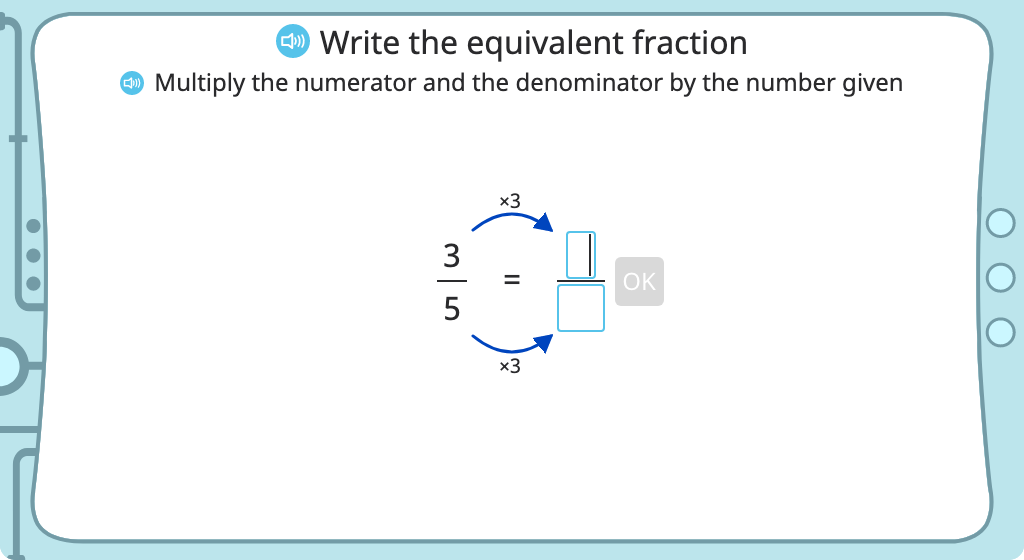
Add fractions with different denominators and rename the sum as a mixed number

Topic E: Extending Fraction Equivalence to Fractions Greater Than 1
To prepare for more complex work with addition and subtraction, students establish a firm understanding of mixed numbers and fractions greater than 1. They convert fractions to mixed numbers and vice versa. They find common denominators when one denominator is a factor of the other and when it is not.
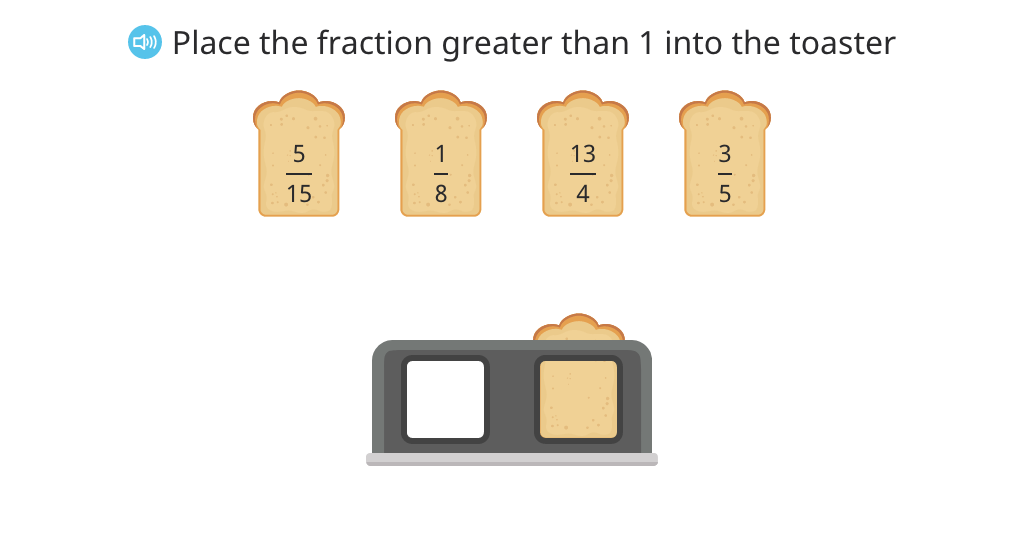
Identify fractions as greater than, less than, or equal to 1
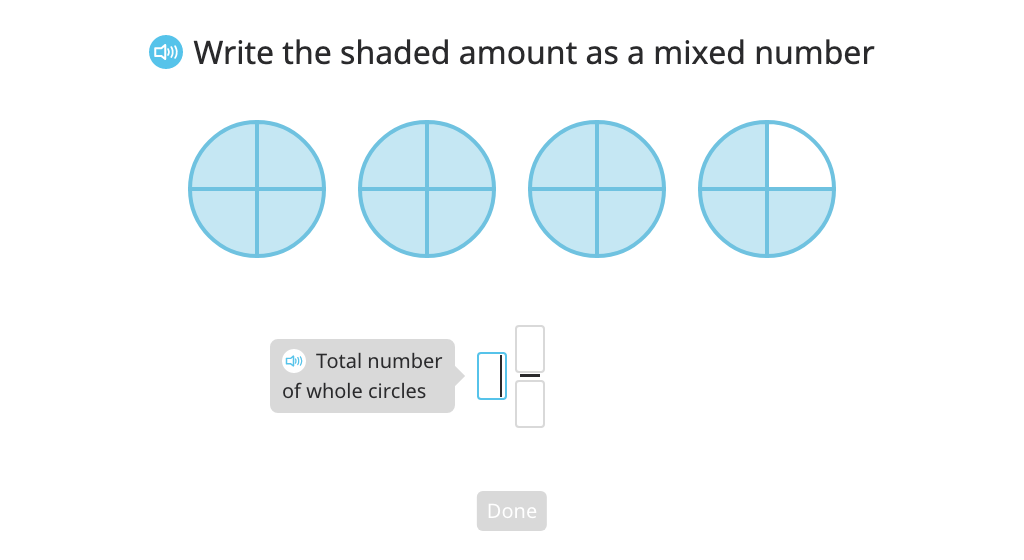
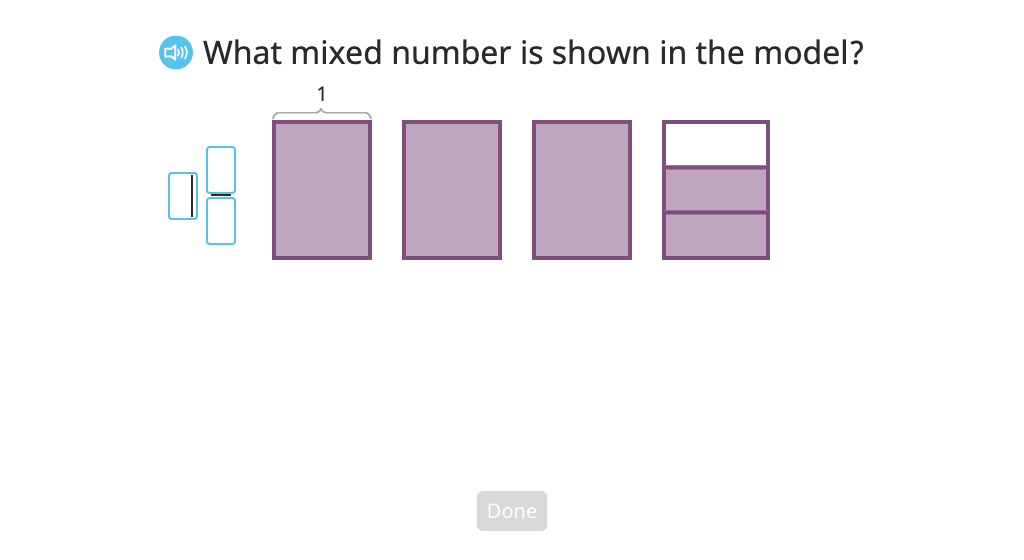
Label a model with a mixed number and identify its written form
Identify a mixed number on a number line
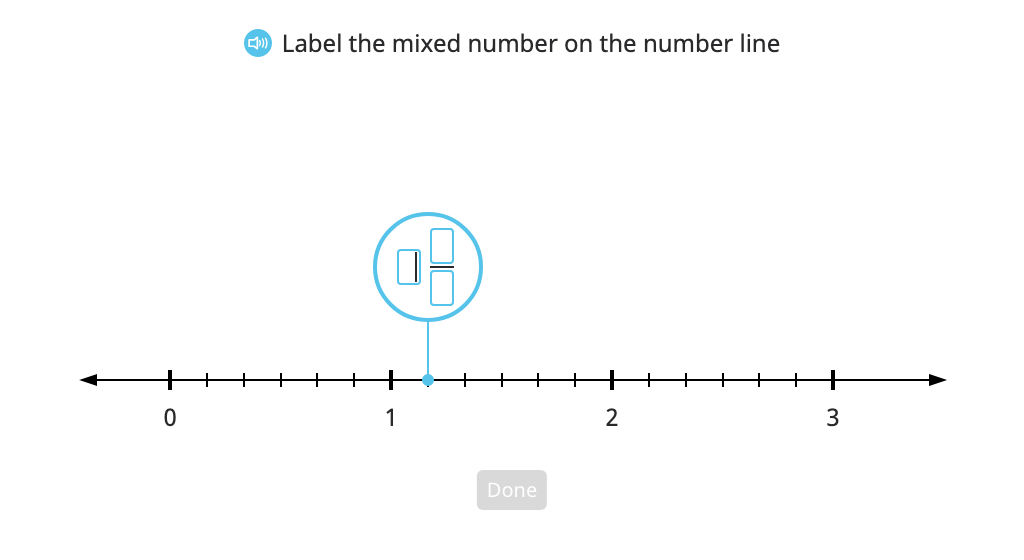
Label a model with a mixed number and a fraction greater than 1
Rename a mixed number as a fraction greater than 1 based on a model
Rename a mixed number as a fraction greater than 1

Rename a fraction greater than 1 as a mixed number based on a model
Rename a fraction greater than 1 as a mixed number

Match fraction addition to a mixed number and a fraction greater than 1
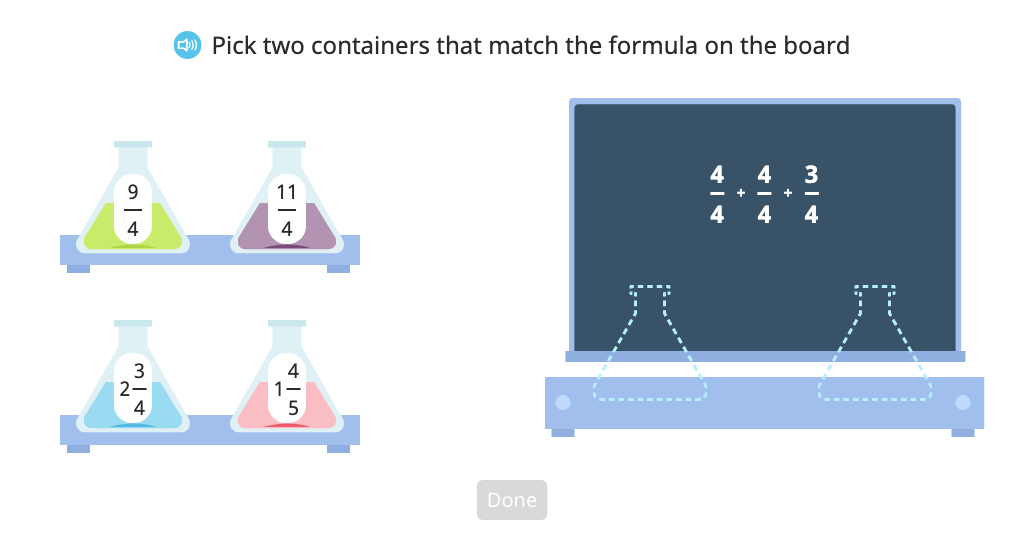
Identify a fraction greater than 1 and rename it as a mixed number
Label models with mixed numbers and compare using <, =, or >
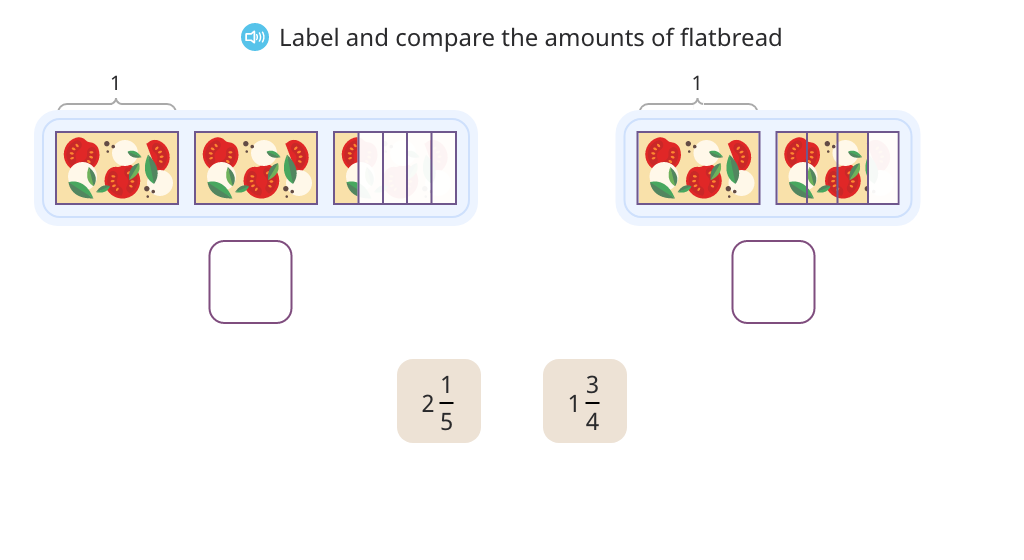
Compare mixed numbers with different denominators (Part 1)

Compare fractions greater than 1 by renaming them as mixed numbers
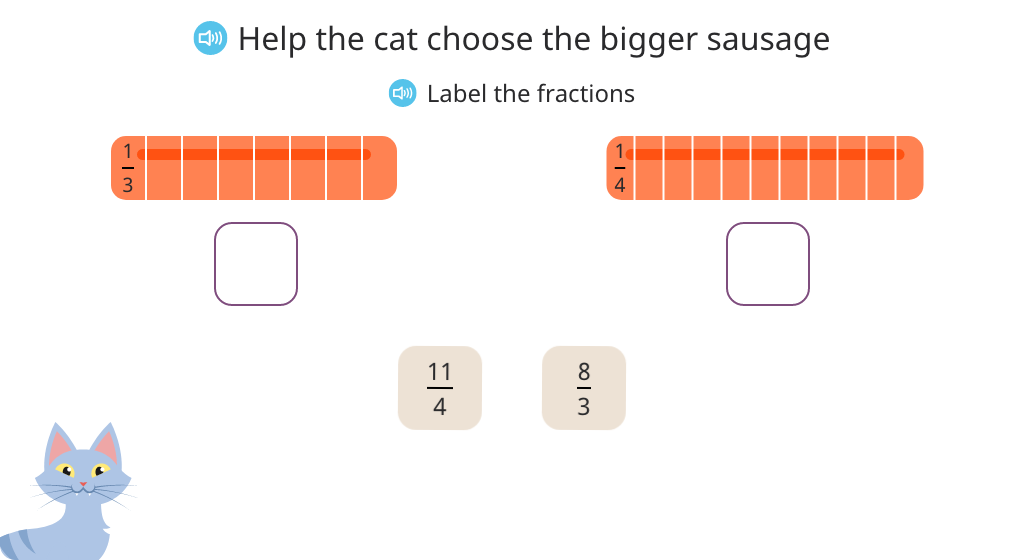
Compare a fraction greater than 1 with a mixed number or a fraction greater than 1

Compare mixed numbers with different denominators (Part 2)
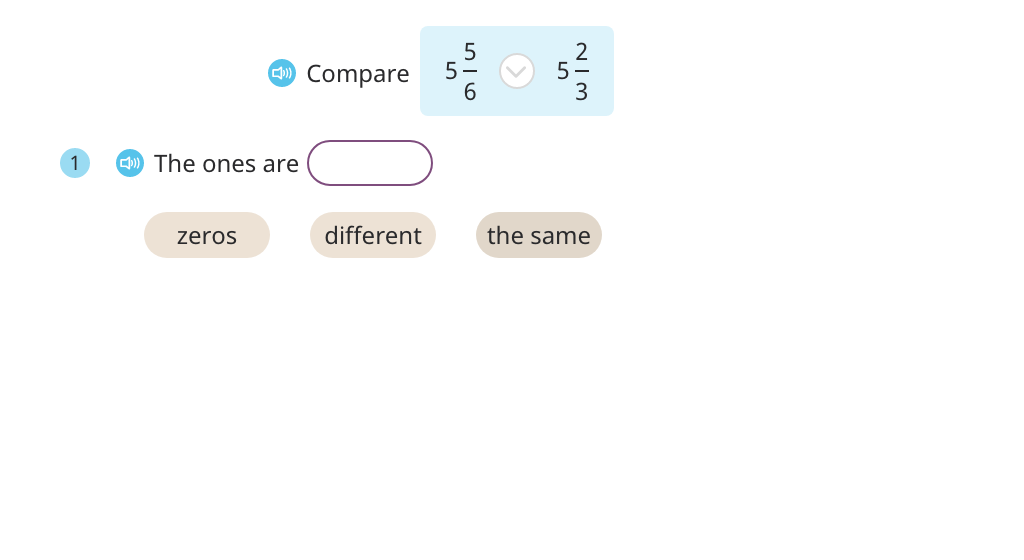
Compare mixed numbers with different denominators (Part 3)
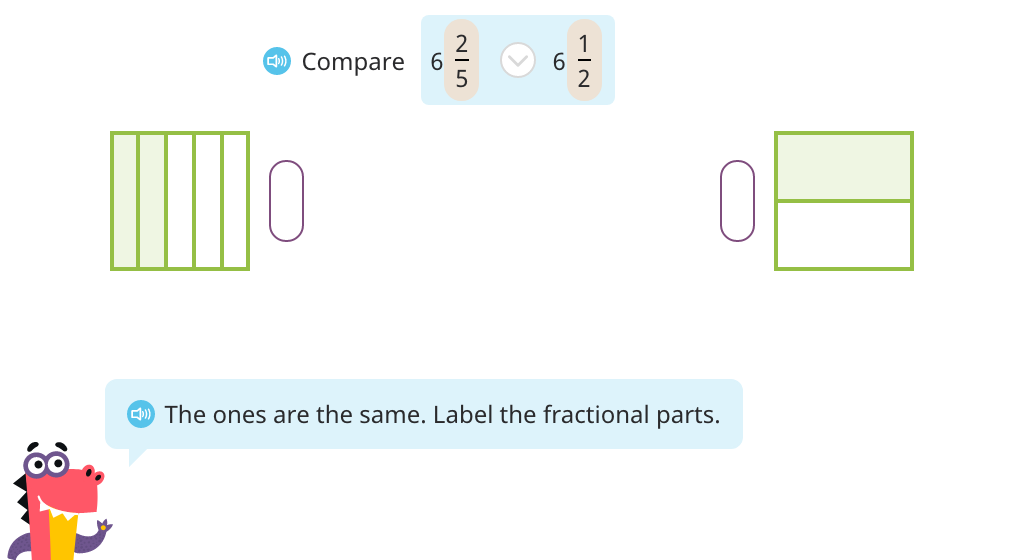
Compare fractions greater than 1
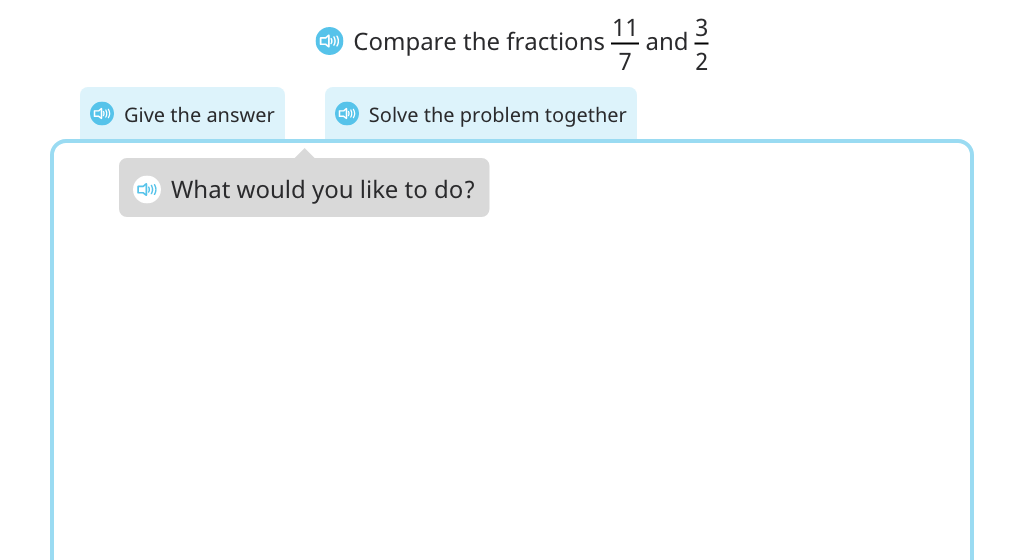
Topic F: Addition and Subtraction of Fractions by Decomposition
Students rely heavily on their understanding of fractions and mixed numbers to complete operations. To add and subtract, they break apart, regroup, and rename numbers. They gradually move from a step-by-step guided strategy to solving problems mentally.
Round a mixed number to the nearest whole with and without a number line
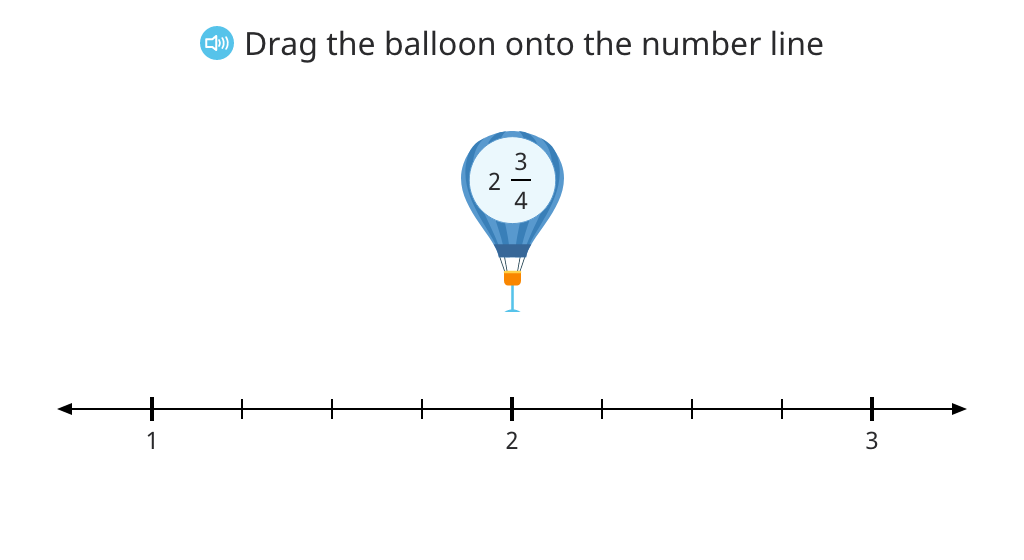
Estimate the sum or difference of two mixed numbers by rounding them to the nearest whole
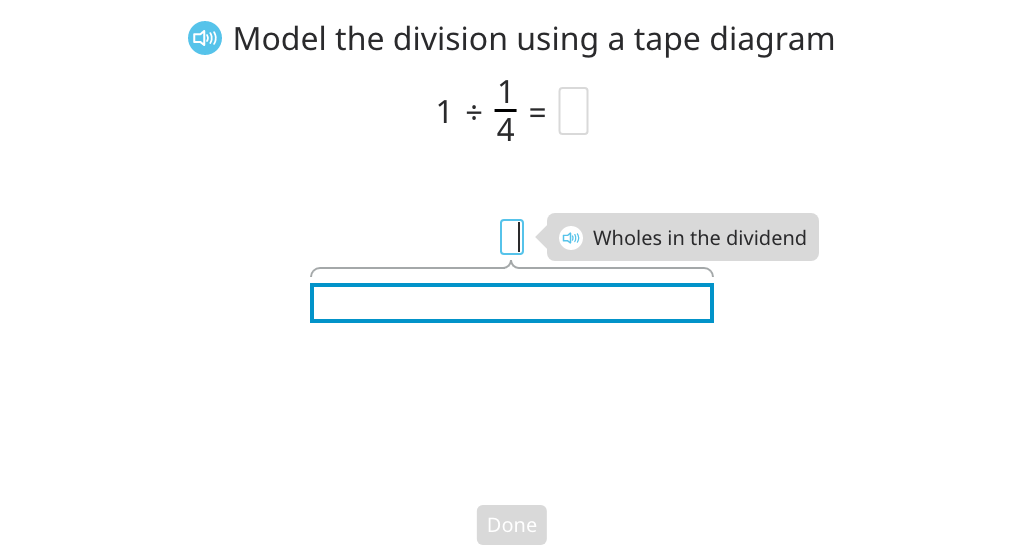
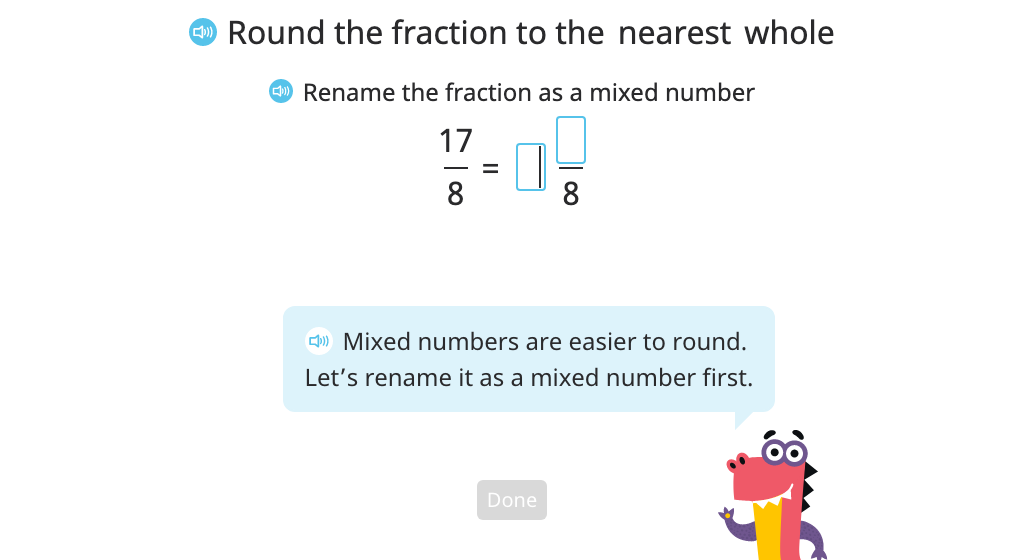
Round an improper fraction to the nearest whole by converting it to a mixed number
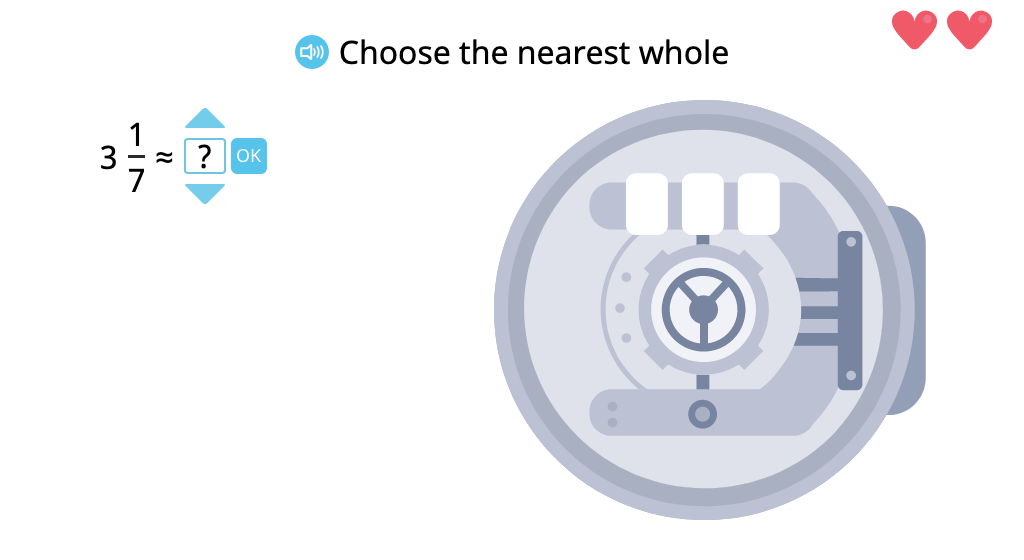
Round mixed numbers and improper fractions to the nearest whole
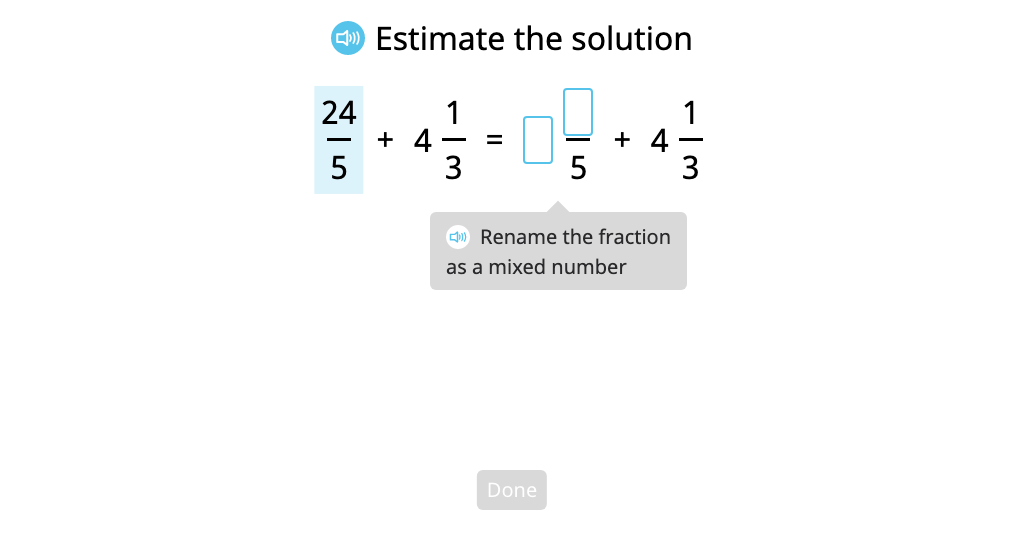
Estimate the sum or difference of a mixed number and an improper fraction by converting the fraction to a mixed number
Add a whole number to a mixed number

Add a mixed number to a fraction with the same denominator

Add a mixed number to a fraction with the same denominator and write the sum without an improper fraction

Add a mixed number to a fraction with the same denominator by completing the whole (Level 1)
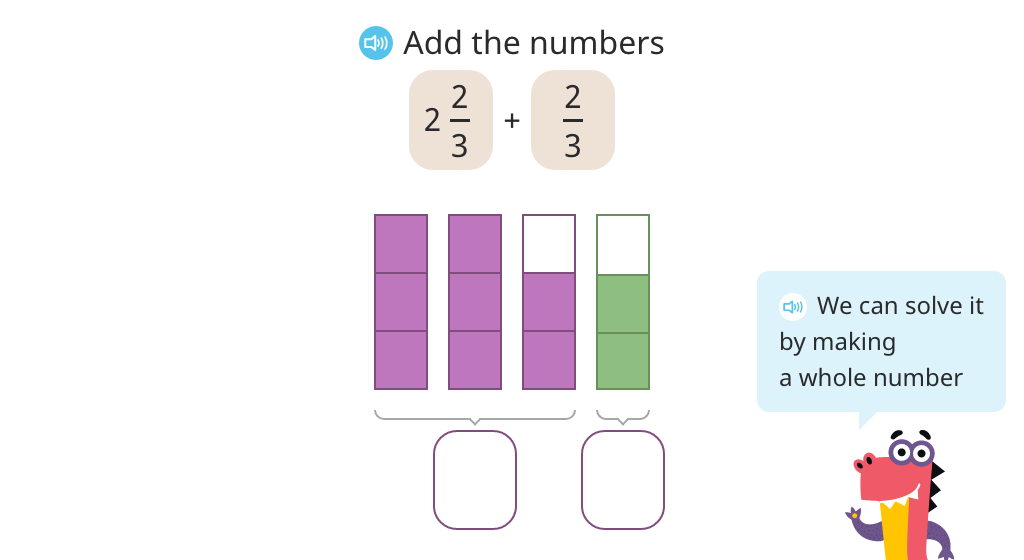
Add a mixed number to a fraction with the same denominator by completing the whole (Level 2)
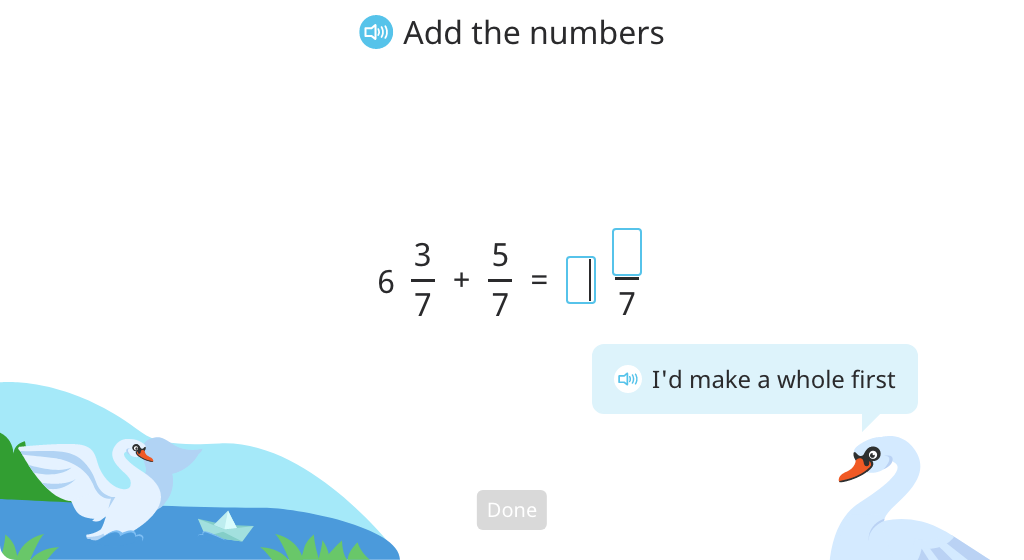
Add two mixed numbers with the same denominator and write the sum without an improper fraction (Level 1)
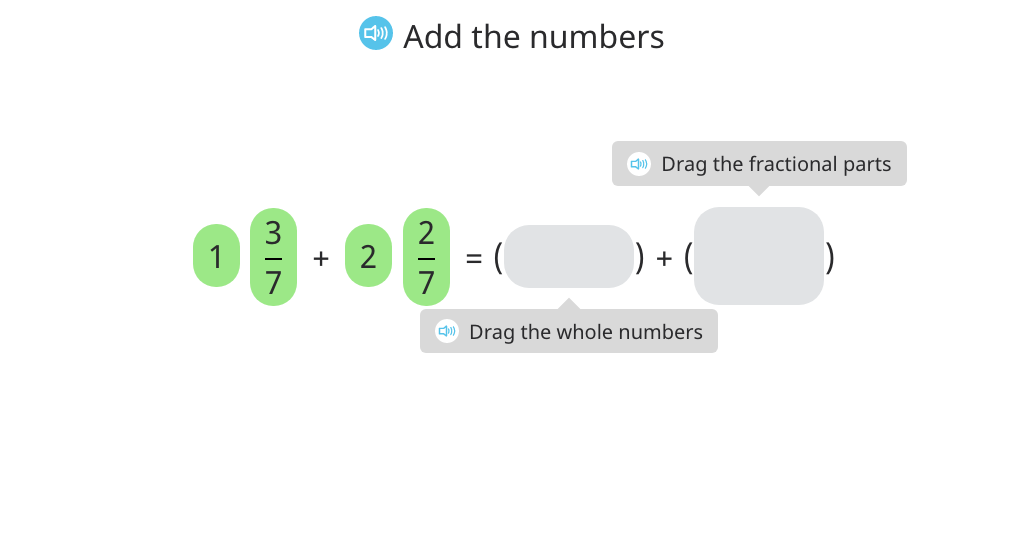
Add two mixed numbers with the same denominator and write the sum without an improper fraction (Level 2)
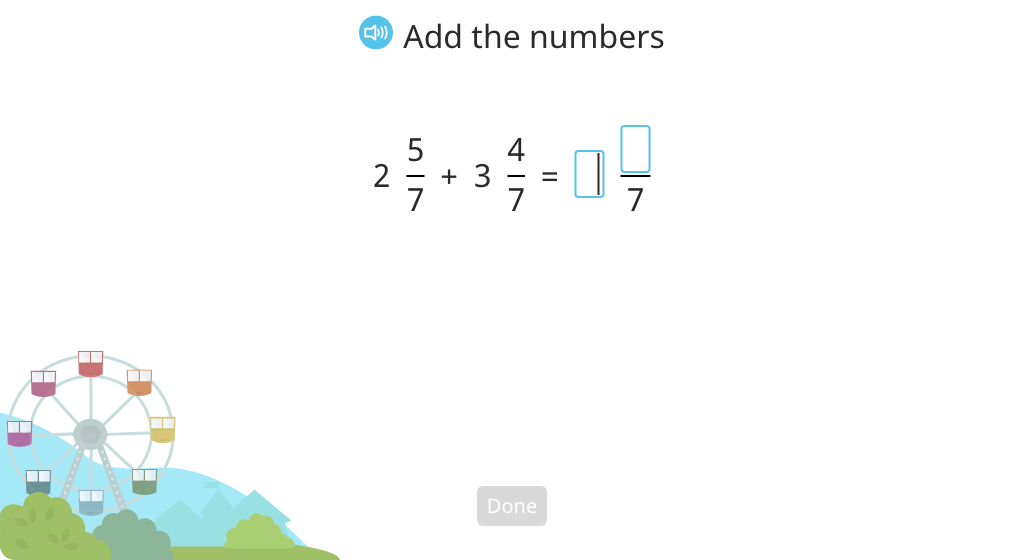
Subtract a fraction from a mixed number with the same denominator (without converting to an improper fraction)

Subtract a fraction from a mixed number with the same denominator by converting to an improper fraction (Level 1)
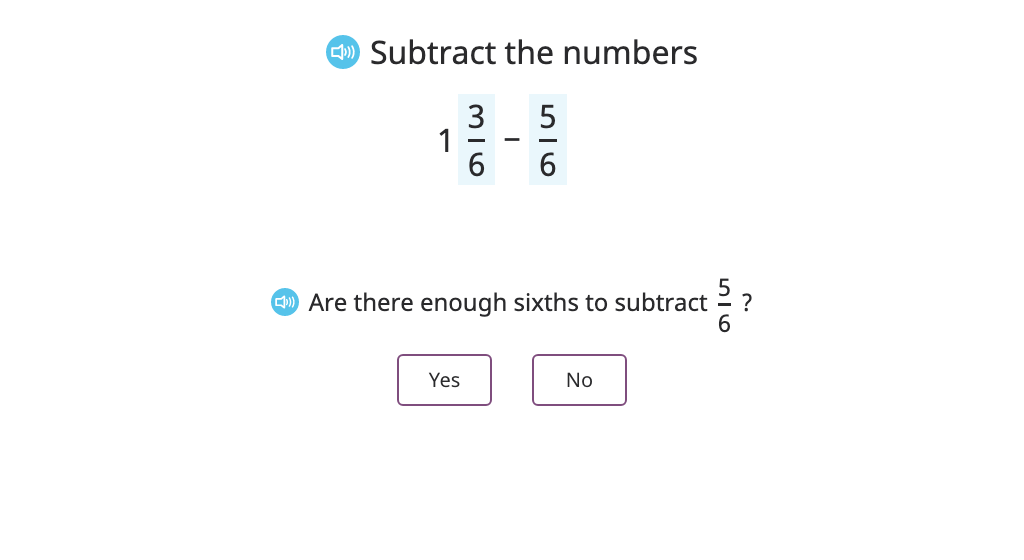
Subtract a fraction from a mixed number with the same denominator by converting to an improper fraction (Level 2)
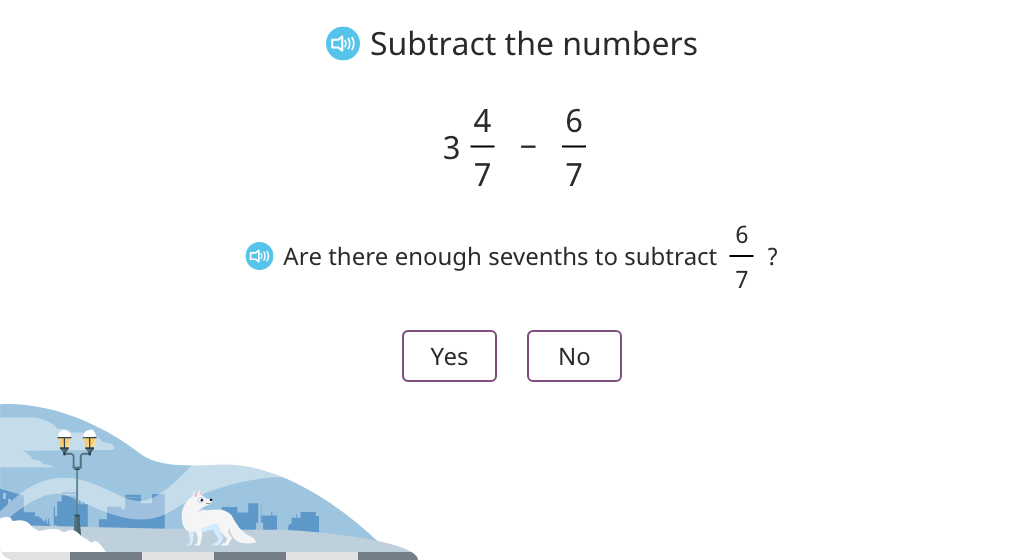
Subtract mixed numbers with the same denominator
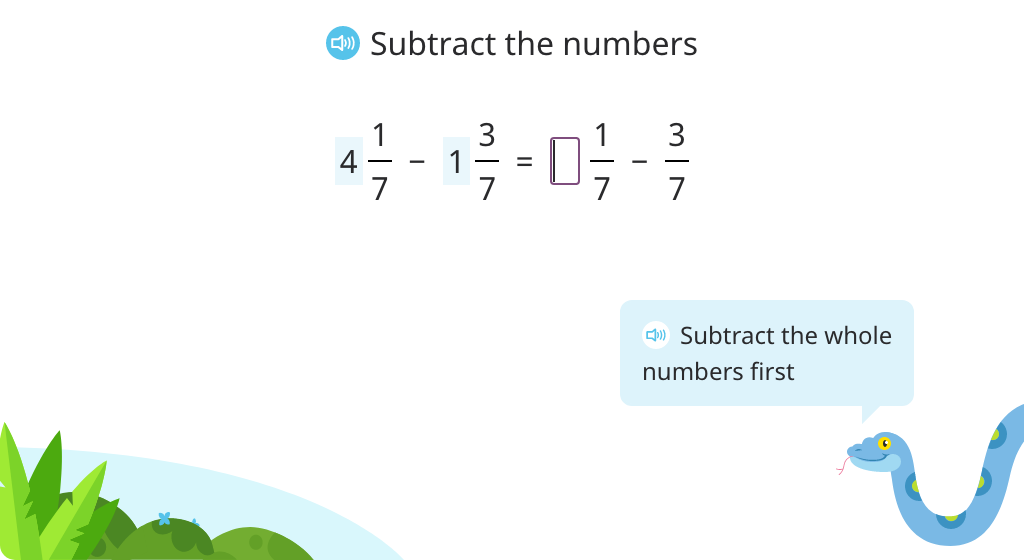
Add and subtract mixed numbers with the same denominator

Topic G: Repeated Addition of Fractions as Multiplication
Students translate their understanding of addition of fractions to multiplication. They transition from work with unit fractions to other fractions and mixed numbers. In solving equations and word problems, students rename solutions as mixed numbers without a fraction greater than 1.
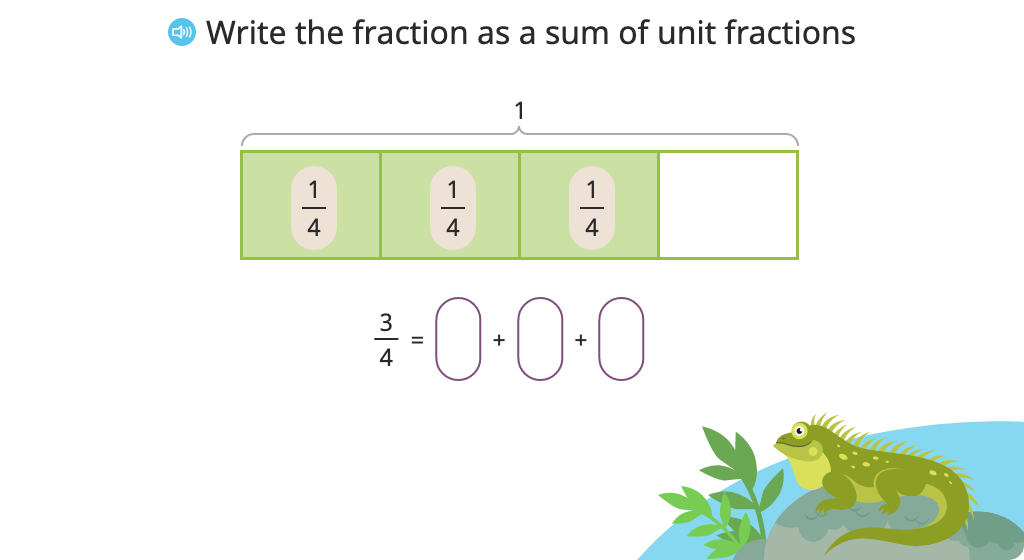
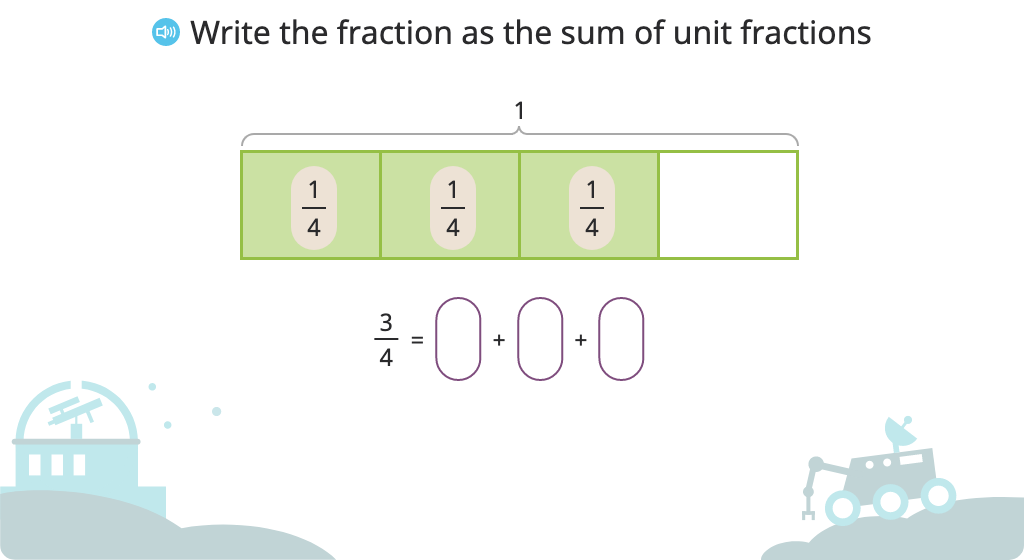
Write a fraction as a sum of unit fractions
Identify multiplication of a unit fraction by a whole number that matches a given fraction
Multiply a whole number by a fraction by splitting it into a multiple of a unit fraction
Multiply a whole number by a fraction
Write repeated addition of fractions as a multiplication statement and rename the product as a mixed number
Multiply a whole number by a mixed number
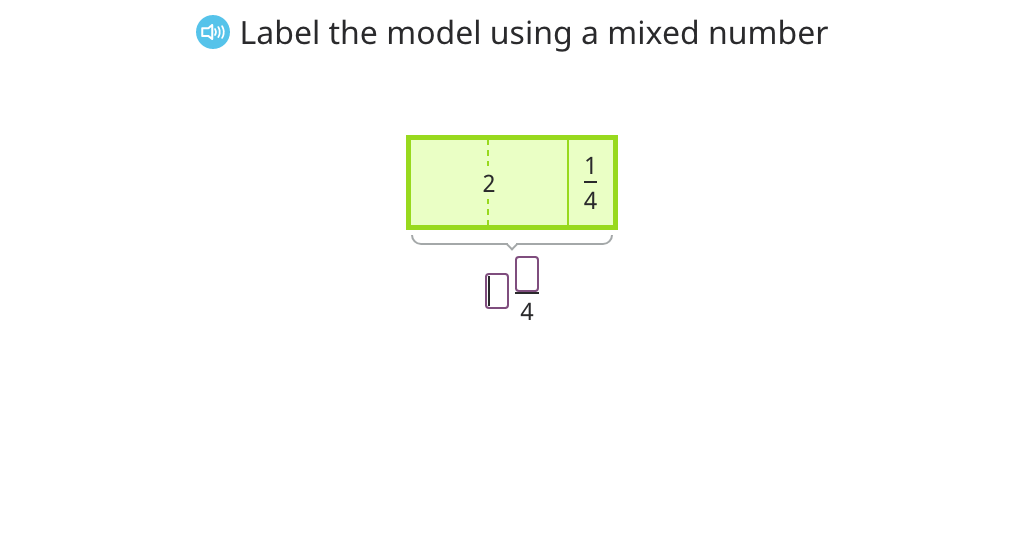
Multiply a whole number by a mixed number and rename without a fraction greater than 1
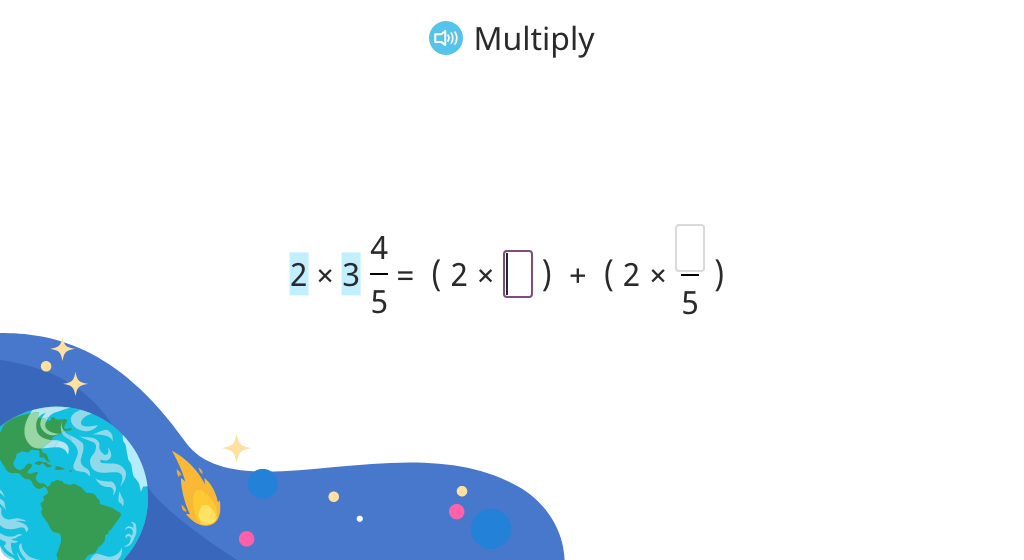
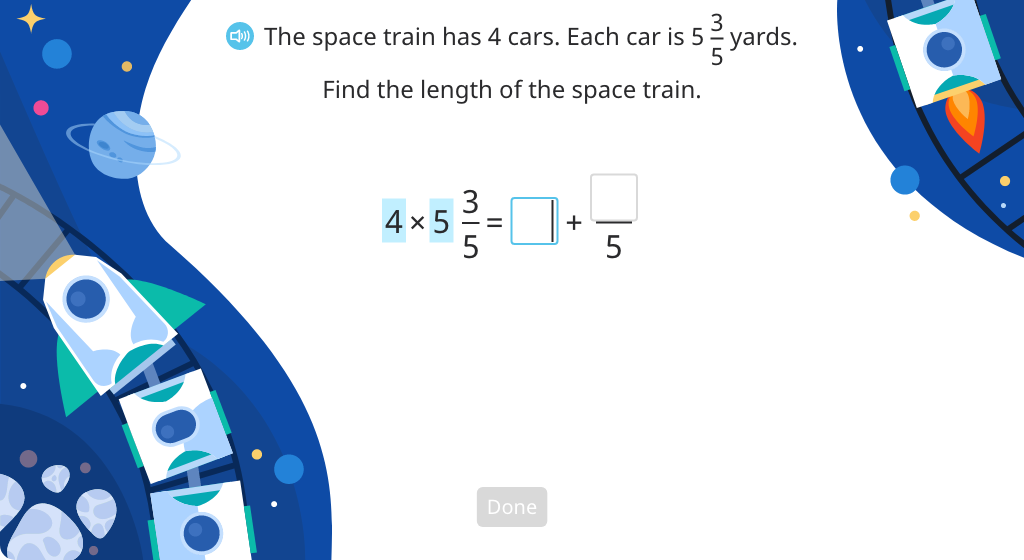
Solve a word problem by multiplying a whole number by a mixed number
MODULE 6. Decimal Fractions
Topic A: Exploration of Tenths
Students develop their understanding of the decimal form of fractions in the tenths. The rely on familiar representations such as the number line, place value chart, and fraction models to support understanding. Students convert fractions less than and greater than one from fraction form to decimal form and word form.
Relate fractions in tenths to decimals with and without a number line

Rewrite a fraction in tenths as a decimal, and vice versa
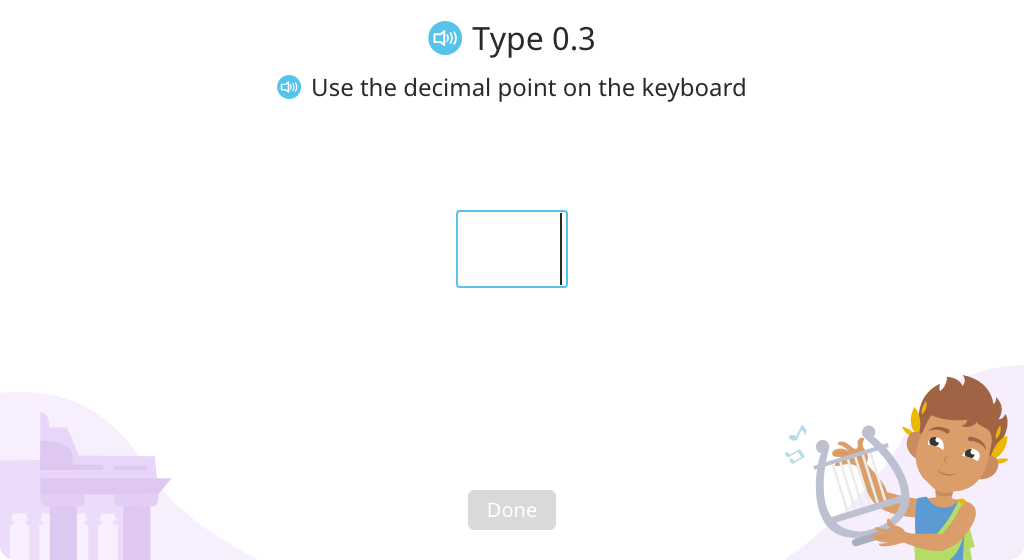
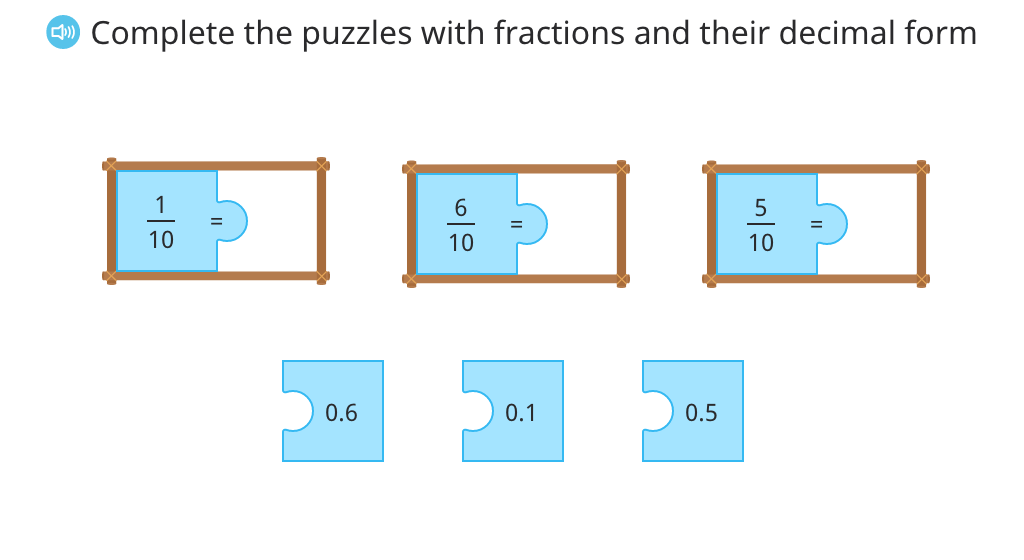
Match fractions in tenths to their decimal form and word form
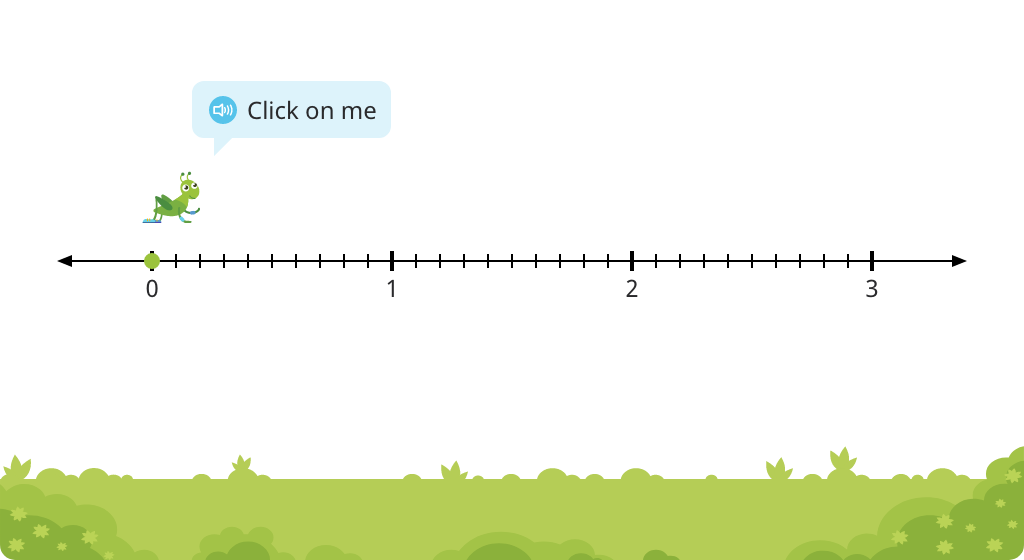
Determine how many more tenths to make a whole using a number line

Represent mixed numbers in decimal form using a number line
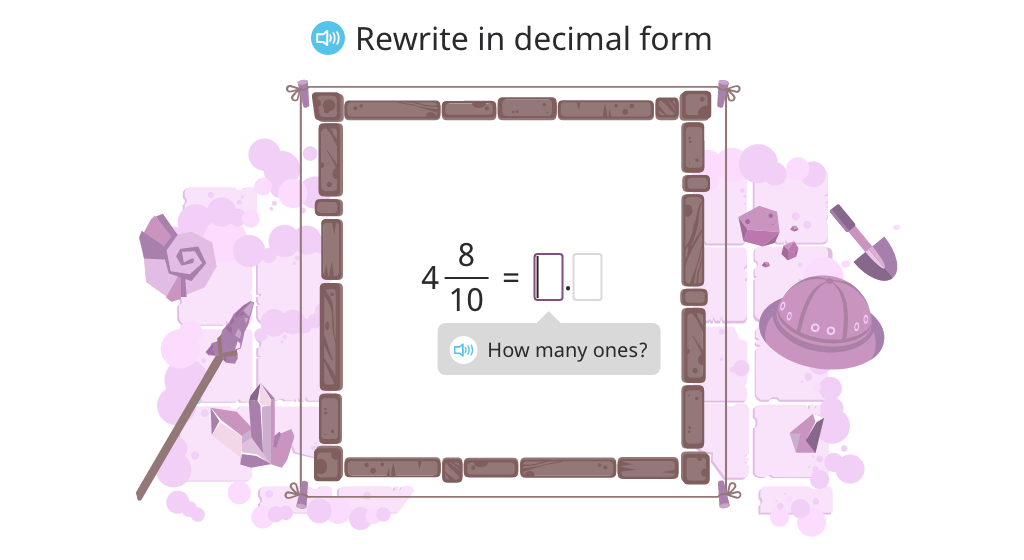
Rewrite a mixed number with tenths as a decimal, and vice versa
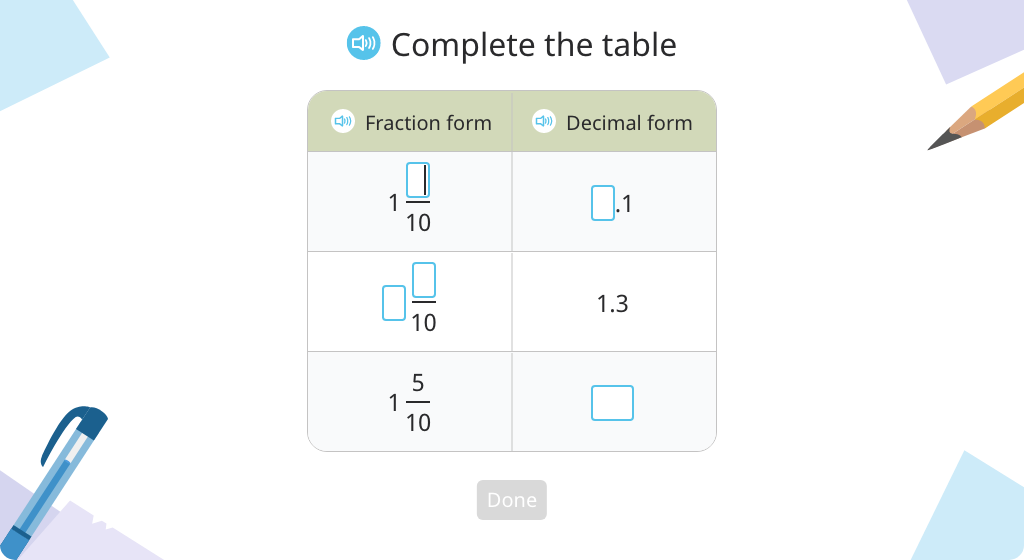
Convert between fraction form, decimal form, and word form with mixed numbers with tenths
Determine how many more tenths to make the next whole using a number line
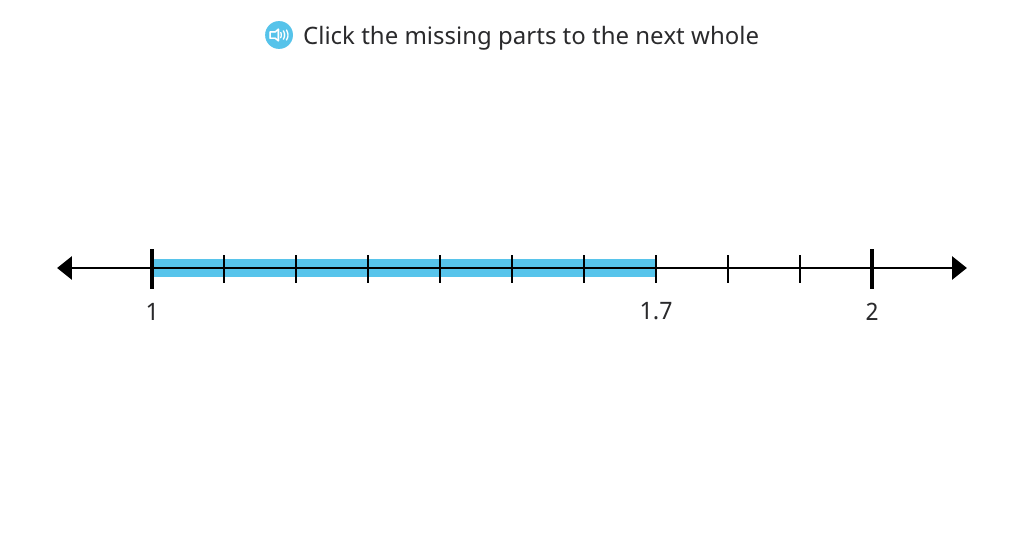
Record a fraction model as a mixed number or a decimal with tenths
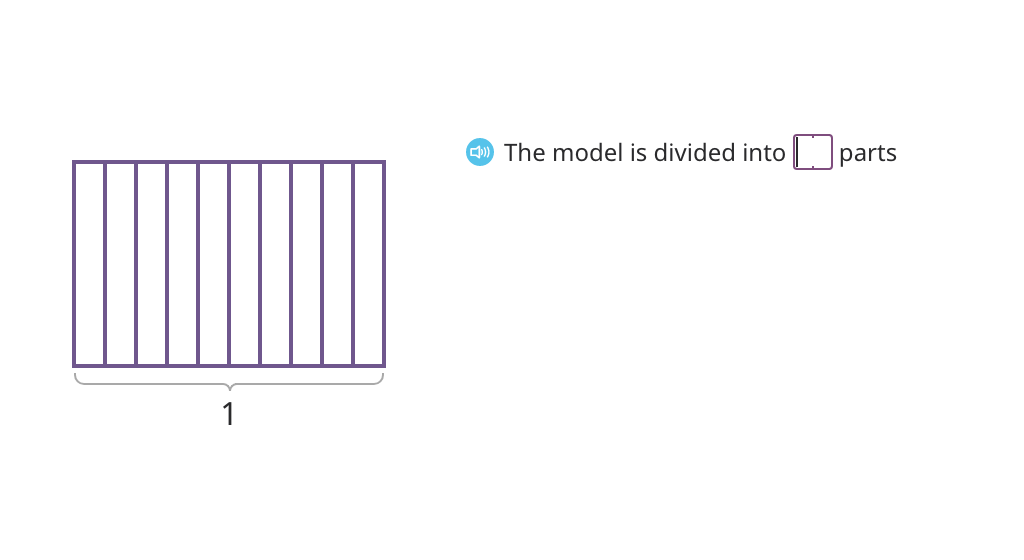
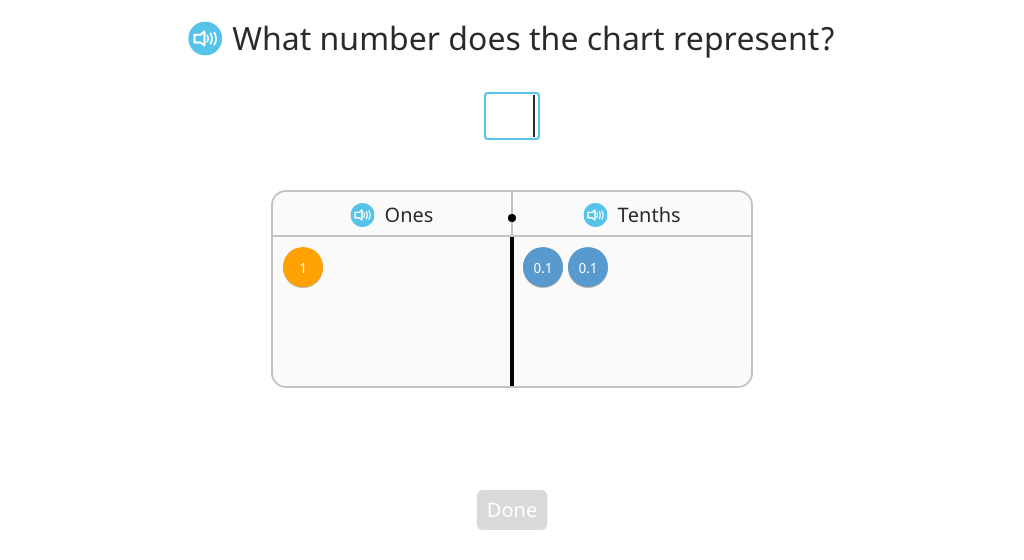
Relate tenths to one whole using a place value chart
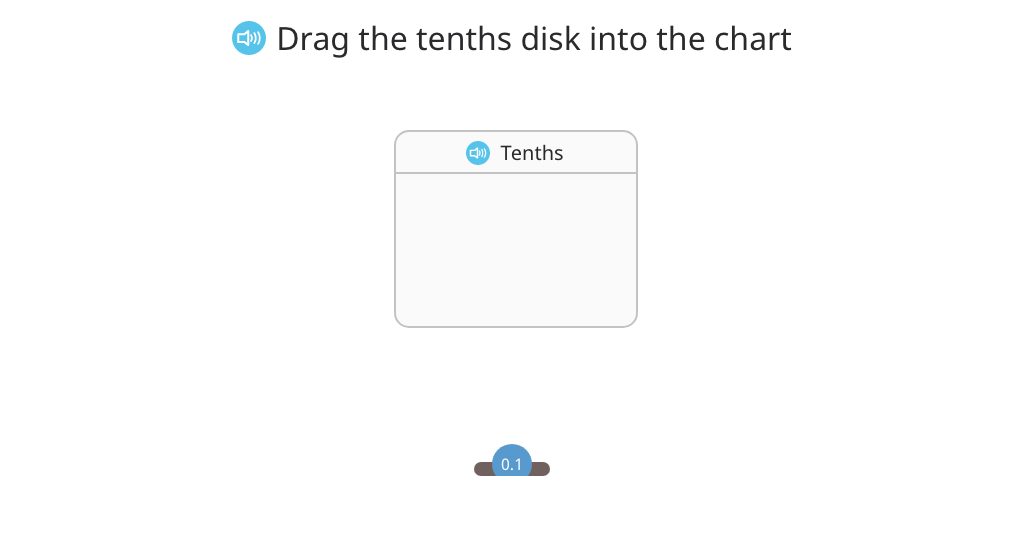
Represent numbers greater than 10 tenths in decimal form
Topic B: Tenths and Hundredths
Students hone their understanding of tenths, hundredths, and the relationship between the two. Beginning with fractional parts only, students convert between fraction, decimal, and unit form. After mastering this, they work with mixed numbers. Along the way, their understanding is supported by area models, disk models, and number lines.
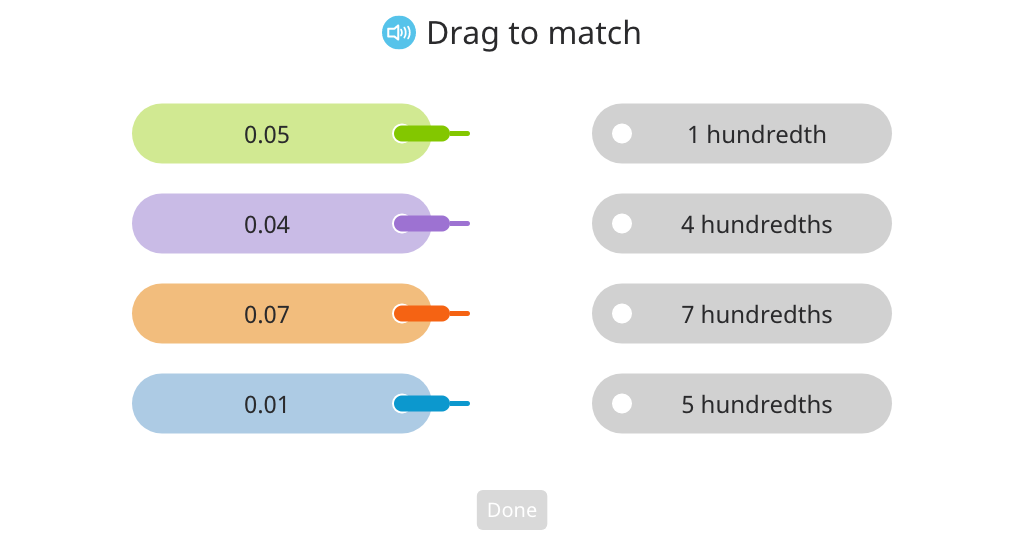
Identify hundredths using fraction and decimal notation
Match hundredths decimals to unit form and rewrite a hundredths decimal in unit form
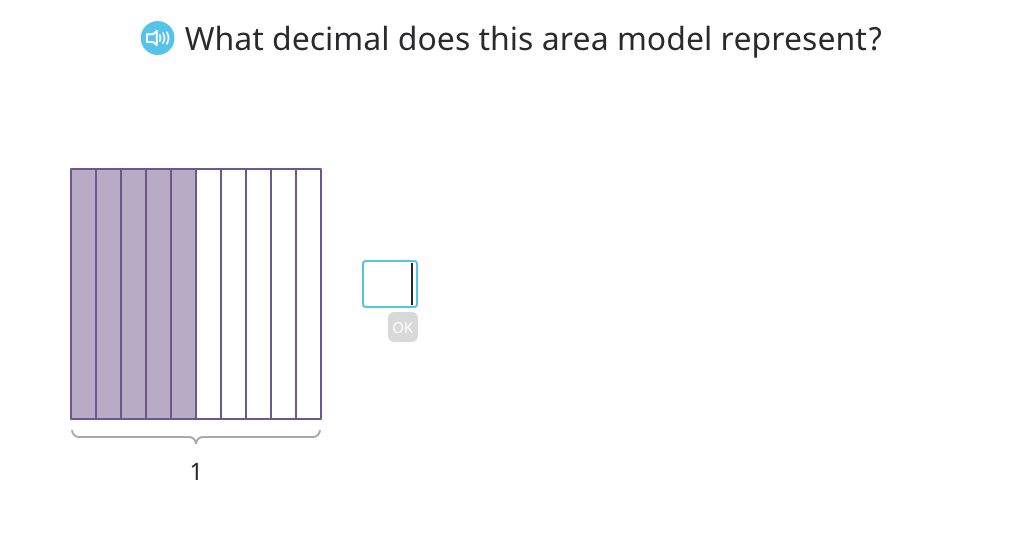
Label tenths and hundredths on an area model using fraction and decimal form
Compare equivalent tenths and hundredths in decimal form
Match equivalent tenths and hundredths in decimal and unit form
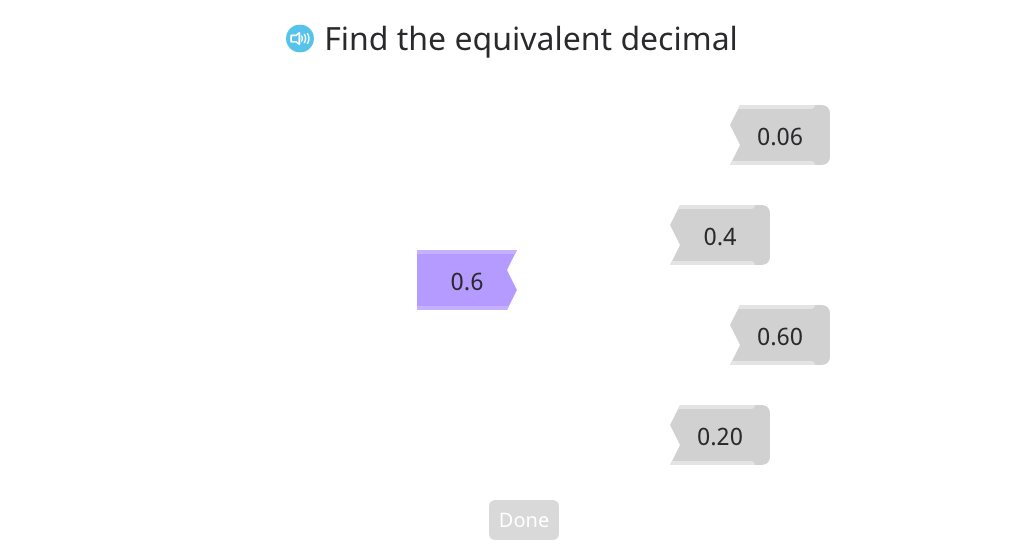
Show tenths and hundredths equivalencies using a disk model

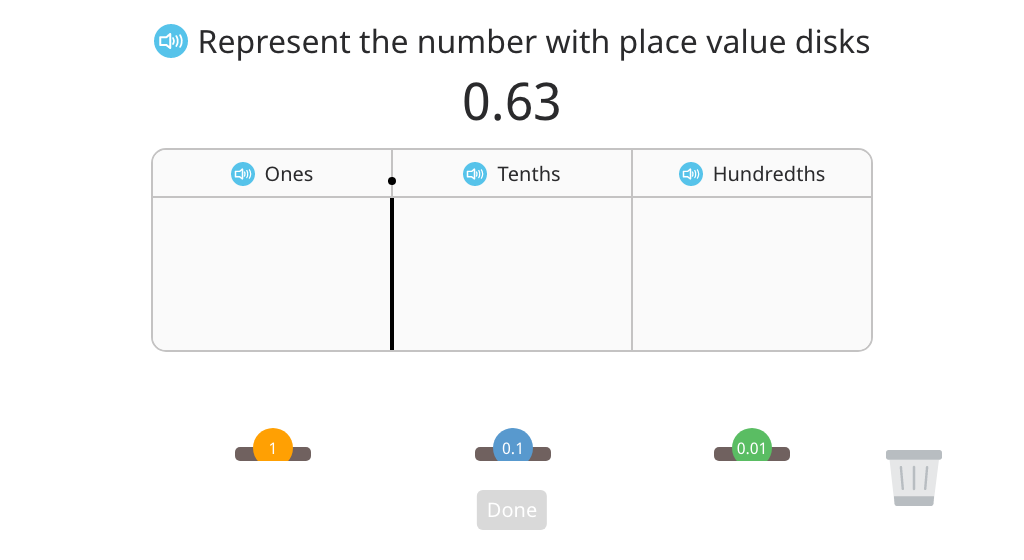
Represent a hundredths number using a disk model
Identify points in the hundredths on a number line

Label a mixed number on an area model using fraction and decimal form
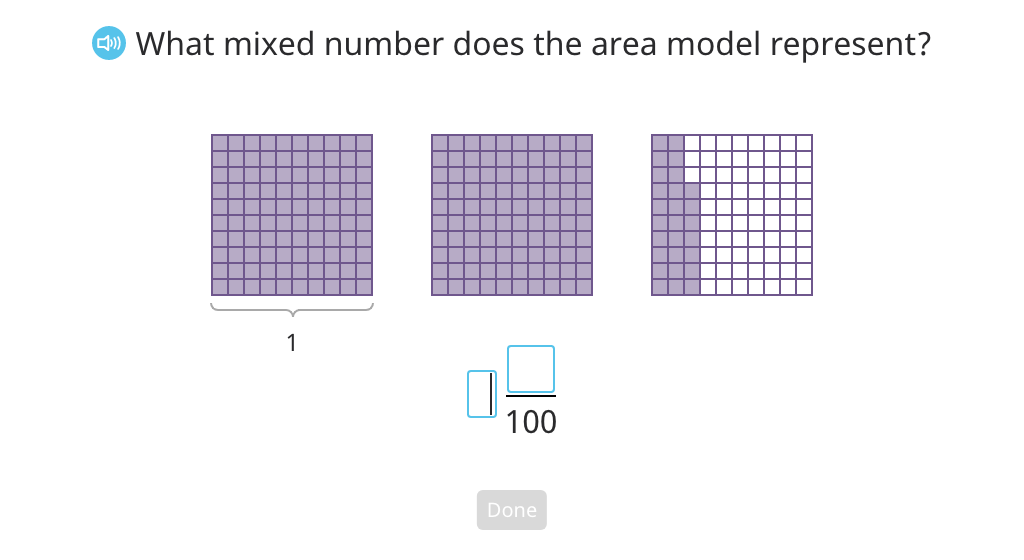
Match mixed numbers in fraction and decimal form, and rewrite a mixed number fraction in decimal form

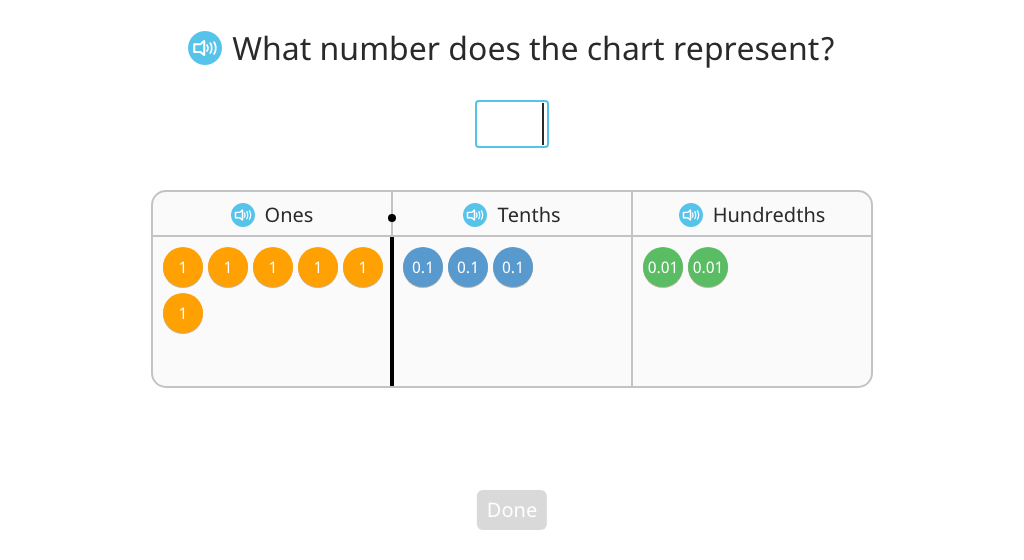
Label a mixed number based on a disk model
Topic C: Decimal Comparison
Students compare decimals in the hundredths using inequality signs and ordering. They rely on familiar representations of the area model, number line, and place value chart to build understanding. They also compare decimals to fractional numbers in unit form and fraction form.
Use <, =, and > to compare decimal measurements of length, mass, and volume
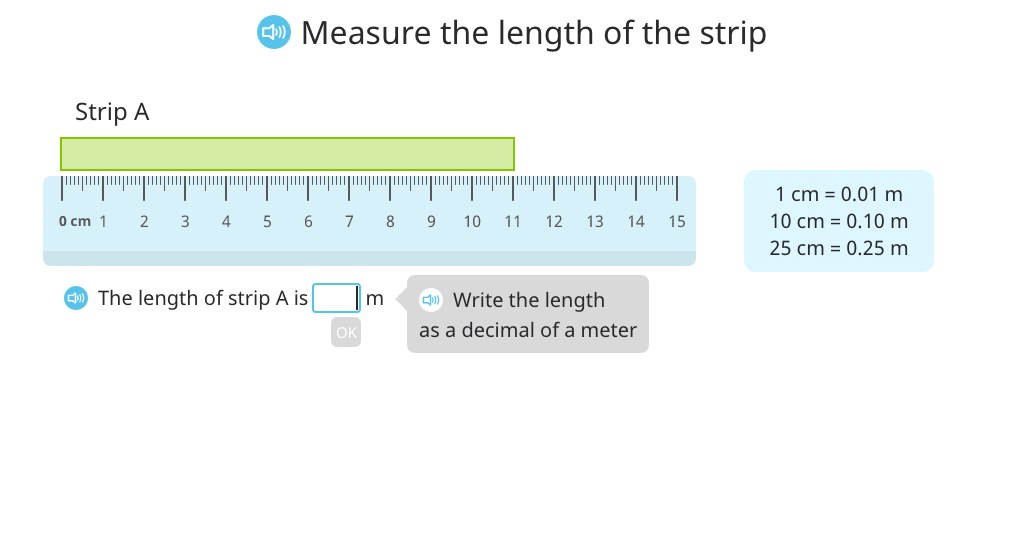
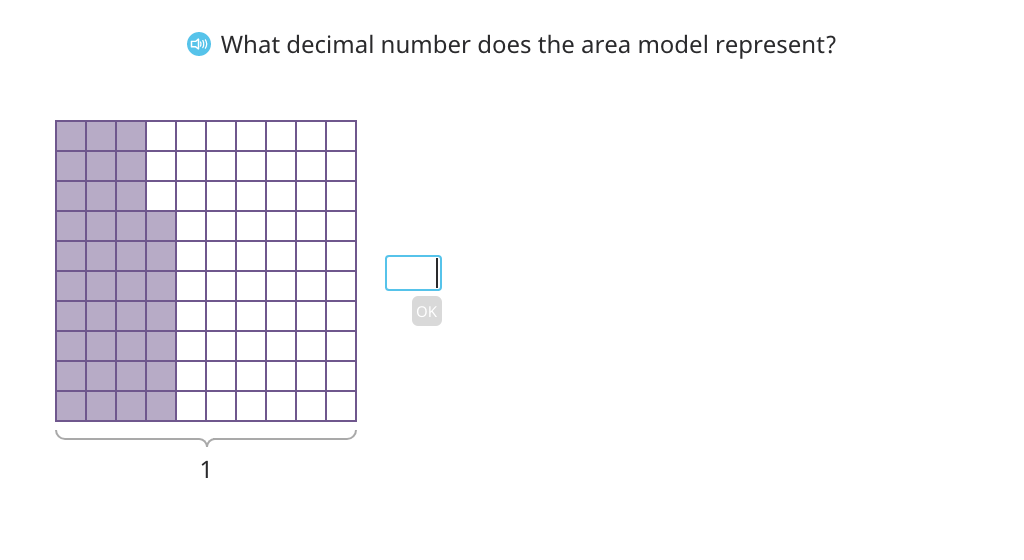
Use <, =, and > to compare decimal numbers based on an area model
Use <, =, and > to compare decimal numbers based on a number line

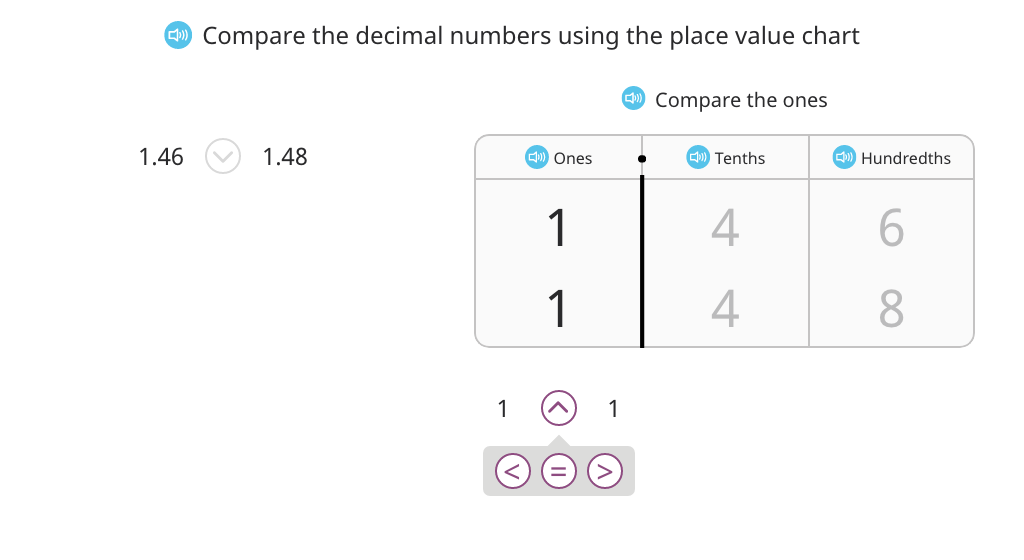
Use <, =, and > to compare decimal numbers based on a place value chart
Complete an inequality by choosing a mixed number, decimal, or decimal in unit form

Complete a double inequality statement based on measurements of length, mass, and volume

Order decimal numbers in a double inequality statement based on a number line

Order decimal numbers in a double inequality statement

Order four decimal numbers in ascending order

Order decimals, fractions, and decimal numbers in unit form in a double inequality statement based on a number line
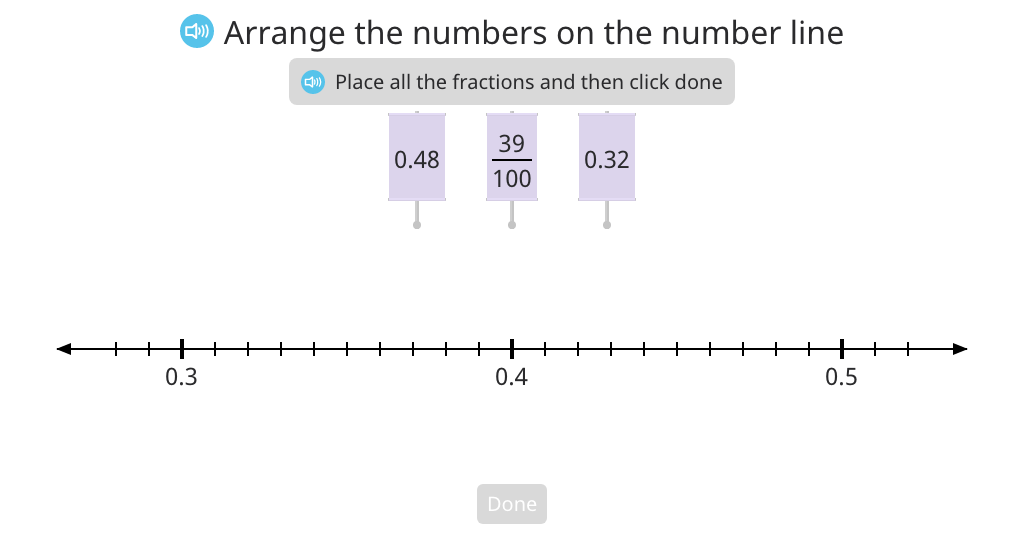
Order decimals, mixed numbers, and decimal numbers in unit form in a double inequality statement

Order four decimals, mixed numbers, and decimal numbers in unit form in ascending order
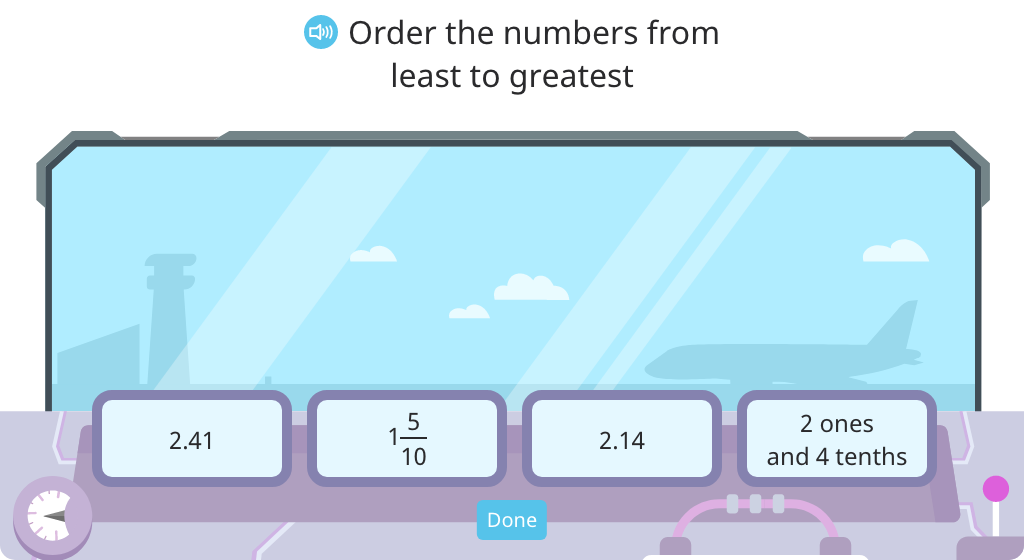
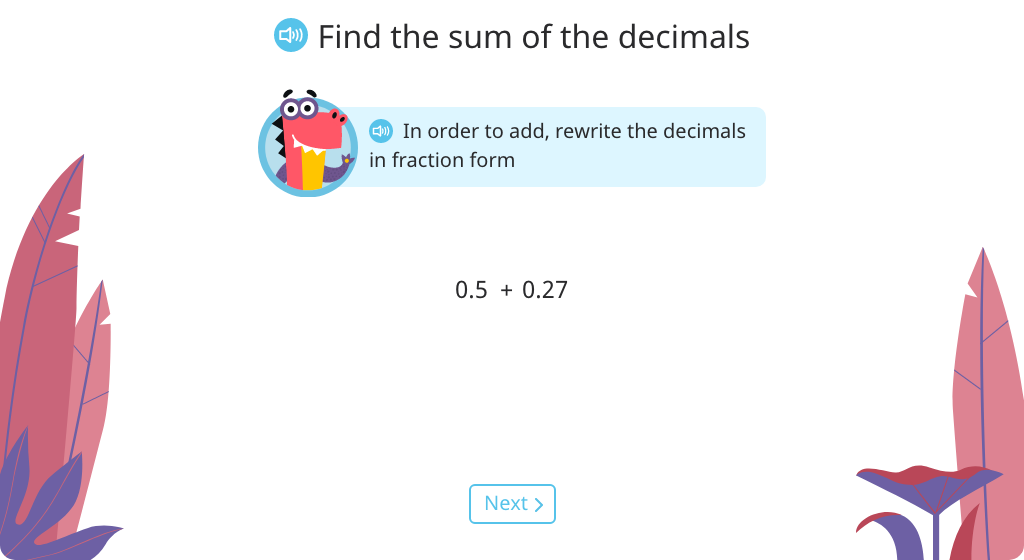
Topic D: Addition with Tenths and Hundredths
Students rely on their mastery of converting between decimals, fractions, and mixed numbers in order to add tenths and hundredths. They learn how to add different units (tenths to hundredths) in both fraction and decimal form. They also learn to record their sum without improper fractions.
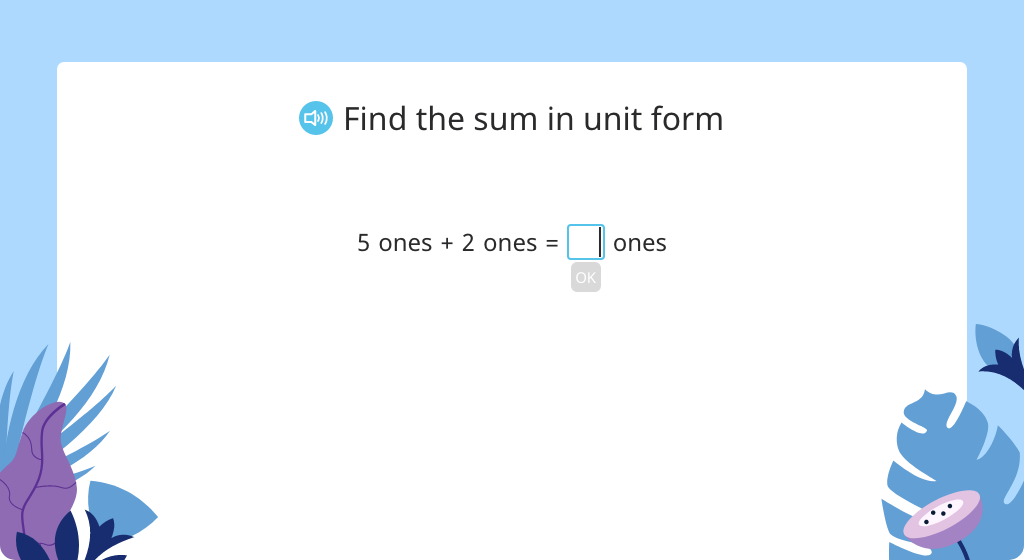
Regroup to add tenths to hundredths with and without a disk model
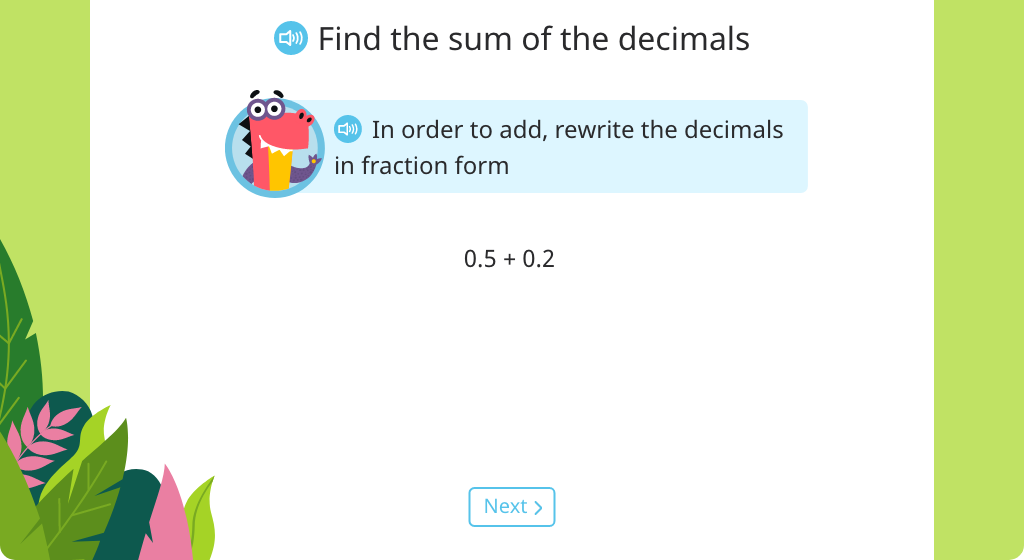
Rewrite decimals in fraction form to add
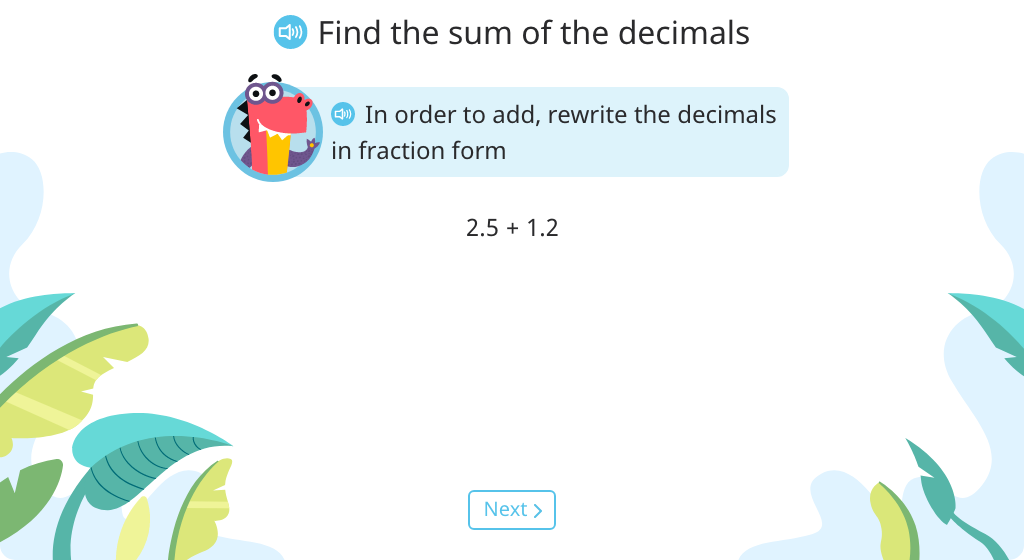
Rewrite mixed number decimals in fraction form to add
Add tenths and hundredths fractions by making an equivalent fraction
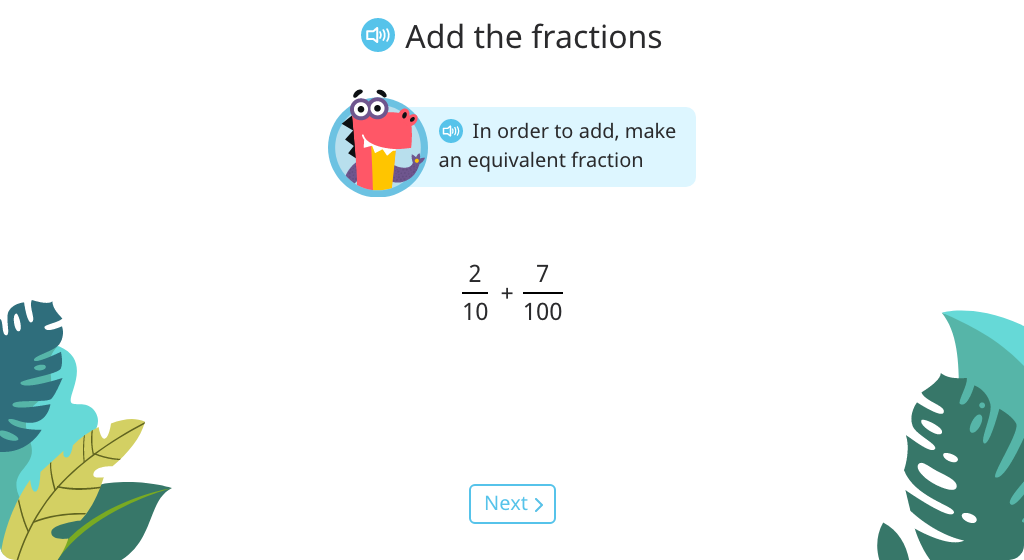
Rewrite decimals in fraction form and find an equivalent fraction to add