Curriculum for Grade 3
Students' strong foundation of math skills facilitates the shift to multiplication and division, moving from concrete procedures toward abstract thinking and automaticity.
MODULE 1. Properties of Multiplication and Division and Solving Problems with Units of 2-5 and 10
Topic A: Multiplication and the Meaning of the Factors
Students build upon their knowledge of addition to identify factors (how many groups, how many objects in each group) and to compose and solve simple multiplication equations. They work with groups of 2-5 identical objects, beginning with models of identical concrete objects, such as bunches of bananas and fingers on a hand. As students progress, they work with more abstract objects (identical beads) and objects in an array.
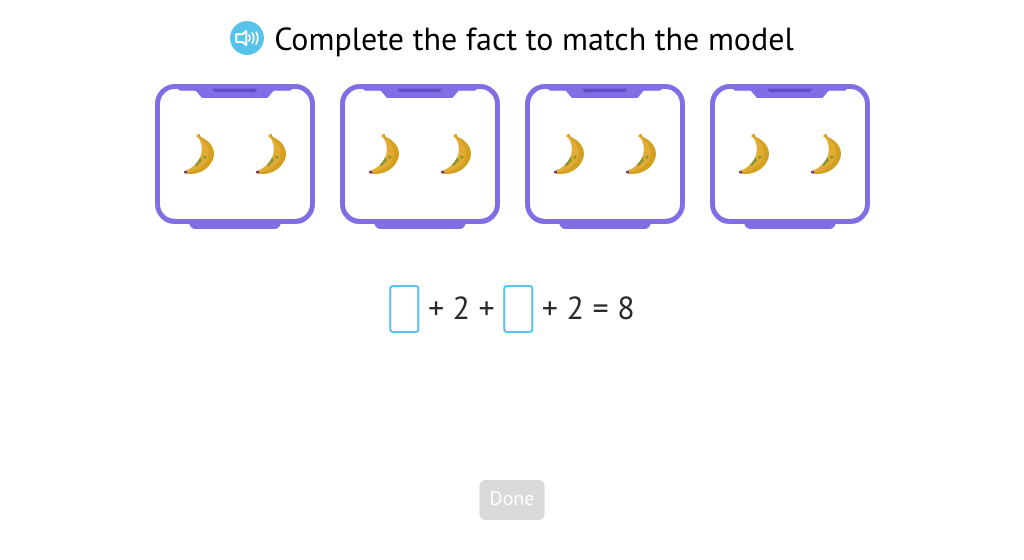
Solve and re-write repeated addition equations

Complete statements describing equal groups and their totals

Use the multiplication sign
Express multiplication equations based on a model
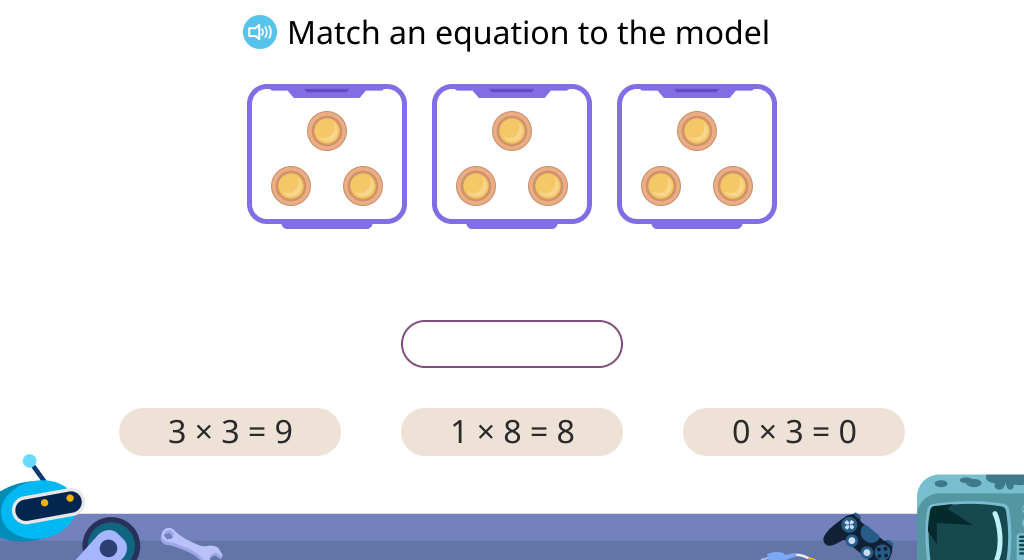
Solve and express multiplication equations based on a model
Compose and solve multiplication equations based on a model
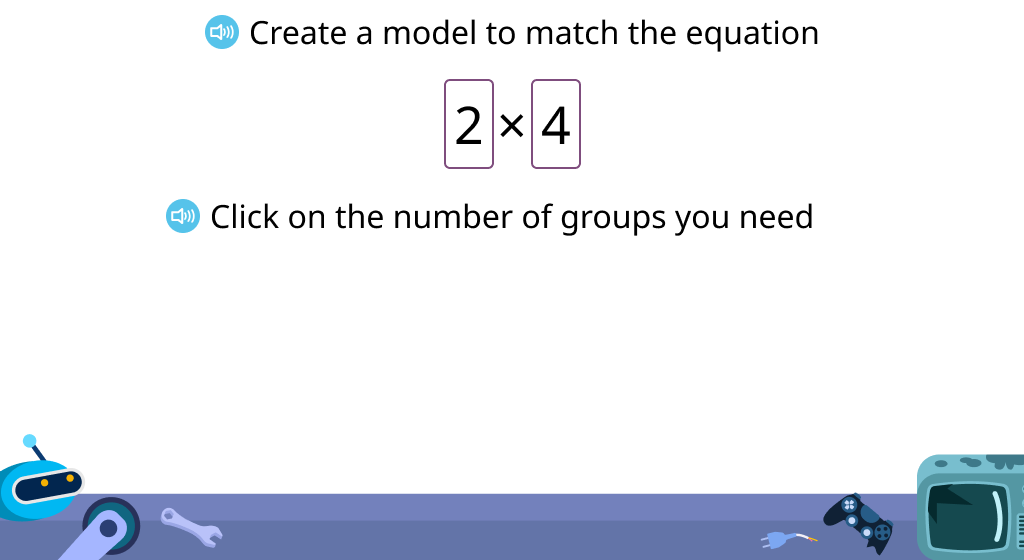
Multiply based on a model of objects in rows
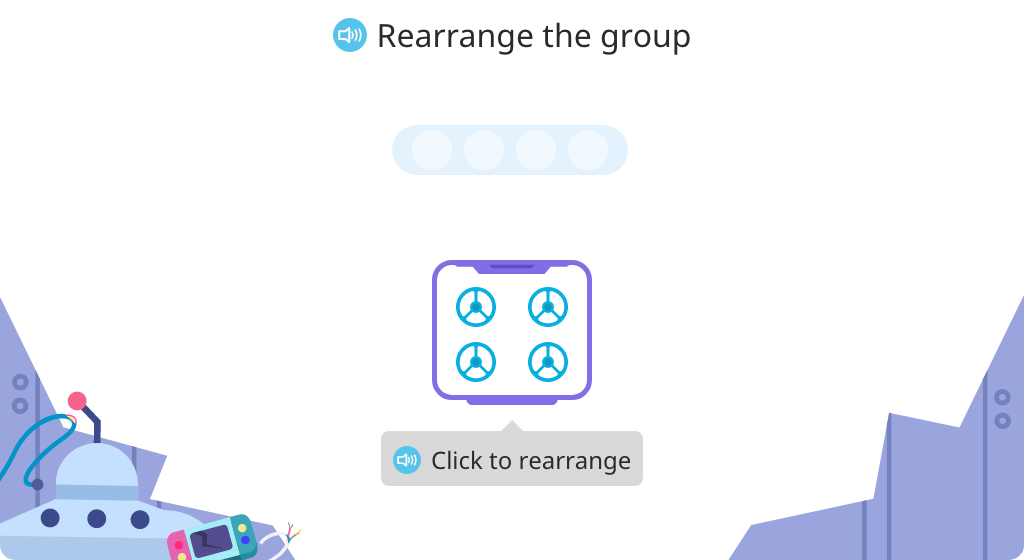
Compose and solve multiplication equations based on an array
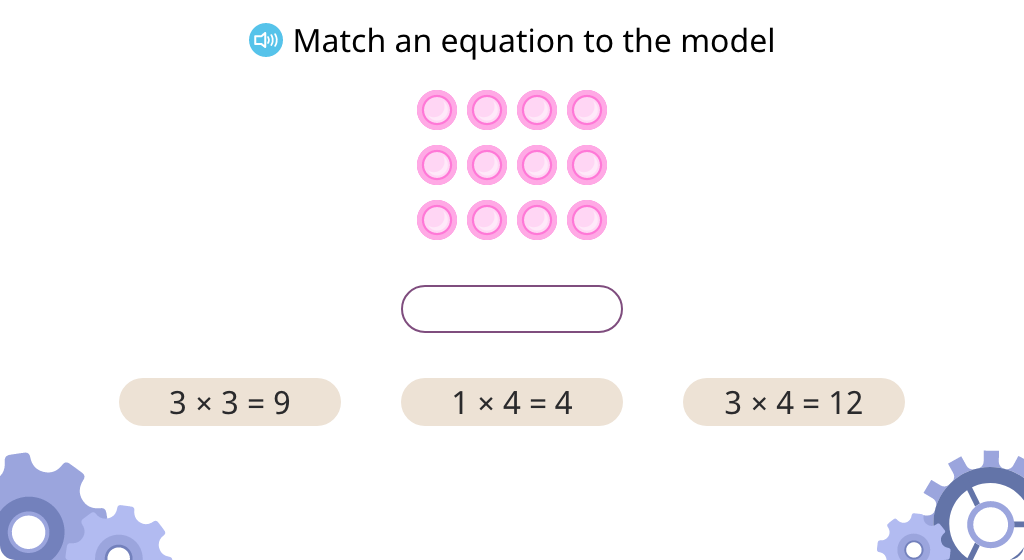
Compose expressions and equations based on a model
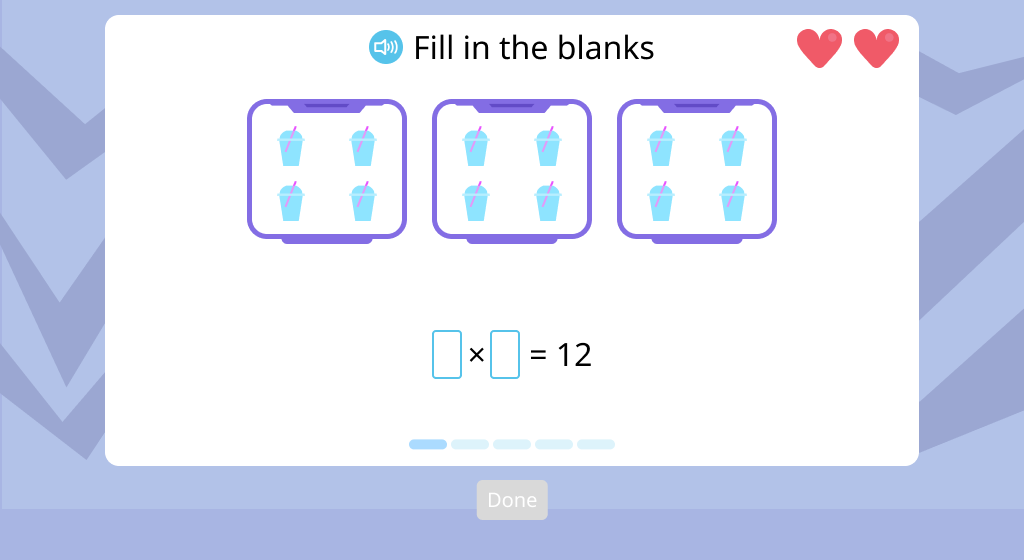
Topic B: Division as an Unknown Factor Problem
Students work with models of real-world objects to solve equal sharing problems. They are introduced to the division symbol. They use the "dealing" method to create groups of a given size. Based on these models, they answer the questions, "How many groups?" and "How many in each group?" They compose and solve division equations.
Use the division symbol

Compose and solve division equations based on a model
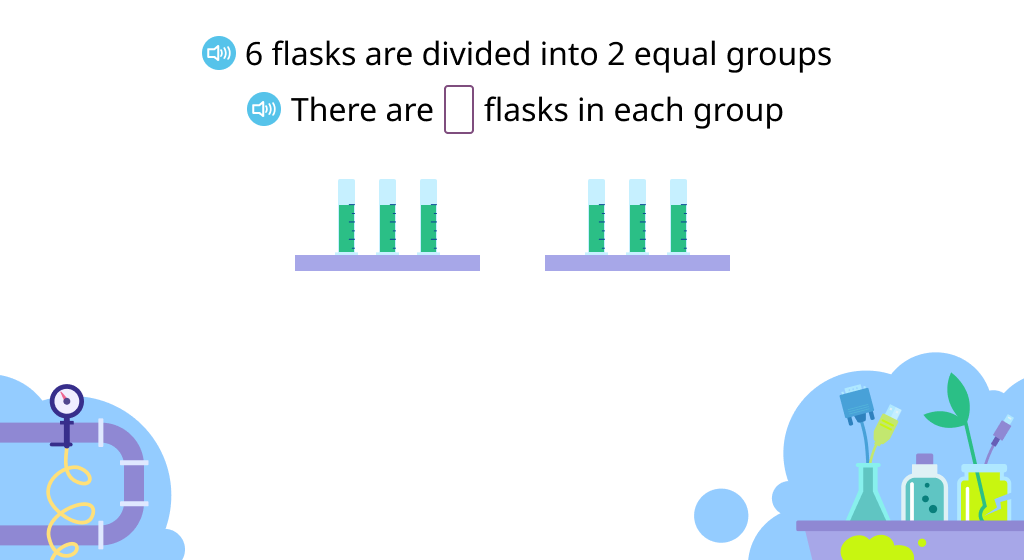
Model division equations and solve
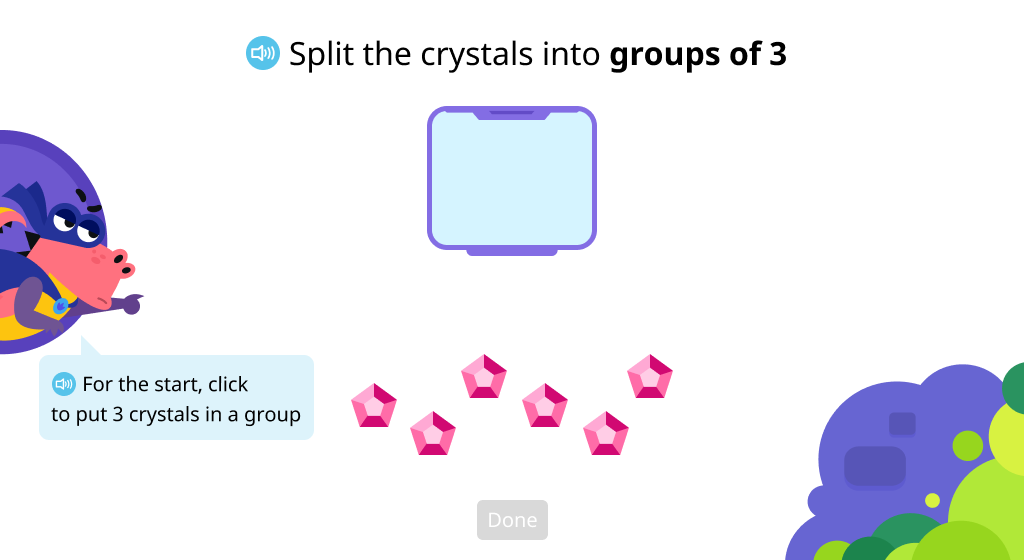
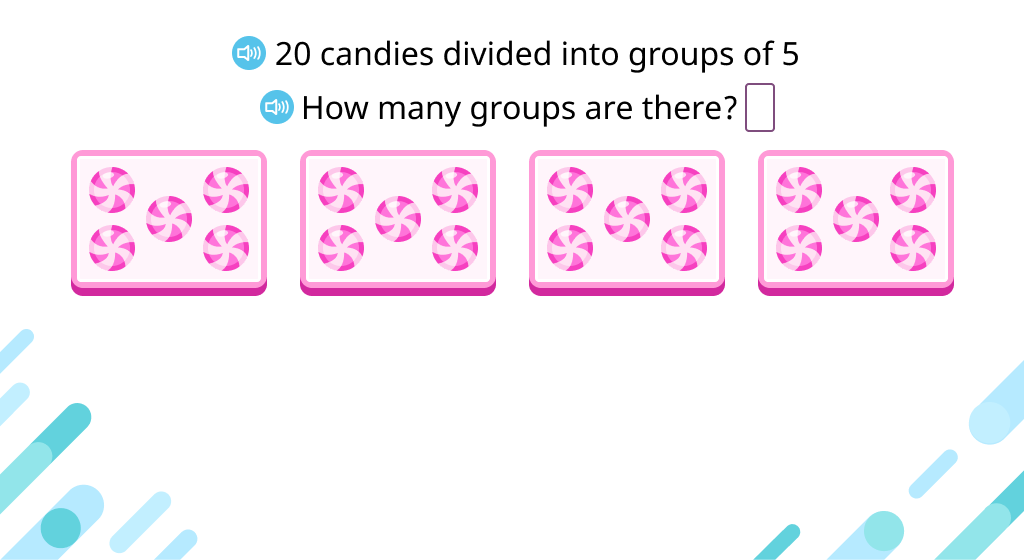
Divide objects into groups
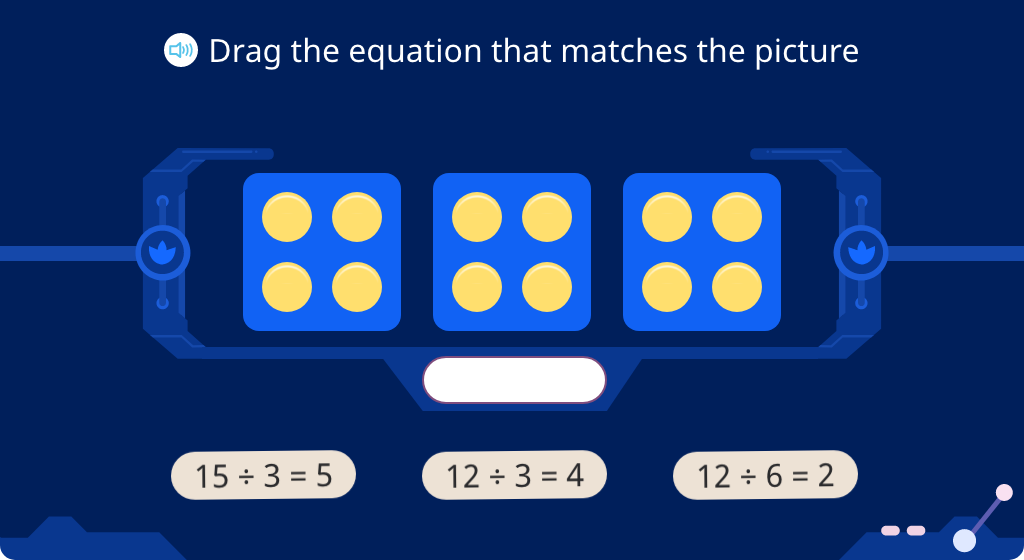
Compose division equations
Solve division word problems

Topic C: Analyzing Arrays to Multiply Using Units of 2 and 3
Students deepen and expand their understanding of multiplication by 2 and 3 with new ways of visualizing the concept. The topic focuses on skip counting and arrays which helps students begin to see patterns as they multiply and solve equations. Students also discover and explore the commutative and distributive properties of multiplication.
Skip count by 2 (Level 1)
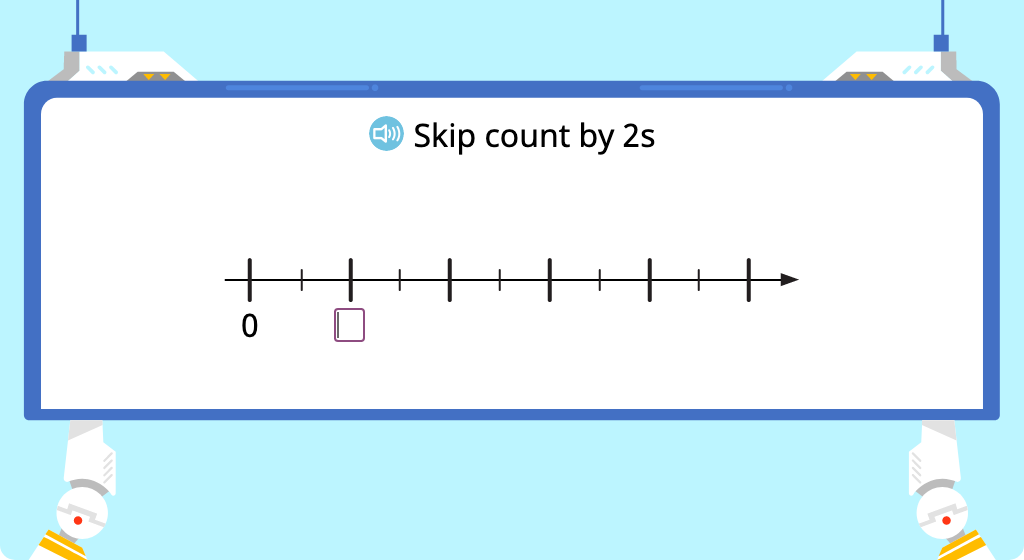
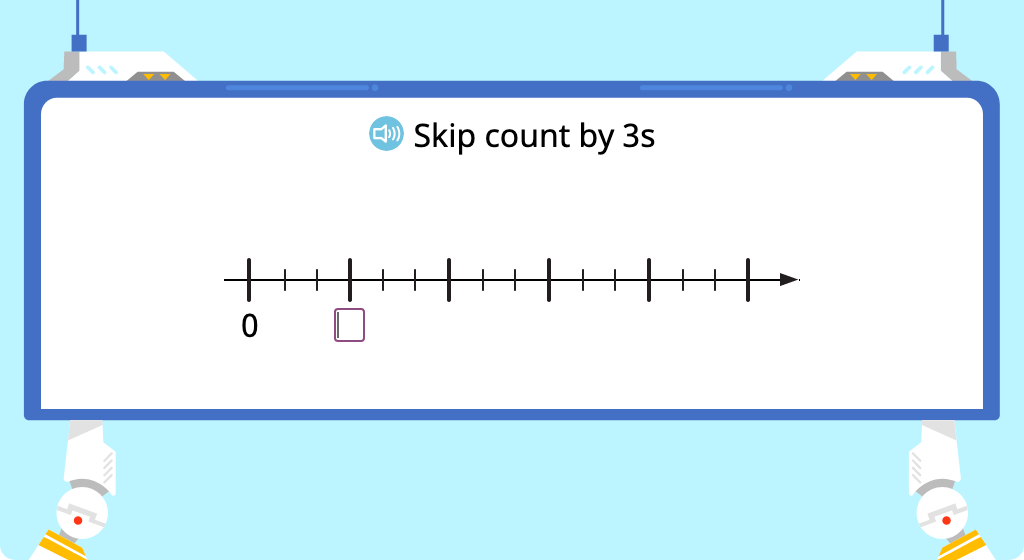
Skip count by 3 (Level 1)
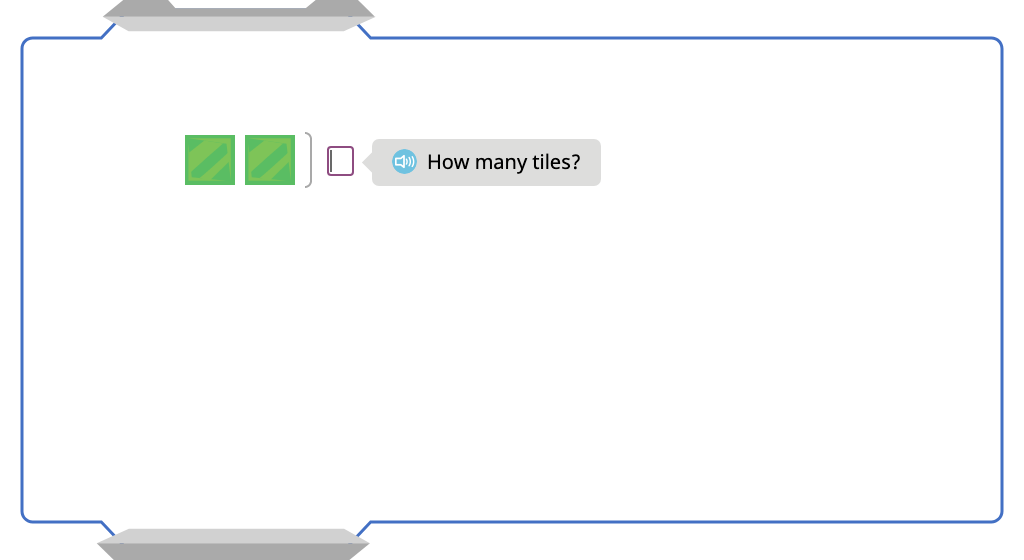
Multiply by 2 with and without an array model (Level 1)
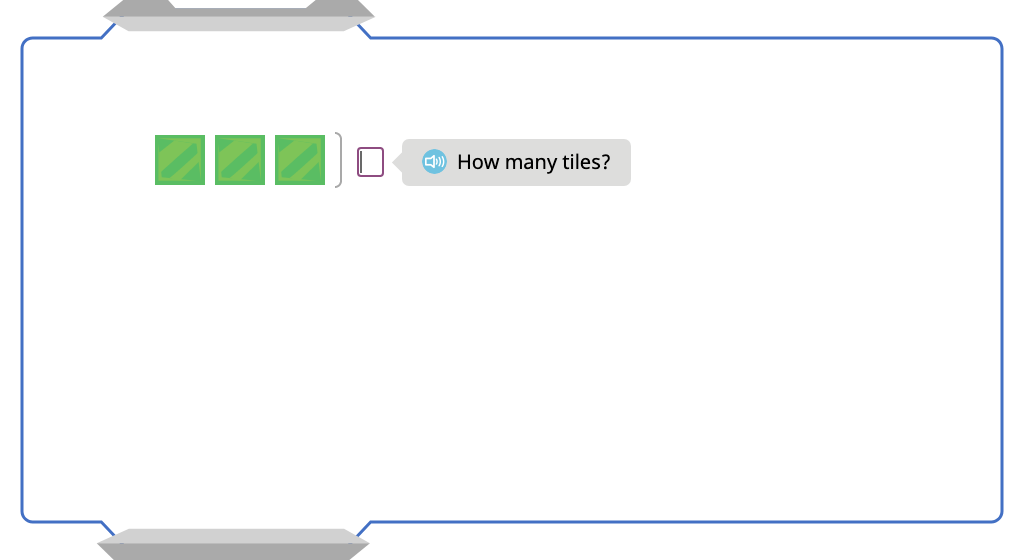
Multiply by 3 with and without an array model (Level 1)
Multiply by 2 to complete a pattern of equations (Level 1)
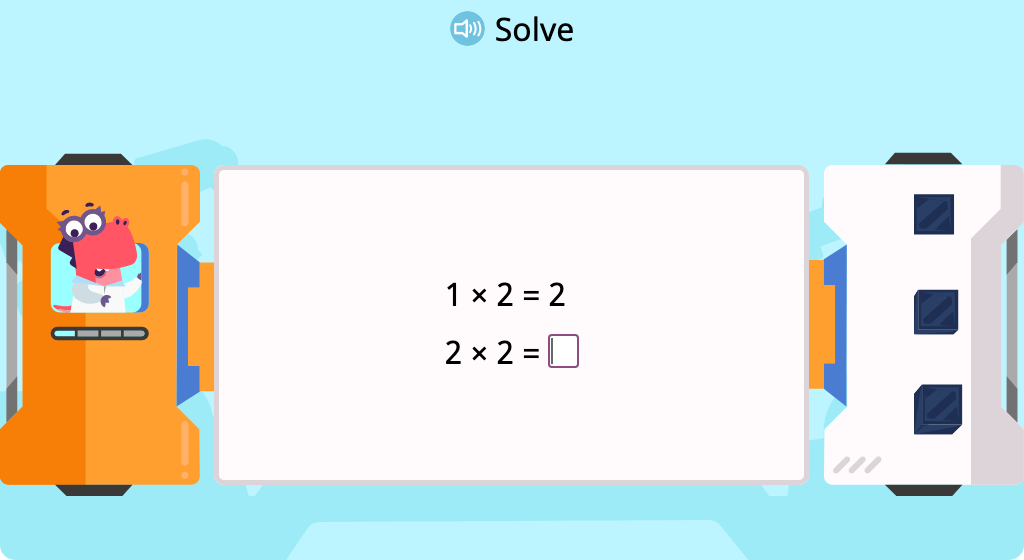
Multiply by 3 to complete a pattern of equations (Level 1)
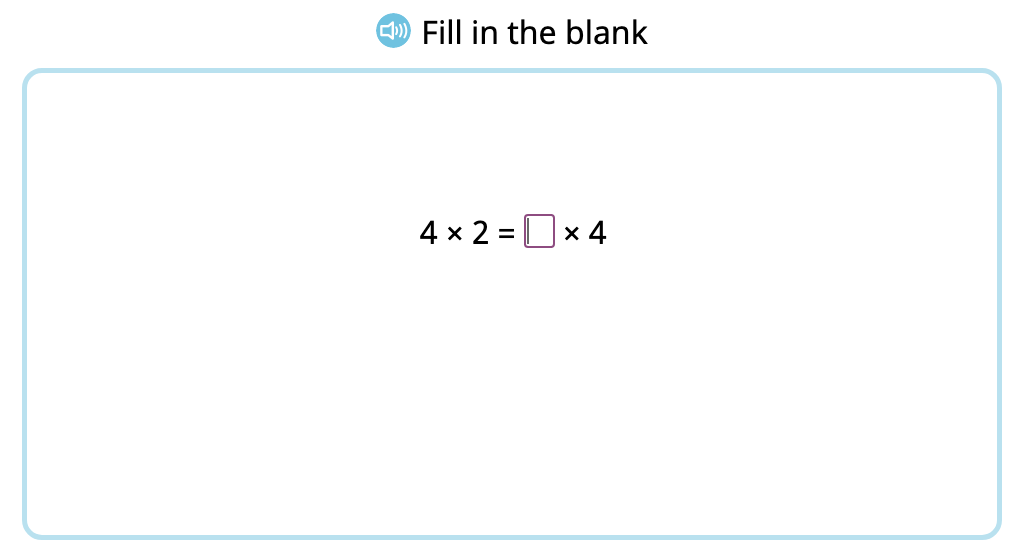
Label arrays with equations to show the commutative property of multiplication by 2

Label arrays with equations to show the commutative property of multiplication by 3

Complete equations to show the commutative property of multiplication by 2 (Level 1)
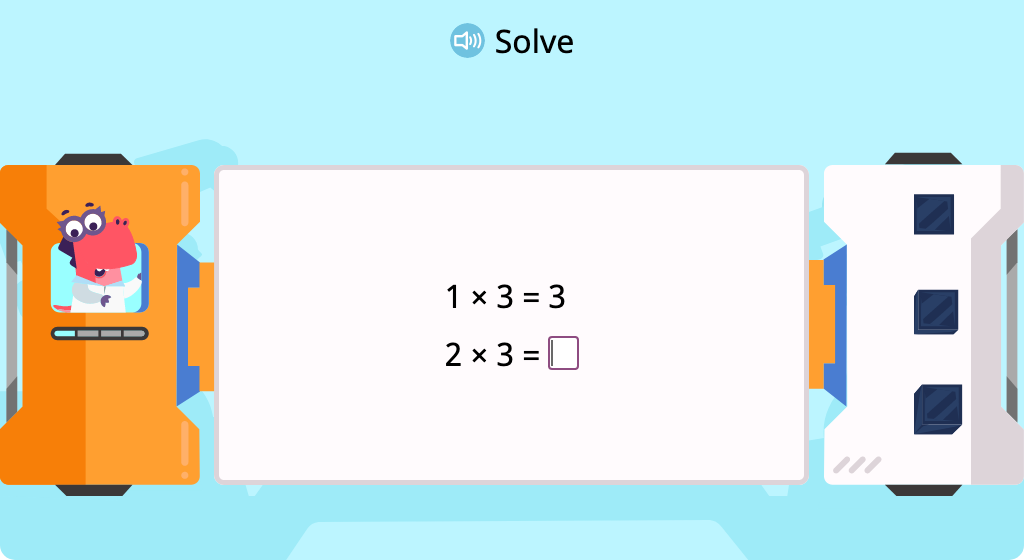
Complete equations to show the commutative property of multiplication by 3 (Level 1)
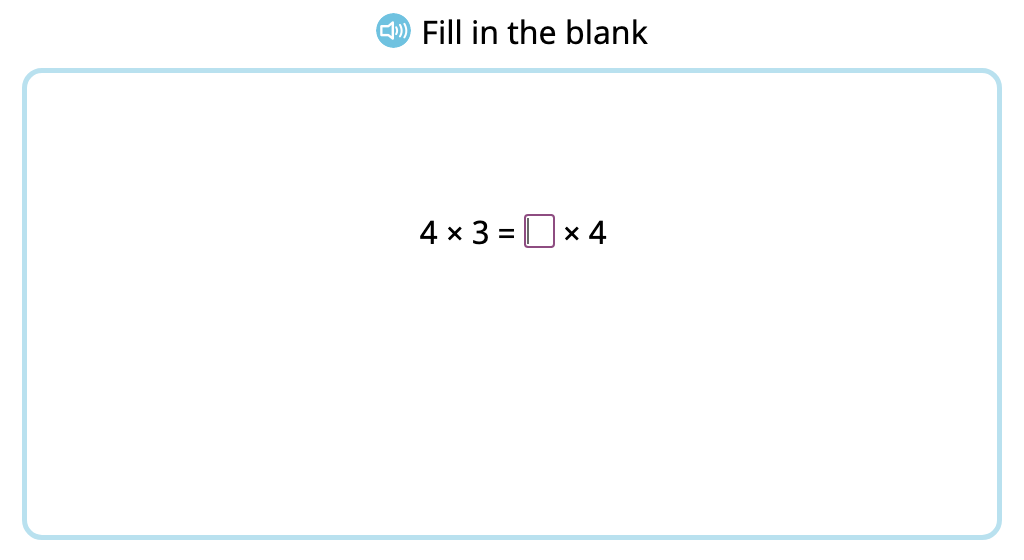
Solve x2 multiplication equations (Level 1, Part 1)
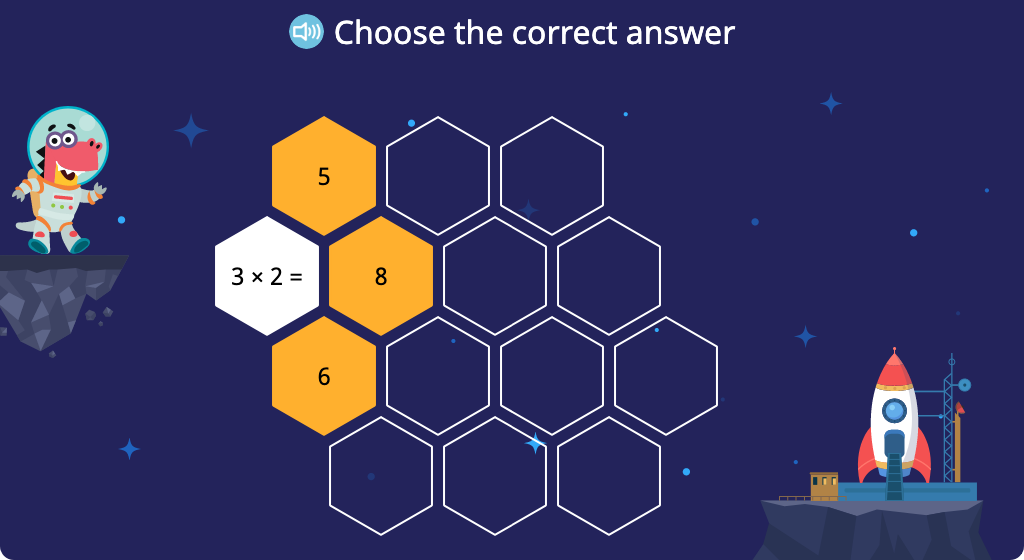
Solve x3 multiplication equations (Level 1, Part 1)
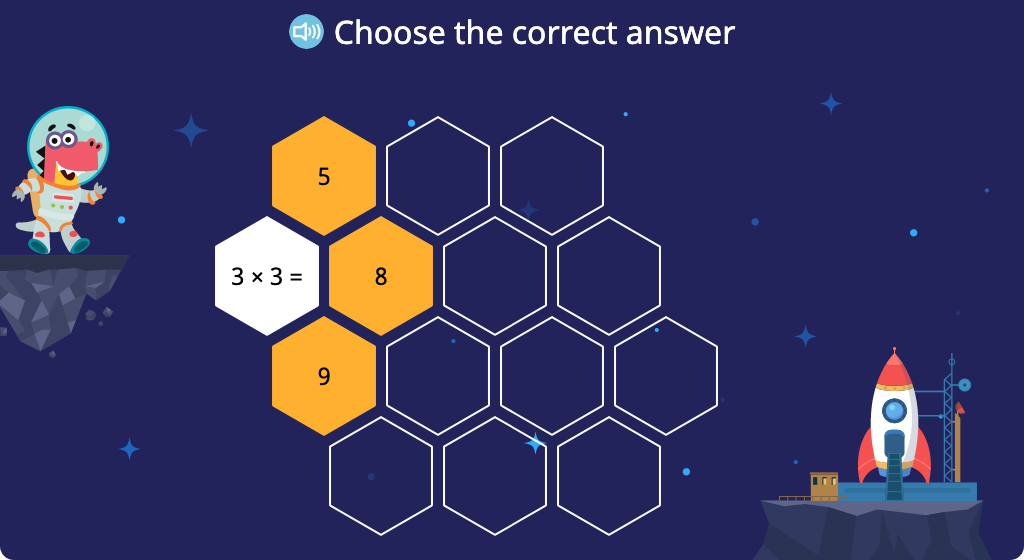
Solve x2 multiplication equations (Level 1, Part 2)

Solve x3 multiplication equations (Level 1, Part 2)

Skip count by 2 (Level 2)
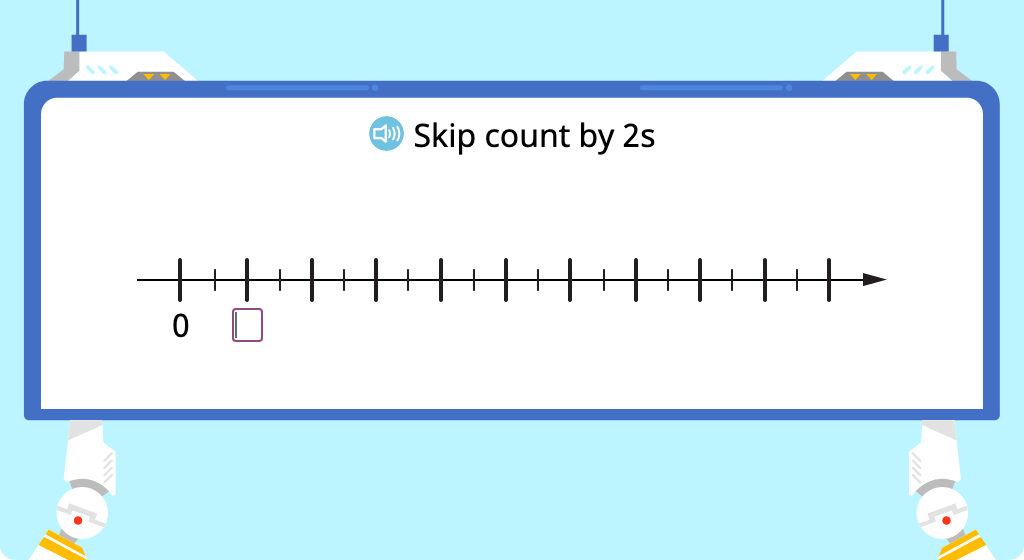
Skip count by 3 (Level 2)
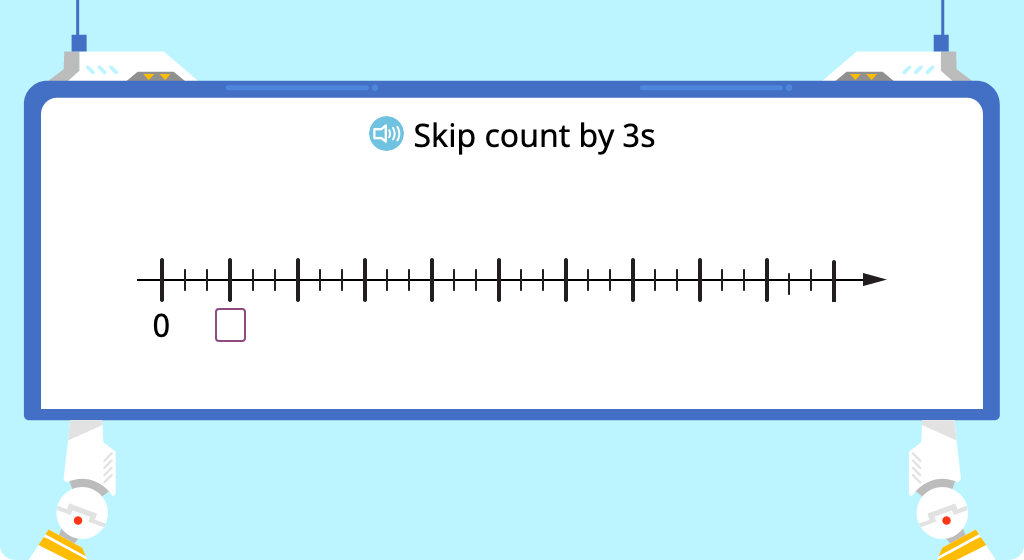
Multiply by 2 with and without an array model (Level 2)
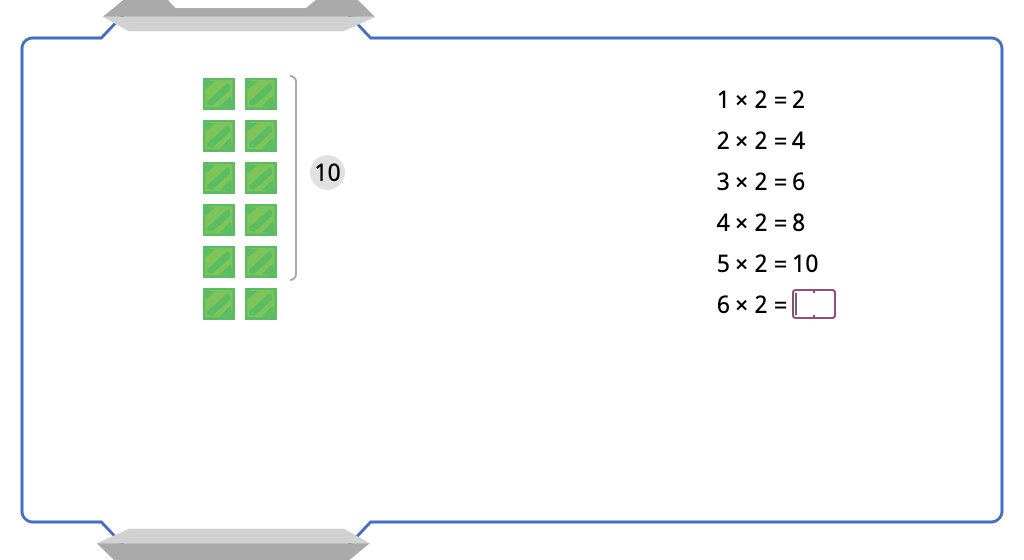
Multiply by 3 with and without an array model (Level 2)

Multiply by 2 to complete a pattern of equations (Level 2)

Multiply by 3 to complete a pattern of equations (Level 2)

Complete equations to show the commutative property of multiplication by 2 (Level 2)
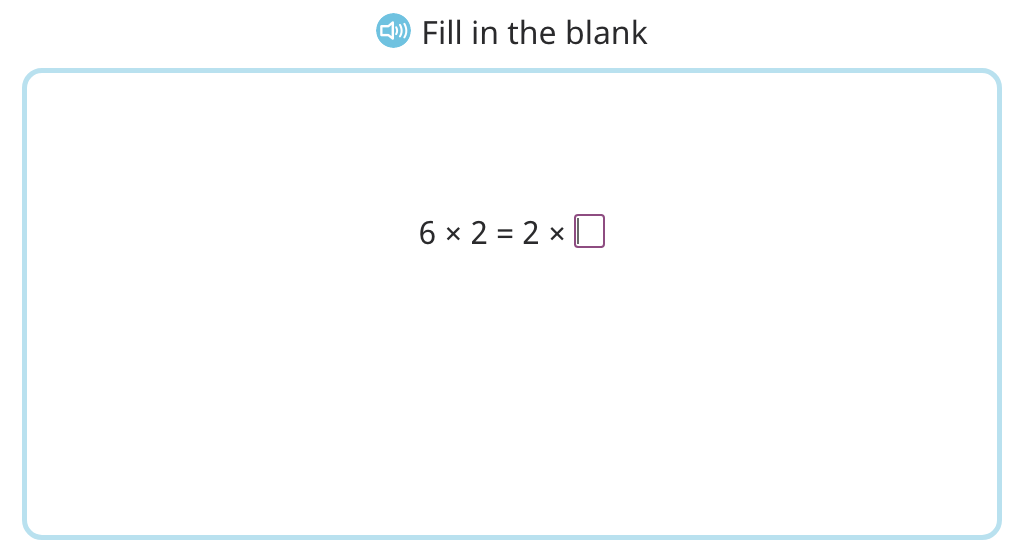
Complete equations to show the commutative property of multiplication by 3 (Level 2)
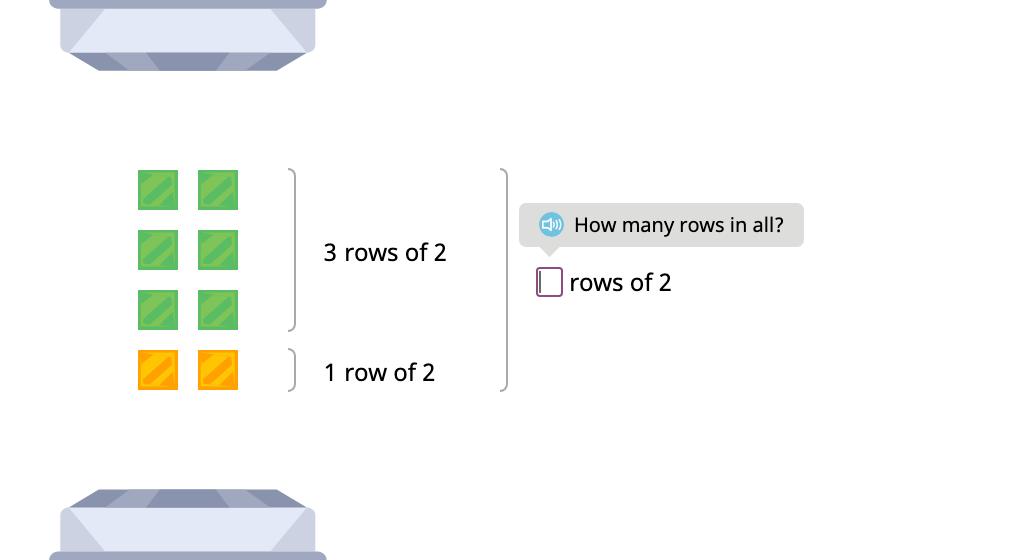
Label arrays with equations to show the distributive property of multiplication by 2 (Part 1)
Label arrays with equations to show the distributive property of multiplication by 2 (Part 2)
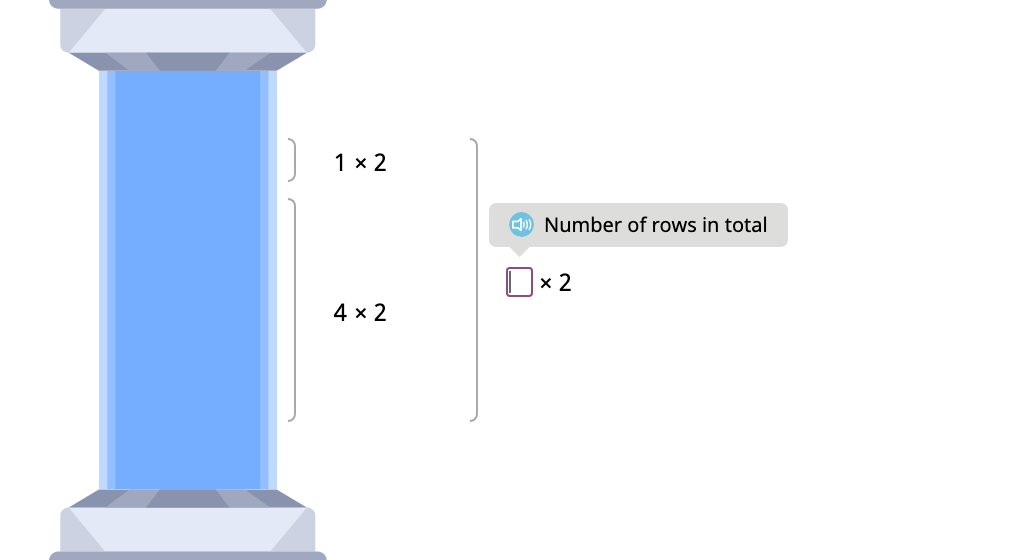
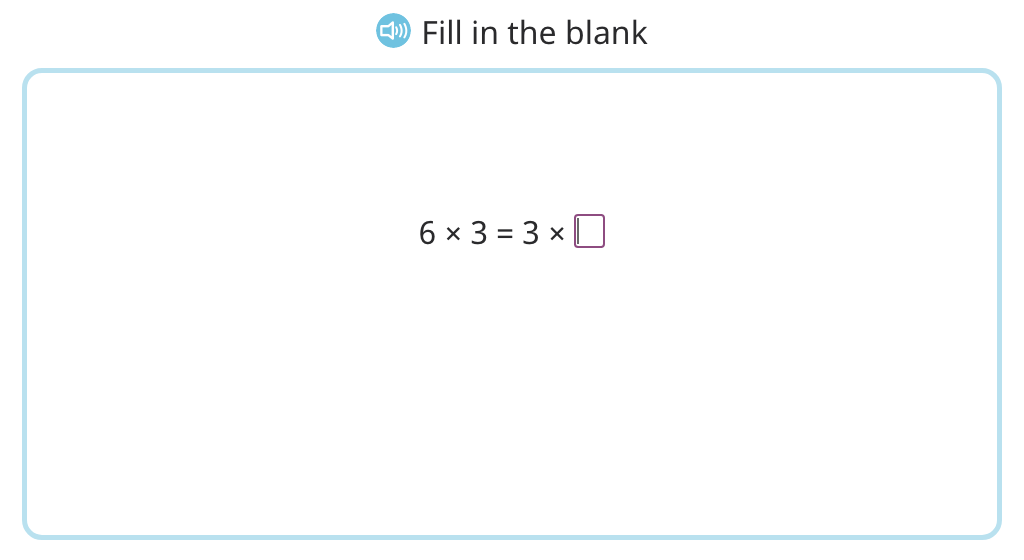
Label arrays with equations to show the distributive property of multiplication by 3 (Part 1)
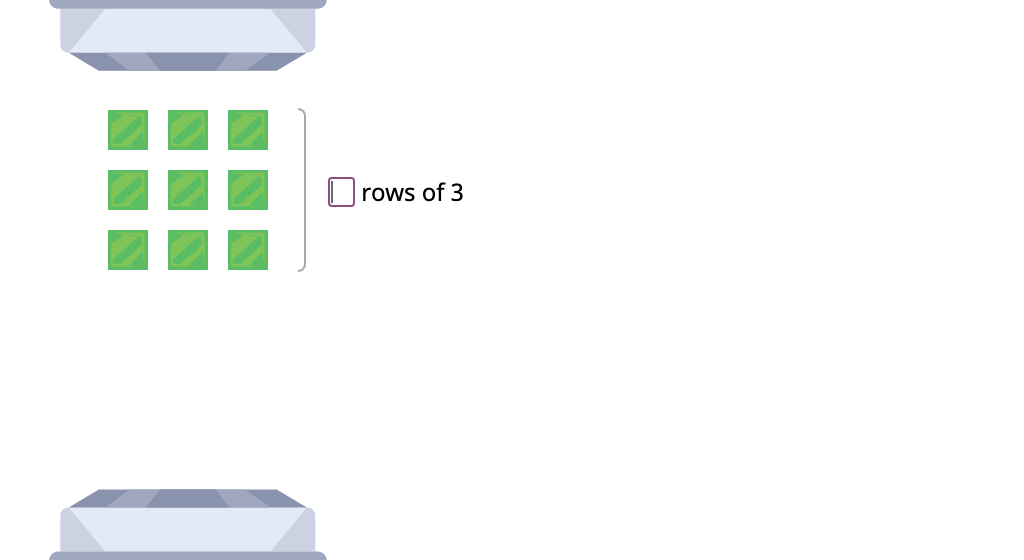
Label arrays with equations to show the distributive property of multiplication by 2 (Part 3)
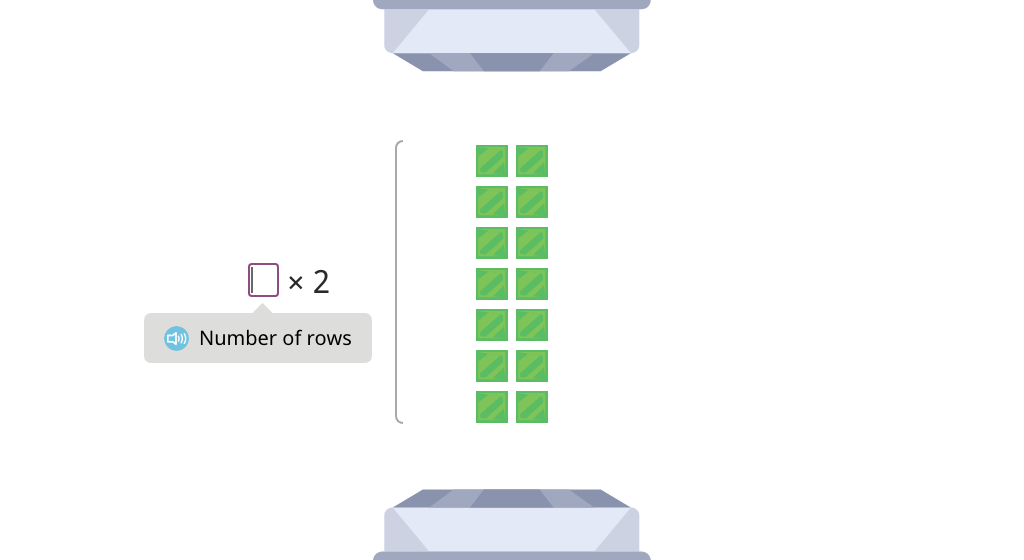
Label arrays with equations to show the distributive property of multiplication by 3 (Part 2)
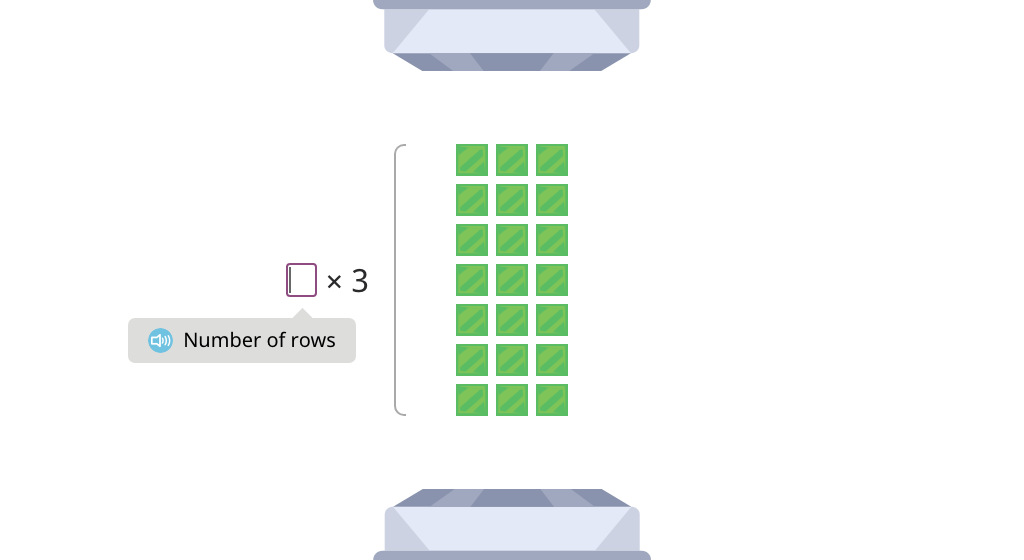
Solve x2 multiplication equations (Level 2, Part 1)
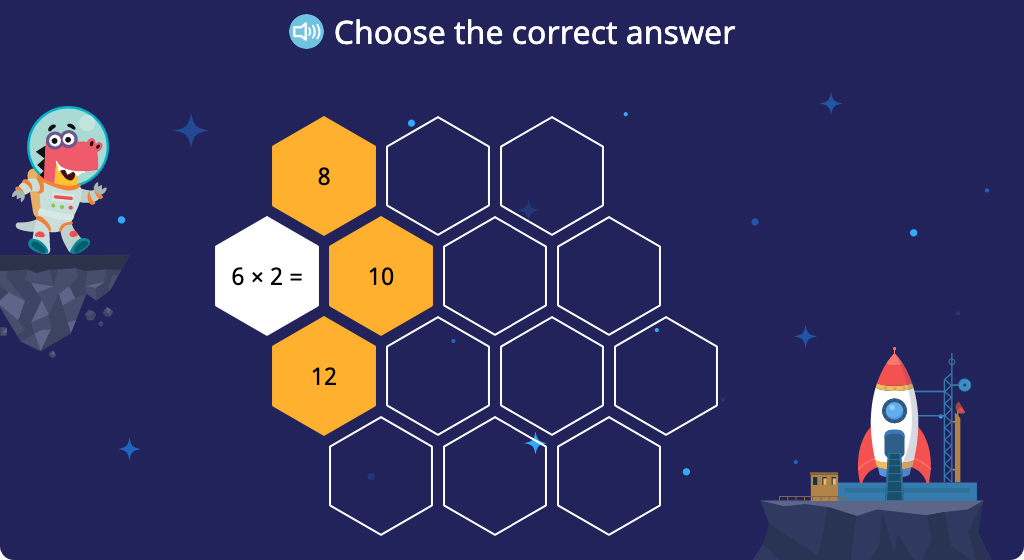
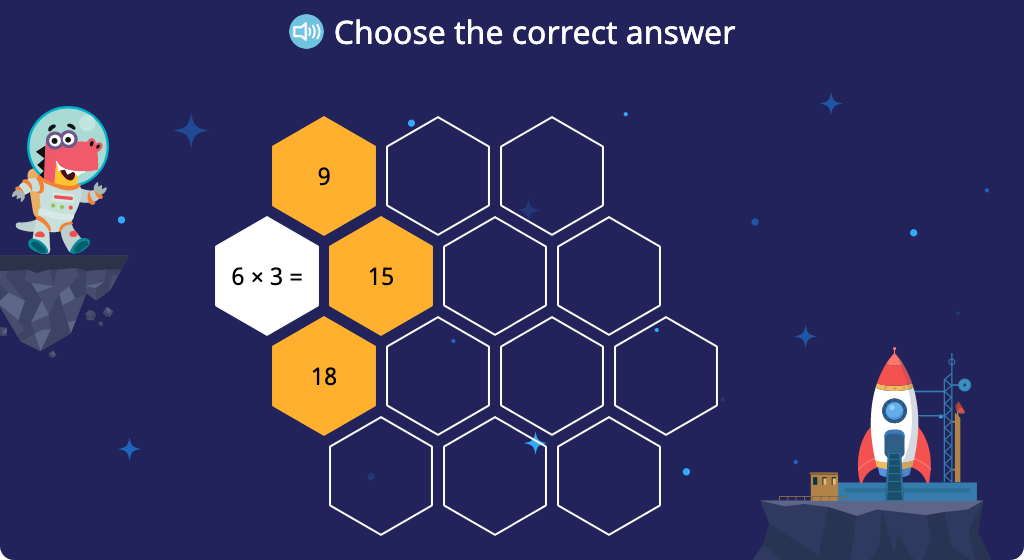
Solve x3 multiplication equations (Level 2, Part 1)
Solve x2 multiplication equations (Level 2, Part 2)

Solve x3 multiplication equations (Level 2, Part 2)

Topic D: Division by 2 and by 3
Students use concrete and abstract objects to understand the concept of division. They then relate division to multiplication to help build understanding and fact fluency. Students begin by solving simple division equations (quotients to 5) and then advance to solving equations with quotients to 10.
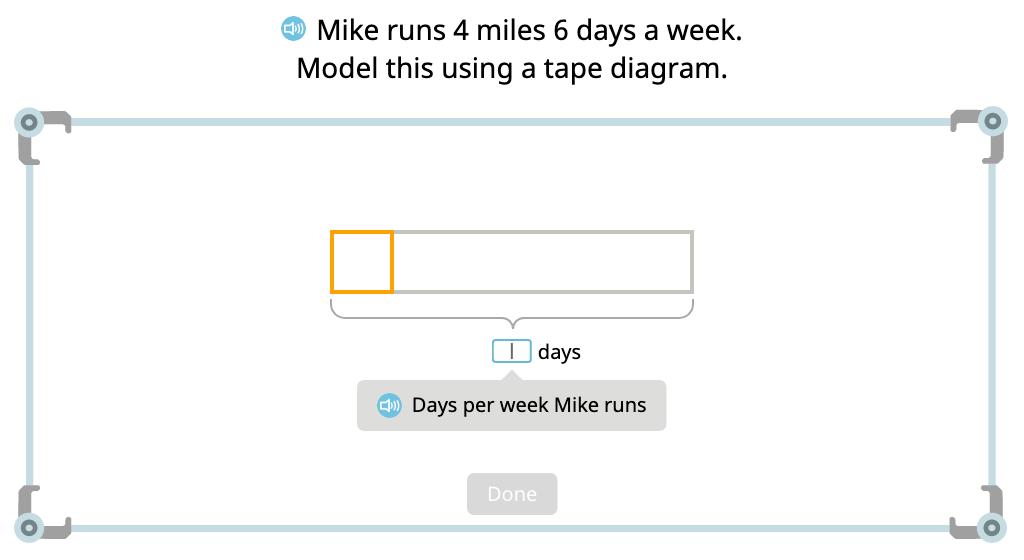
Distribute objects equally to create a tape diagram (How many in each group?)
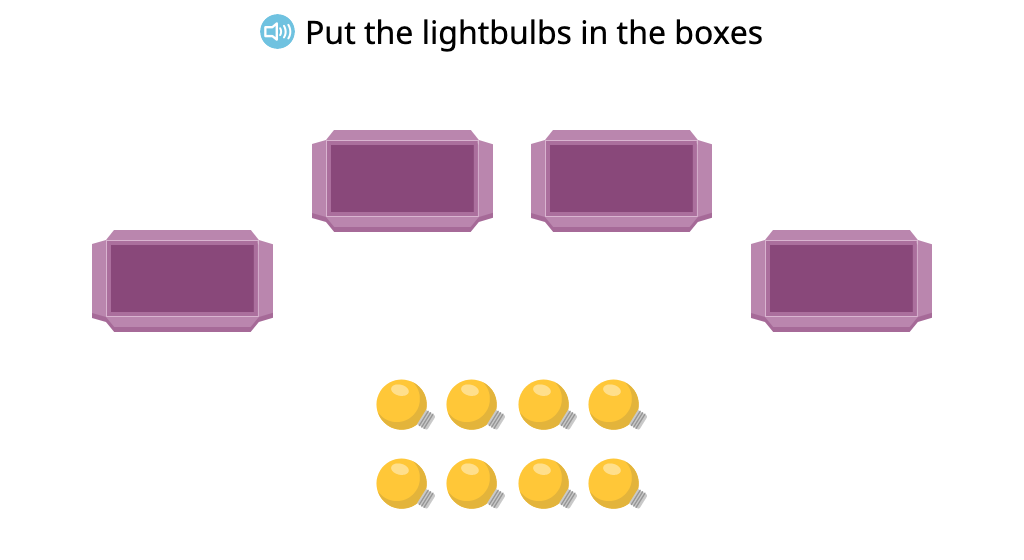
Represent a tape diagram as a division equation (How many in each group?)
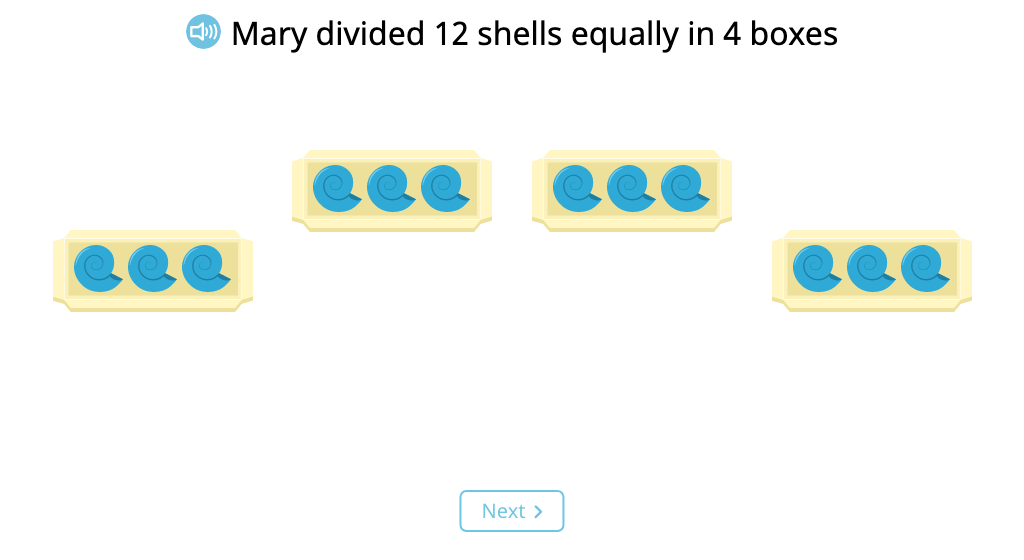
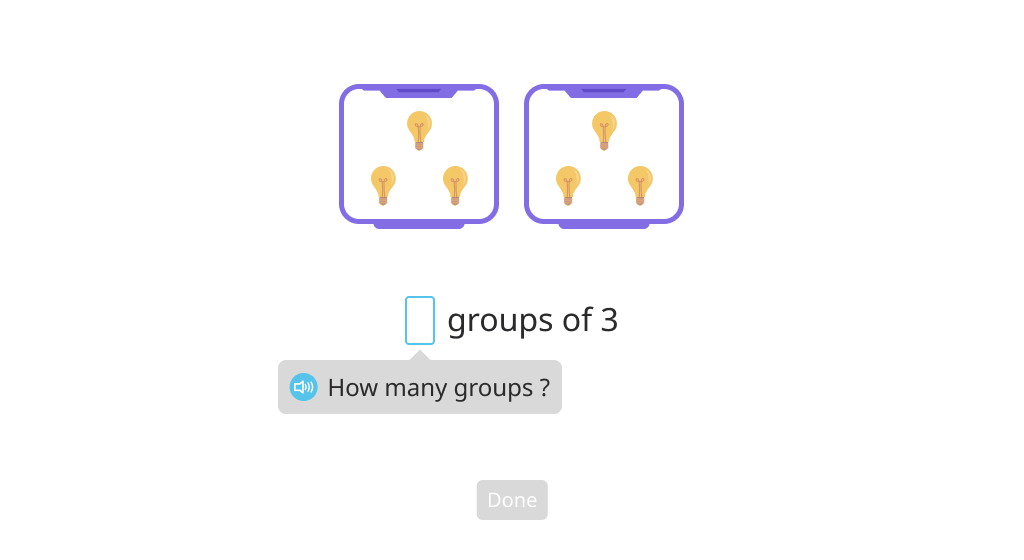
Distribute objects equally to create a tape diagram (How many groups?)
Represent a tape diagram as a division equation (How many groups?)
Complete equations to relate multiplication to division (Part 1)
Complete equations to relate multiplication to division (Part 2)
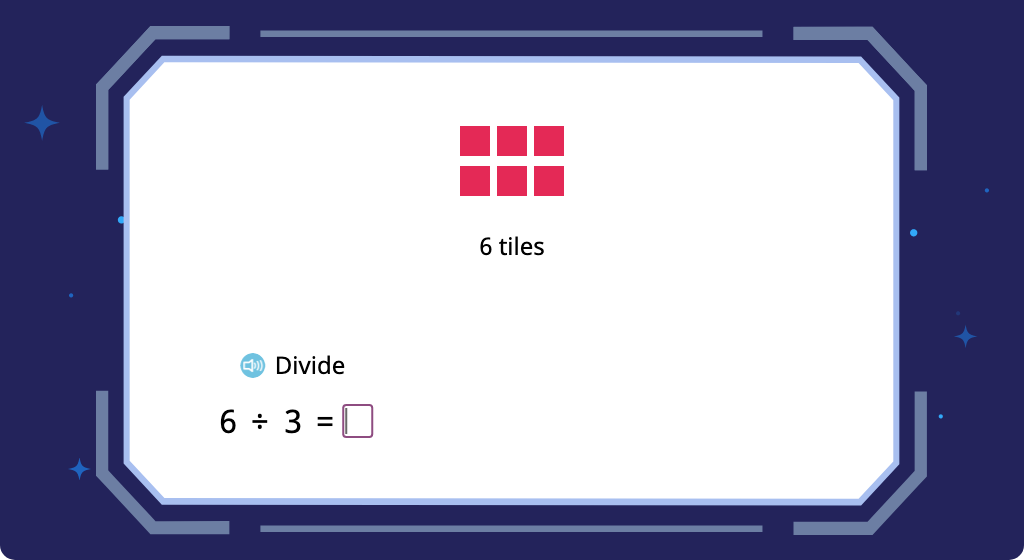
Match a division fact to its related multiplication fact
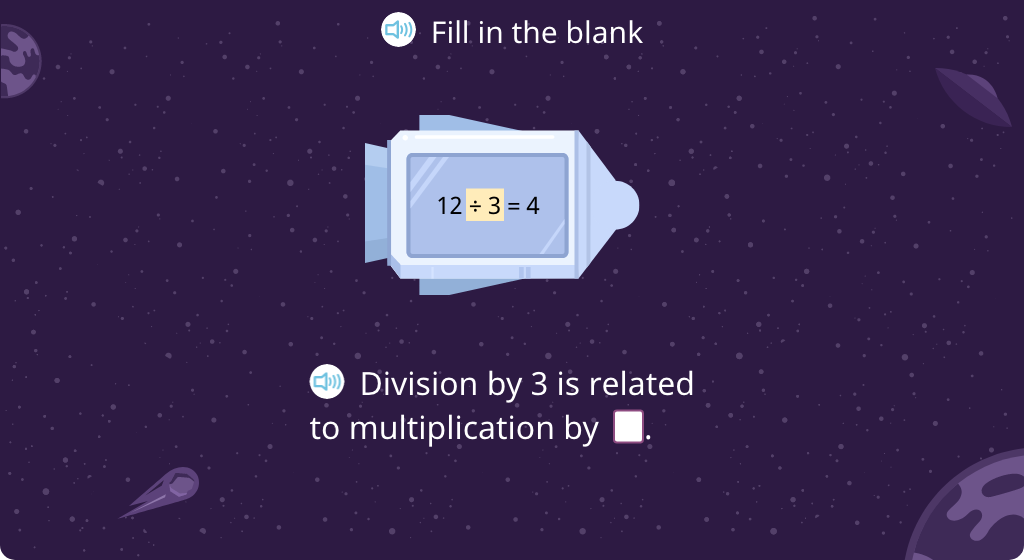
Solve division equations by using the related multiplication fact
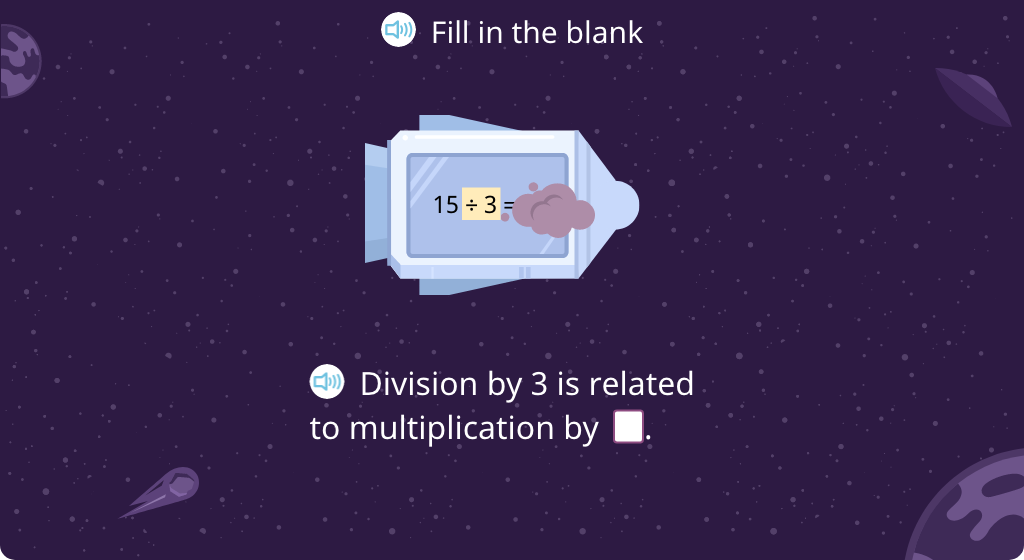
Solve division equations with a divisor of 2 (Level 1)
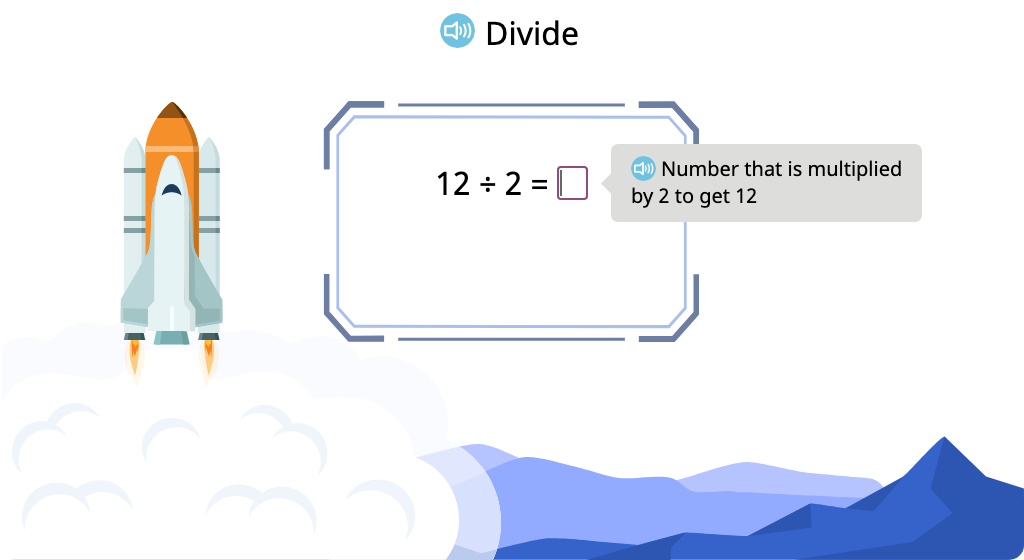
Solve division equations with a divisor of 3 (Level 1)

Solve division equations with a divisor of 2 or 3

Solve division equations with a divisor of 2 (Level 2)
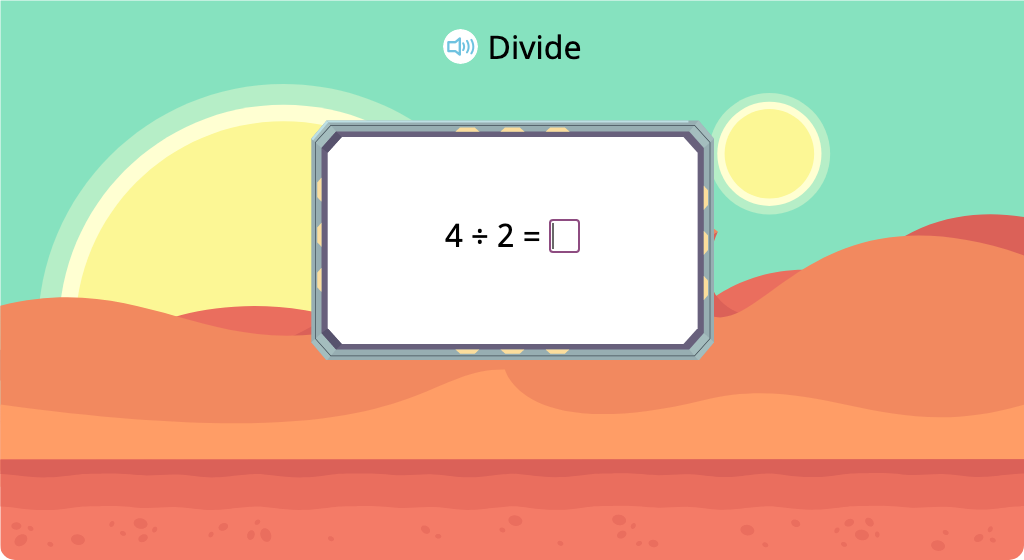
Solve division equations with a divisor of 2 (Level 3)

Solve division equations with a divisor of 3 (Level 2)

Solve division equations with a divisor of 3 (Level 3)

Topic E: Multiplication and Division by 4
Building upon previous learning about multiplication and division, students apply their understanding to facts using 4 as a product or divisor. They work with familiar manipulatives and progression of skills to build understanding and fluency.
Skip count by 4
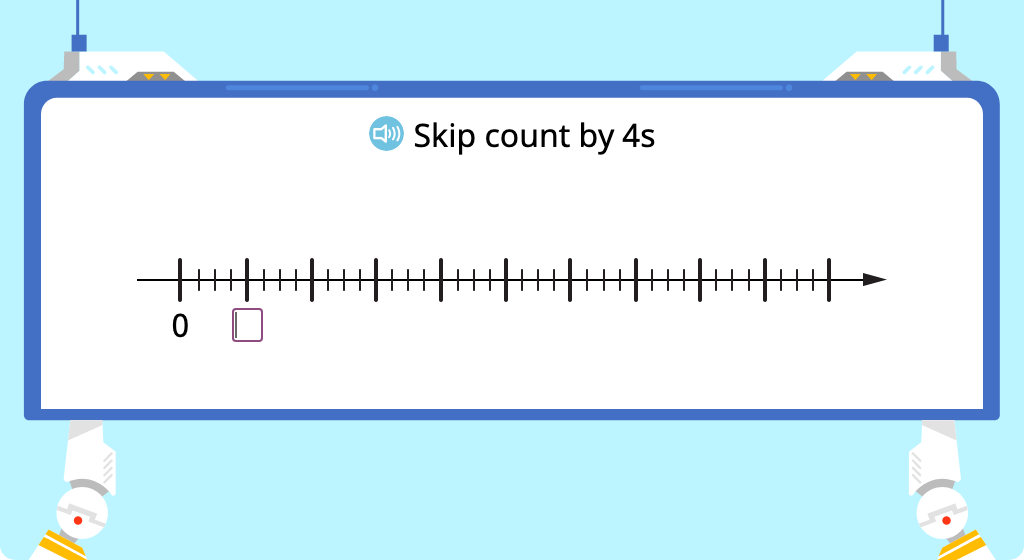
Multiply by 4 with and without an array model
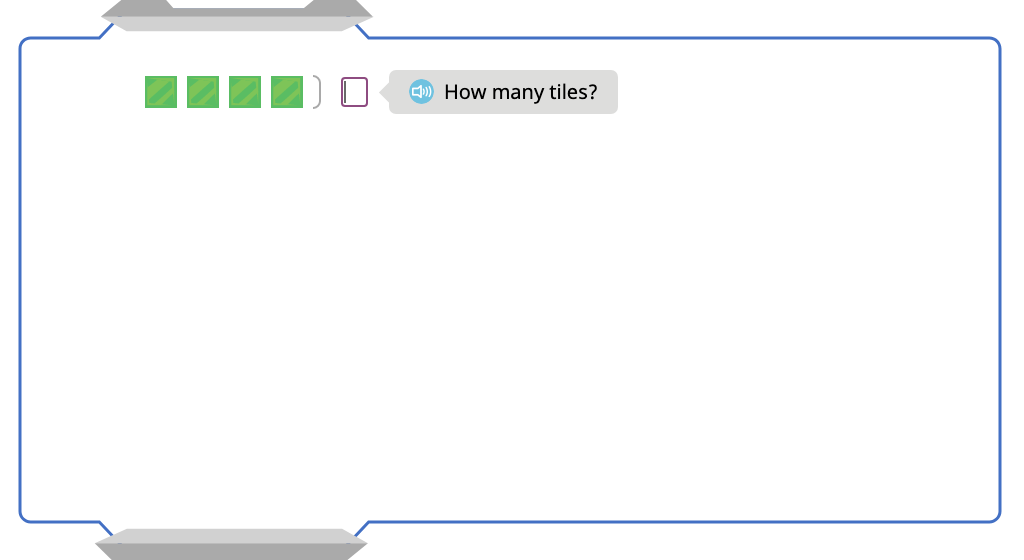
Multiply by 4 to complete a pattern of equations

Solve x4 multiplication equations

Represent a tape diagram as a multiplication equation (Level 1)
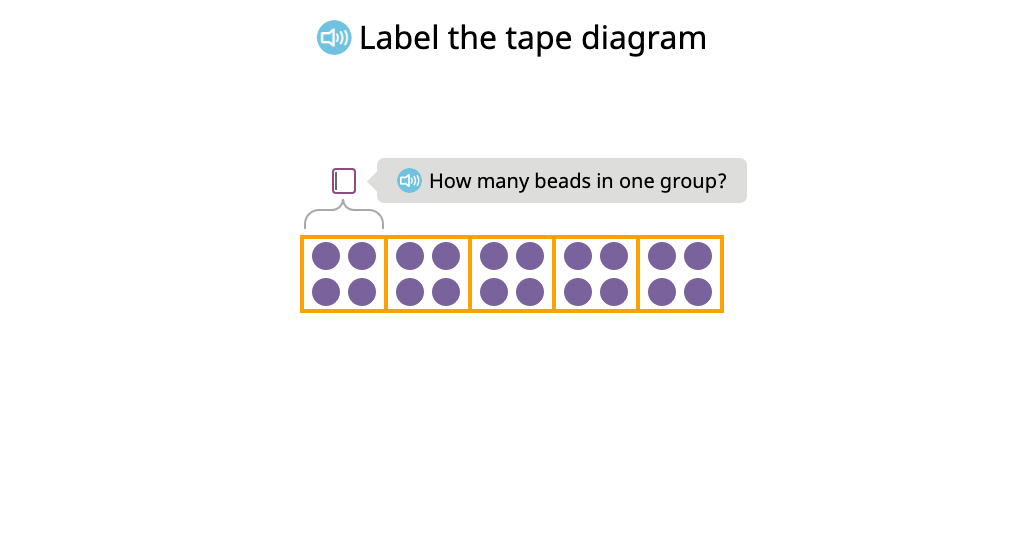
Represent a tape diagram as a multiplication equation (Level 2)

Label a tape diagram to represent a multiplication equation
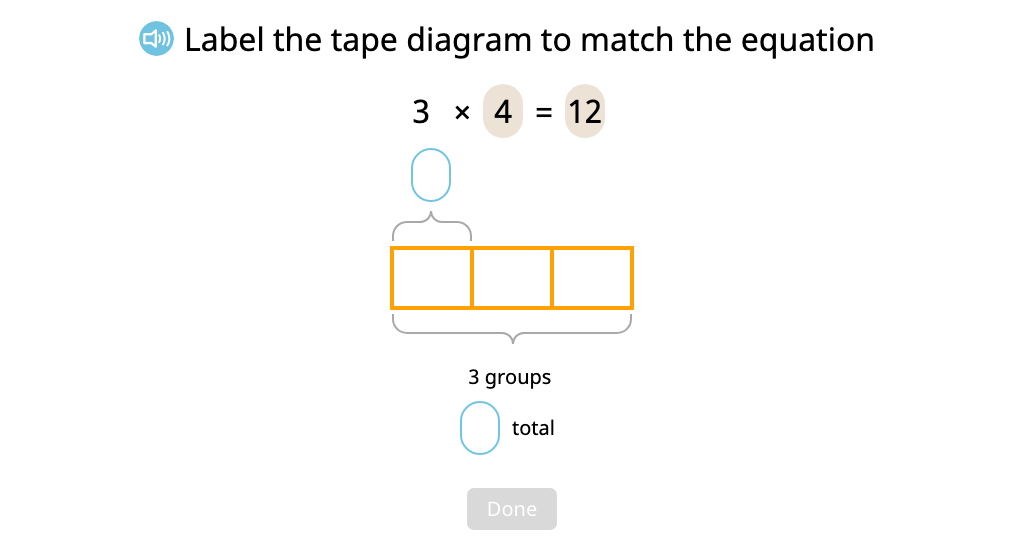
Identify factors and product in a multiplication equation
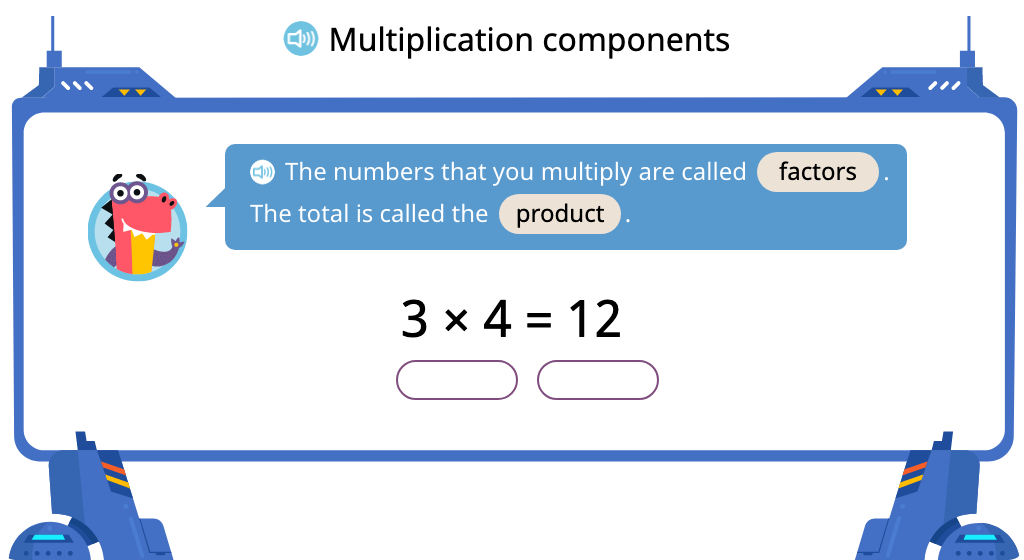
Label arrays with equations to show the commutative property of multiplication (Level 1)
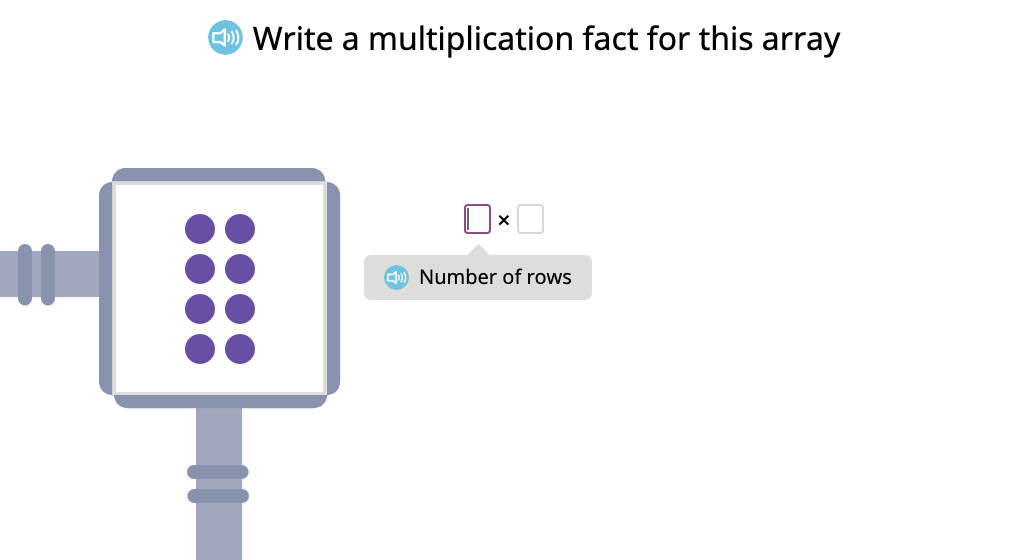
Label arrays with equations to show the commutative property of multiplication (Level 2)
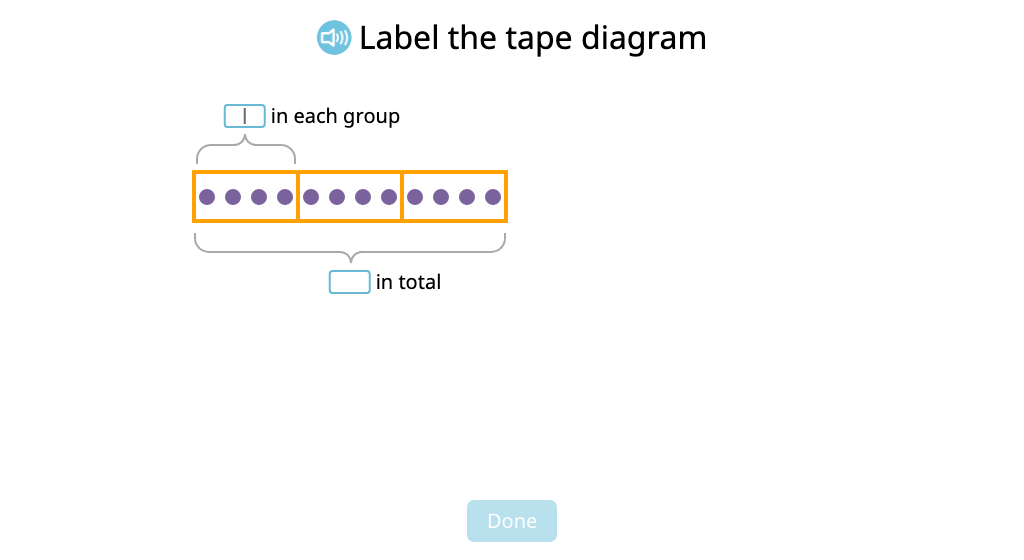
Label tape diagrams with equations to show the commutative property of multiplication

Solve multiplication equations based on the commutative property
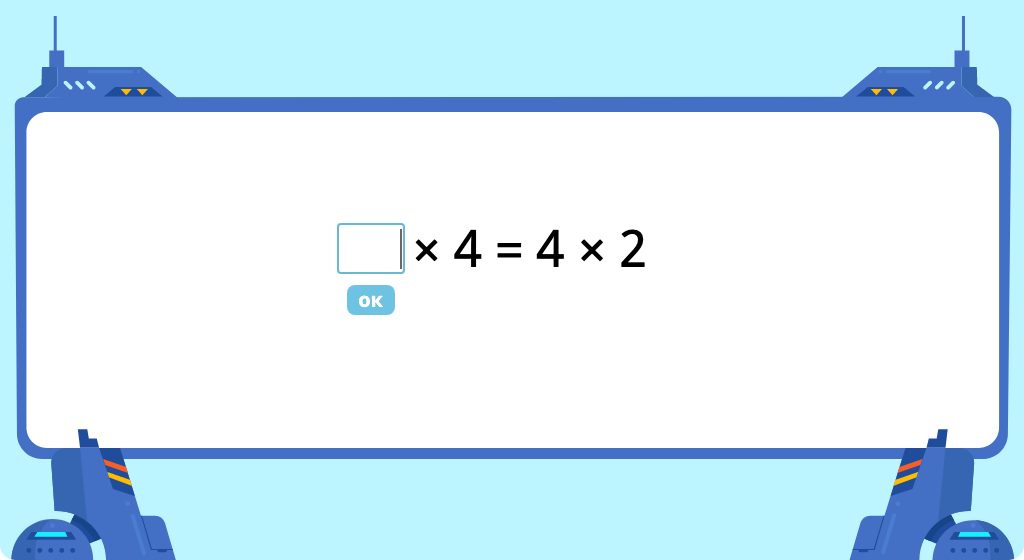
Solve word problems using tape diagrams and multiplication equations
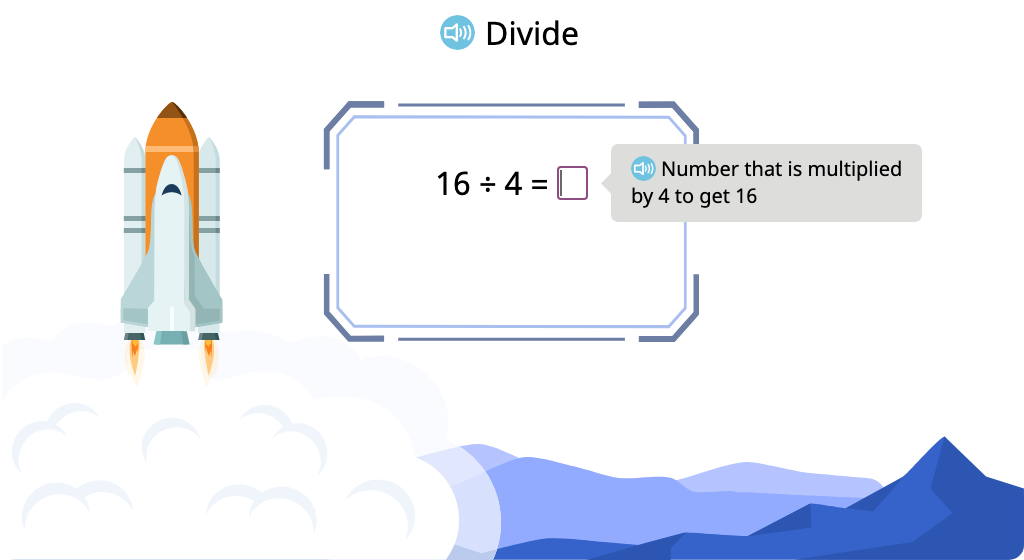
Solve division equations by using the related multiplication fact
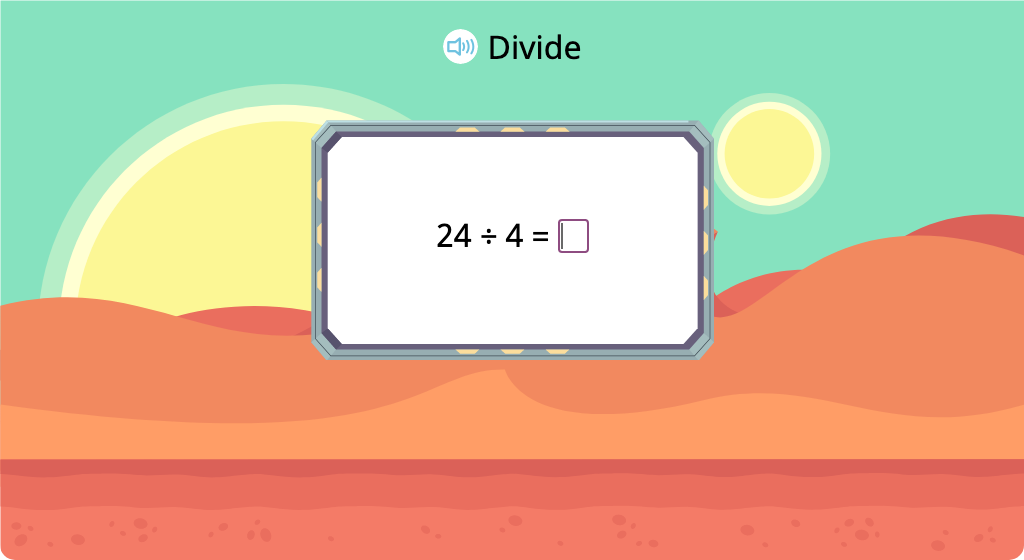
Solve division equations with a divisor of 4 (Level 1)

Solve division equations with a divisor of 4 (Level 2)
Topic F: Multiplication and Division by 5
Building upon previous learning about multiplication and division, students apply their understanding to facts using 5 as a product or divisor and 10 as a product. They also develop understanding of the distributive property of multiplication and division. Students build connections between equations, arrays, tape diagrams, and word problems.
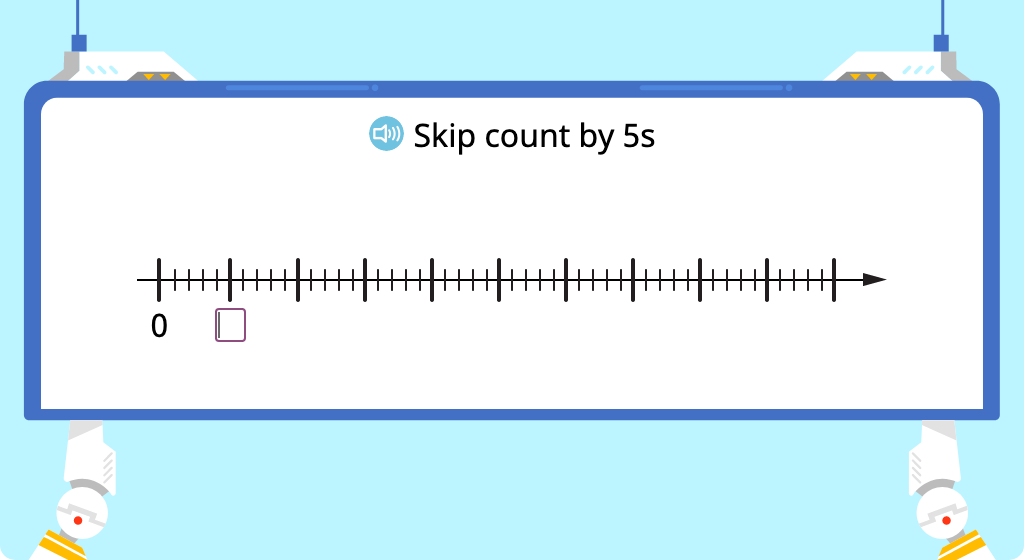
Skip count by 5
Multiply by 5 with and without an array model
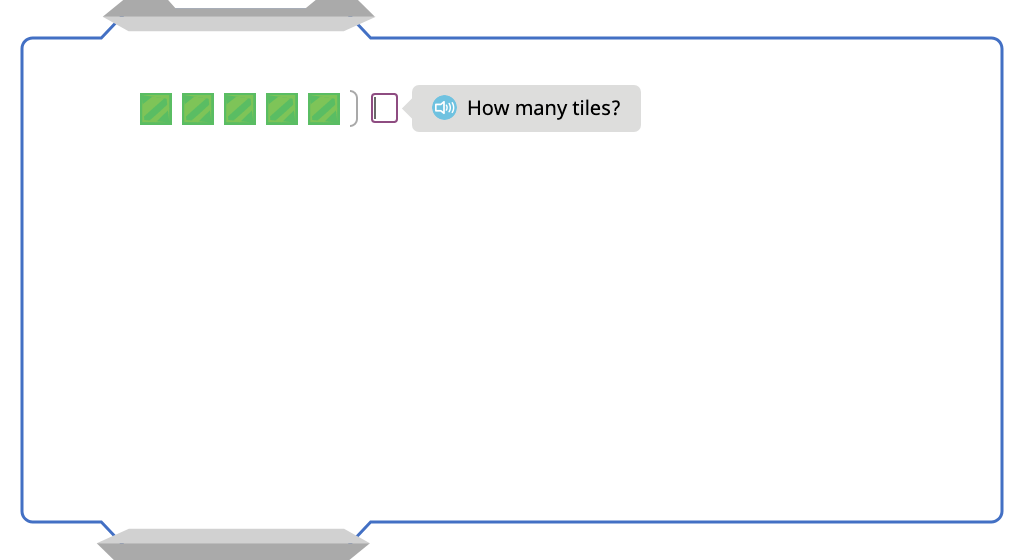
Multiply by 5 to complete a pattern of equations

Solve x5 multiplication equations

Solve division equations by using the related multiplication fact
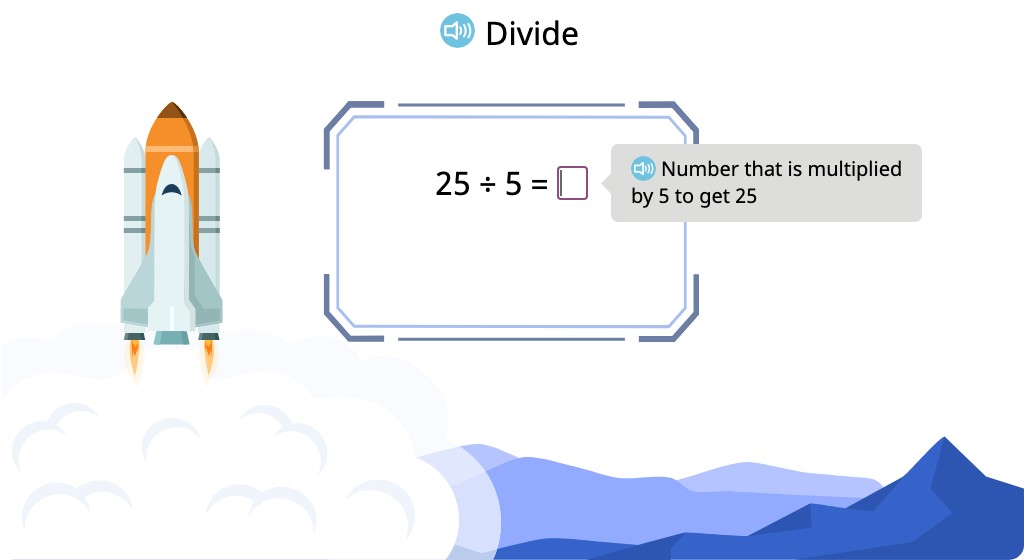
Solve division equations with a divisor of 5 (Level 1)

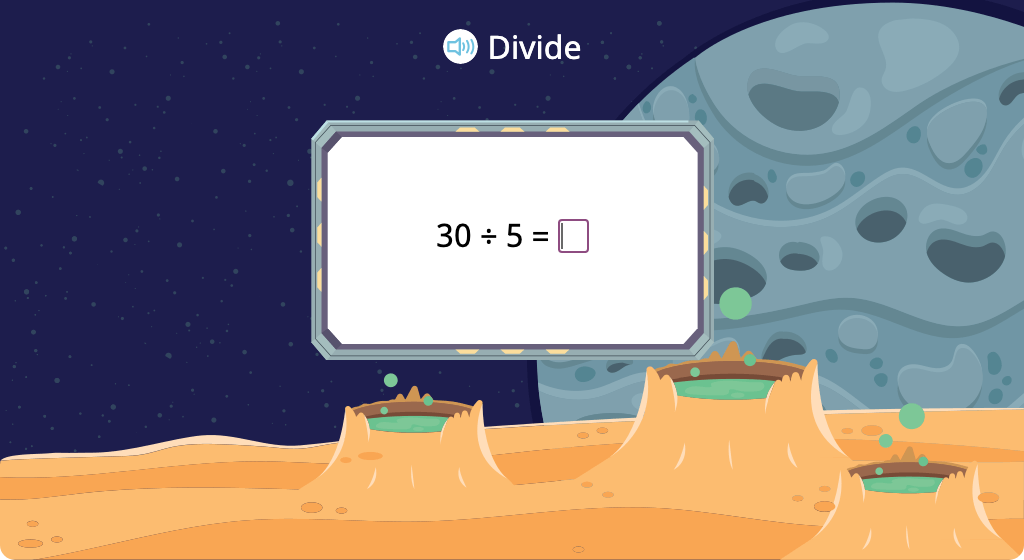
Solve division equations with a divisor of 5 (Level 2)
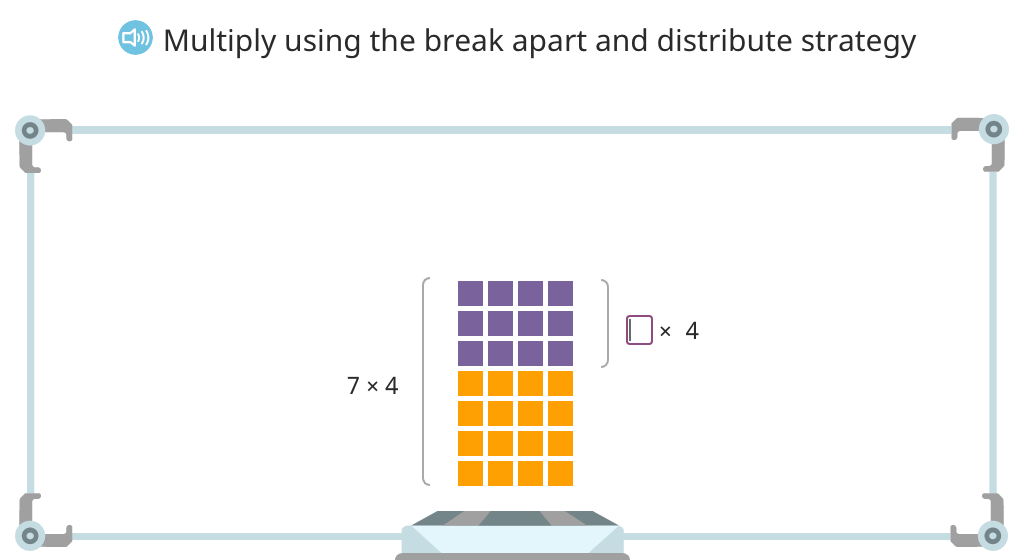
Label arrays with equations to show the distributive property of multiplication
Complete expressions based on the distributive property of multiplication
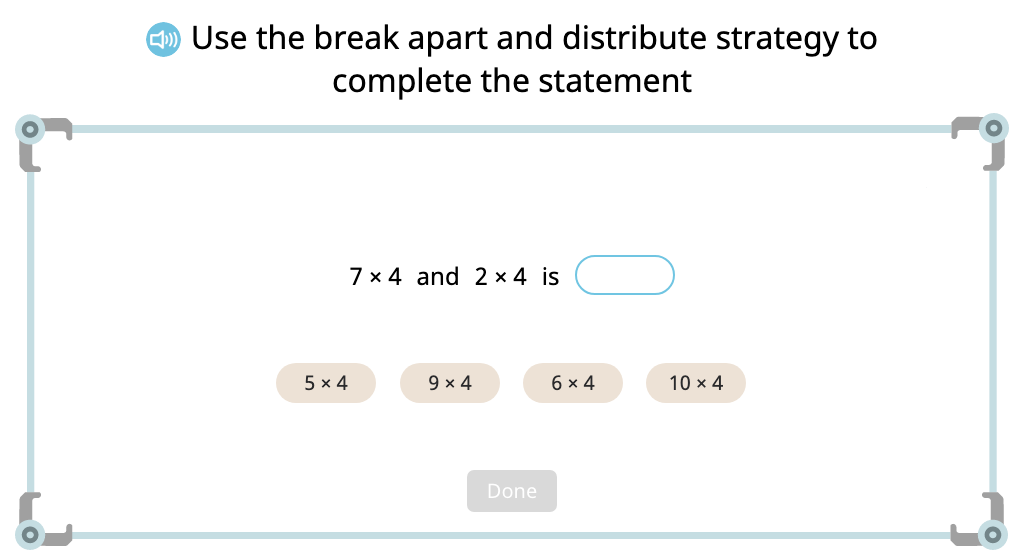
Compose a division equation based on an array
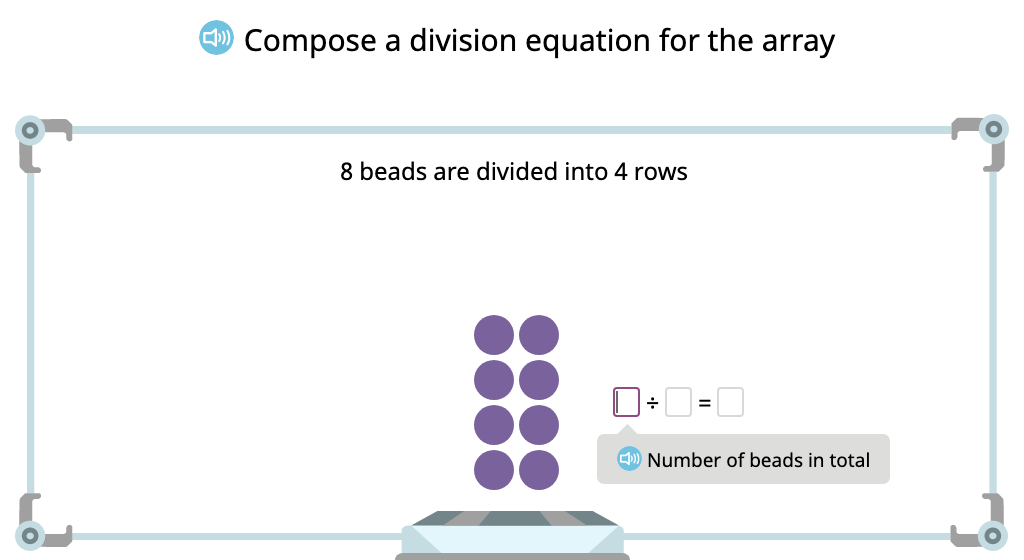
Compose a division equation based on an array to show the distributive property of division
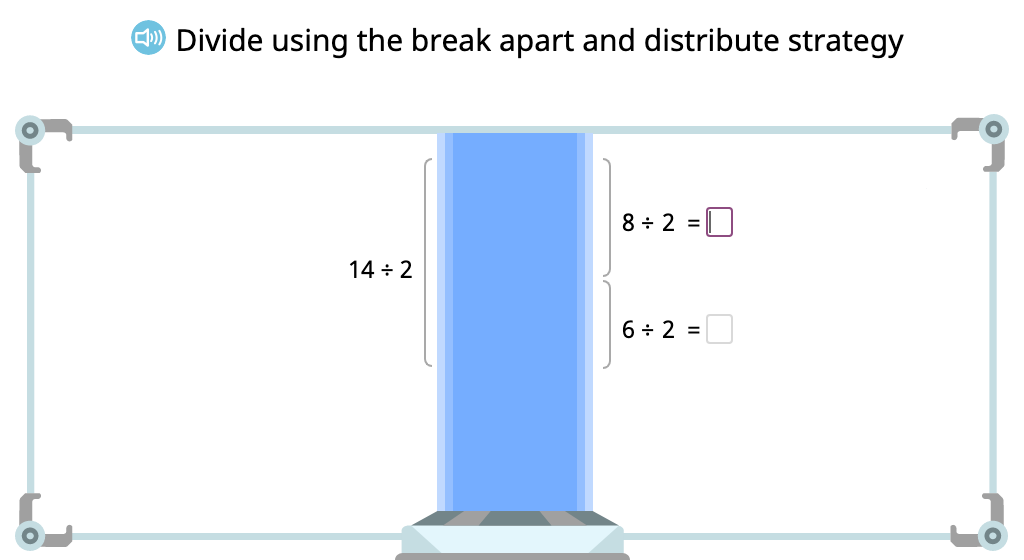
Solve a division equation based on an array by using the distributive property of division
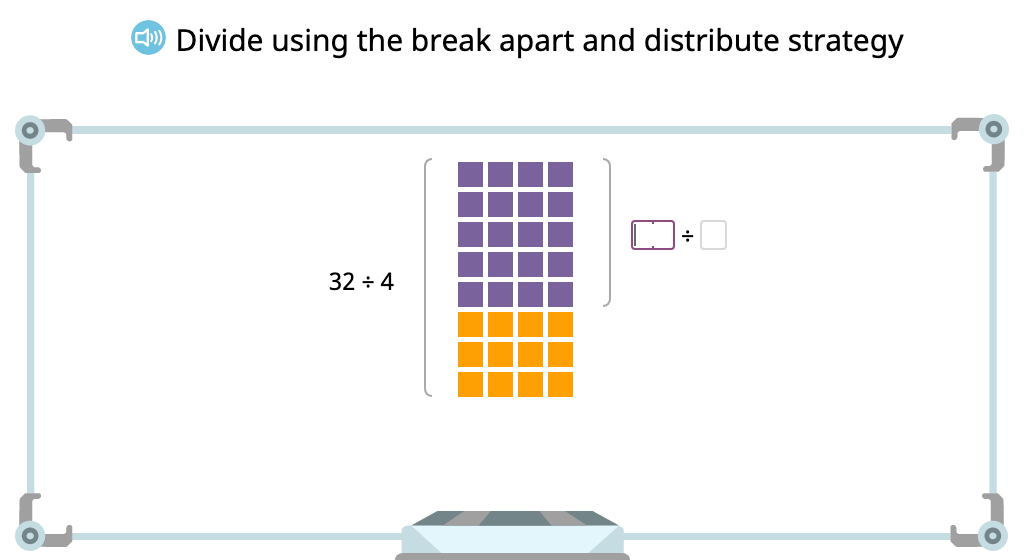
Complete expressions based on the distributive property of division
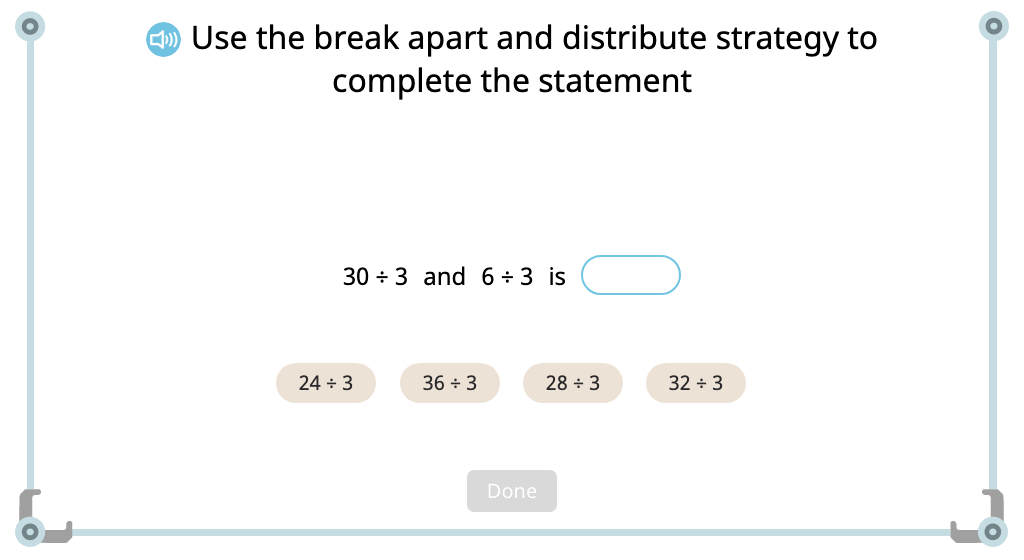
Skip count by 10

Multiply by 10 to complete a pattern of equations (Level 1)
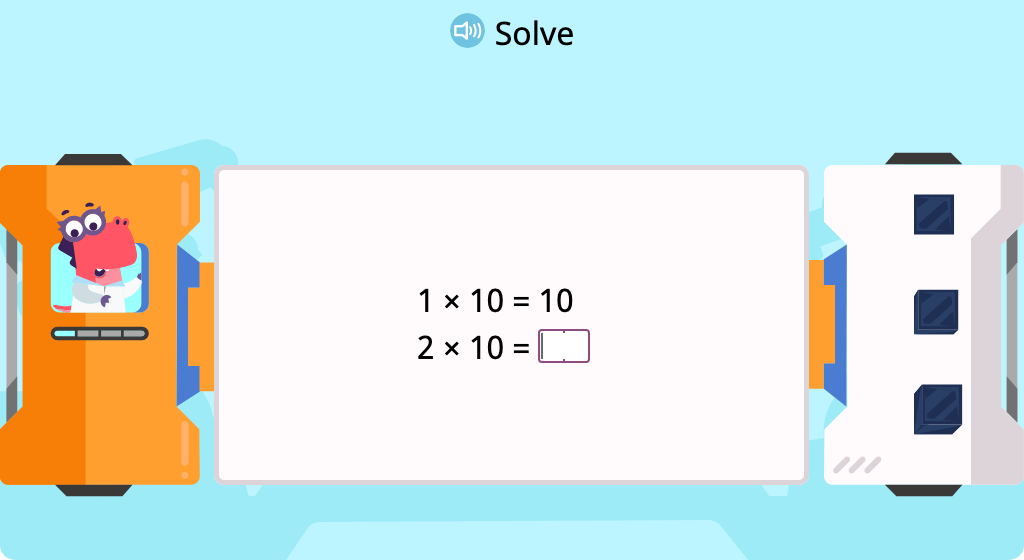
Multiply by 10 to complete a pattern of equations (Level 2)

Solve x10 multiplication equations

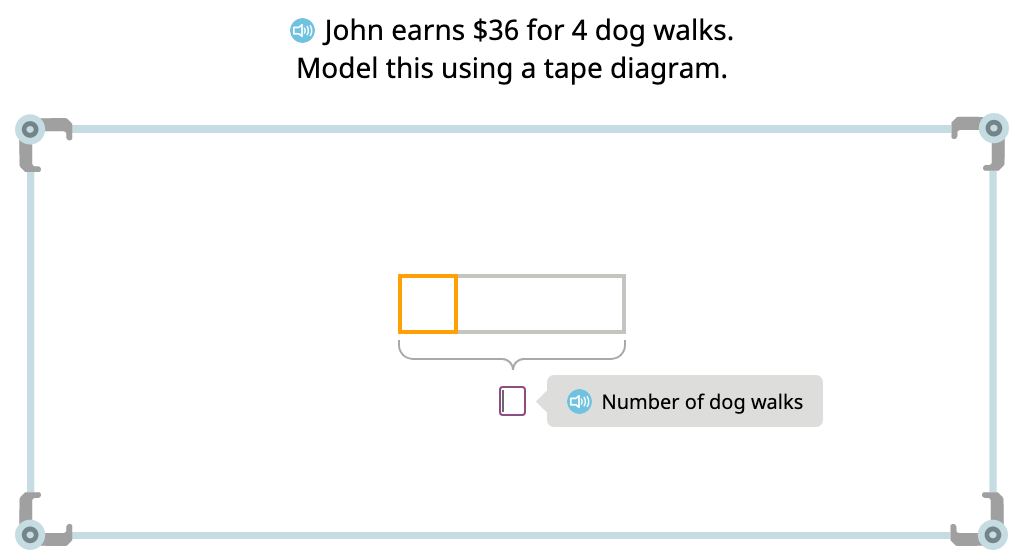
Solve word problems using tape diagrams and division equations (Level 1)
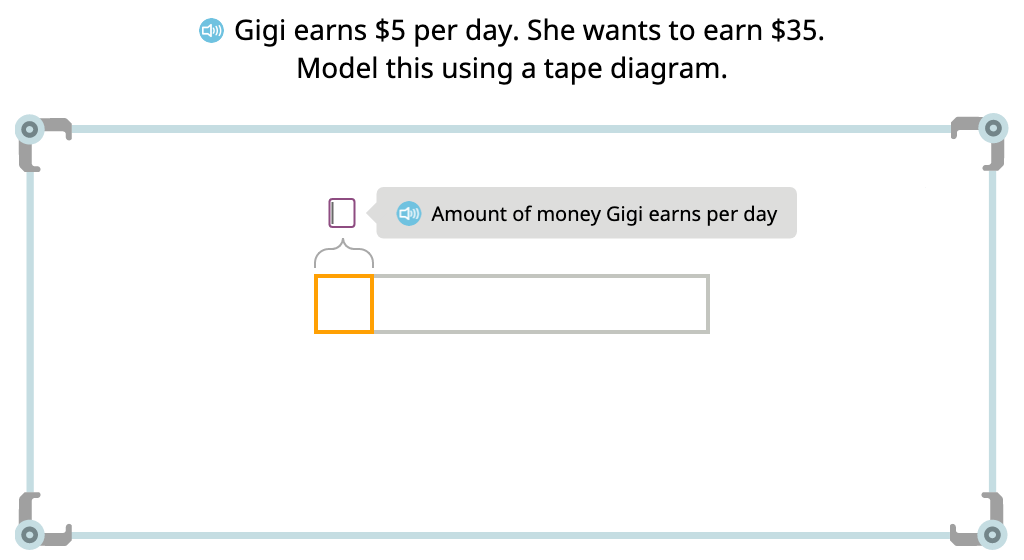
Solve word problems using tape diagrams and division equations (Level 2)
MODULE 2. Place Value and Problem Solving with Units of Measure
Topic A: Time Measurement and Problem Solving
Students review telling time on an analog clock and learn to write time as hours and minutes. They also learn how to use addition and subtraction skills to calculate start and end times and time intervals and apply this to word problems.
Review telling time to five minutes
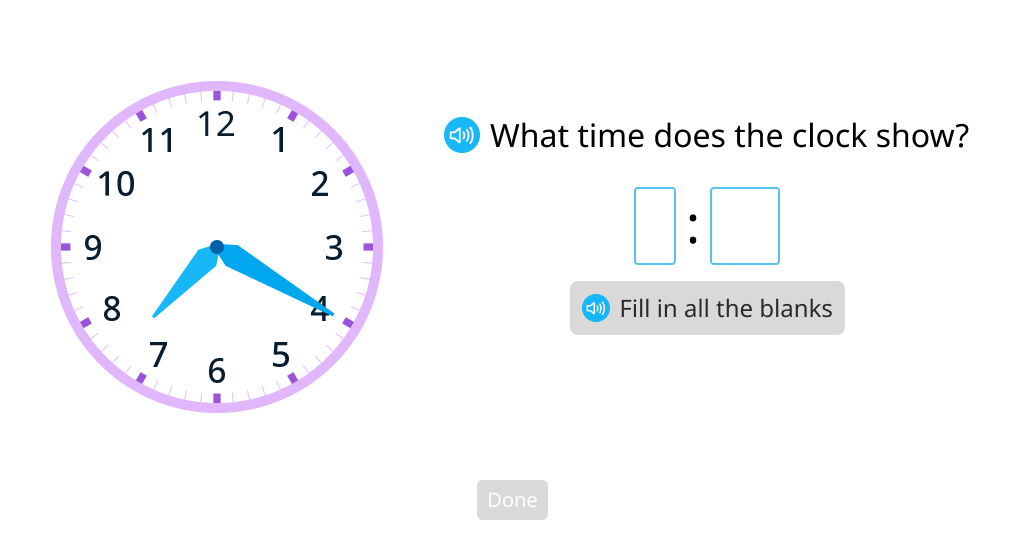
Tell time to the minute (Level 1)

Tell time to the minute (Level 2)
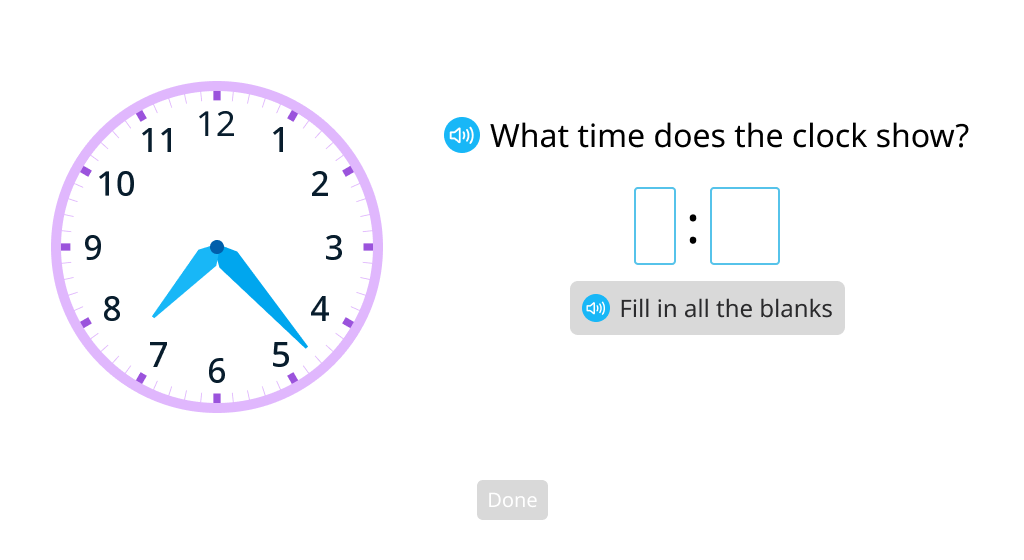
Identify the start and end times of a scenario
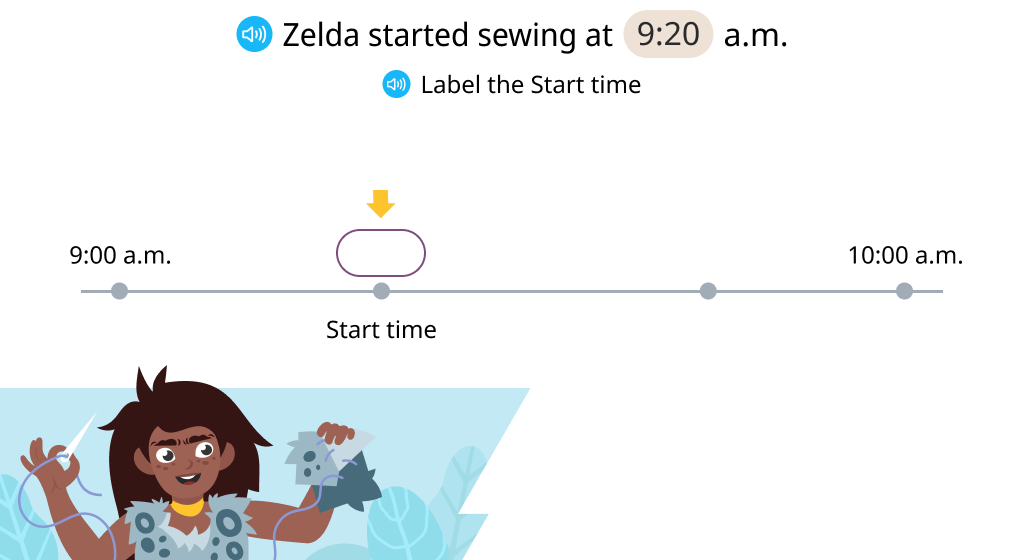
Calculate the time interval
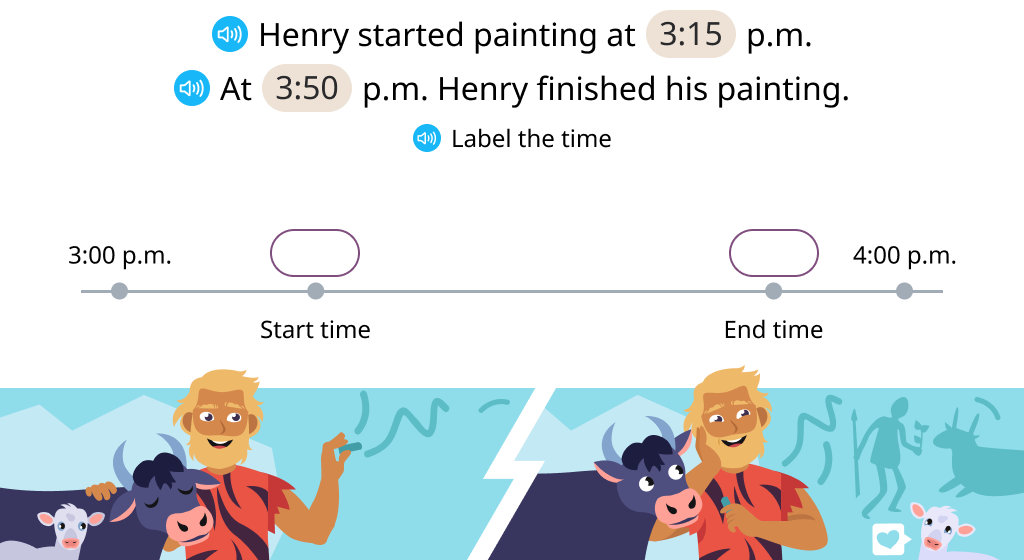
Calculate time intervals using a timeline

Calculate time intervals, without a timeline

Rewrite time as hr and min
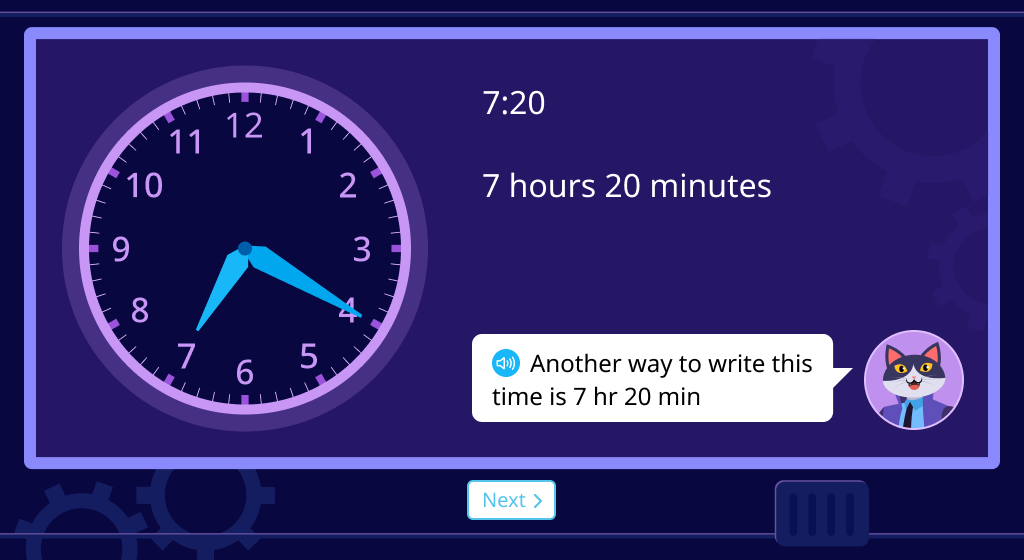
Calculate the end time using addition
Calculate the end time using column addition (Level 1)
Calculate the end time using column addition (Level 2)
Calculate the end time using column addition (Level 3)
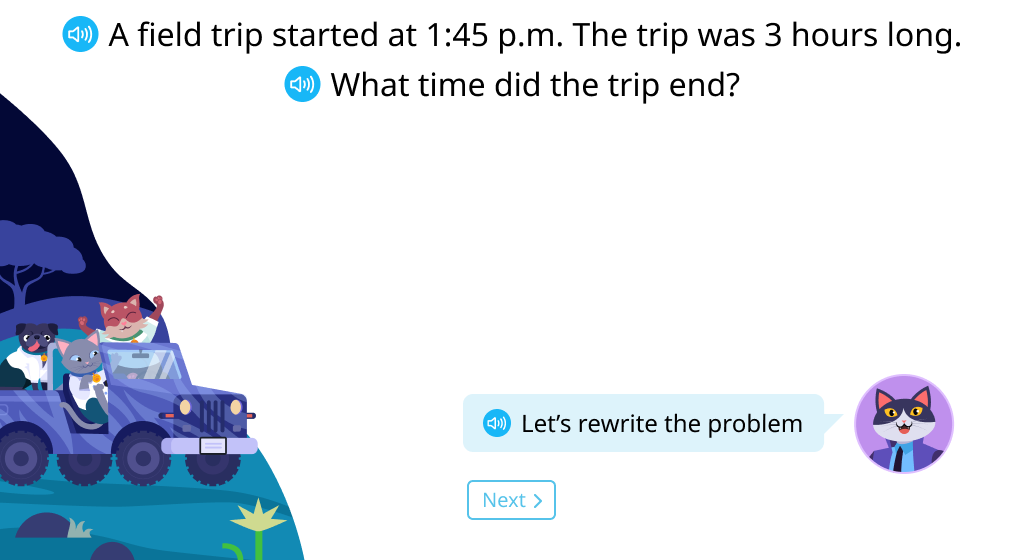
Calculate the start time using subtraction
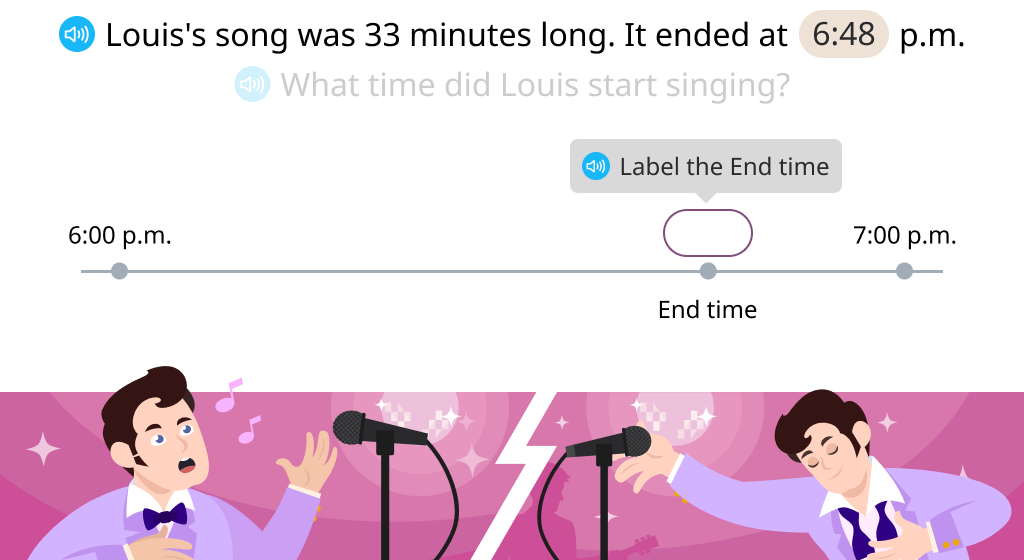
Calculate the start time using column subtraction (Level 1)

Calculate the start time using column subtraction (Level 2)

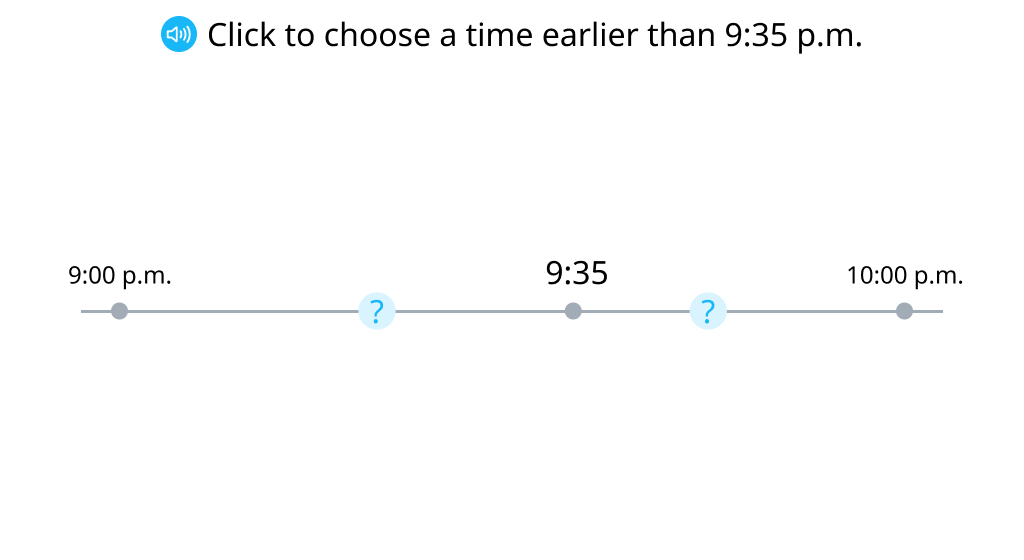
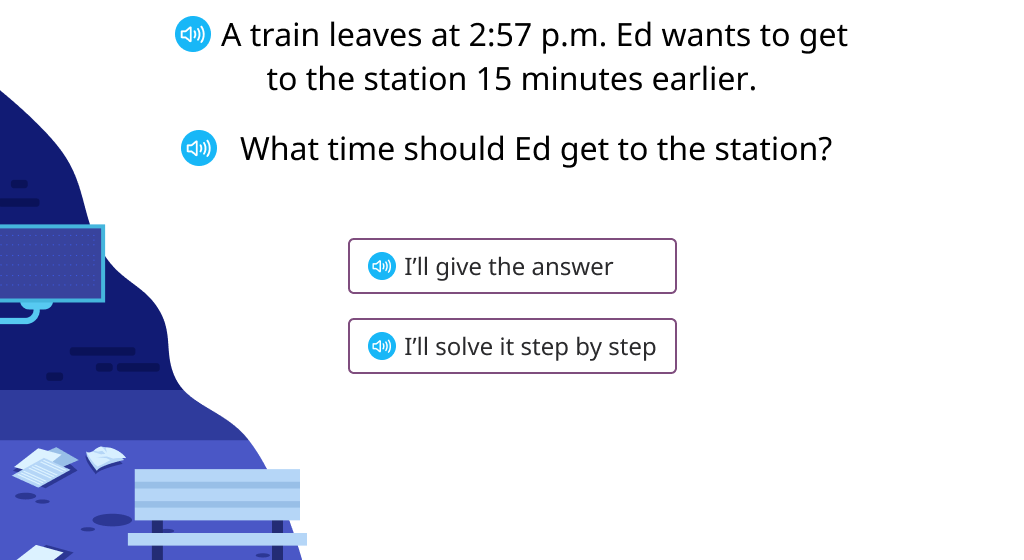
Find the time a certain number of minutes earlier than a given time
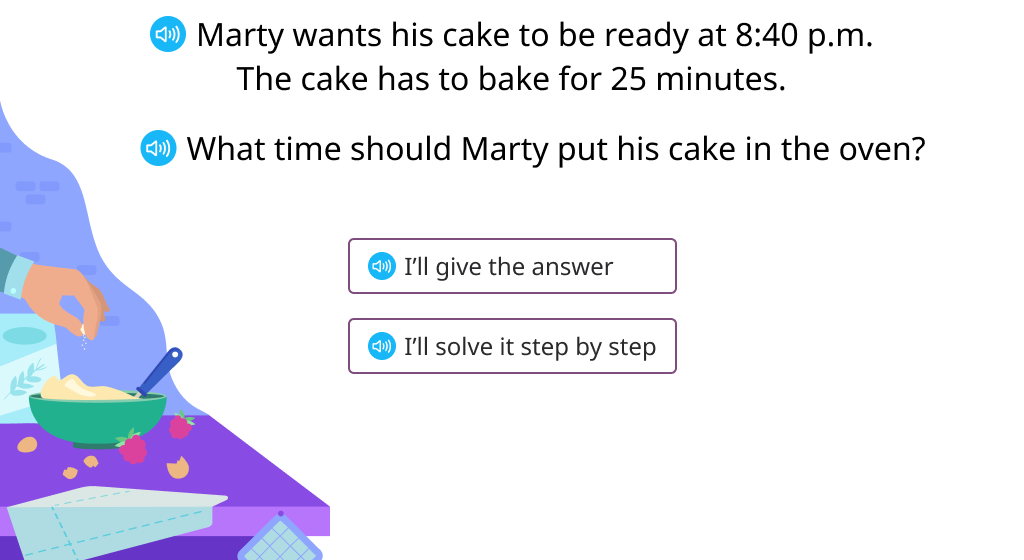
Calculate the start time when the end time and time intervals are known (Level 1)
Calculate start time when the end time and time interval are known (Level 2)
Topic B: Measuring Weight and Liquid Volume in Metric Units
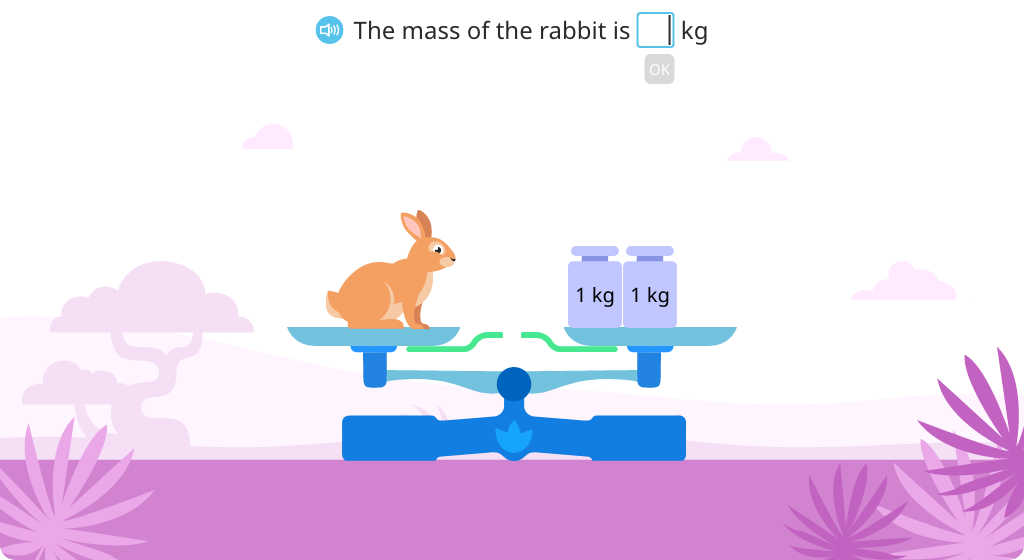
Students use a scale and a pan balance with weights to determine the mass of objects. They learn to read a scale between labeled increments and to add and subtract mass measurements to solve problems. To learn how to measure capacity, students pour liquid into labeled containers. They learn the relationship between kilograms and grams and between liters and milliliters.
Measure the mass of objects in kilograms using a scale

Measure the mass of objects in kilograms using a pan balance

Measure the mass of objects in grams using a pan balance
Compare grams and kilograms

Tutorial: Drag the lace to match objects
Match the estimated mass in grams and kilograms to objects

Determine mass measurements on a scale that is only labeled in increments of 10

Add or subtract to compare or find the total mass of objects measured on a scale

Tutorial: Click on highlighted words to access definition

Determine visually which of two objects has a greater capacity
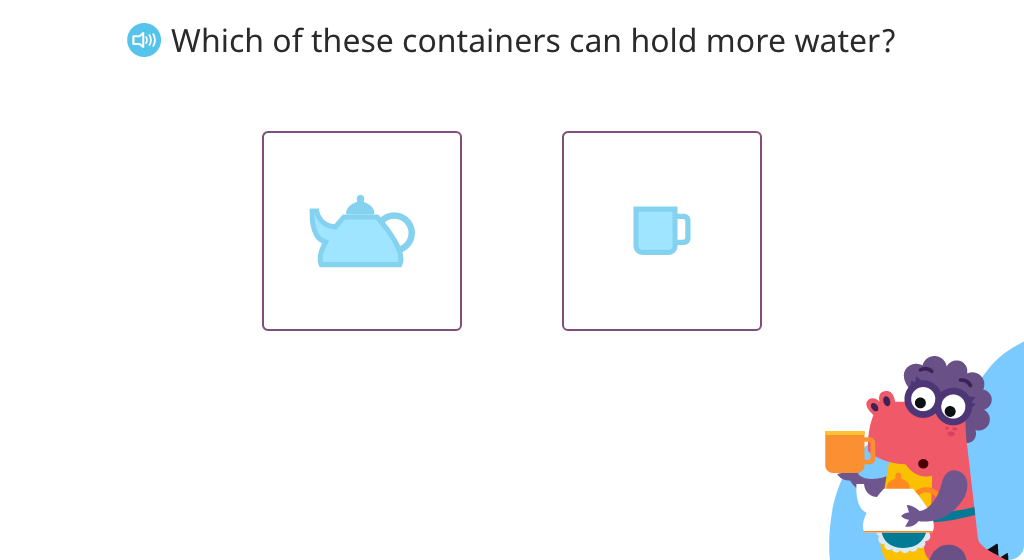
Measure capacity using non-standard units and liters

Measure capacity in liters
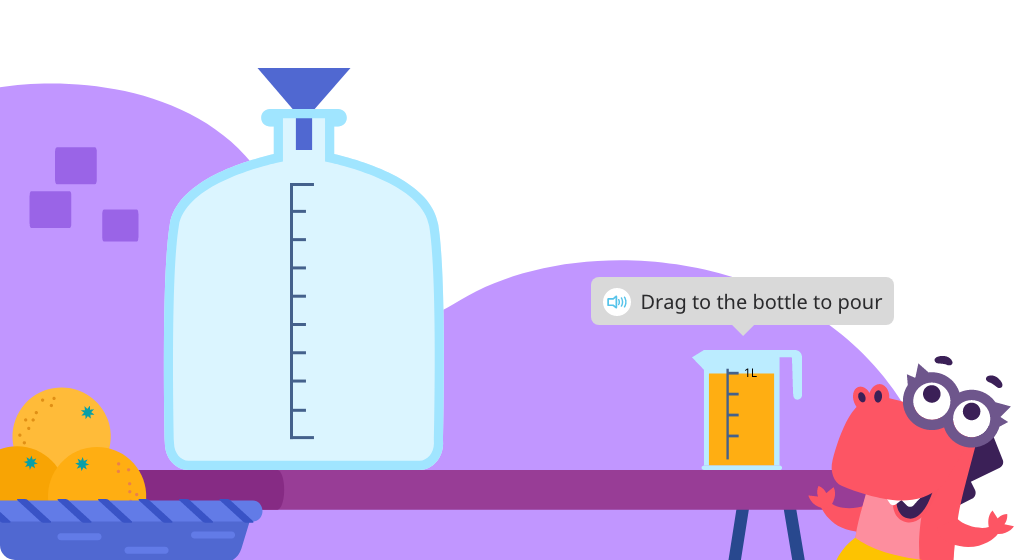
Measure capacity in milliliters
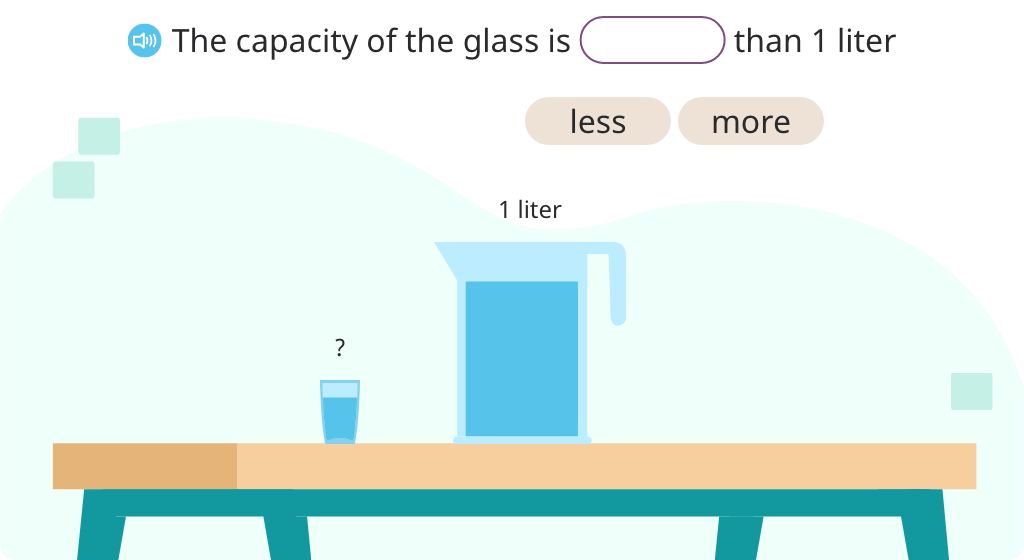
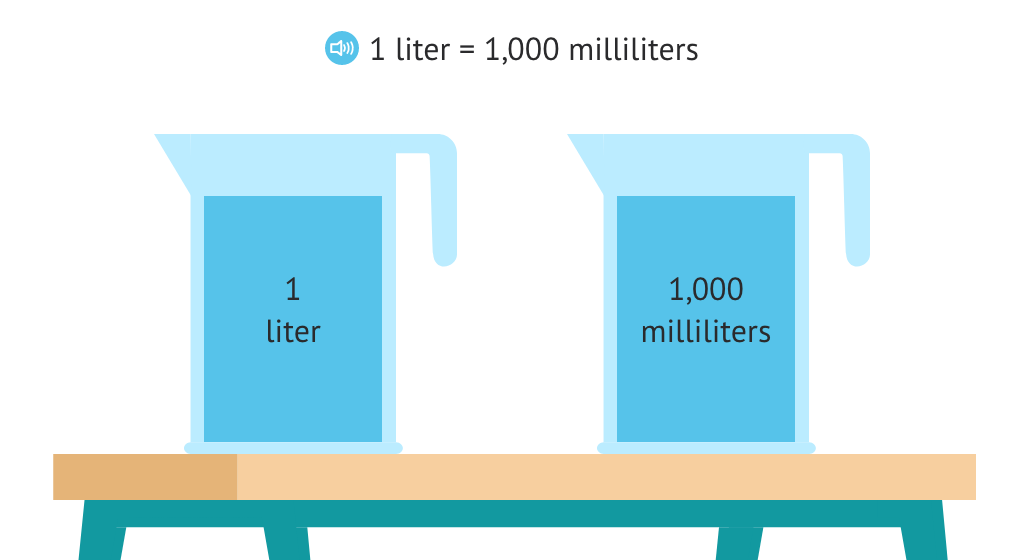
Learn about the relationship between liters and milliliters, and compare the two units of measure
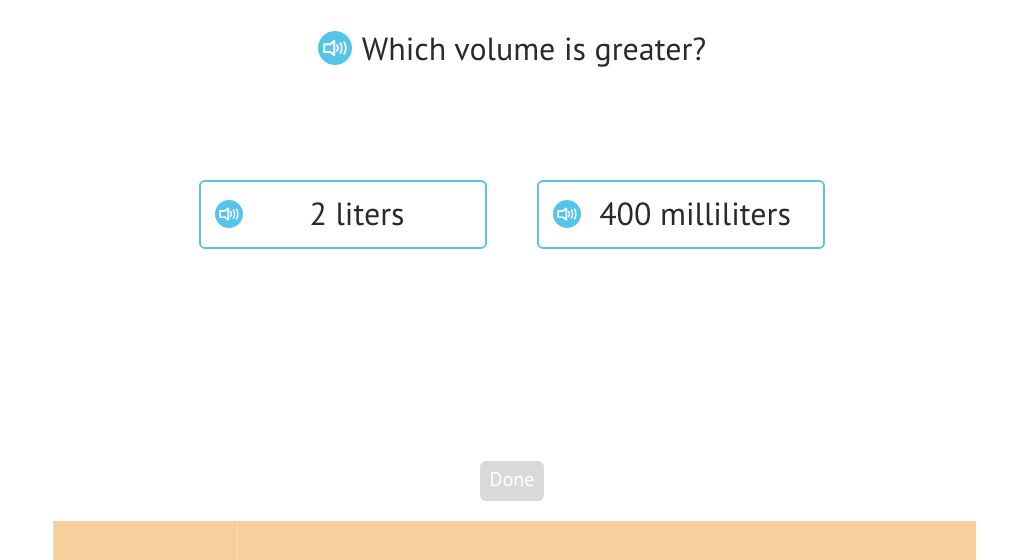
Compare measures in liters and milliliters to determine which is greater or if they are equal
Measure capacity in milliliters
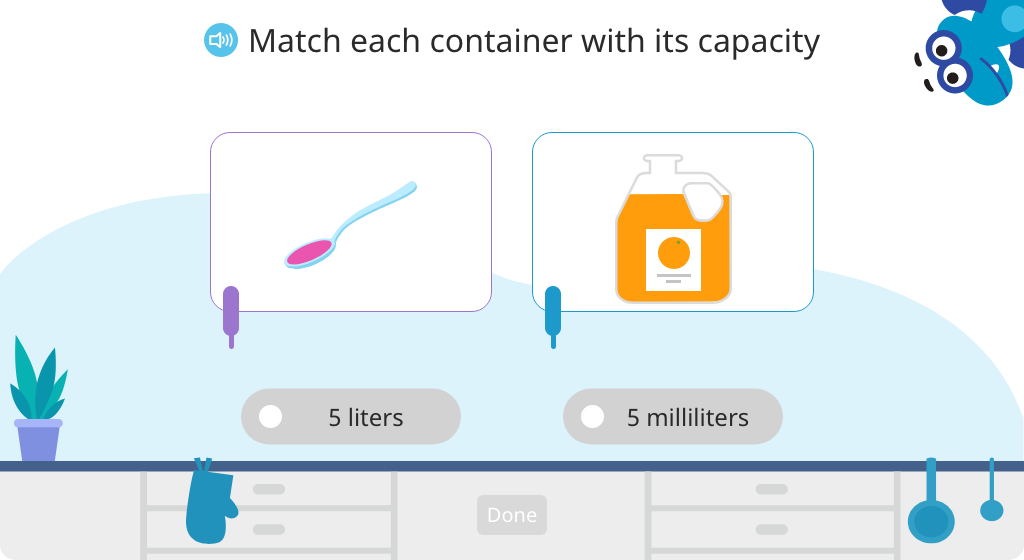
Topic C: Rounding to the Nearest Ten and Hundred
Using a number line to provide context, they learn the rule for rounding up or down to the nearest ten and hundred. Finally, students round 2-, and 3-digit numbers to any given place value.
Identify numbers in the tens, hundreds, or thousands place

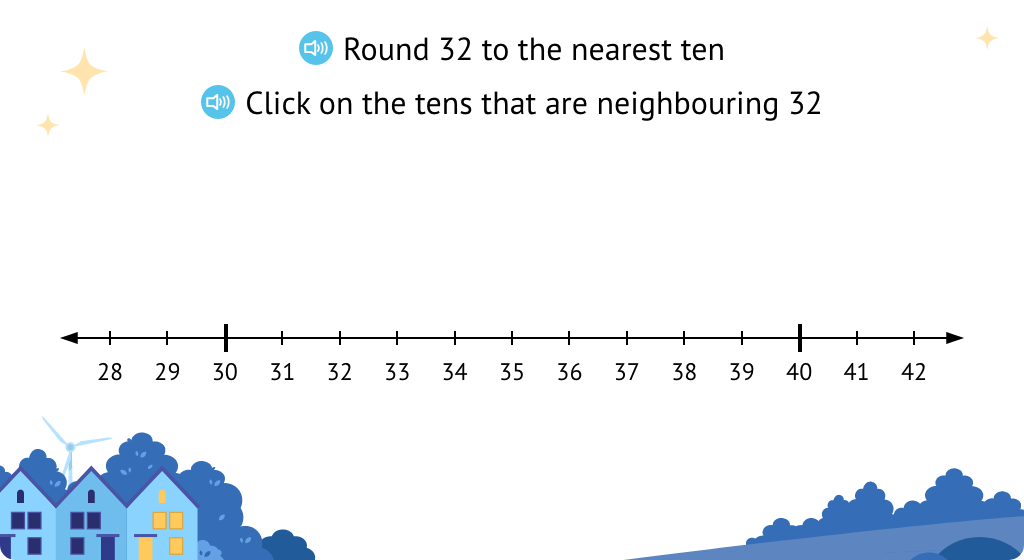
Identify the neighboring tens of a given number on a number line

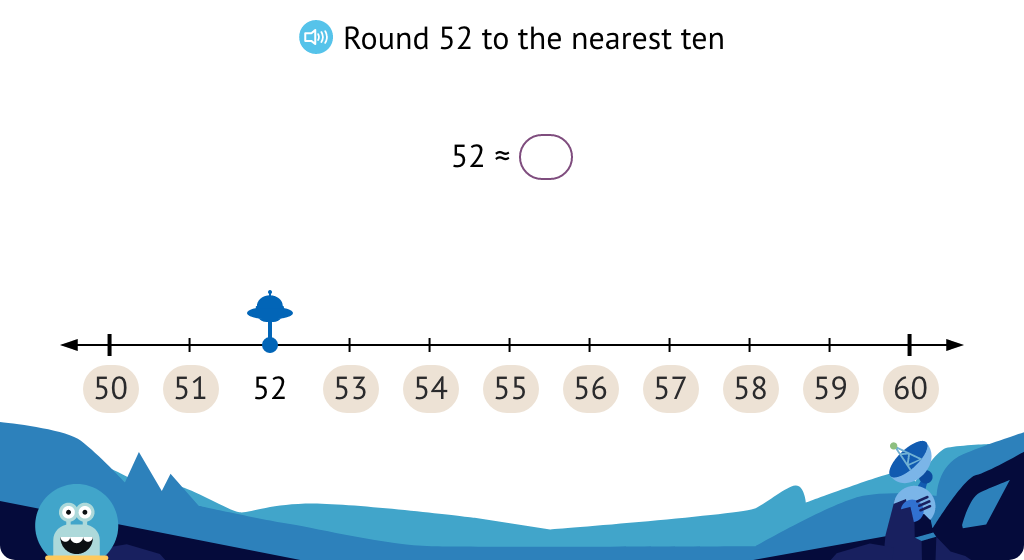
Discover the concept of rounding
Round to the nearest ten using a number line and learn about the approximation symbol

Use the approximation symbol when rounding to the nearest ten using a number line for reference
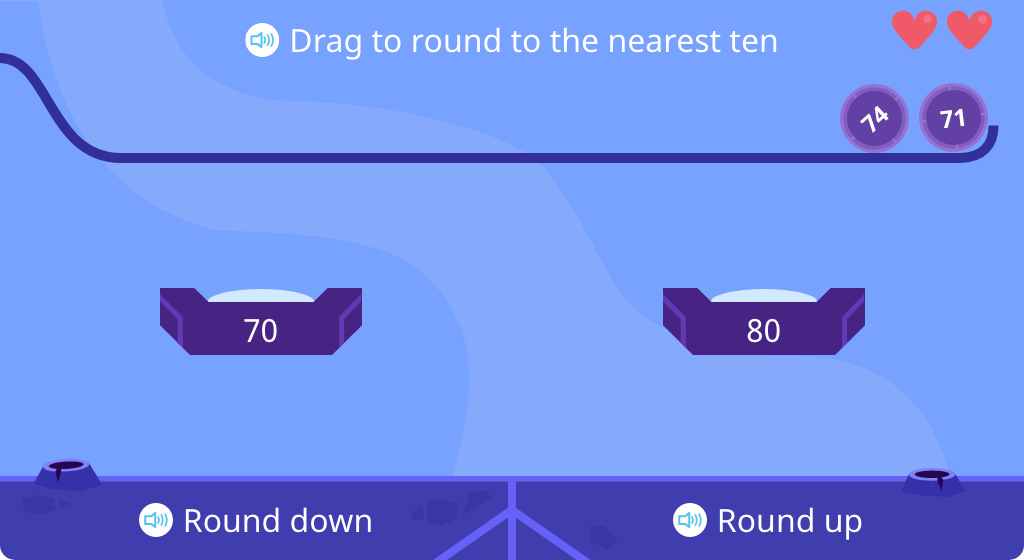
Round to the nearest ten and learn the language "round up" or "round down."
Round to the nearest ten using the language "round up" or "round down."
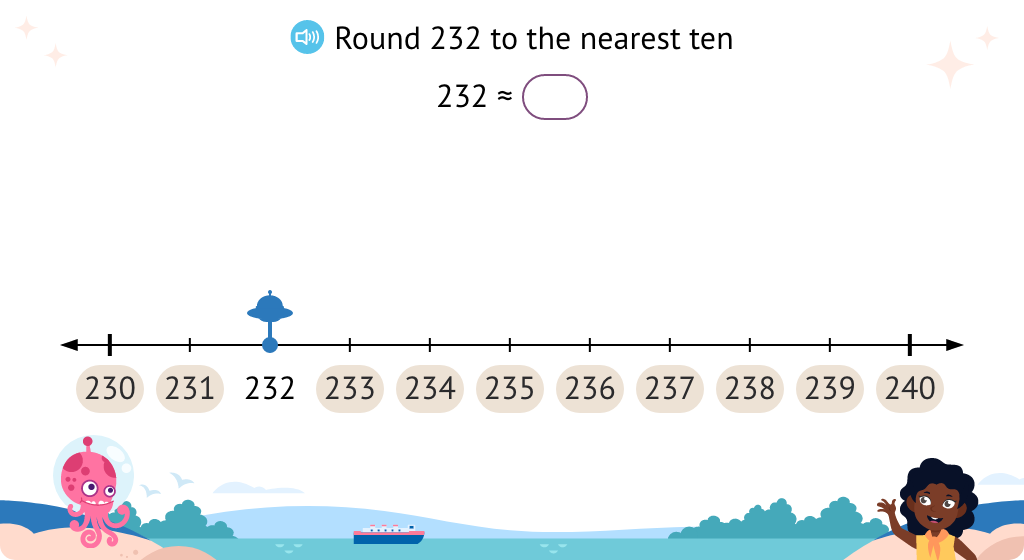
Learn the rule for rounding numbers that are exactly in the middle of two tens

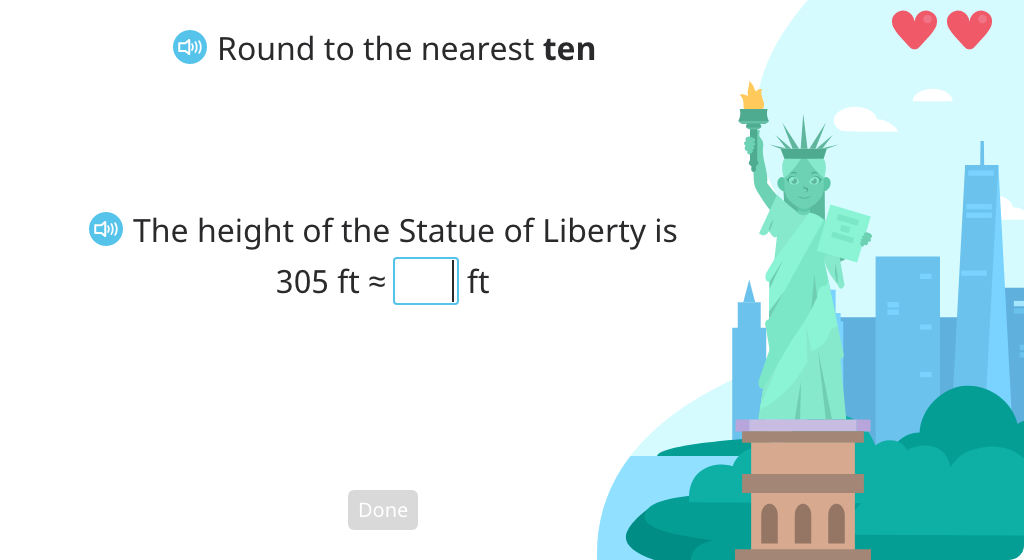
Round a given number to the nearest ten (Part 1)
Round a given number to the nearest ten using the rule for rounding

Round a given number to the nearest ten (Part 2)

Determine the neighboring hundreds of a given number on a number line

Identify the neighboring hundreds of a given number and round to the nearest hundred

Learn the rule for rounding numbers that are exactly in the middle of two hundreds

Determine whether a given number rounds up or down to the nearest hundred
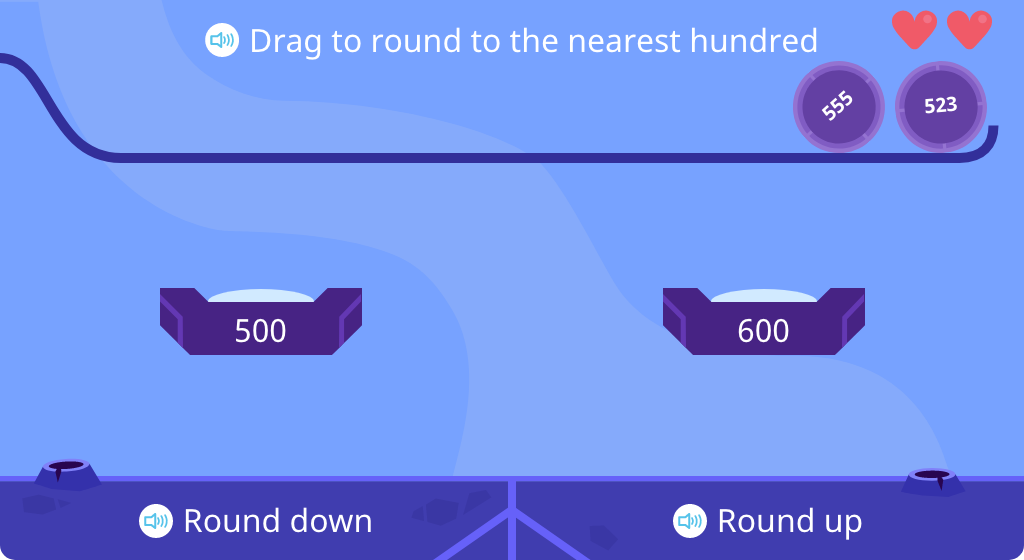
Round a given number to the nearest hundred using the rule for rounding

Round a given number up or down to the nearest hundred

Round the same number to the tens and hundreds

Determine the place to which a number was rounded

Round numbers to the tens or hundreds (Level 1)

Round numbers to the tens or hundreds (Level 2)
Topic D: Two- and Three-Digit Measurement Addition Using the Standard Algorithm
Students review the standard algorithm for addition with regrouping and then use it to solve word problems involving measurements. As they progress, they receive fewer prompts to complete the standard algorithm.
Add 2-digit numbers using the standard algorithm with regrouping
Add 2-digit numbers using the standard algorithm with regrouping to solve word problems
Add 3-digit numbers using the standard algorithm with regrouping (Level 1)
Add 3-digit numbers using the standard algorithm with regrouping (Level 2)

Add 3-digit numbers using the standard algorithm with regrouping to solve word problems (Level 1)

Add 3-digit numbers using the standard algorithm with regrouping to solve word problems (Level 2)
Add 3-digit numbers using the standard algorithm with regrouping (Level 3)

Add 3-digit numbers using the standard algorithm with regrouping to solve word problems (Level 3)

Topic E: Two- and Three-Digit Measurement Subtraction Using the Standard Algorithm
Students review the standard algorithm for subtraction with regrouping and then use it to solve word problems involving measurements. As they progress, they receive fewer prompts to complete the standard algorithm.
Subtract 2-digit numbers using the standard algorithm with regrouping
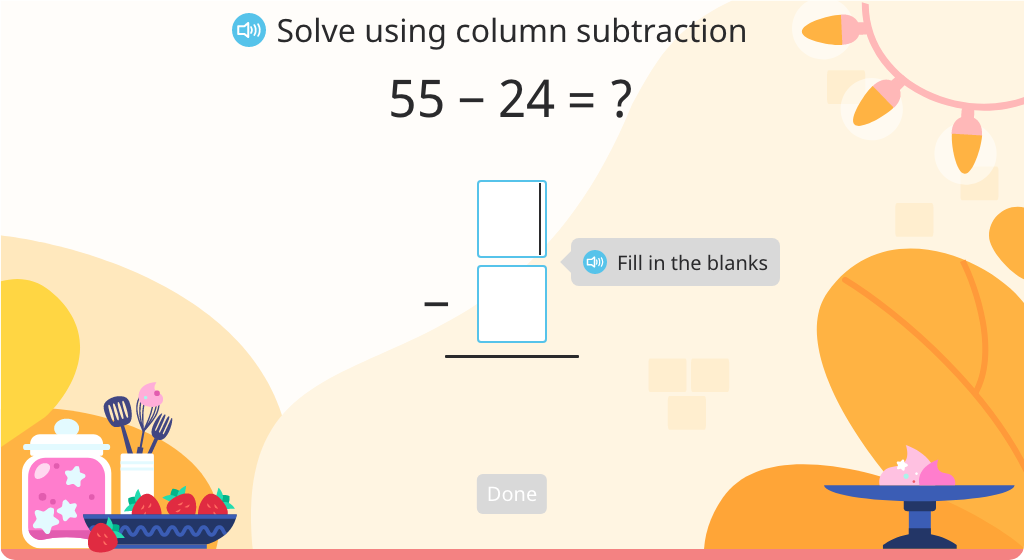
Subtract 2-digit numbers using the standard algorithm with regrouping to solve word problems

Subtract 3-digit numbers using the standard algorithm with regrouping (Level 1)
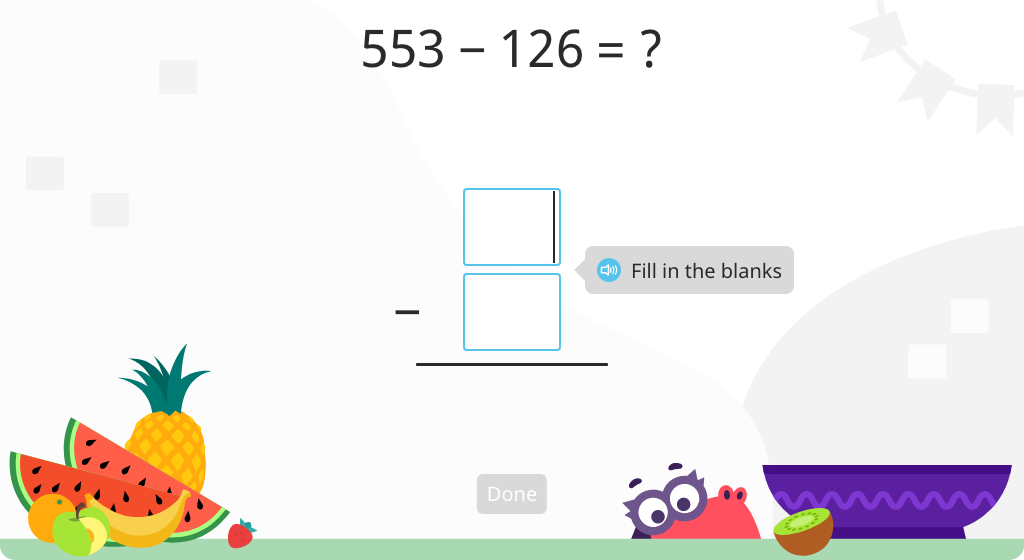
Subtract 3-digit numbers using the standard algorithm with regrouping (Level 2)

Subtract 3-digit numbers using the standard algorithm with regrouping to solve word problems (Level 1)
Subtract 3-digit numbers using the standard algorithm with regrouping (Level 3)

Subtract 3-digit numbers using the standard algorithm with regrouping (Level 4)

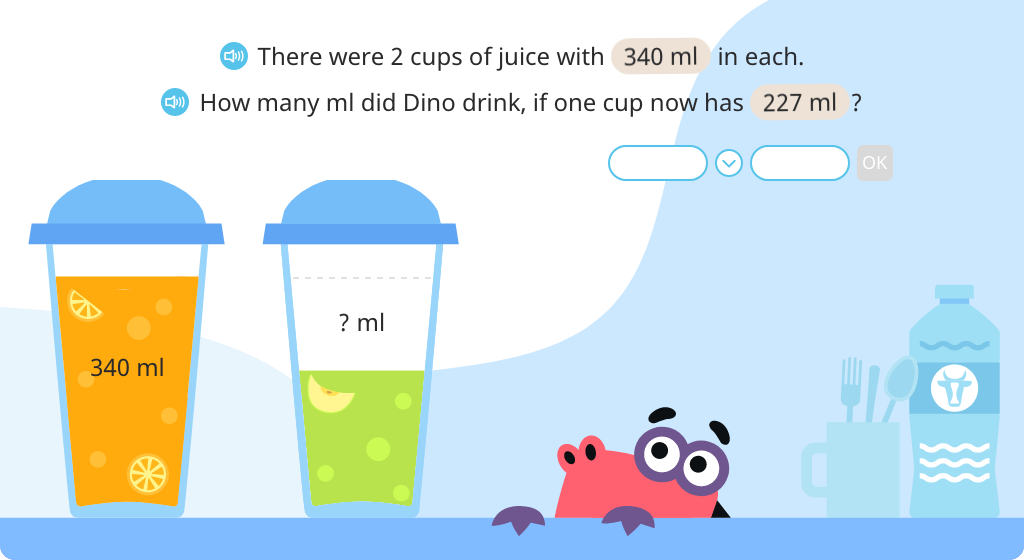
Subtract 3-digit numbers using the standard algorithm with regrouping to solve word problems (Level 2)

MODULE 3. Multiplication and Division with Units of 0, 1, 6-9, and Multiples of 10
Topic A: The Properties of Multiplication and Division
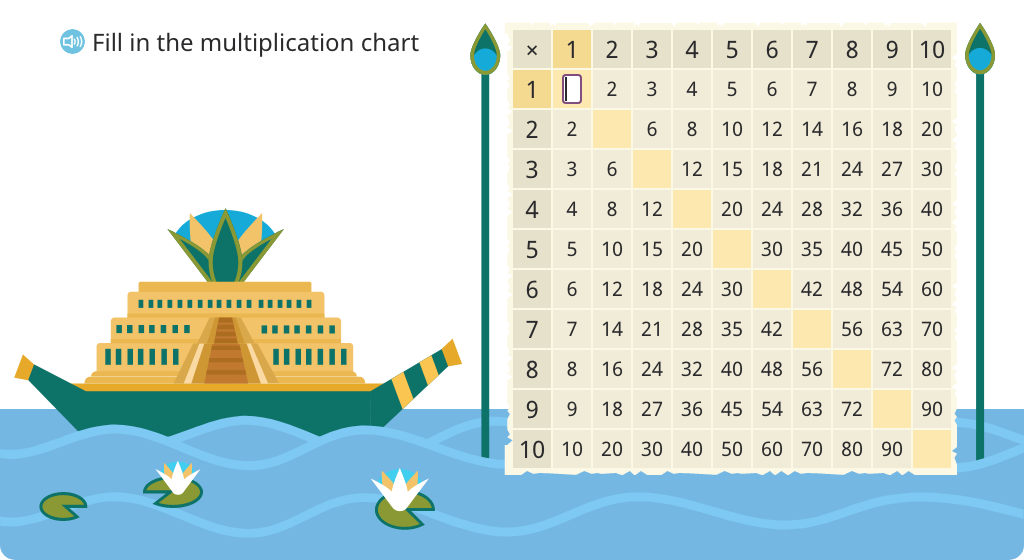
Students enrich their understanding of multiplication and division by introducing the multiplication chart and the commutative property (or 'turnaround facts') of multiplication. They continue to build fact fluency, adding factors 6-9 to their repertoire.
Illustrate the commutative property by labeling arrays and tape diagrams

Solve equations that illustrate the commutative property

Determine missing products in a multiplication chart (factors to 5)
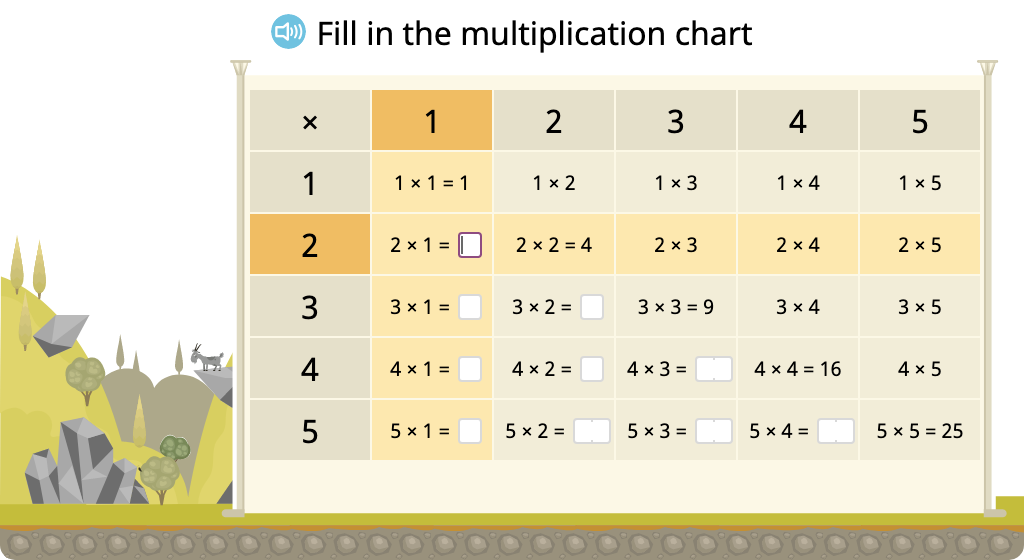
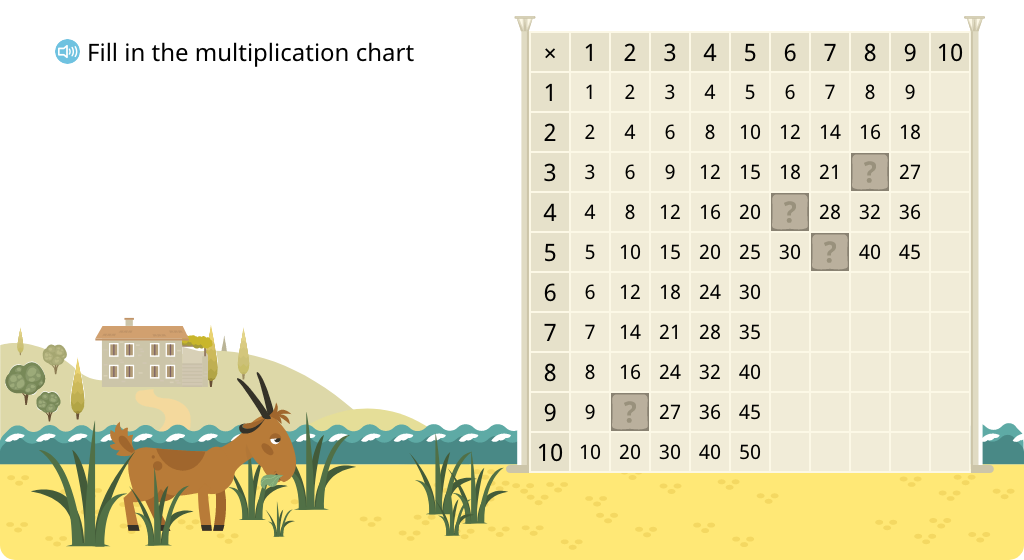
Determine missing products in a multiplication chart (one factor > 5)
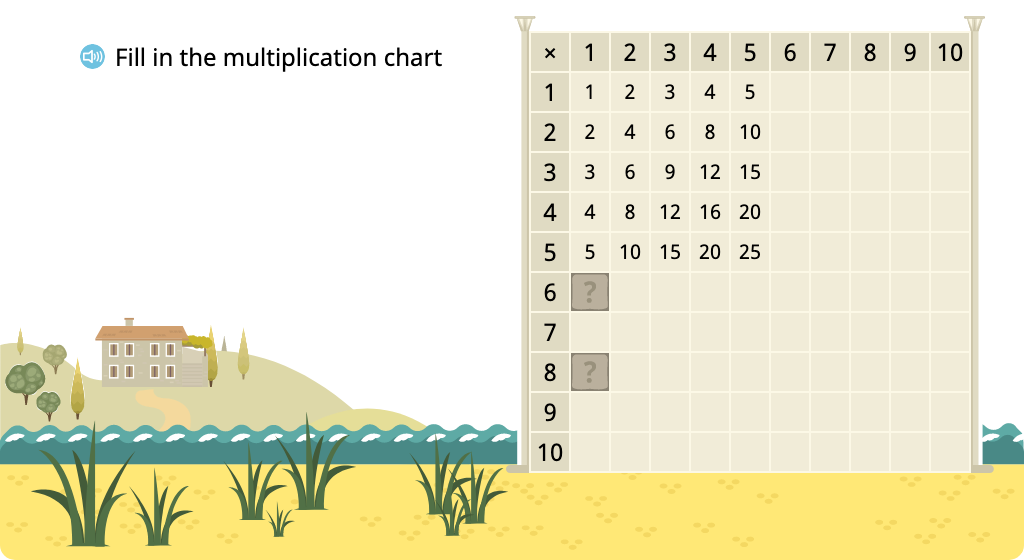
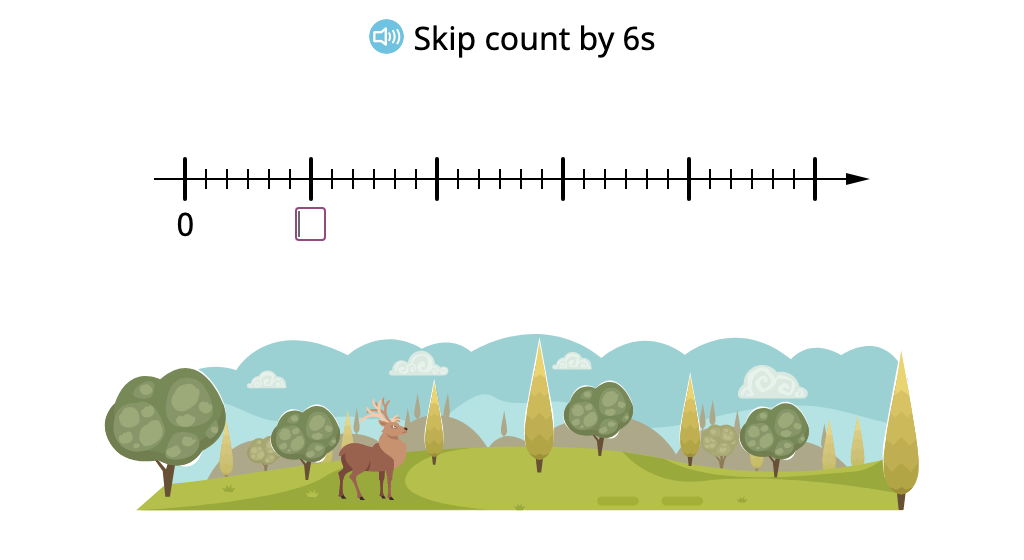
Skip count by 6
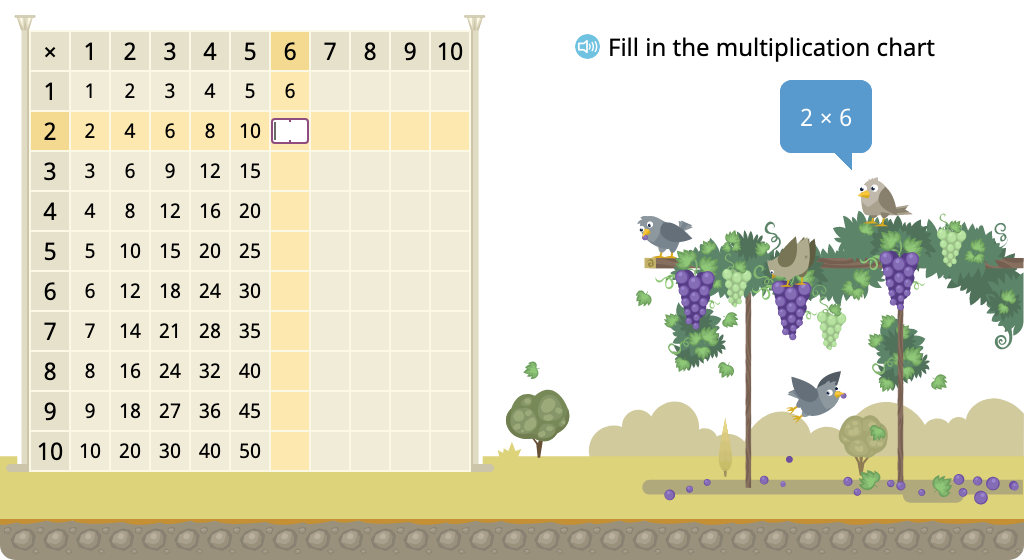
Determine multiples of 6 in a multiplication chart
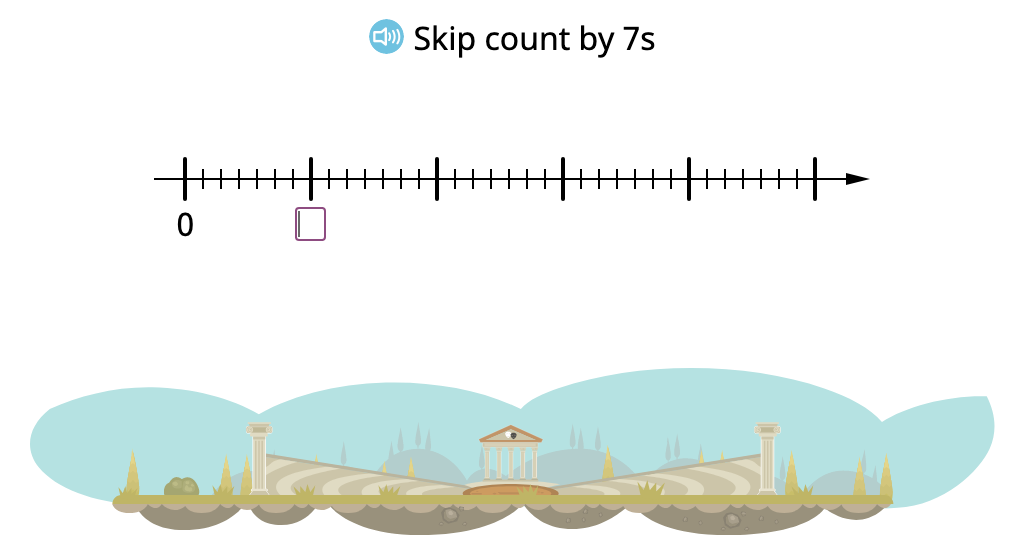
Skip count by 7
Determine multiples of 7 in a multiplication chart
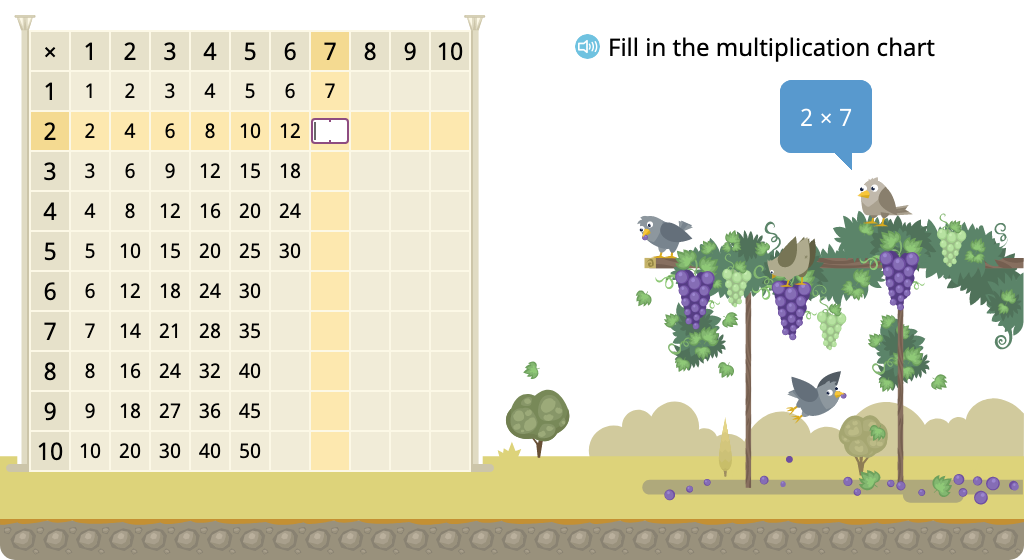
Skip count by 8
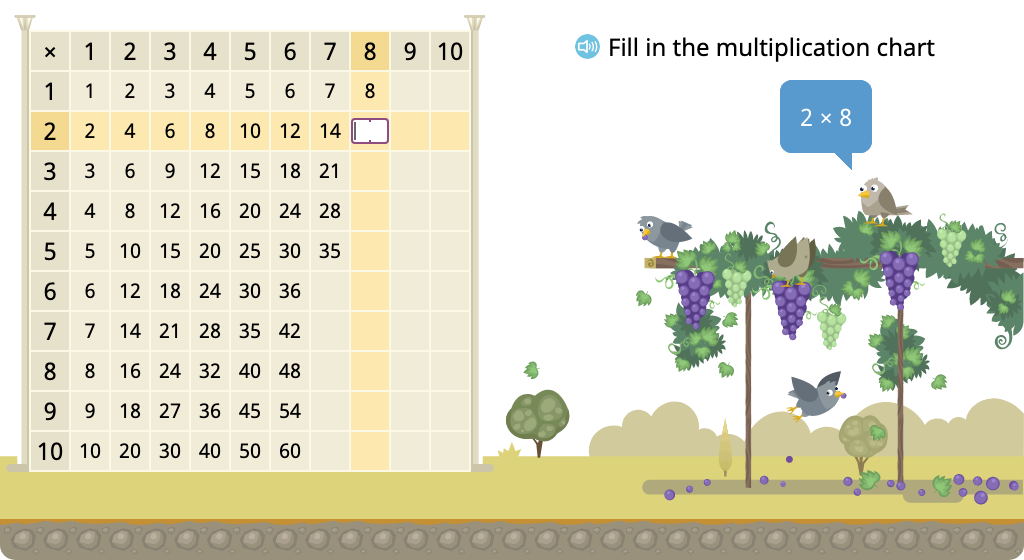
Determine multiples of 8 in a multiplication chart
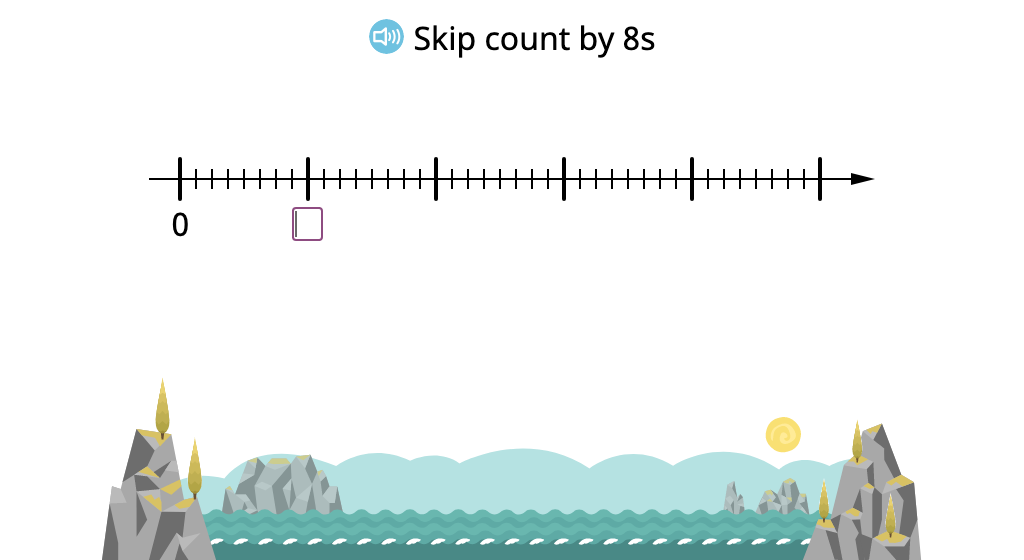
Skip count by 9
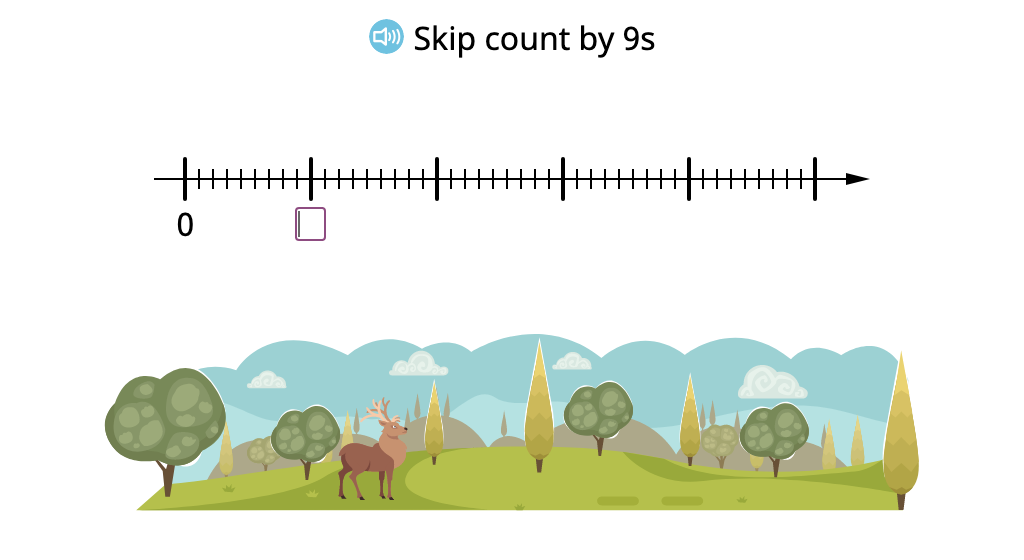
Determine multiples of 9 in a multiplication chart
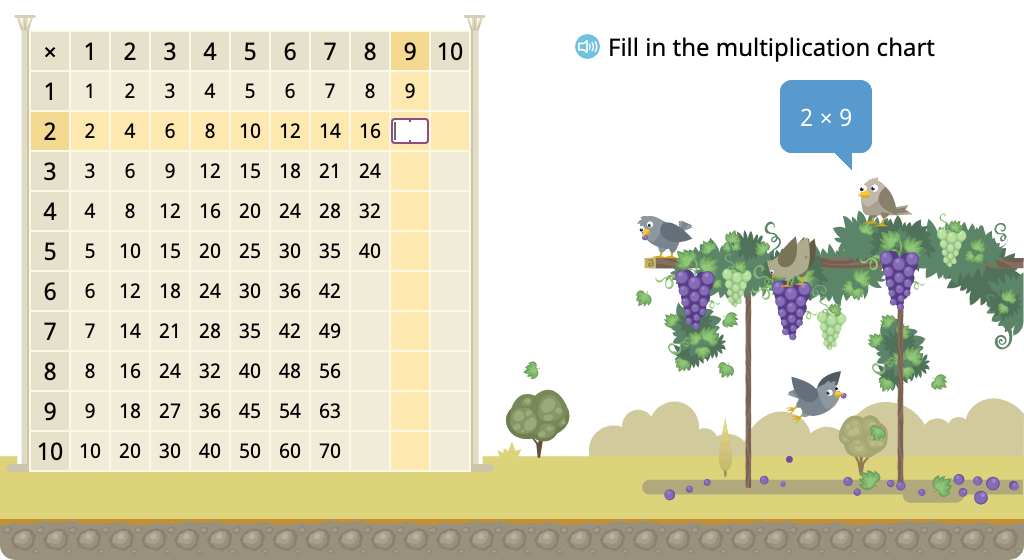
Determine missing products in a multiplication chart (one factor > 5)
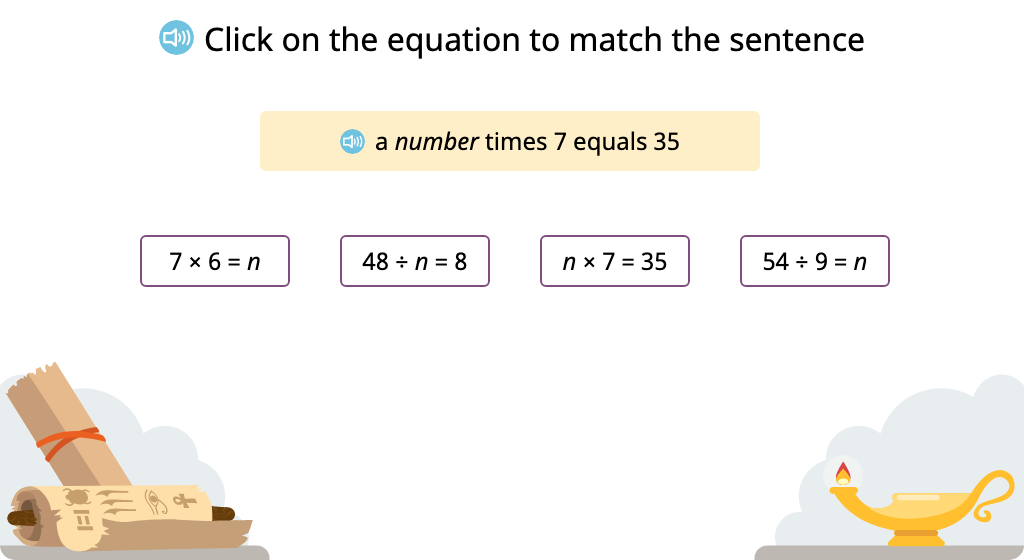
Solve for an unknown represented by a letter in multiplication equations

Solve for an unknown represented by a letter in division equations

Match an equation containing an unknown to a statement
Solve for an unknown represented by a letter in multiplication and division equations

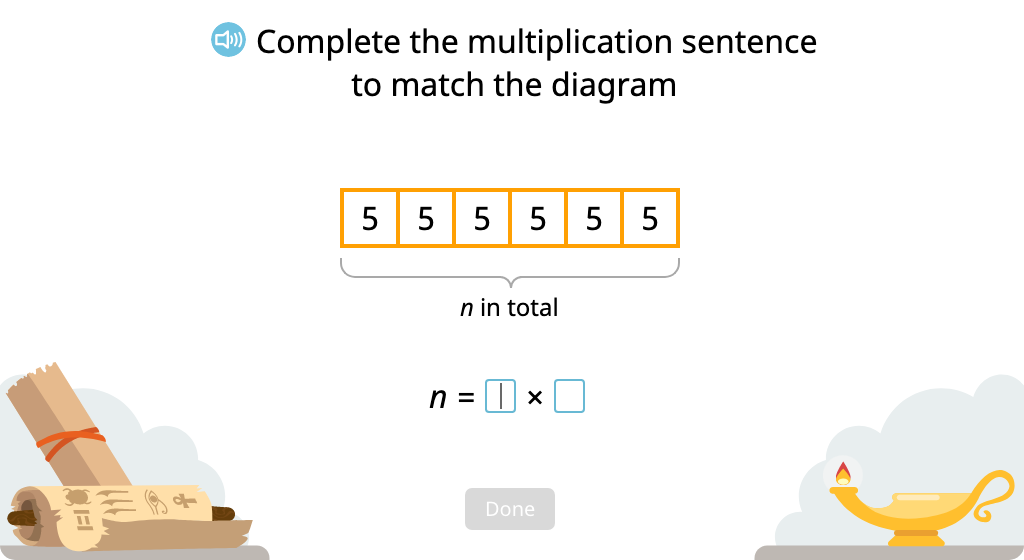
Compose and solve a multiplication equation based on a tape diagram
Solve a multiplication word problem using a tape diagram

Topic B: Multiplication and Division Using Units of 6 and 7
Students begin with familiar tasks taken to a more challenging level with higher factors. They deepen their understanding of the relationship between multiplication and division as well as their fact fluency.
Skip count by 6
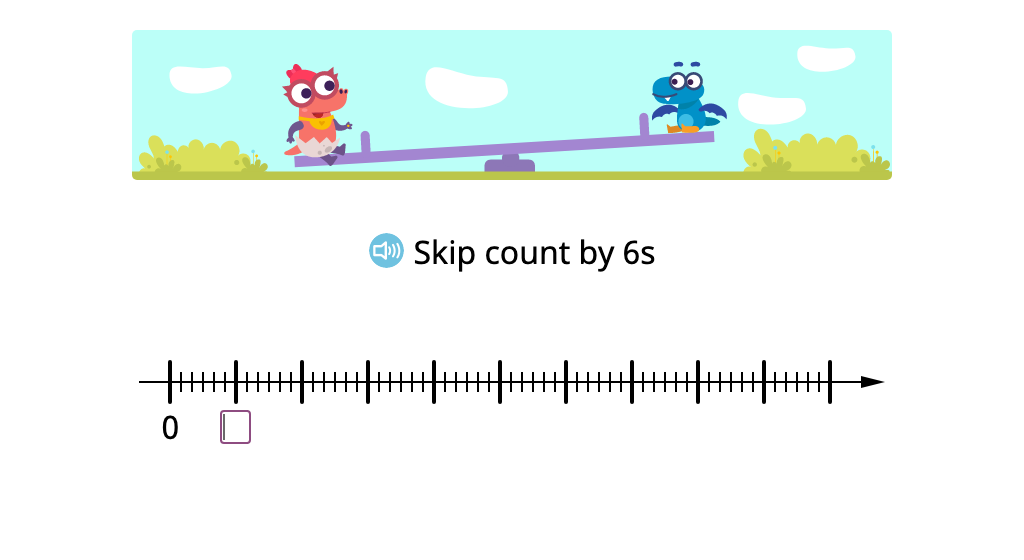
Determine multiples of 6 in a multiplication chart
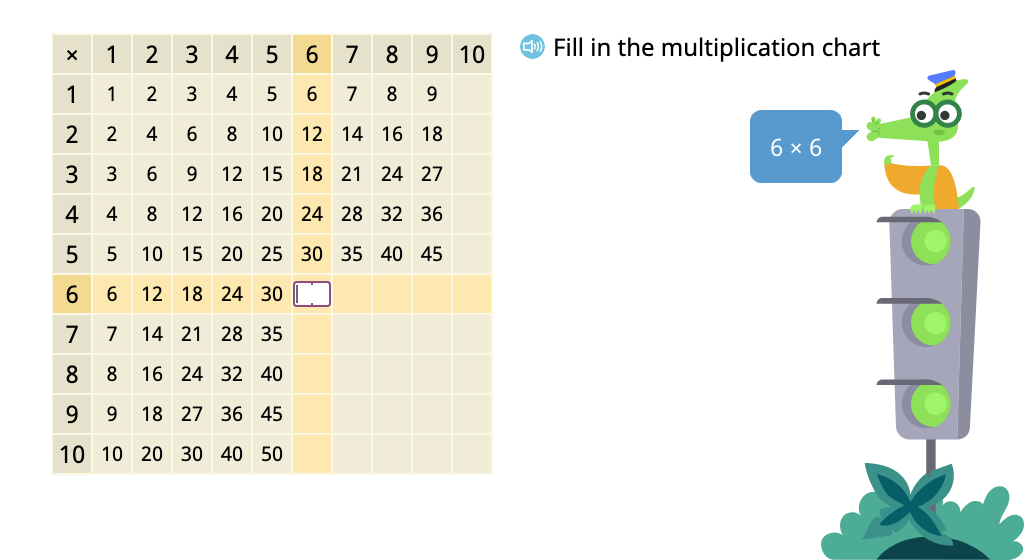
Determine products of 6 in a times table with and without an array model
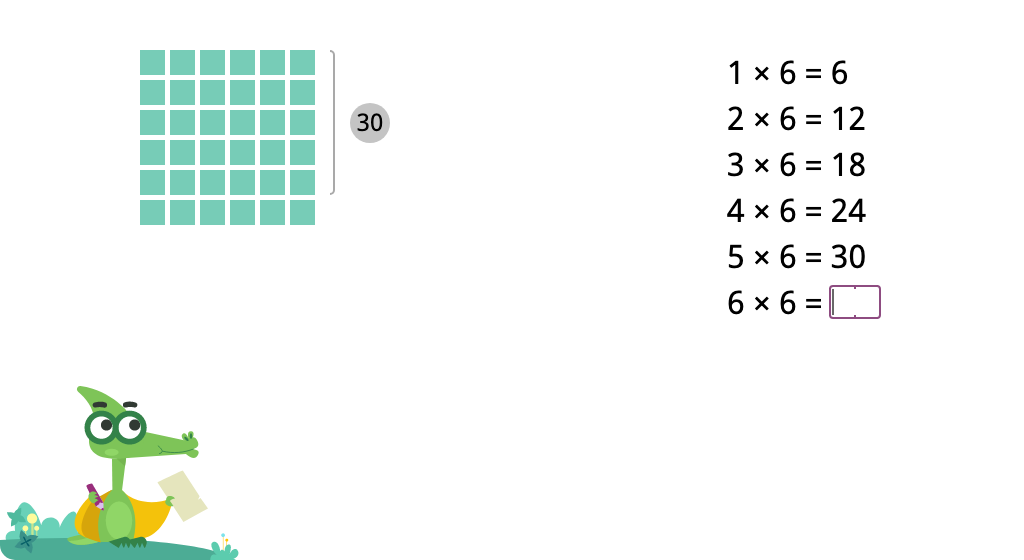
Determine products of 6 in a times table

Solve division problems with a divisor of 6 based on its relationship to multiplication
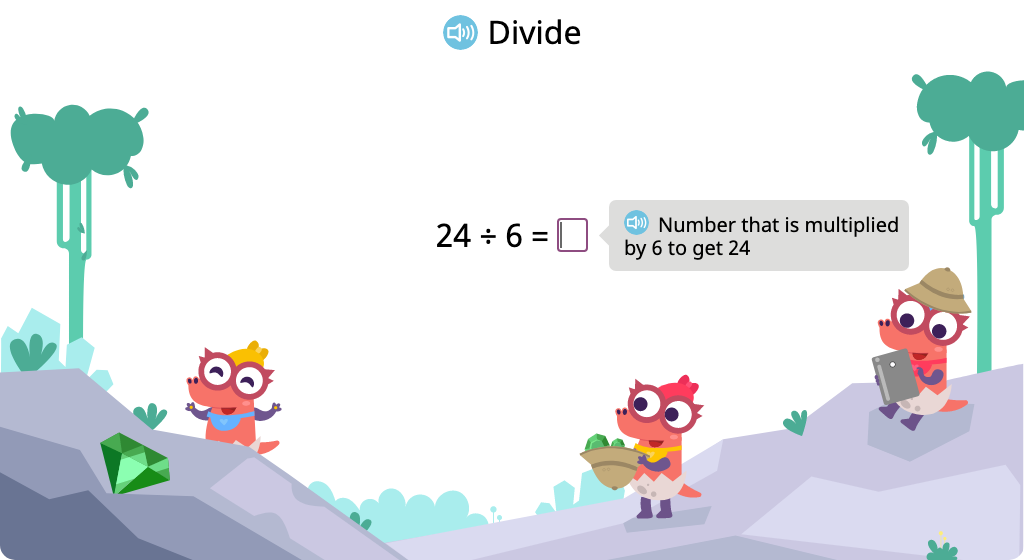
Solve division problems with a divisor of 6 (Level 1)
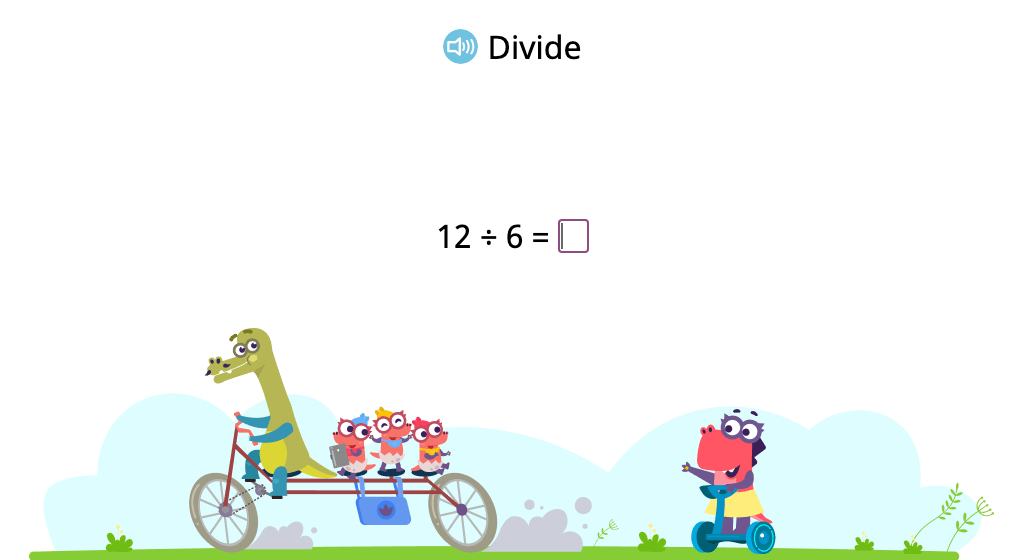
Solve division problems with a divisor of 6 (Level 2)
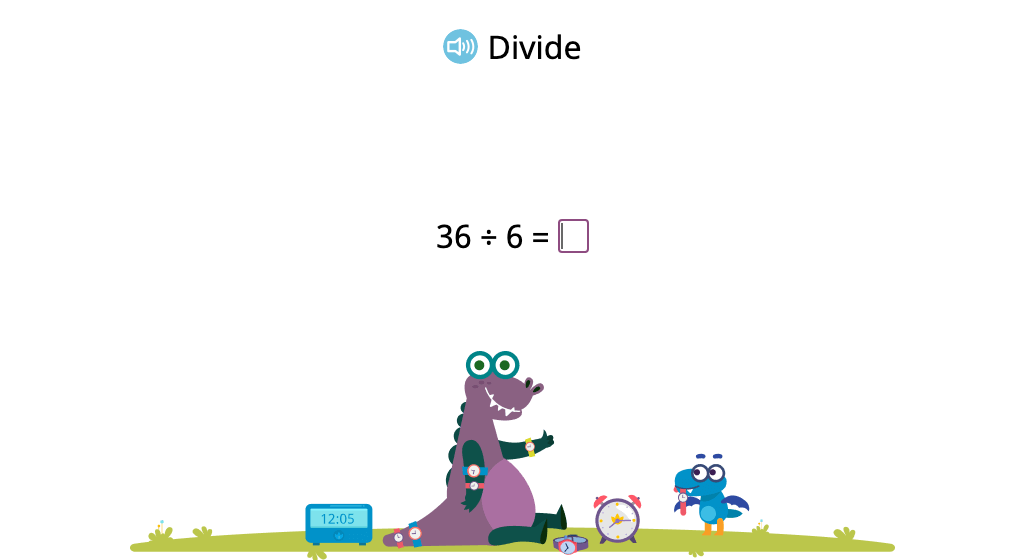
Skip count by 7
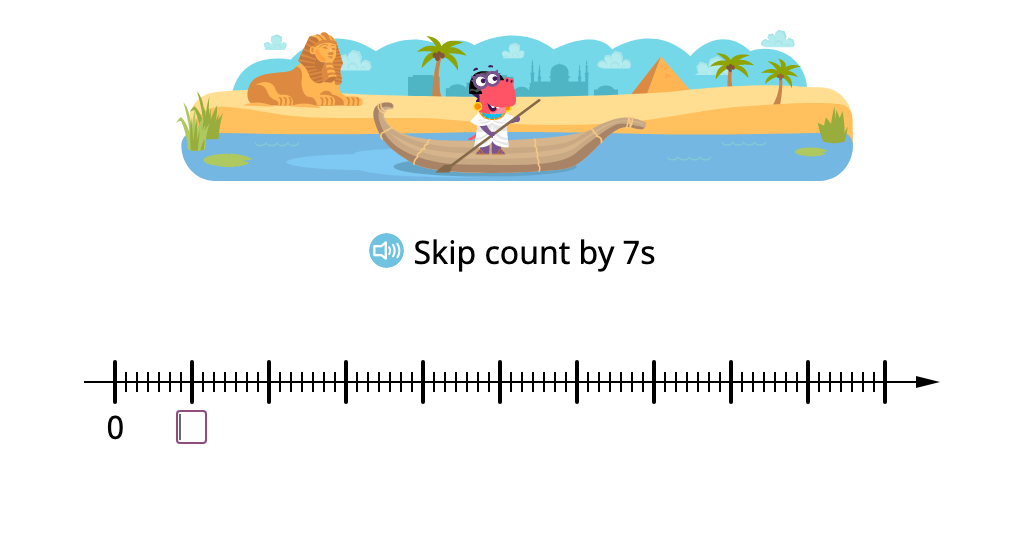
Determine multiples of 7 in a multiplication chart

Determine products of 7 in a times table with and without an array model
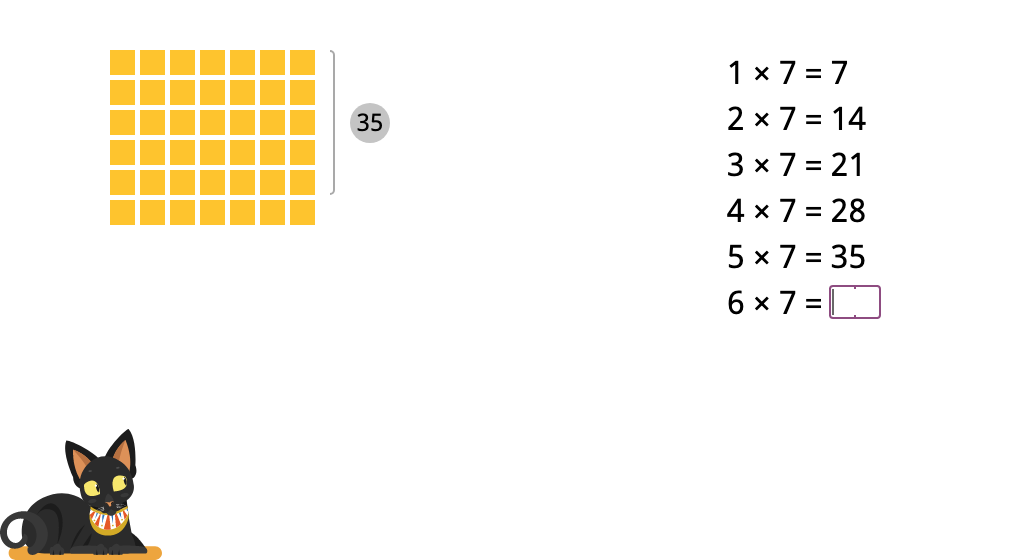
Determine products of 7 in a times table

Solve division problems with a divisor of 7 based on its relationship to multiplication

Solve division problems with a divisor of 7 (Level 1)

Solve division problems with a divisor of 7 (Level 2)

Solve multiplication equations using the break apart and distribute strategy
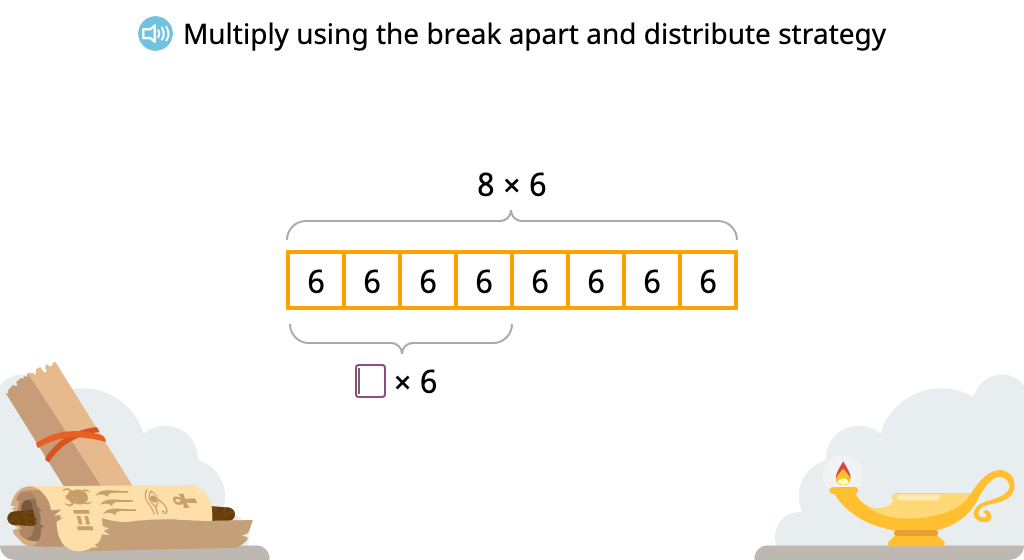
Solve for an unknown represented by a letter in multiplication equations

Solve for an unknown represented by a letter in division equations

Solve a word problem using a tape diagram and the relationship between multiplication and division
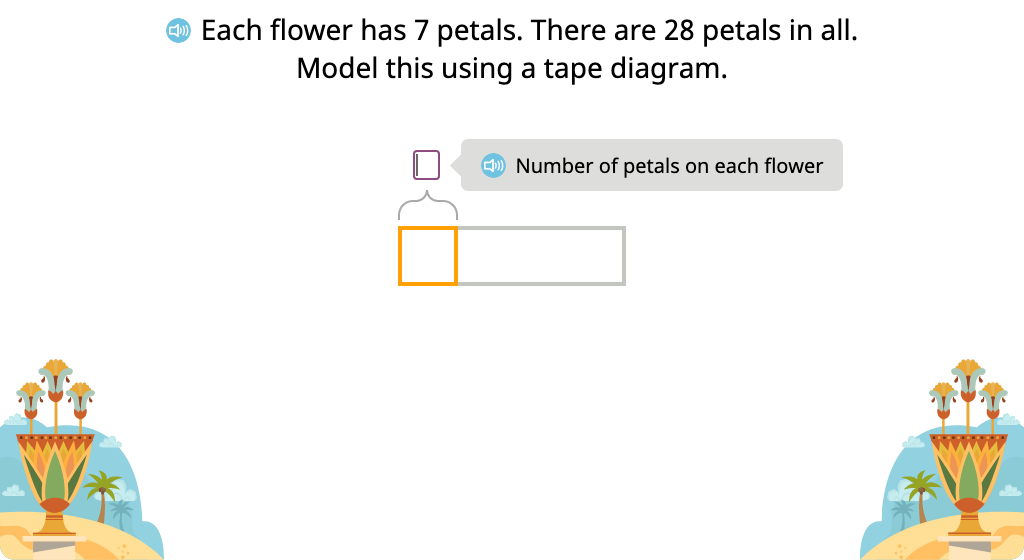
Topic C: Multiplication and Division Using Units up to 8
In addition to extending students' mastery of multiplication and division to include 8, they are also introduced to multi-step equations that use parentheses. Using illustrations and step-by-step instruction, students learn that parentheses and order of operations do not affect multiplication-only equations. They also continue to build their mastery of the break apart and distribute strategy.
Skip count by 8
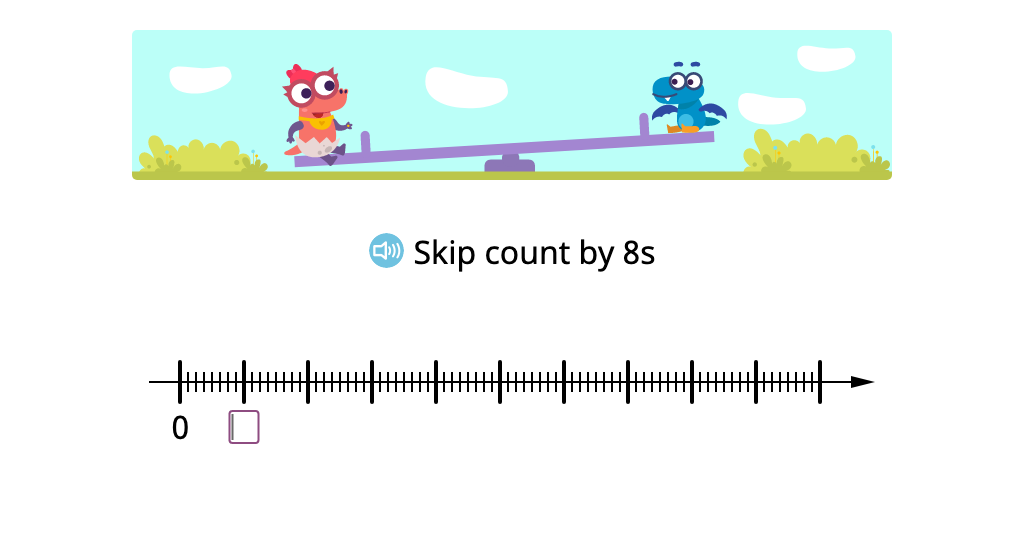
Determine multiples of 8 in a multiplication chart
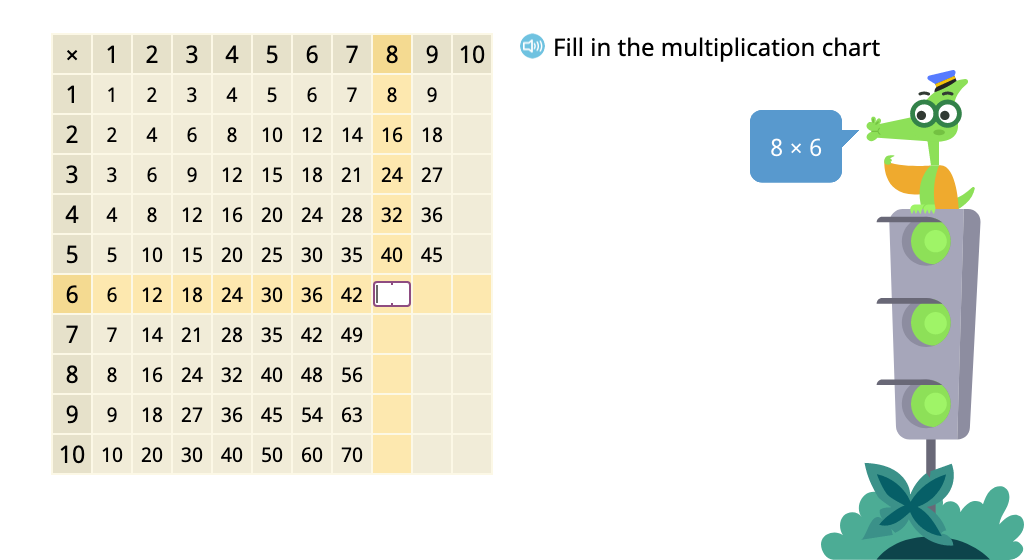
Determine products of 8 in a times table with and without an array model
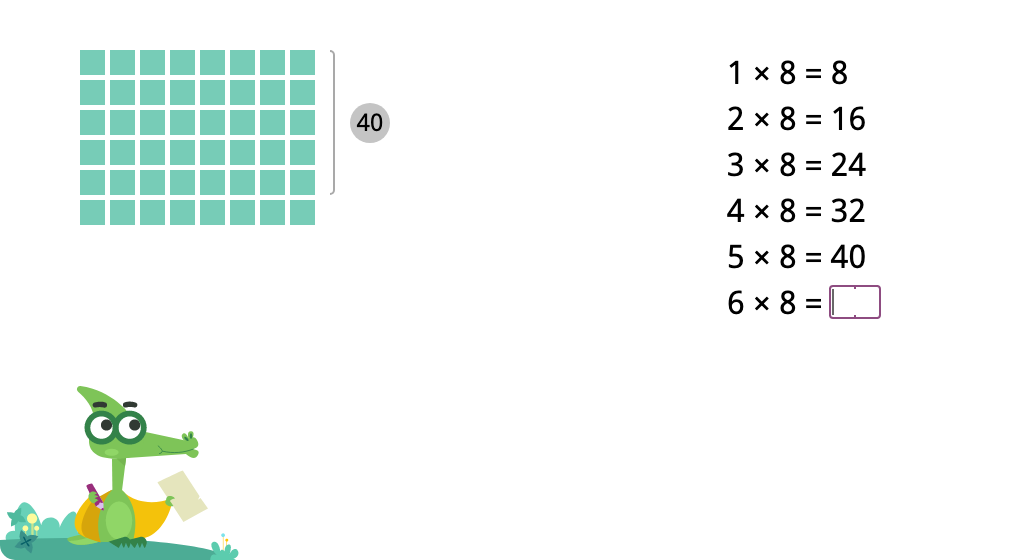
Determine products of 8 in a times table

Solve division problems with a divisor of 8 based on its relationship to multiplication
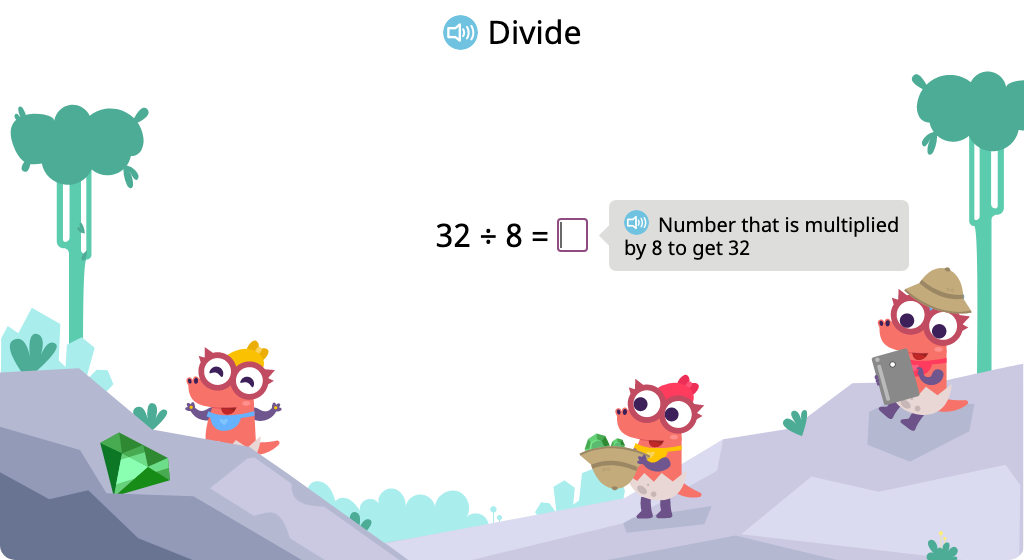
Solve division problems with a divisor of 8 (Level 1)
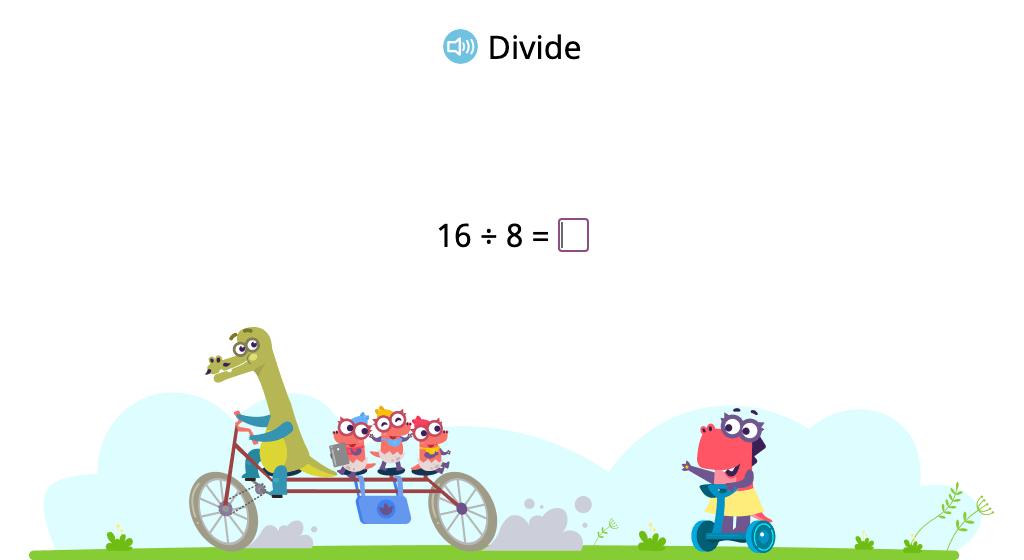
Solve division problems with a divisor of 8 (Level 2)
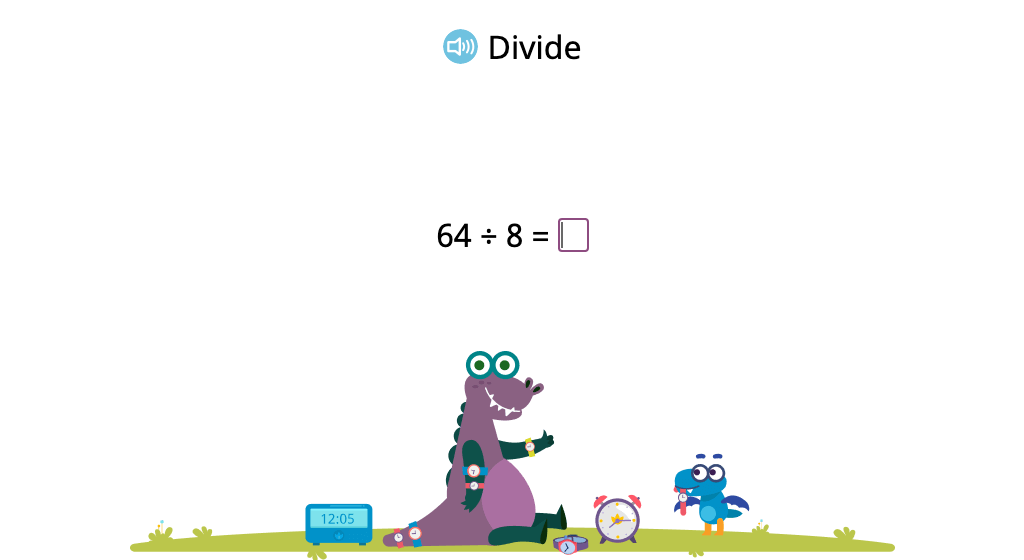
Identify equal expressions

Review operations
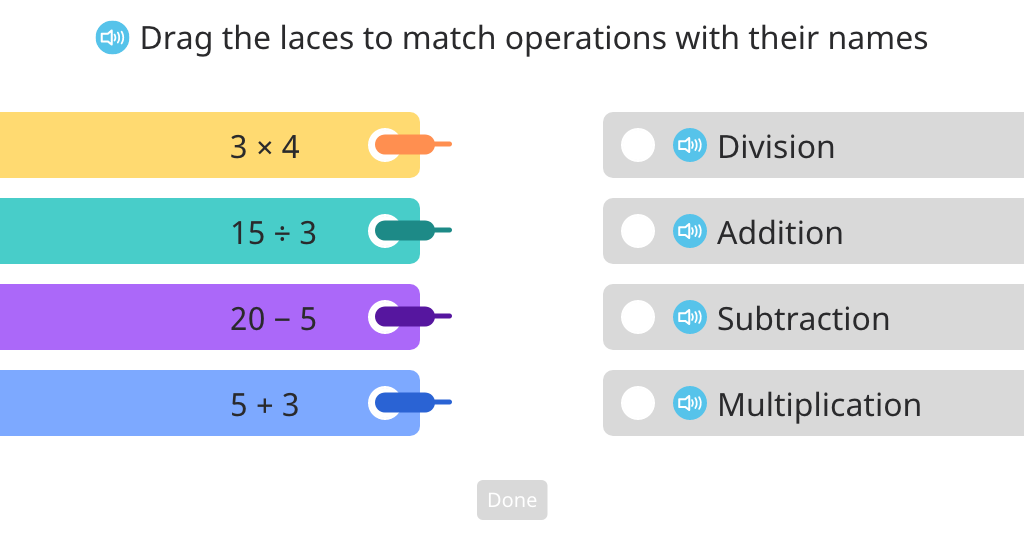
Use parentheses to show the order of operations

Solve two-operation expressions with parentheses (Level 1)
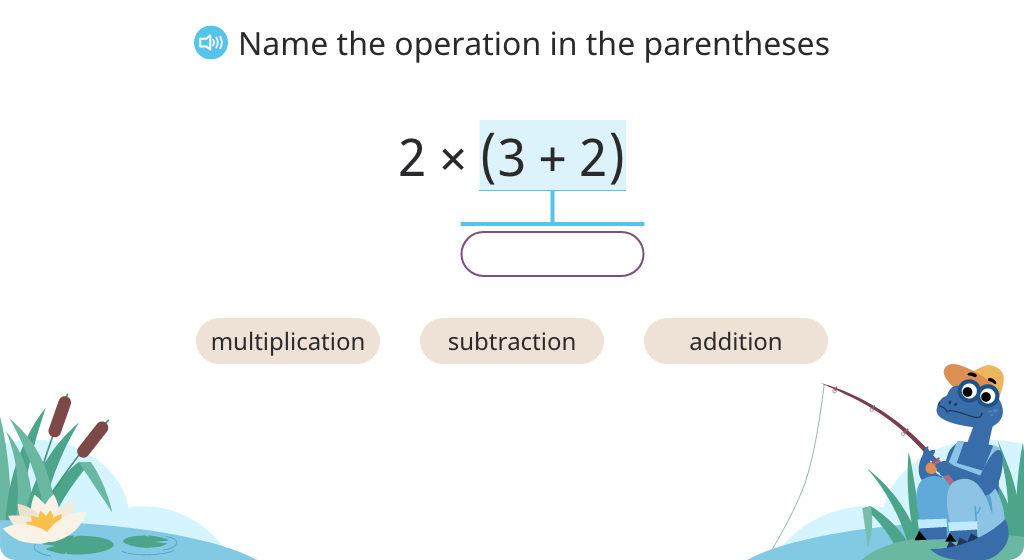
Solve two-operation expressions with parentheses (Level 2)

Solve two-operation expressions with parentheses (Level 3)

Solve two-operation expressions with parentheses (Level 4)

Solve two-operation expressions with parentheses (Level 5)
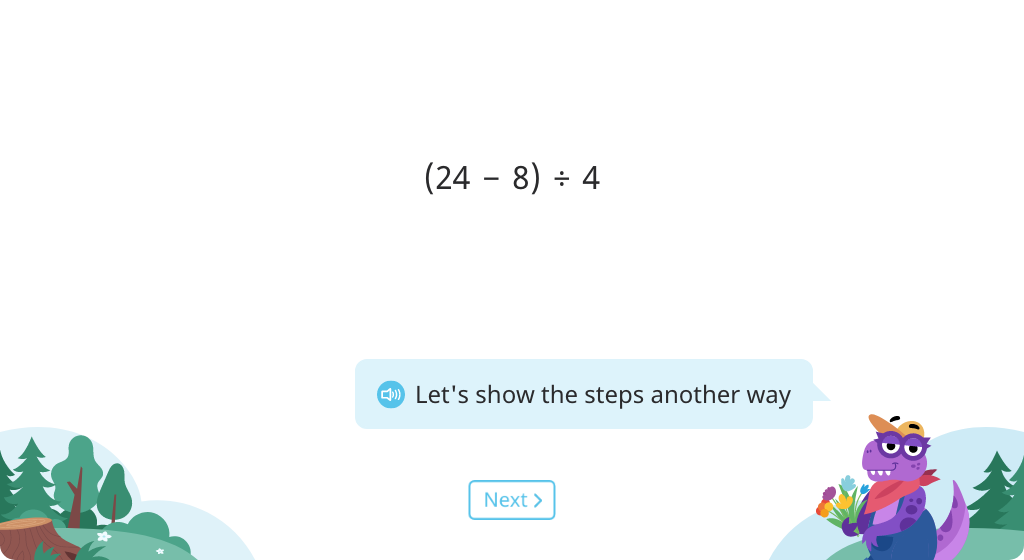
Solve three-operation expressions with parentheses

Solve multi-operation expressions with parentheses
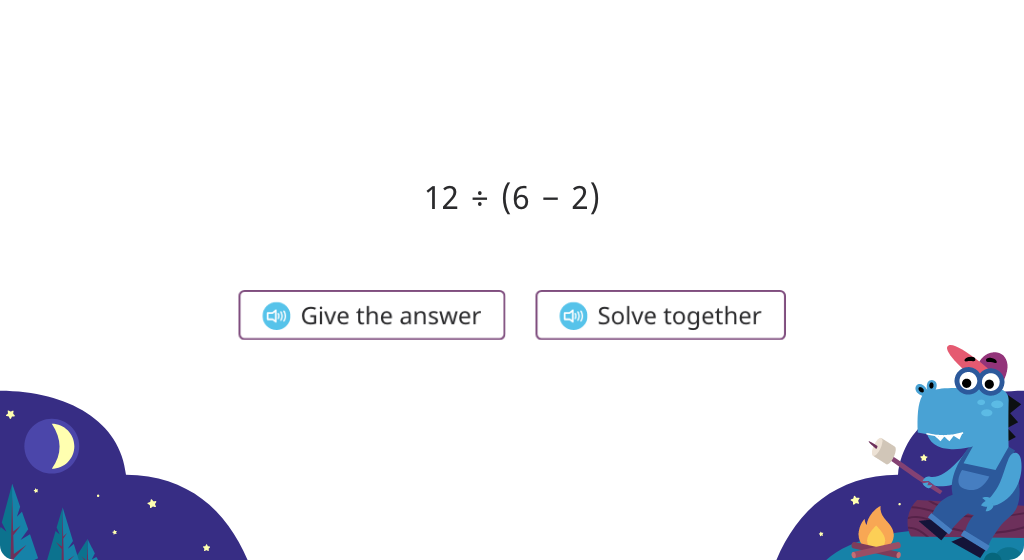
Solve the same expression with a different order of operations
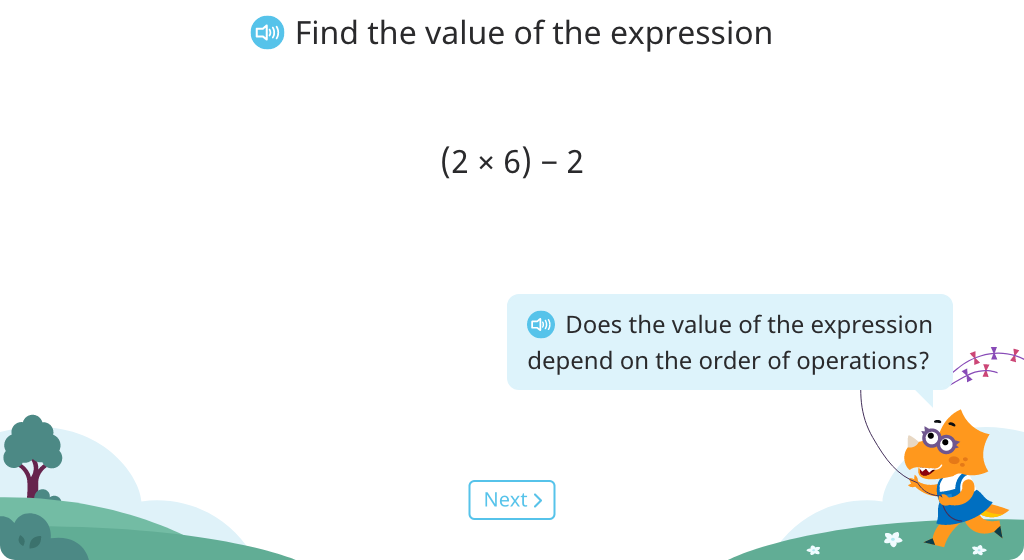
Match equal expressions

Determine which expression is true

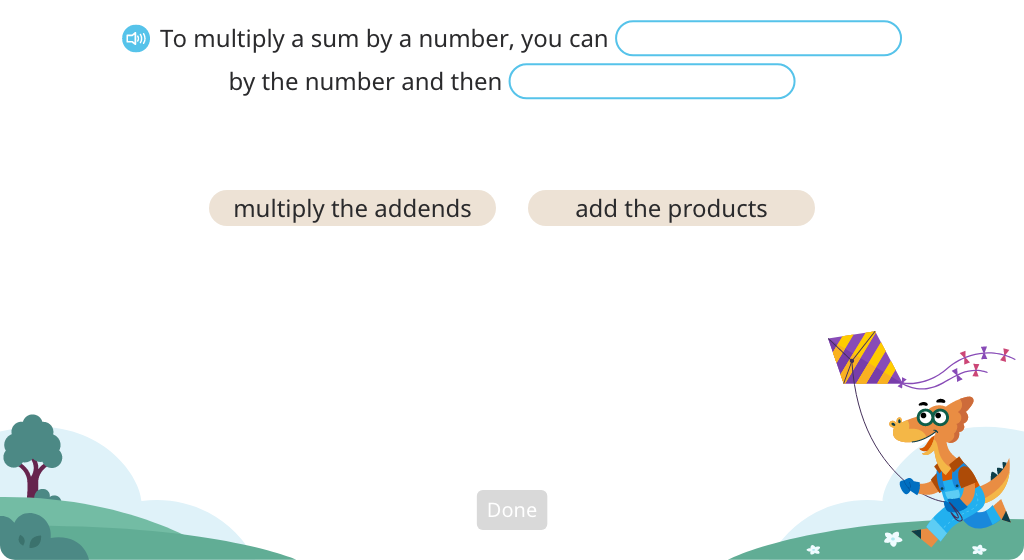
Explore the distributive property of multiplication
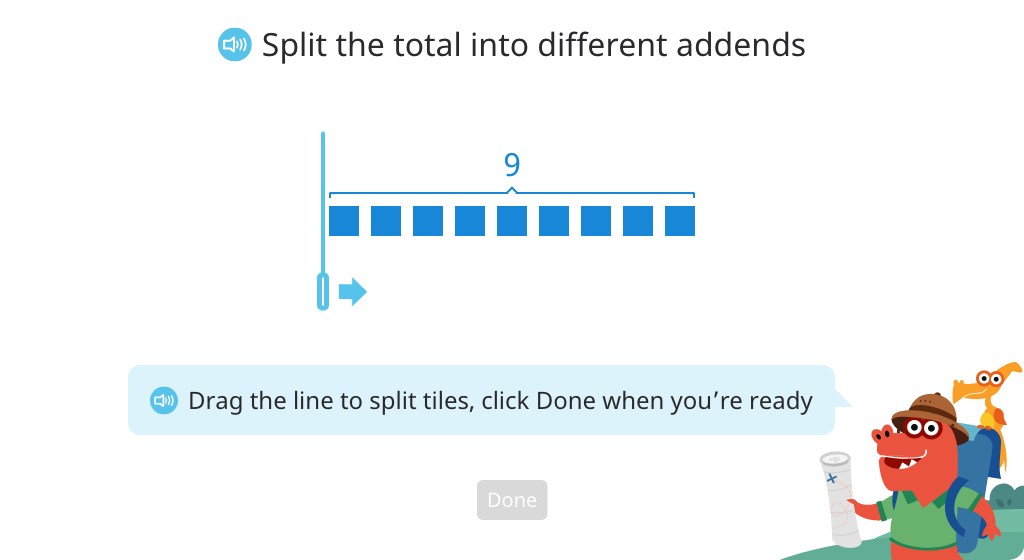
Use the distributive property of multiplication to solve equations (Level 1)

Use the distributive property of multiplication to solve equations (Level 2)
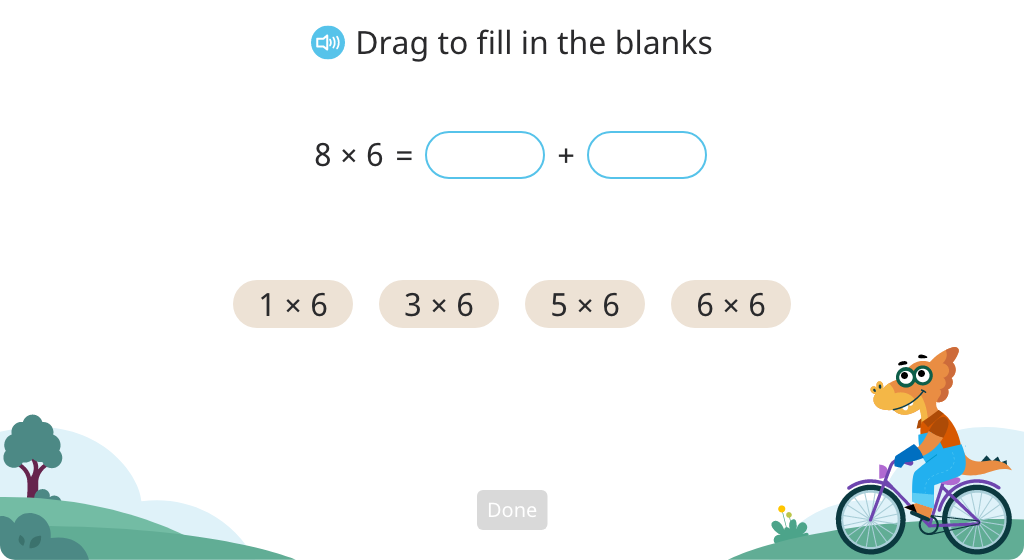
Use the distributive property of multiplication to solve equations (Level 3)
Topic D: Multiplication and Division Using Units of 9
Students apply and extend previous understanding to include 9 as a factor or divisor. We also introduce a strategy specifically for multiplying by 9.
Skip count by 9
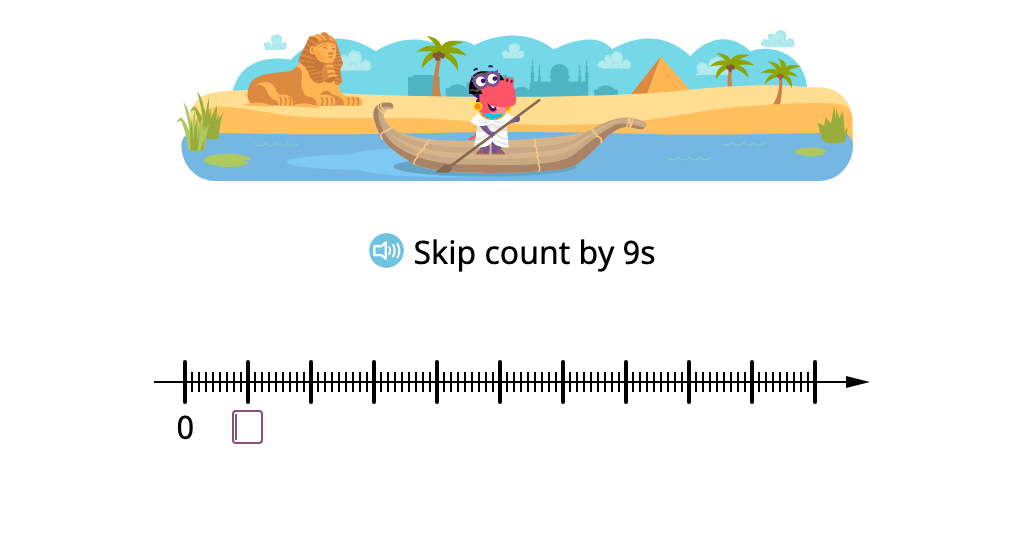
Determine multiples of 9 in a multiplication chart

Determine products of 9 in a times table with and without an array model
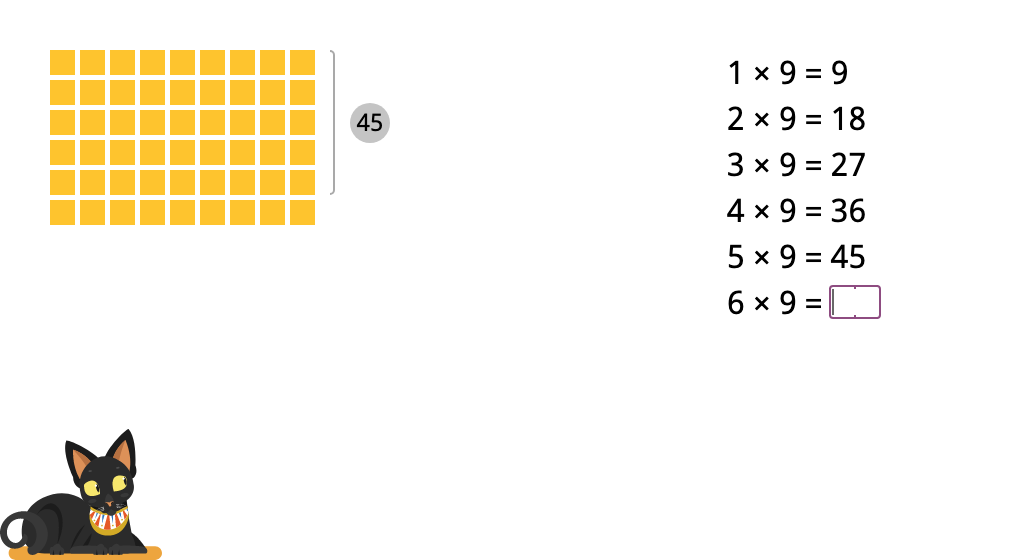
Determine products of 9 in a times table

Solve division problems with a divisor of 9 based on its relationship to multiplication
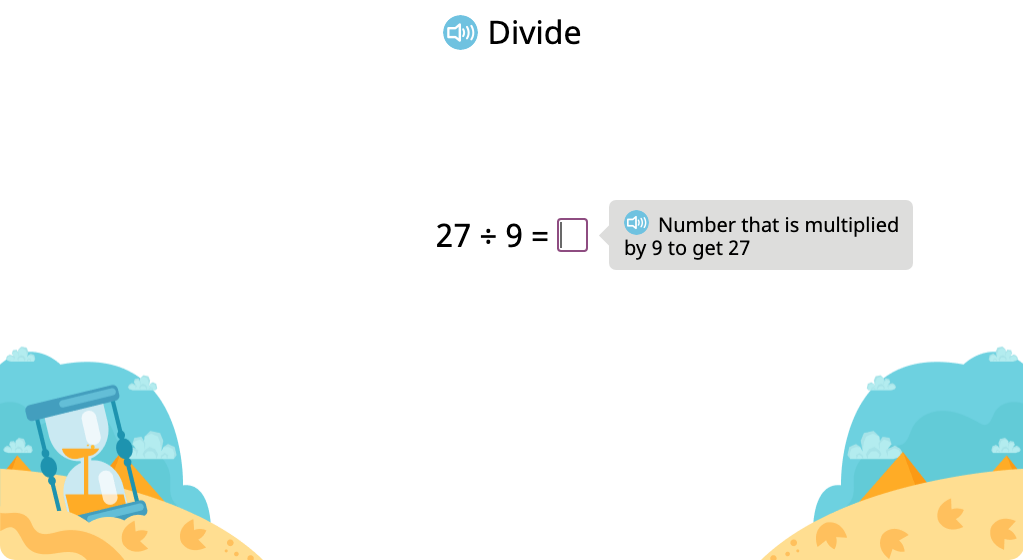
Solve division problems with a divisor of 9 (Level 1)

Solve division problems with a divisor of 9 (Level 2)

Solve multiplication equations using the break apart and distribute strategy
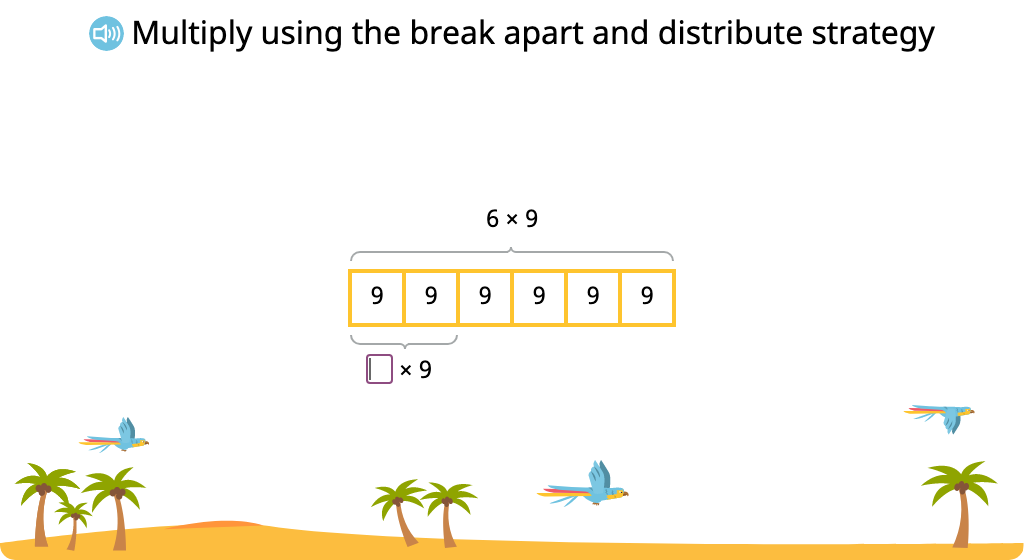
Solve multiplication equations using the 9 = 10-1 strategy
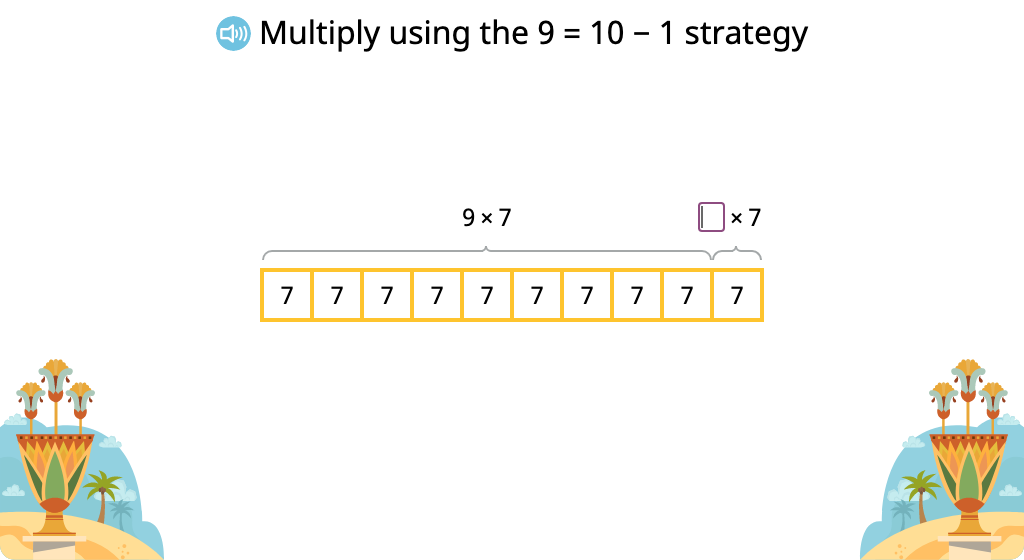
Topic E: Analysis of Patterns and Problem Solving Including Units of 0 and 1
Students dig deeper into concepts of multiplication and division as they work with 1 and 0. In addition to working with these numbers as factors, dividends, and divisors, students use a letter to represent an unknown number in an equation and are introduced to let statements regarding such letters.
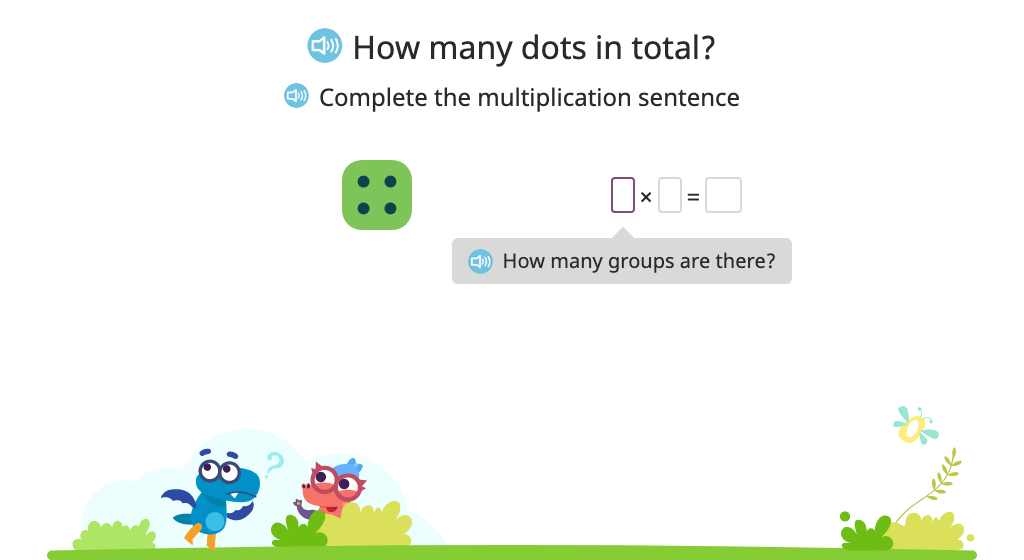
Compose a multiplication sentence (including 1 x n) to represent a mode

Solve multiplication problems that use 1 as a factor (including 1 x n)
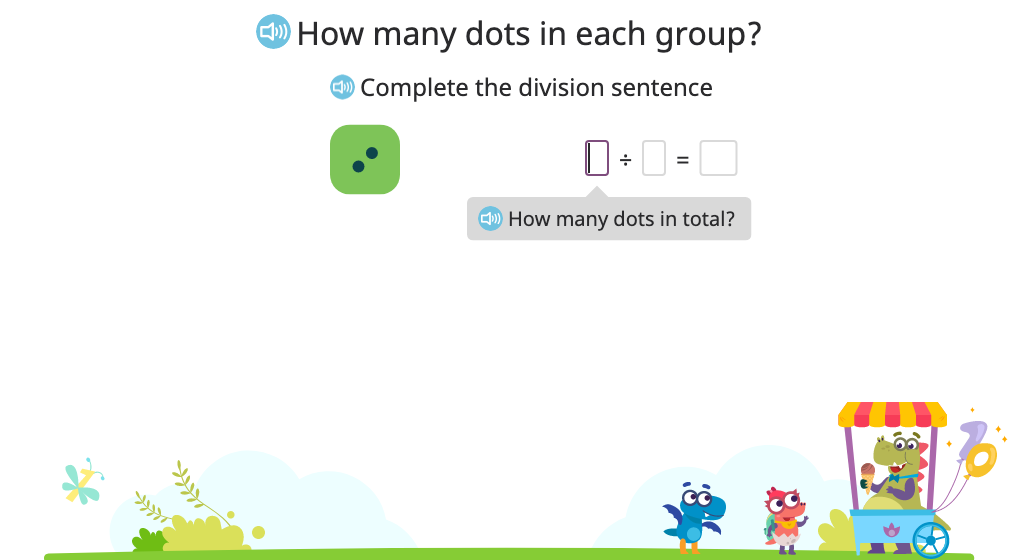
Solve division problems that use 1 as a divisor (including n / 1)
Compose a multiplication sentence (including n x 1) to represent a model
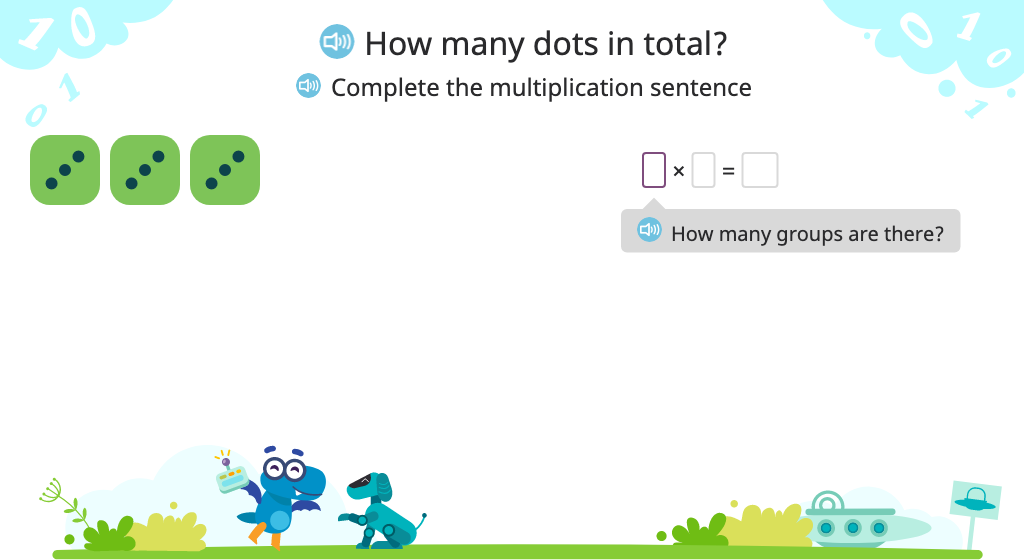
Solve multiplication problems that use 1 as a factor (including n x 1)
Solve division problems in which a number is divided by itself
Solve for an unknown (represented by a letter) in multiplication and division problems that include 1
Compose a multiplication sentence (including n x 0) to represent a model
Solve multiplication problems that use 0 as a factor (including n x 0 and 0 x n)
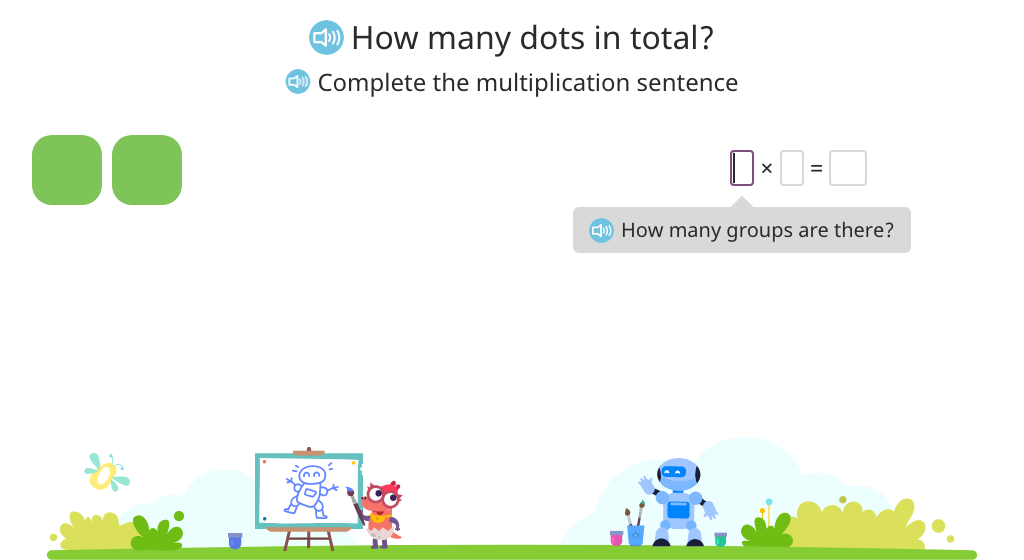
Solve division problems that use 0 as a dividend (including 0 / n)
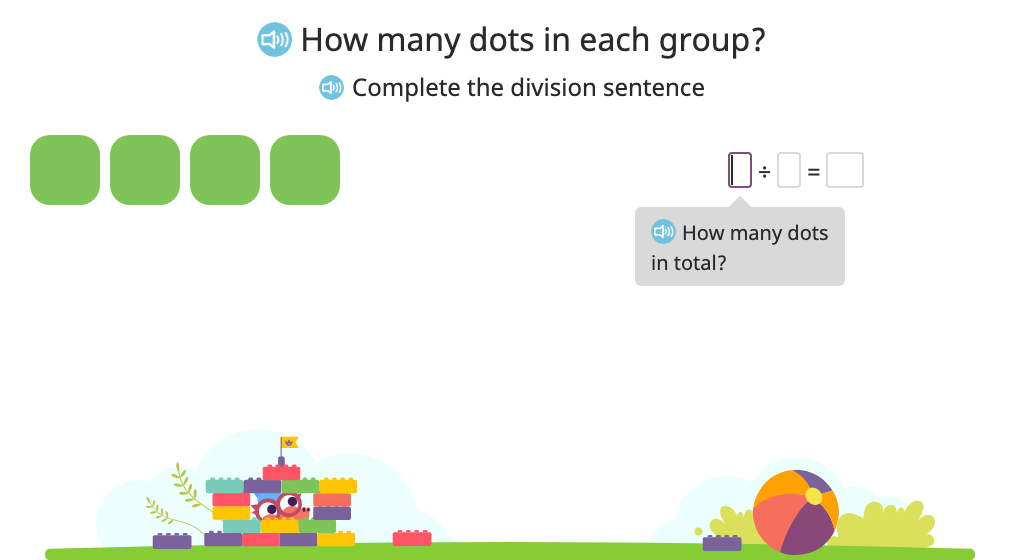
Solve for an unknown (represented by a letter) in multiplication and division problems that include 0

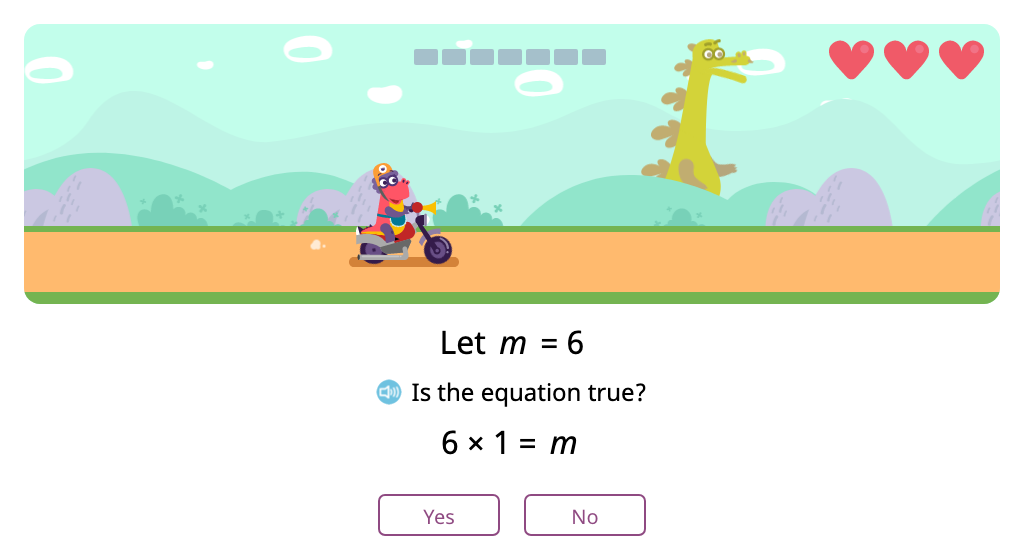
Determine whether a multiplication or division equation with an unknown represented by a letter is true based on a let statement
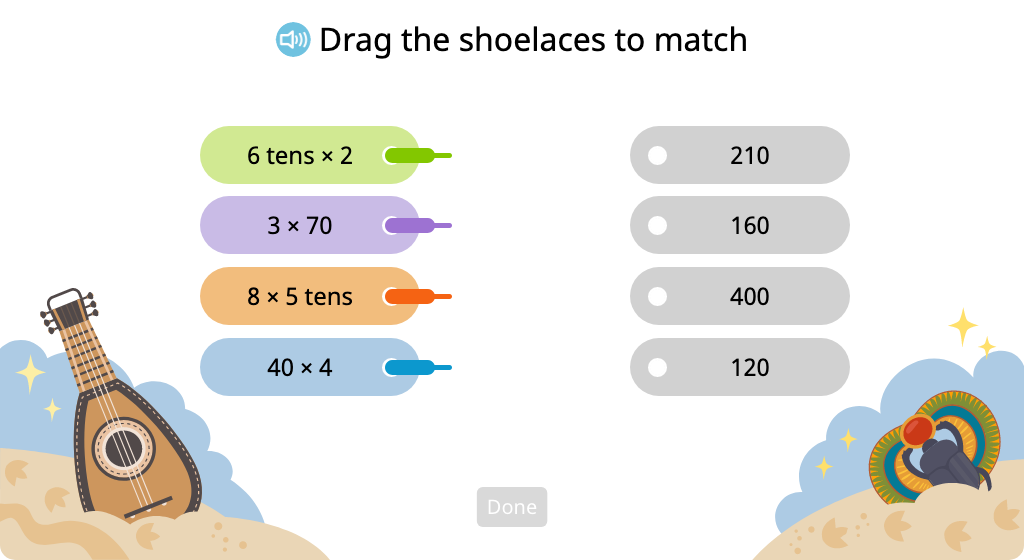
Topic F: Multiplication of Single-Digit Factors and Multiples of 10
Building upon students' fact fluency with single-digit factors, we introduce multiplying a single-digit factor by a multiple of ten. Students relate word-based multiplication (e.g., 4 x 3 tens = 12 tens) to numeric equations (e.g., 4 x 30 = 120).
Solve for missing products on a multiplication chart in which 10 is a factor

Relate a product of n tens to the product as a number n0

Match numeric products to multiplication equations that use numbers and words (n tens)
Use properties of multiplication to simplify and solve equations

Solve multiplication equations that have a single digit and a multiple of ten as factors
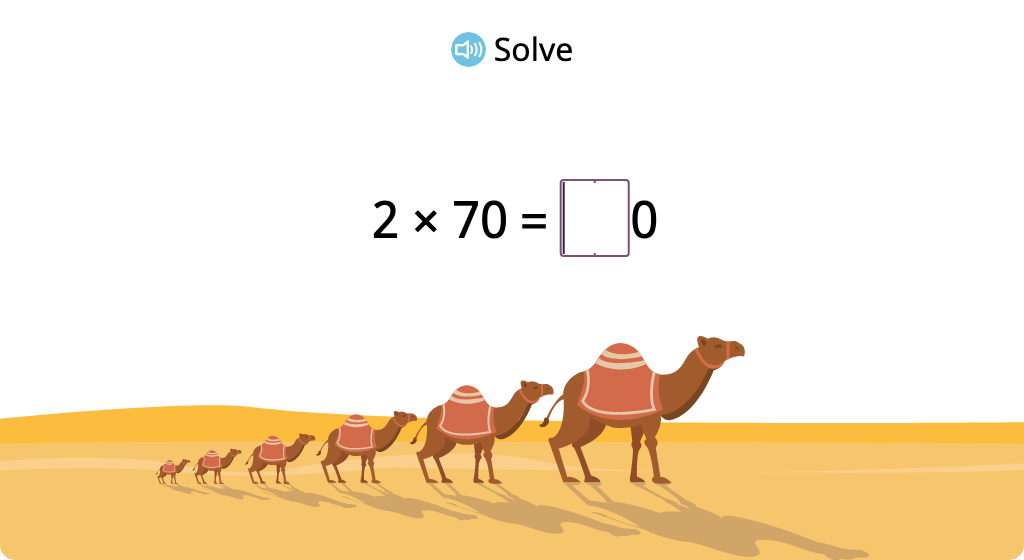
Solve for missing products on a multiplication chart that are square numbers
MODULE 4. Multiplication and Area
Topic A: Foundations for Understanding Area
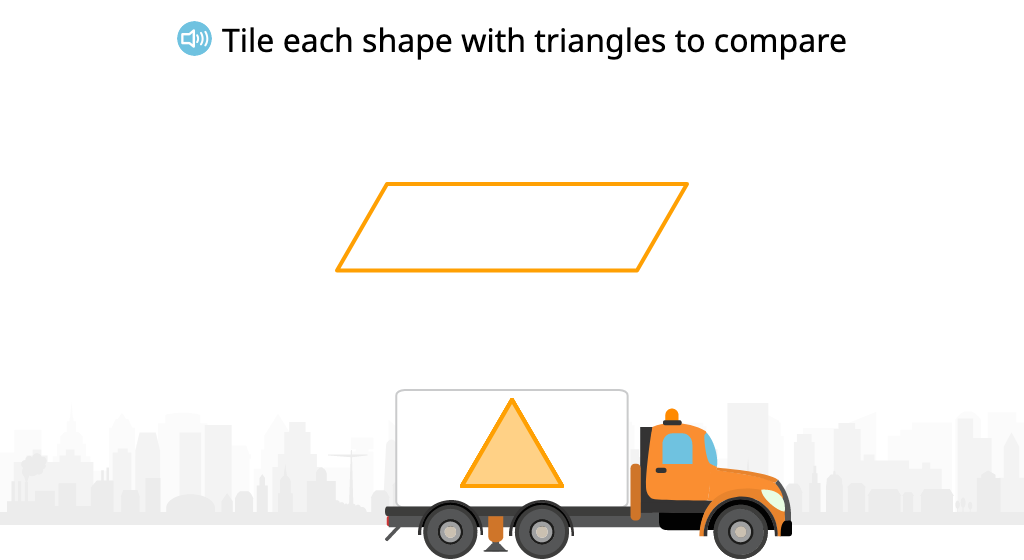
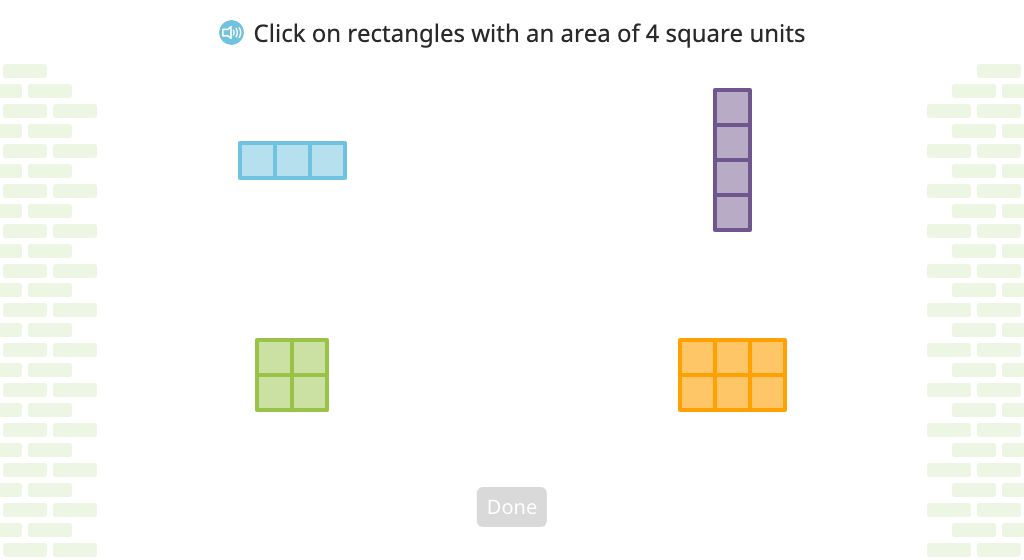
Students are introduced to the very basics of area using tiling. They learn to use square units, measure sides of a rectangle, skip count rows of tiles, and rearrange tiles to form a different rectangle with the same area.
Identify 2-dimensional shapes
Tile 2-dimensional shapes to compare their area
Determine and compare area by tiling with square units
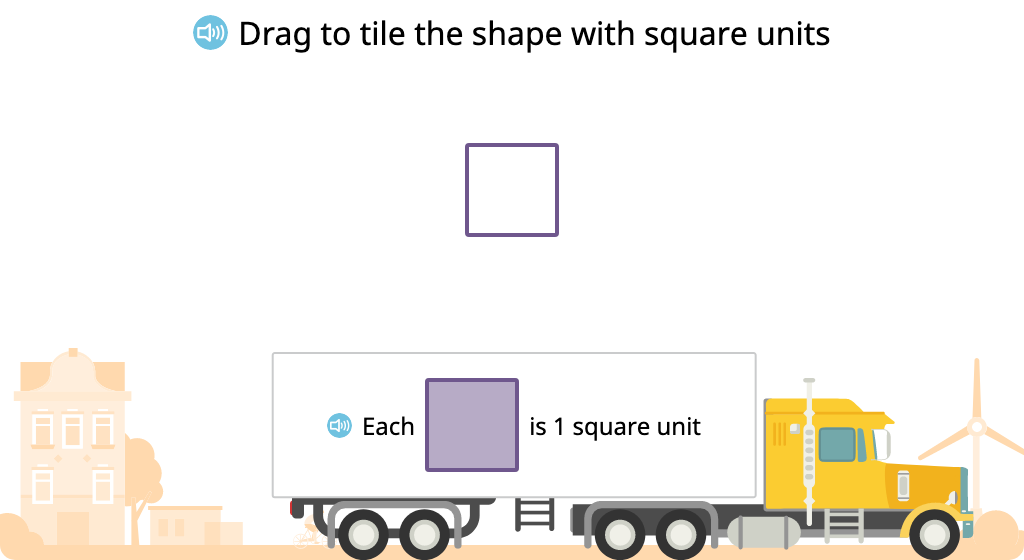
Identify shapes that have a given area
Determine area by tiling with square centimeters or inches
Determine area of a rectangle made by rearranging tiles from another rectangle
Determine area by skip counting tiles in each row
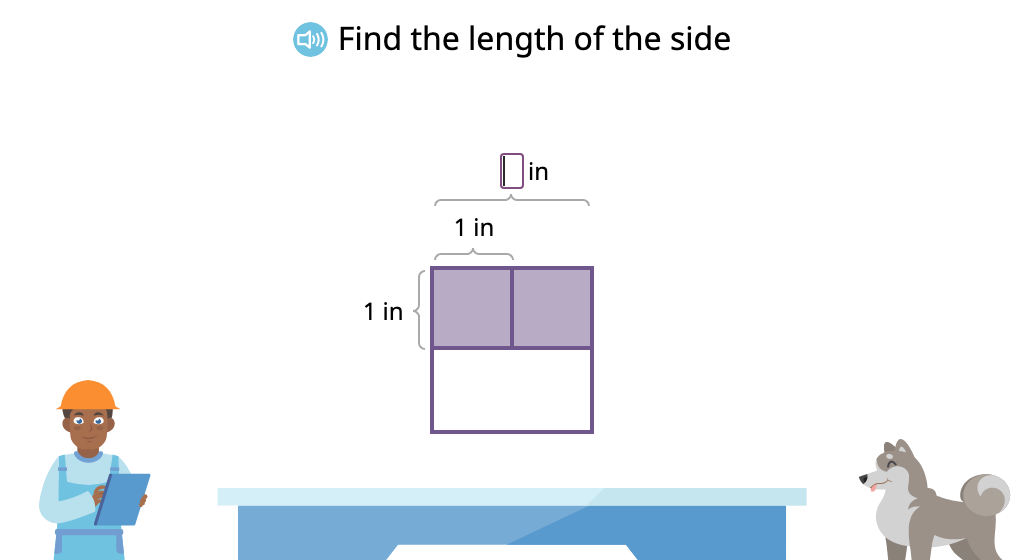
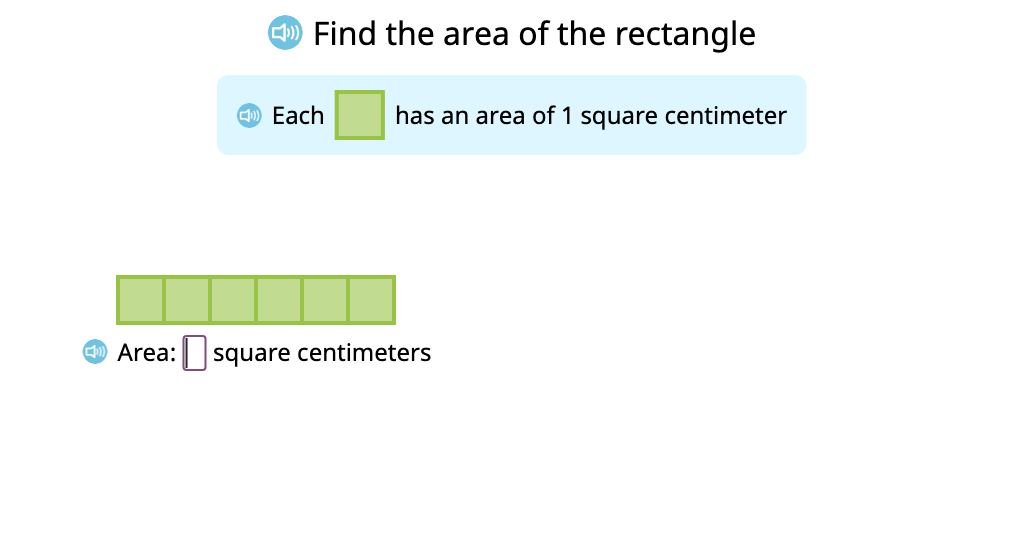
Topic B: Concepts of Area Measurement
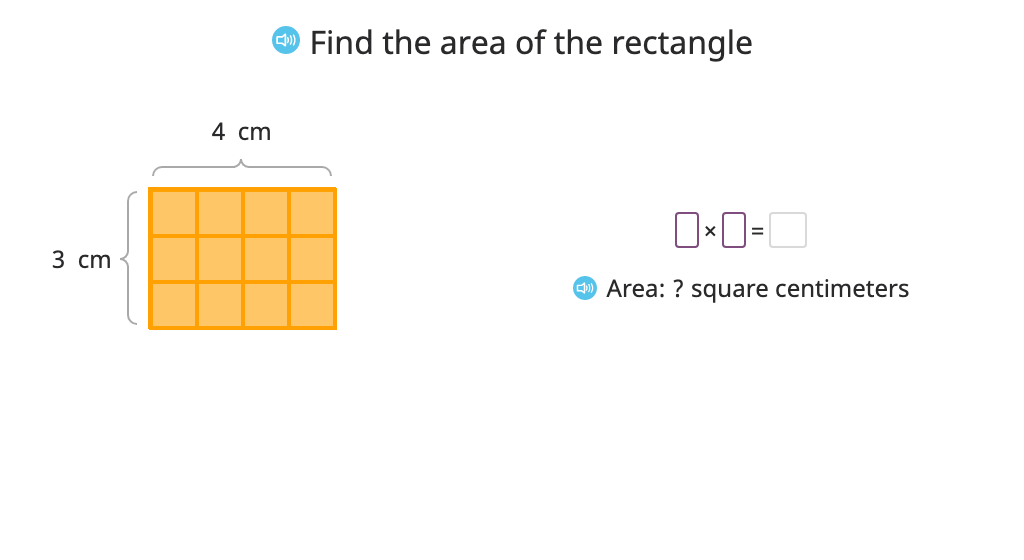
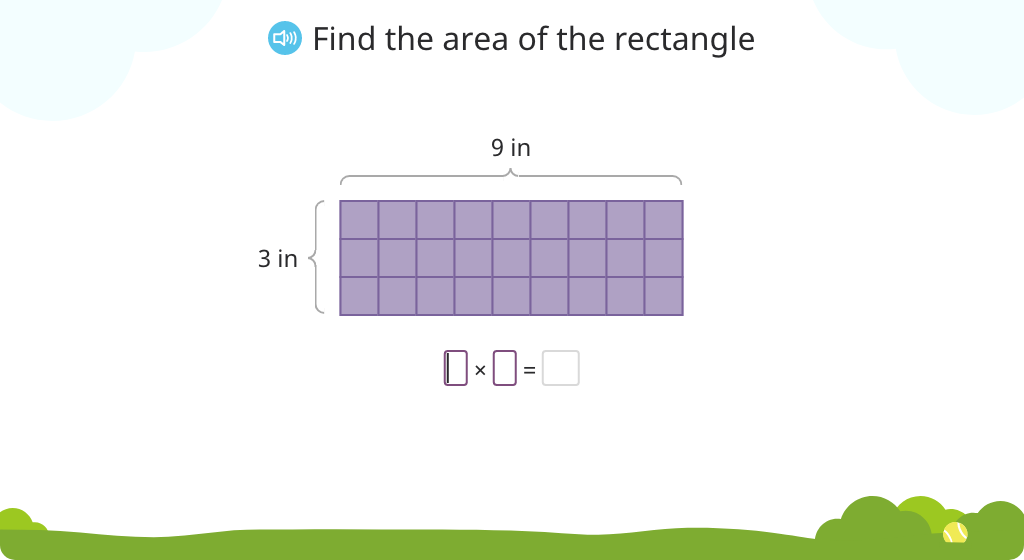
Building upon the previous module, students start by skip counting tiles in a rectangle to determine its area. They then progress to multiplication using a tiled rectangle and one with only labeled measurements. Students rearrange tiles to determine the measurements of a different rectangle that has the same area. They also solve for an unknown side represented by a letter.
Tutorial: Click on the book to see the multiplication table

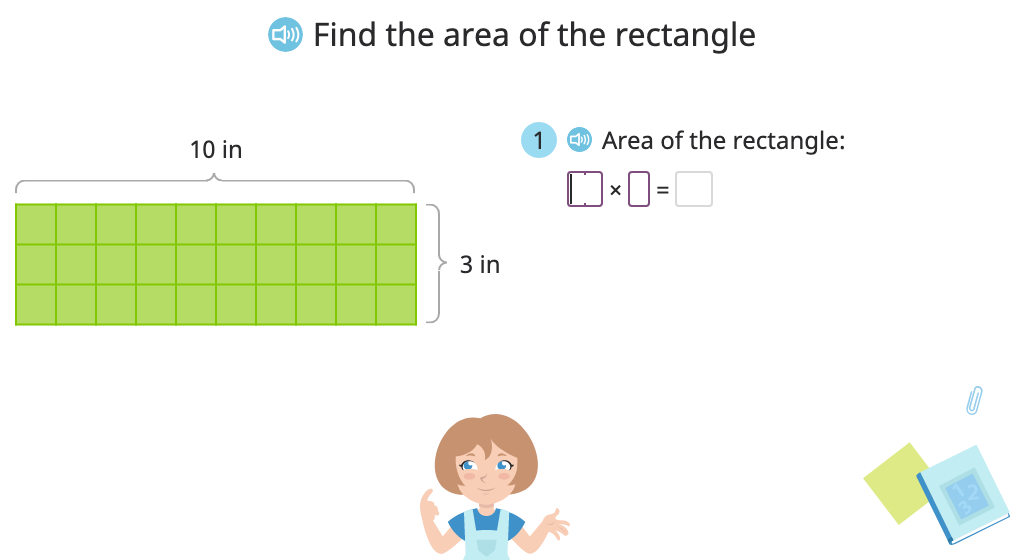
Multiply to find the area of a tiled rectangle (Level 1)
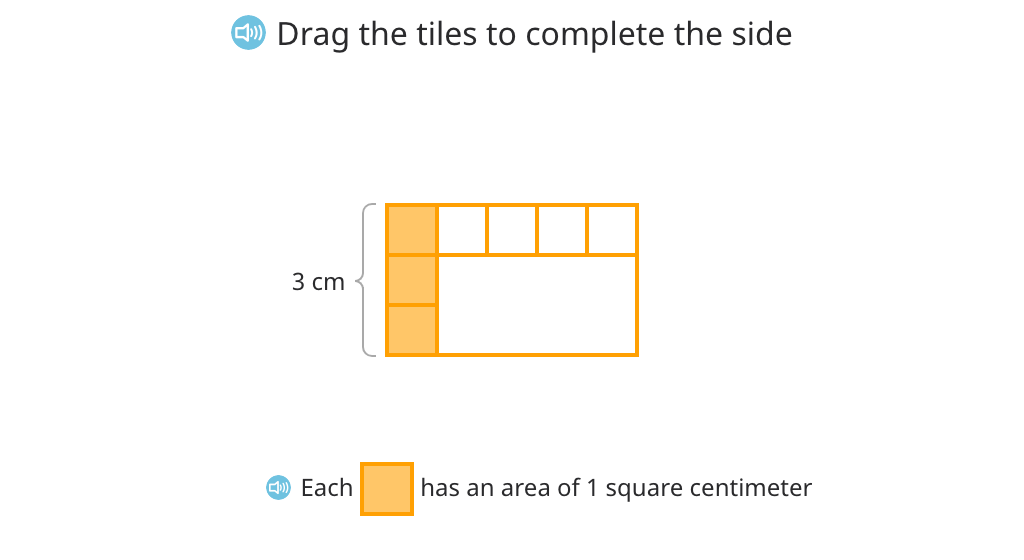
Multiply to find the area of a tiled rectangle (Level 2)
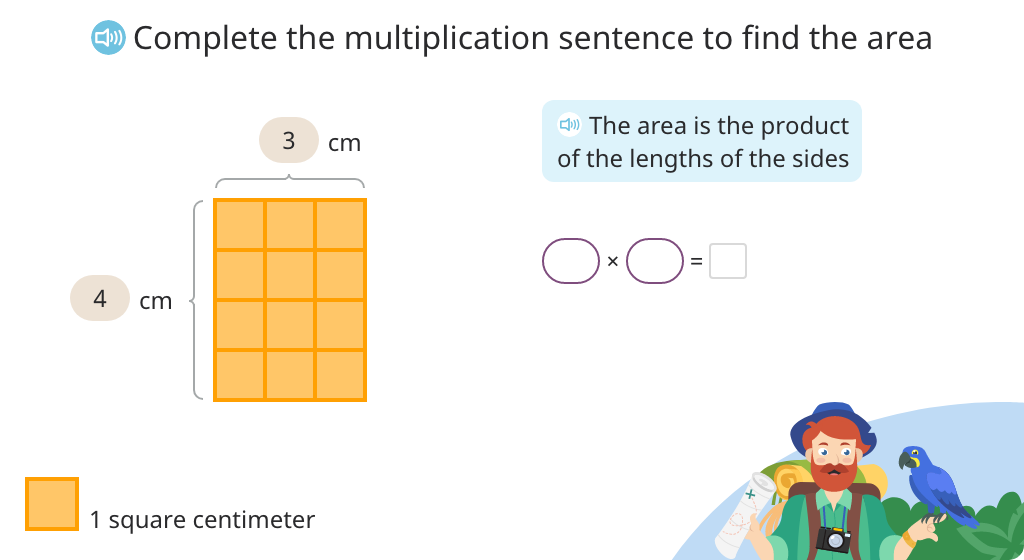
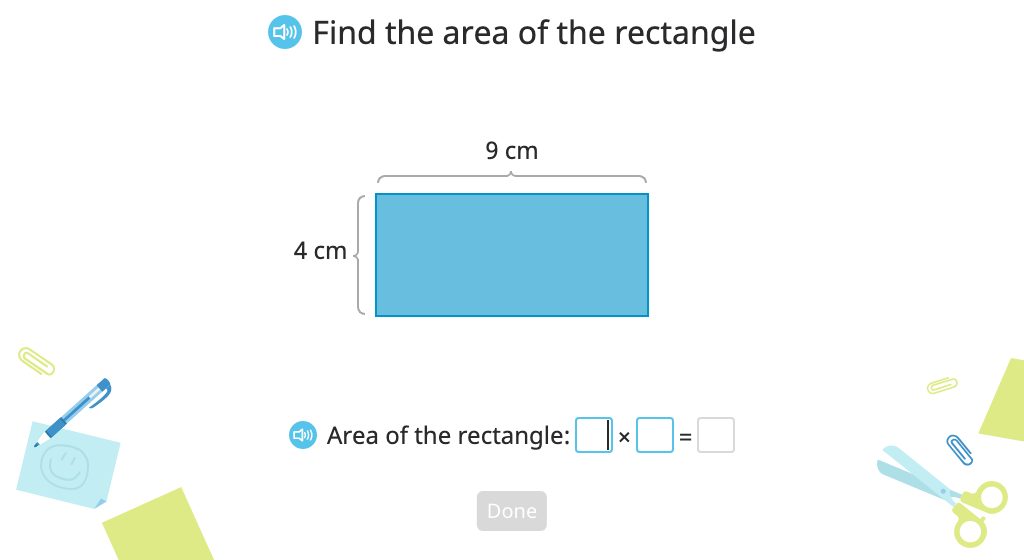
Determine the area of a rectangle by multiplying the lengths of the sides (Level 1)
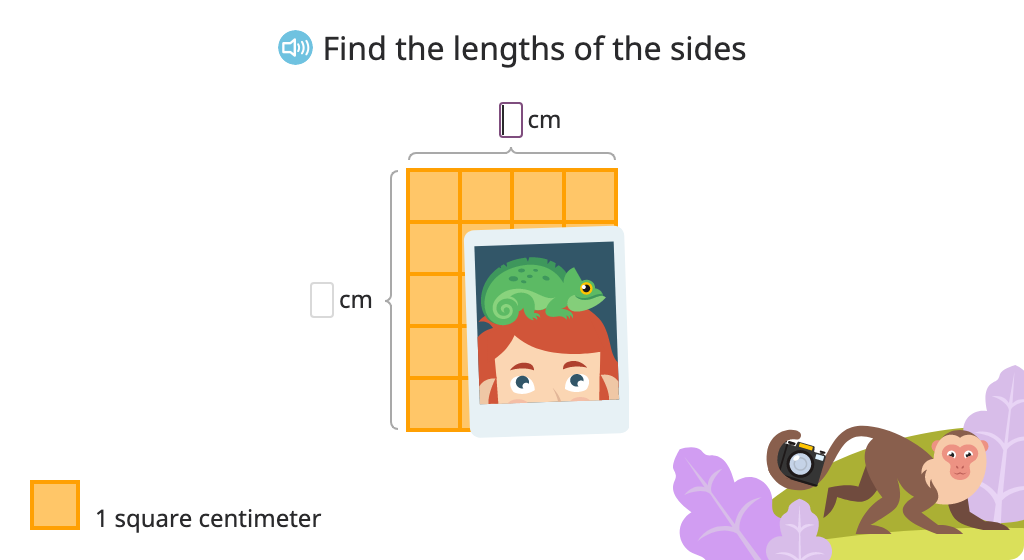
Determine the area of a rectangle by multiplying the lengths of the sides (Level 2)
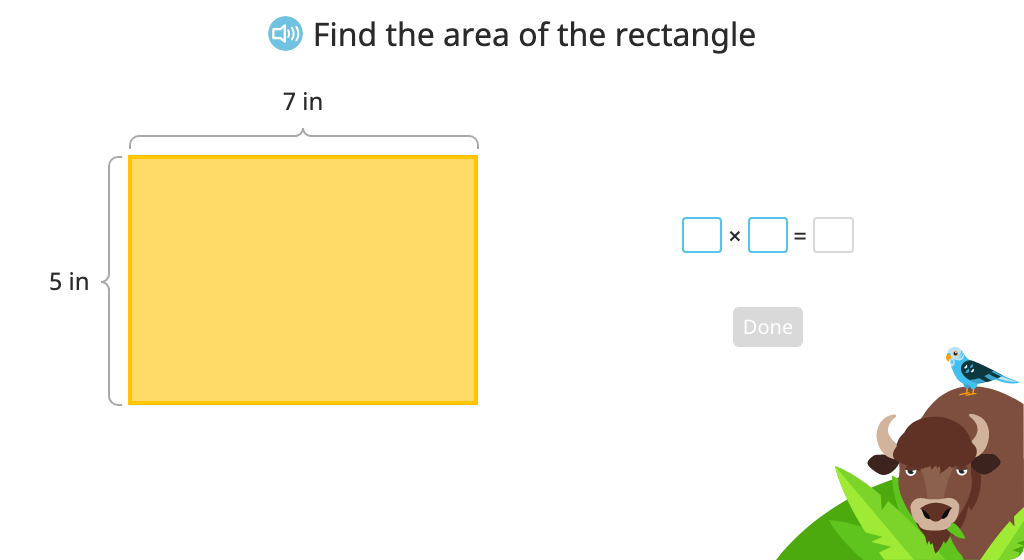
Determine the area of a rectangle based on the equal area of a different rectangle
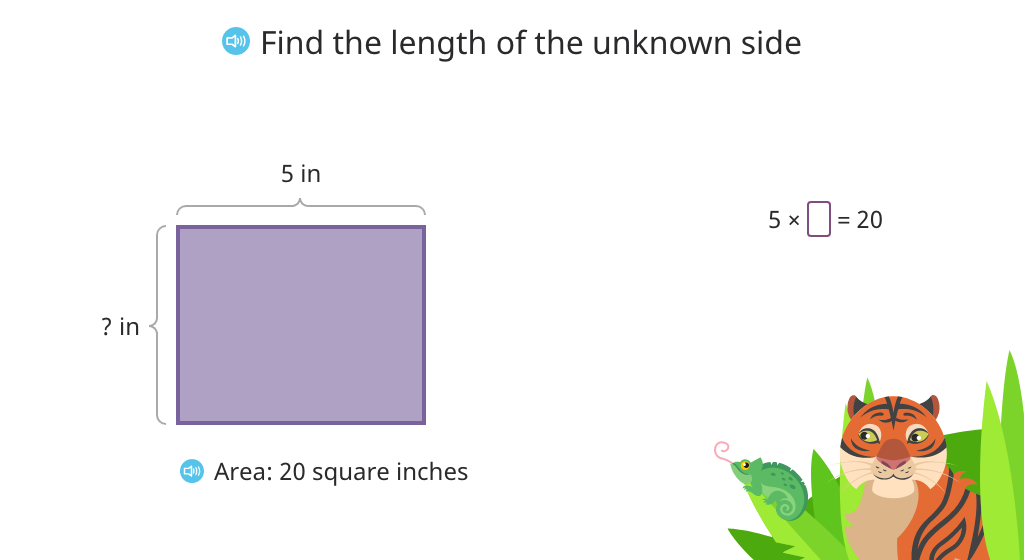
Determine the length of a side based on the area of a rectangle
Topic C: Arithmetic Properties Using Area Models
Students dig deeper into their understanding of multiplication and area by using area models of rectangles. They compare parts to the whole, find missing parts, and manipulate equations to demonstrate properties. Exercises begin by using rectangles with gridlines and then advance to using those without.
Multiply to find area by splitting a rectangle into smaller parts
Use the distributive property of multiplication to find the area of a rectangle split into smaller parts
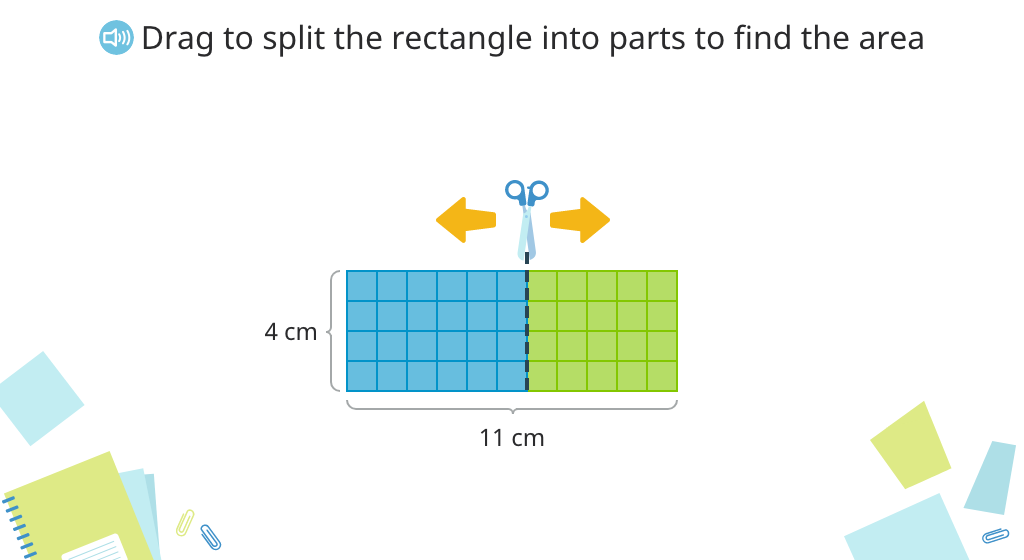
Subtract to find the area of a covered part of a rectangle
Multiply or subtract to find areas of rectangles without gridlines
Topic D: Applications of Area Using Side Lengths of Figures
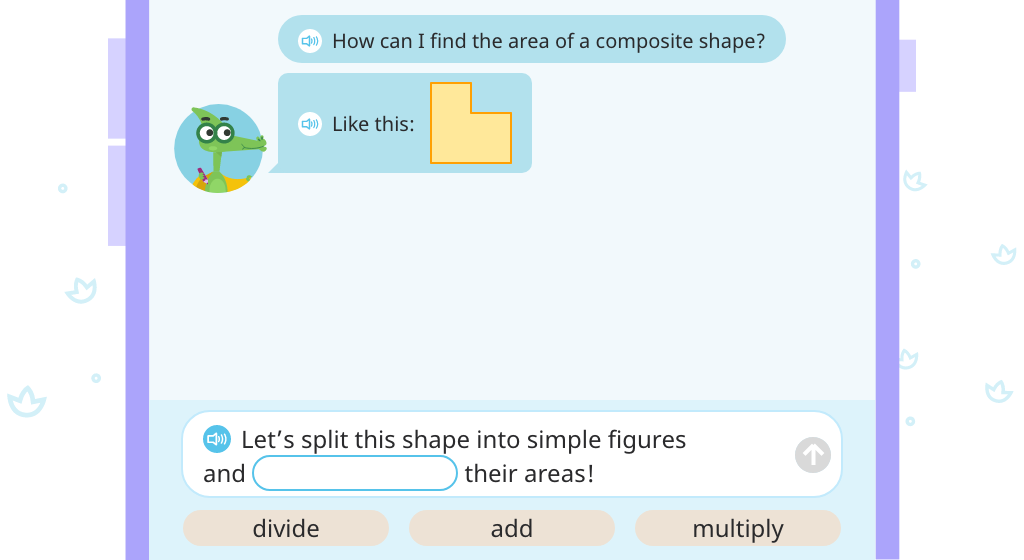
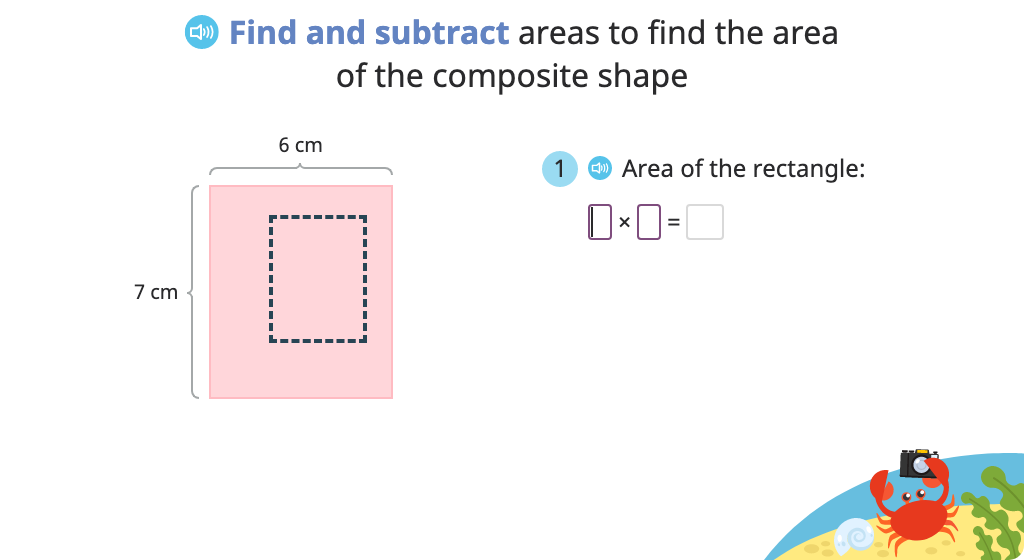
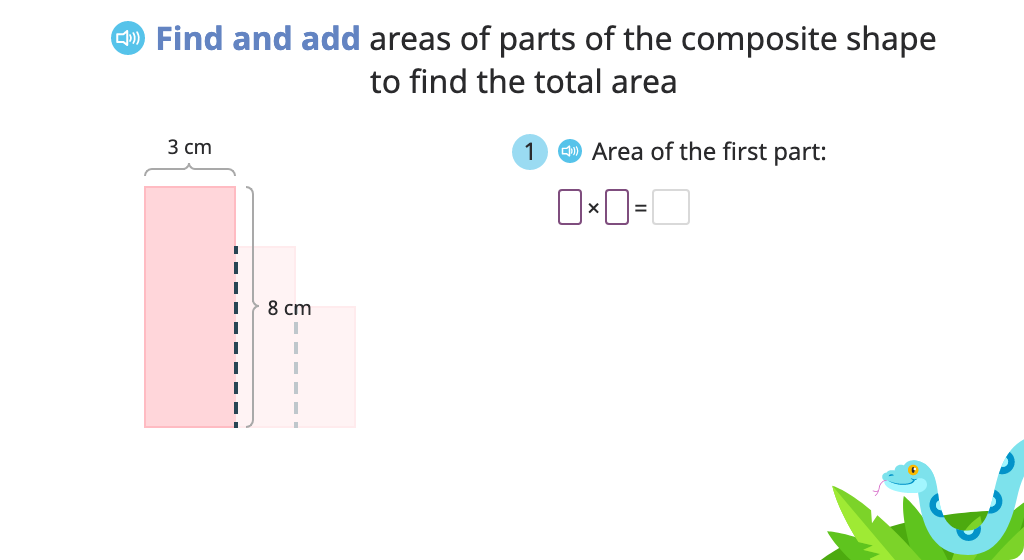
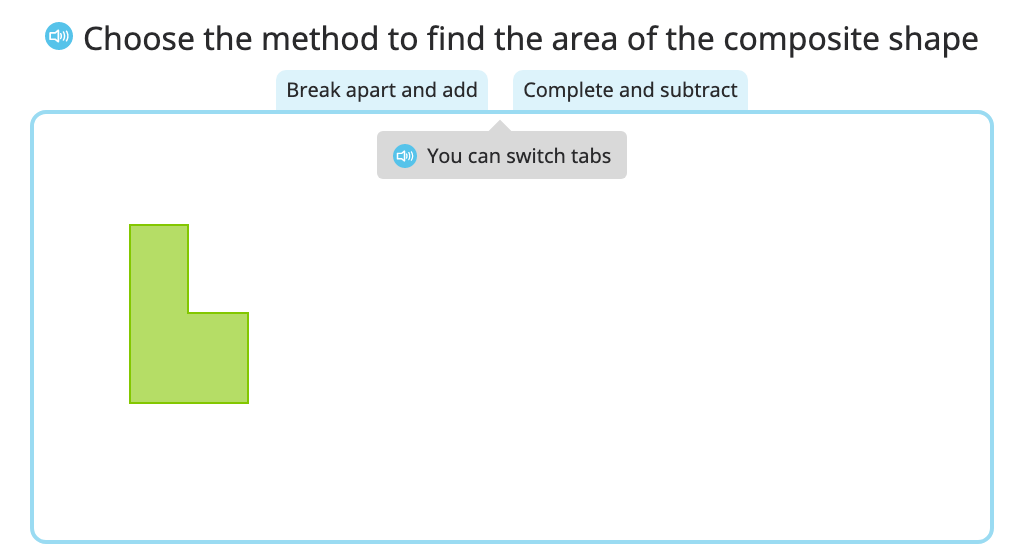
Students learn two different approaches to finding the area of a composite shape based on side lengths. In the first, they break the shape into smaller rectangles and add those areas together. In the second, they "complete" the shape to find the total area and then subtract the area of the "missing piece". Students begin by using shapes with unit squares shown and then progress to those without.
Determine area of a composite shape by splitting it into two rectangles and adding the areas (Part 1)
Determine area of a composite shape by completing the rectangle and subtracting the area of the missing piece (Part 1)
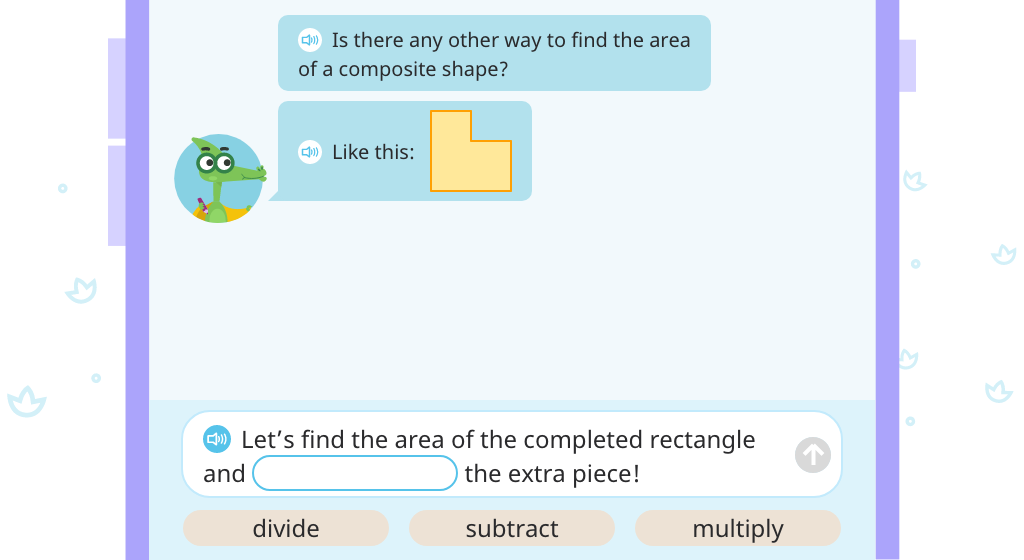
Determine area of a composite shape by completing the rectangle and subtracting the area of the missing piece (Part 2)
Determine area of a composite shape by splitting it into two rectangles and adding the areas (Part 2)
Determine the area of a composite shape using either the "break apart and add" or "complete and subtract" strategy
MODULE 5. Fractions as Numbers on the Number Line
Topic A: Partition a Whole into Equal Parts
Students establish a foundation for understanding fractions by working with equal parts of a whole. They use halves, thirds, fourths, fifths, sixths, sevenths, and eighths of shapes including circles, rectangles, line segments, and other shapes. Students partition shapes, label sections, shade fractions, and even solve word problems involving equal sharing. Throughout the topic, they do not use fraction notation (e.g., 2 thirds).
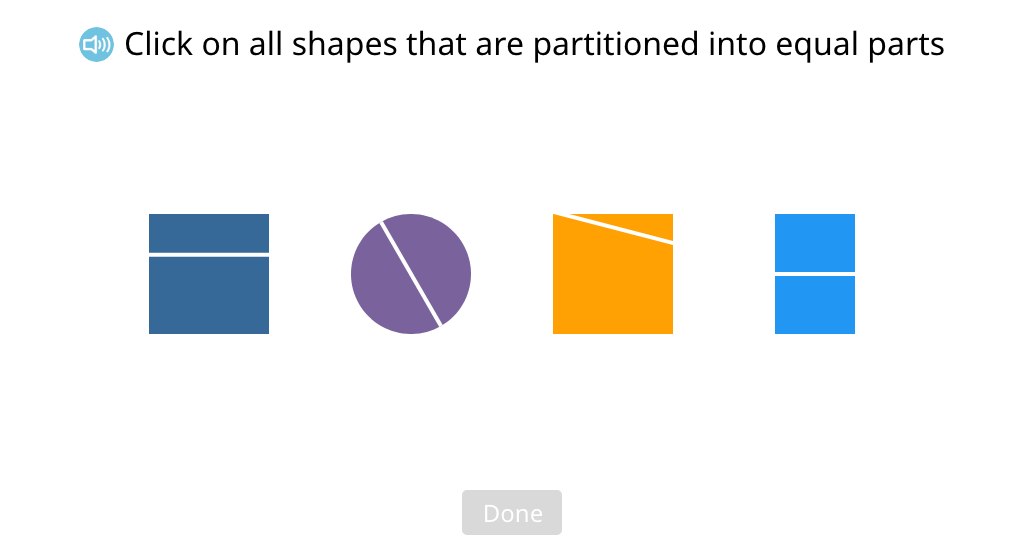
Identify shapes that are partitioned into equal parts
Identify and label halves, fourths, and eighths
Identify and label thirds, fifths, sixths, and sevenths

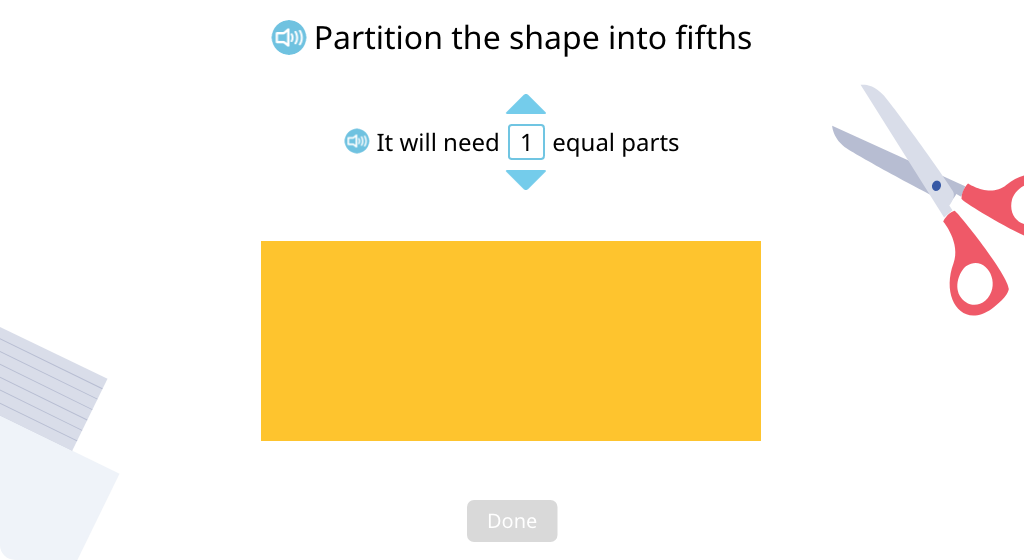
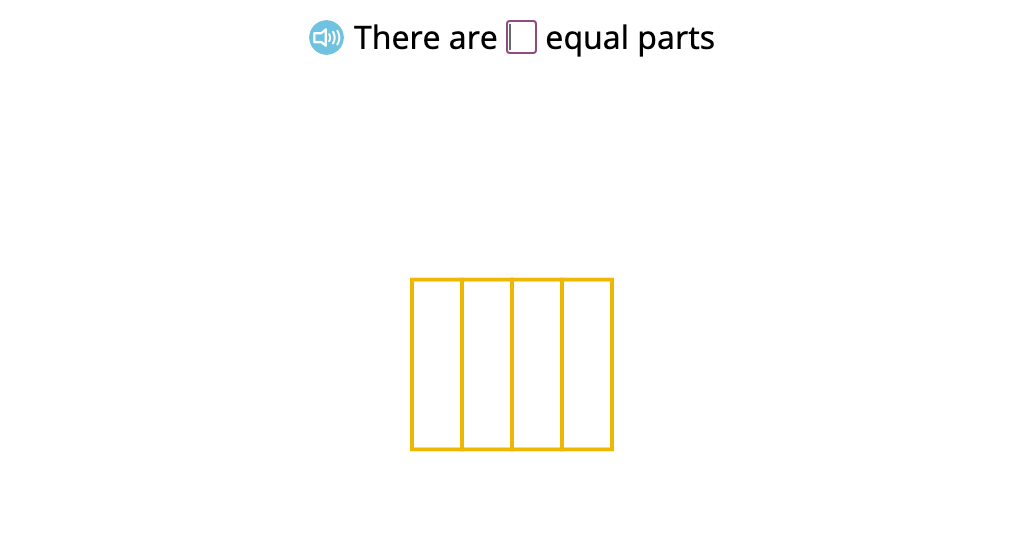
Determine the number of equal parts needed to partition a shape into a given denominator
Identify the shaded portion of a shape as a unit fraction

Sort shapes based on the unit fraction shaded

Identify the shaded portion of a shape
Identify shapes that have a given portion shaded
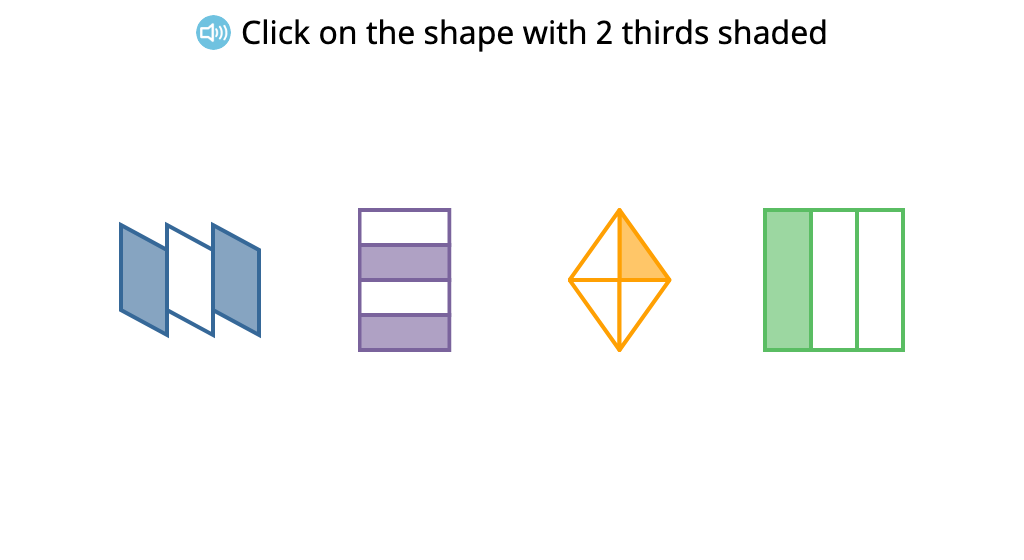
Partition and shade a shape to represent a given portion
Solve word problems involving equal parts of a whole
Topic B: Unit Fractions and their Relation to the Whole
Students build upon their knowledge from Topic 5A to transition from word form to standard form in identifying fractions. They begin with unit fractions and advance to more complex fractions, including complements of a whole and improper fractions. Throughout the topic, students are presented with a variety of shapes, sizes, and colors of figures. While they do not use the term "improper fractions," they learn the underlying concept of fractional parts that form more than one whole.
Identify unit fractions written in standard form
Label part of a figure with a unit fraction written in standard form
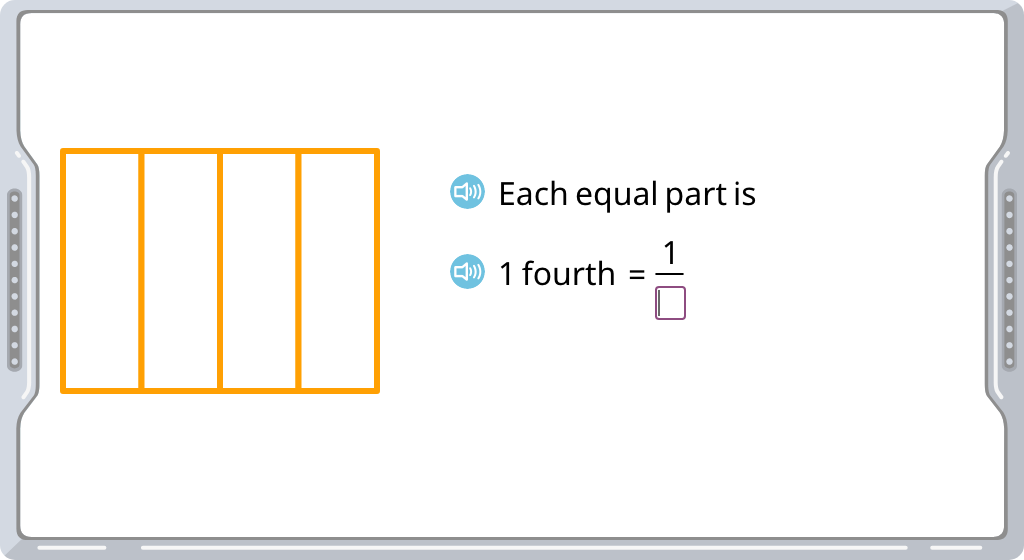
Identify the part of a figure that is shaded with a unit fraction
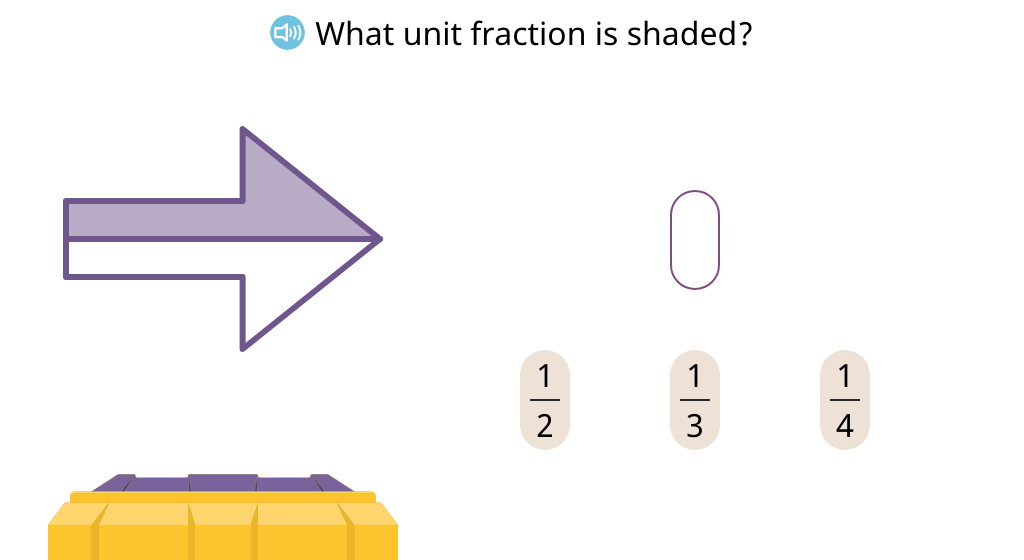
Identify figures that have a given unit fraction shaded
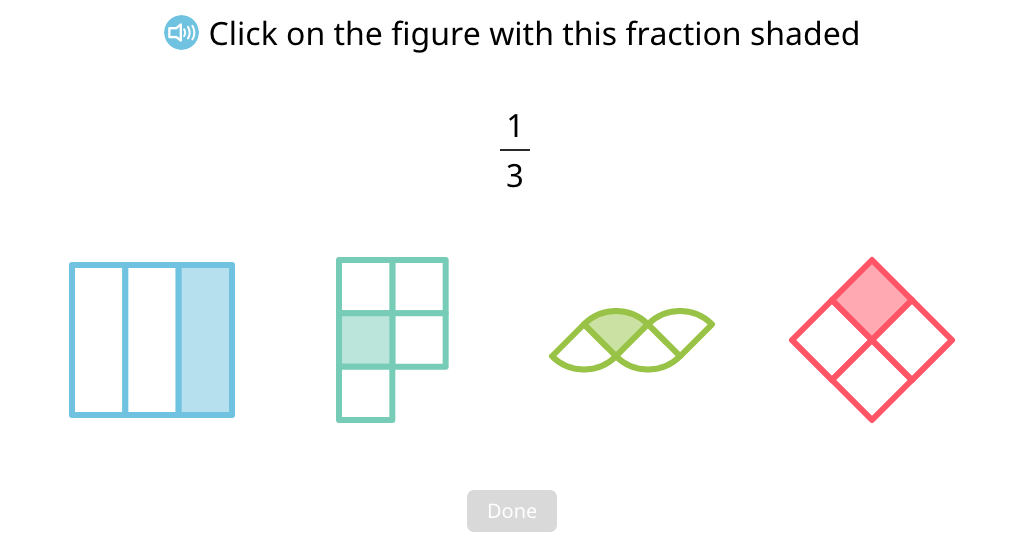
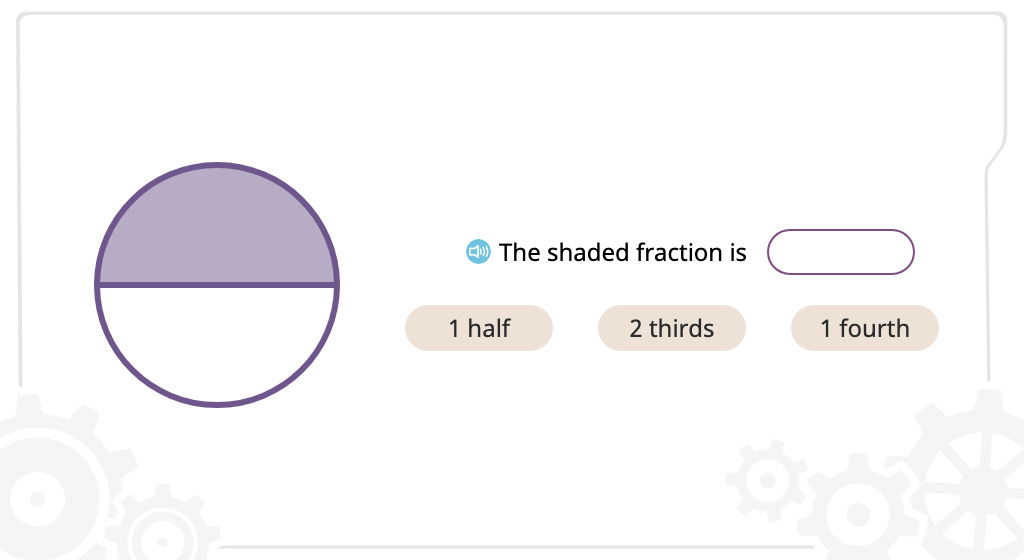
Write a unit fraction to identify the shaded part of a figure
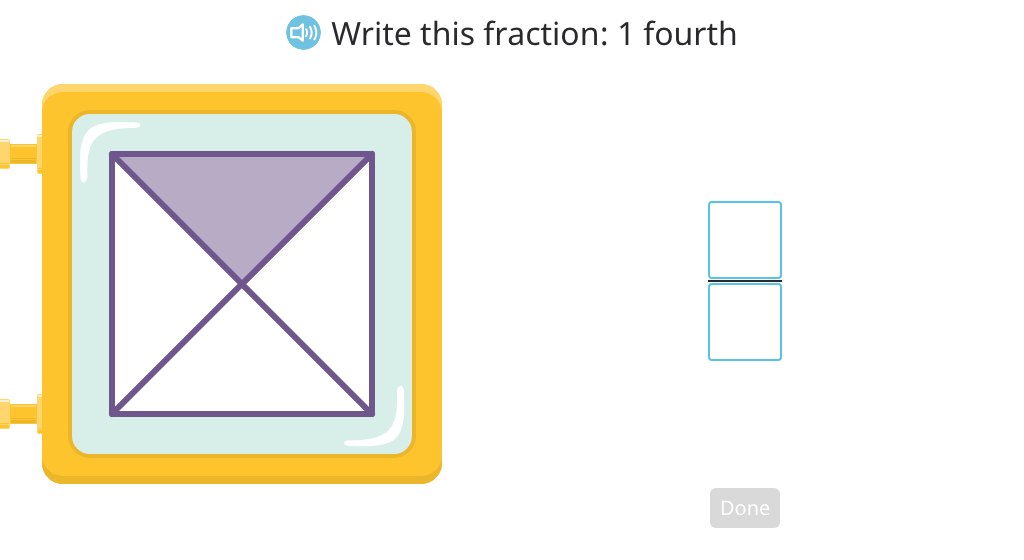
Identify the shaded part of a figure
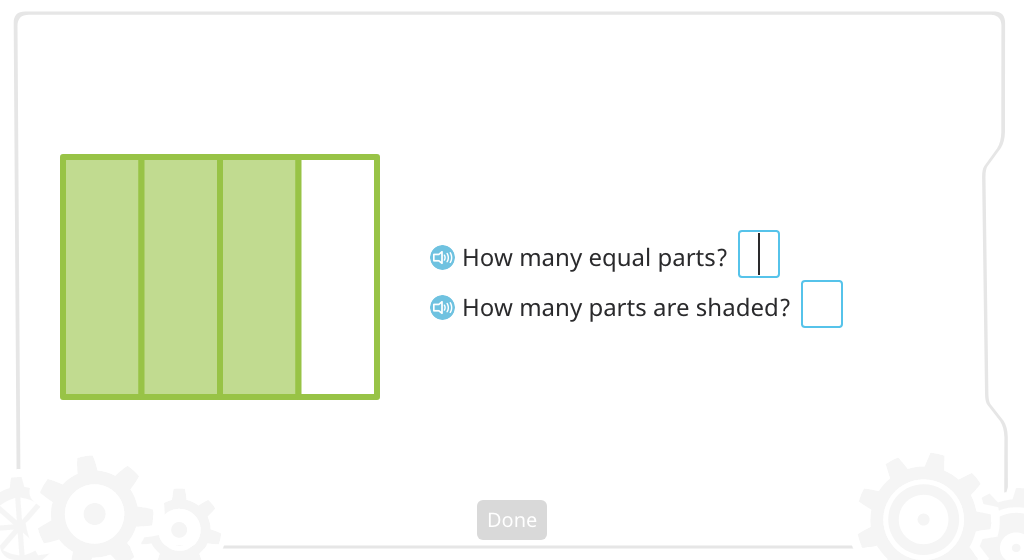
Label the shaded part of a figure with a fraction written in standard form
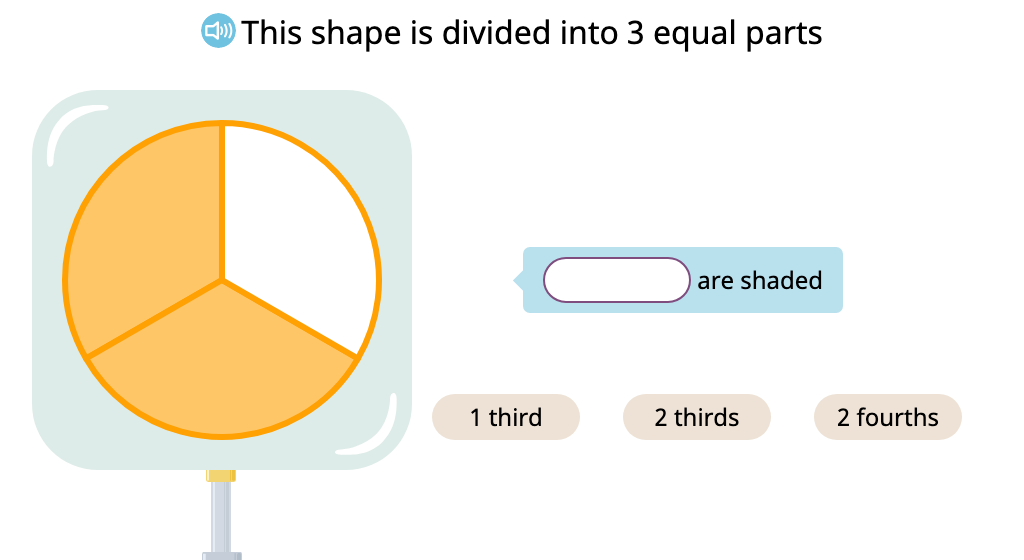
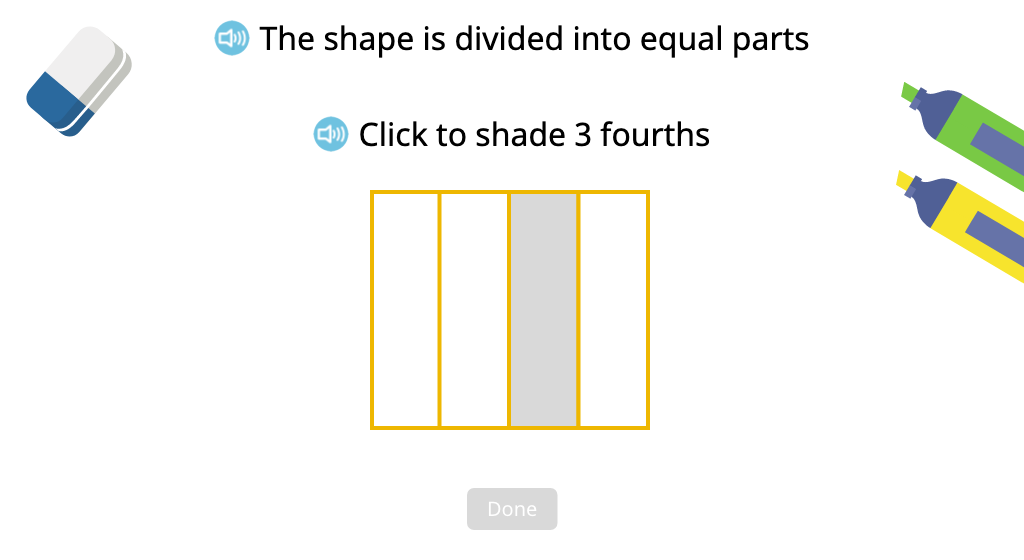
Shade parts of a figure to represent a given fraction
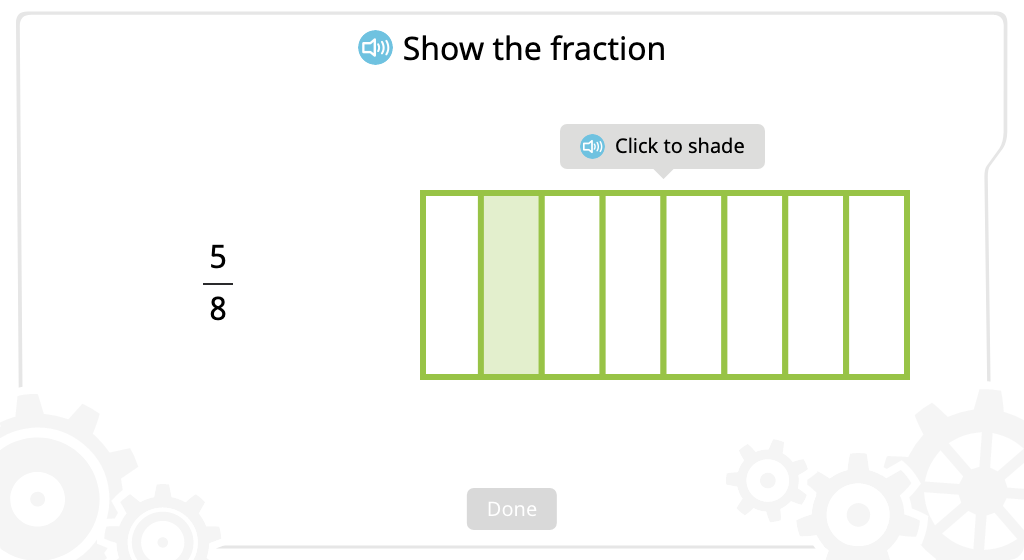
Identify figures that have a given fraction shaded and fractions that represent the shaded part of a figure
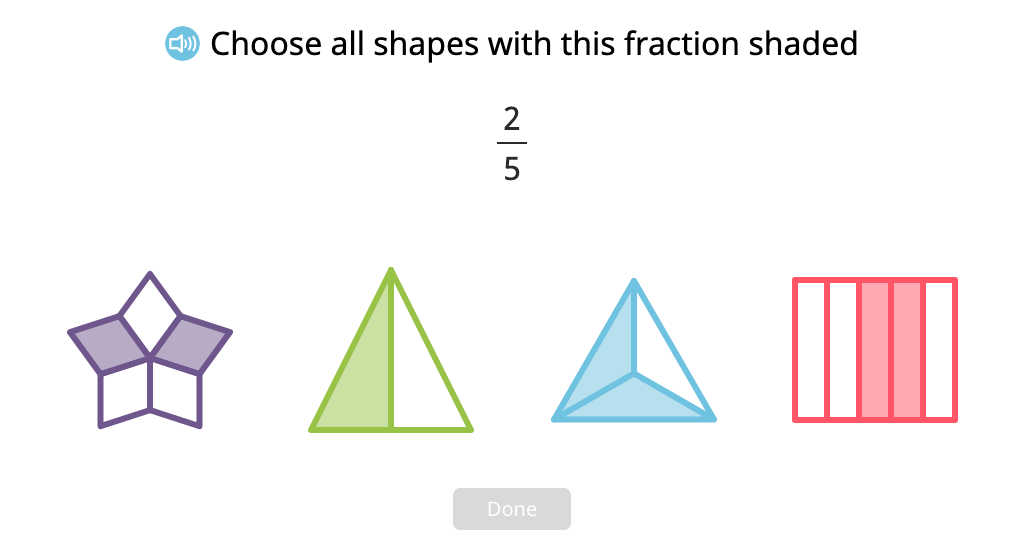
Write a fraction to identify the shaded part of a figure (Level 1)
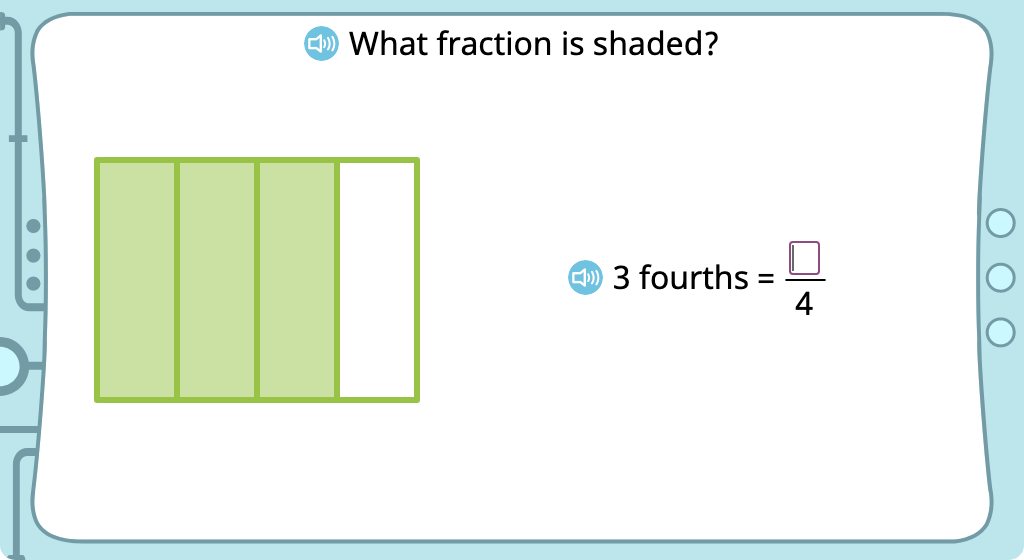
Label the shaded part of a figure with a fraction written in standard form and word form
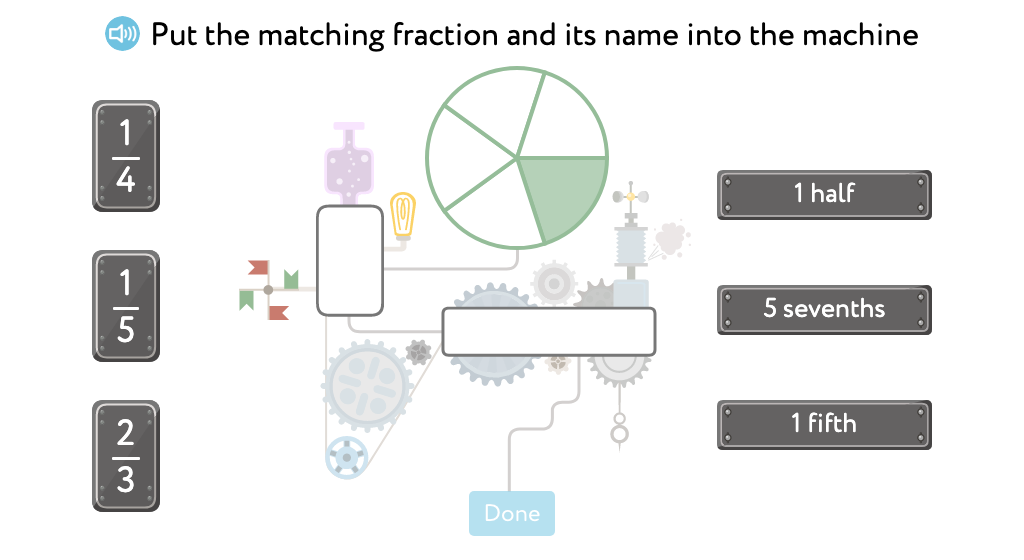
Write a fraction to identify the shaded part of a figure (Level 2)
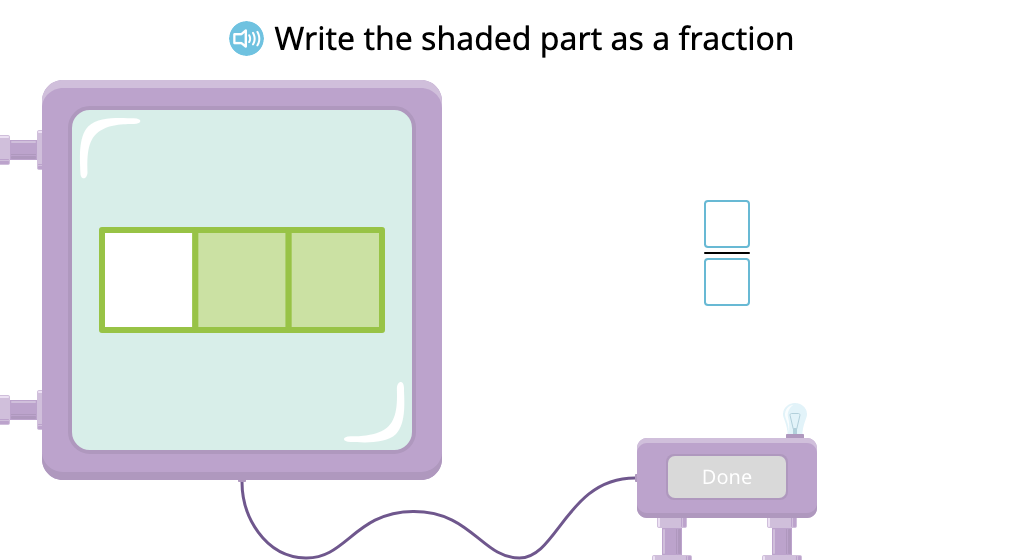
Label shaded and unshaded parts of a figure (Level 1)
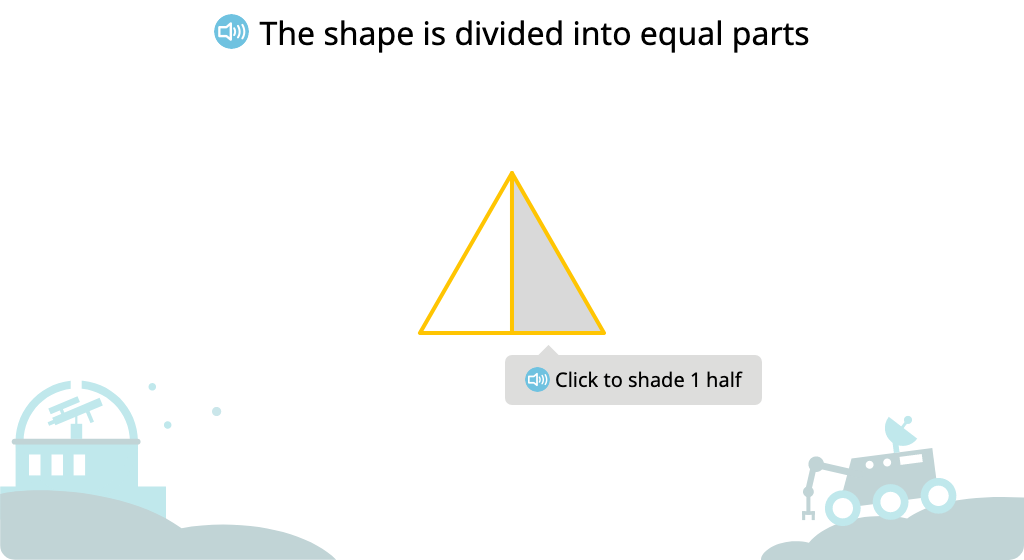
Label shaded and unshaded parts of a figure (Level 2)
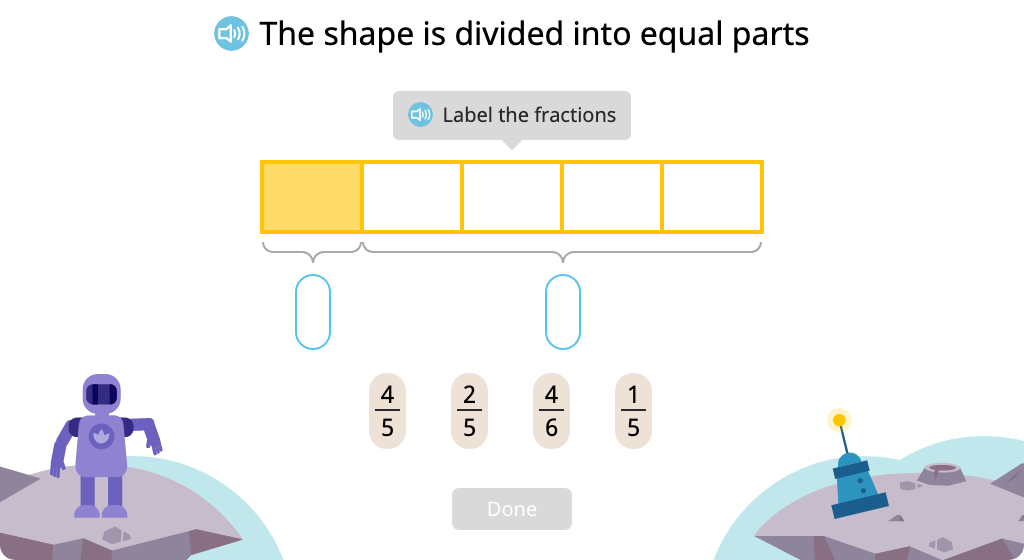
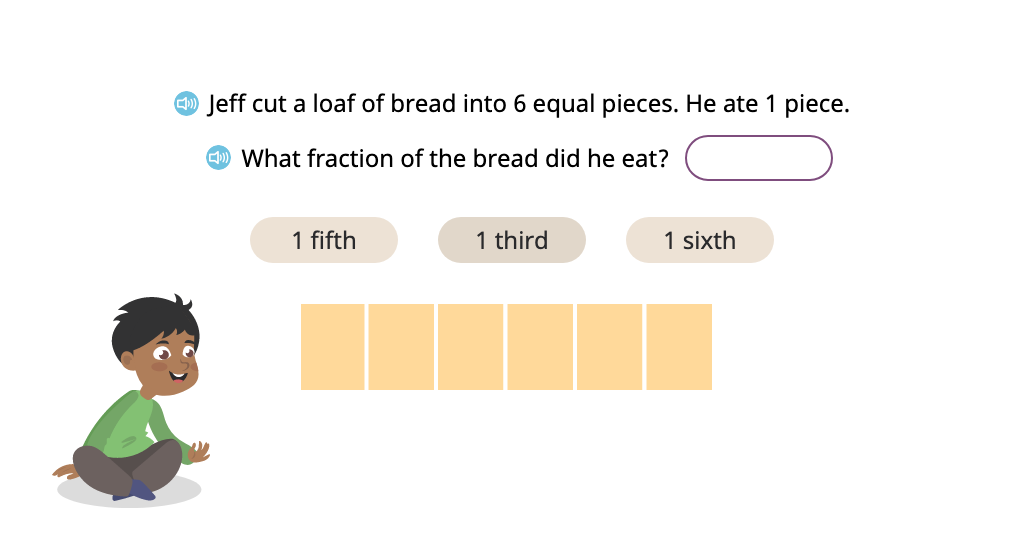
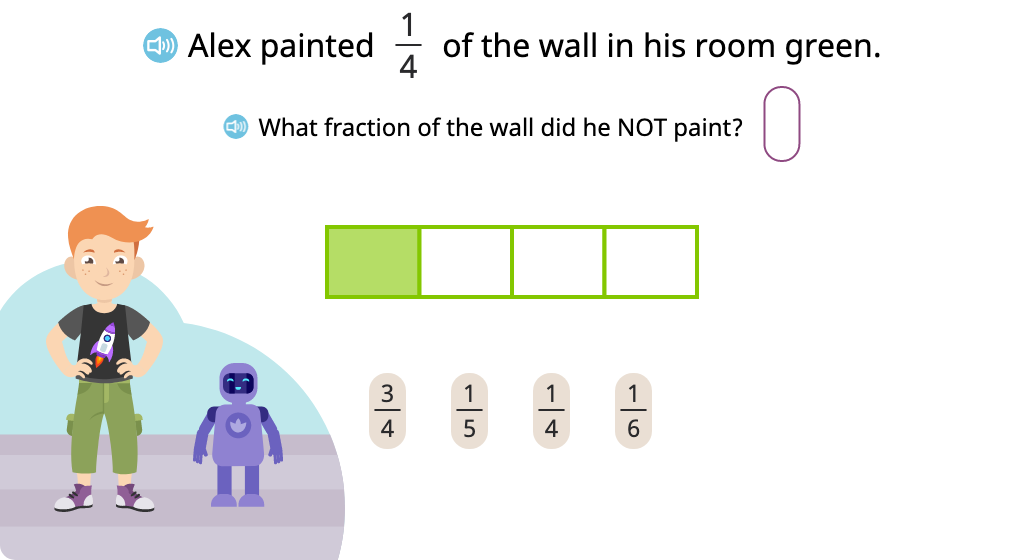
Solve word problems involving complementary fractions
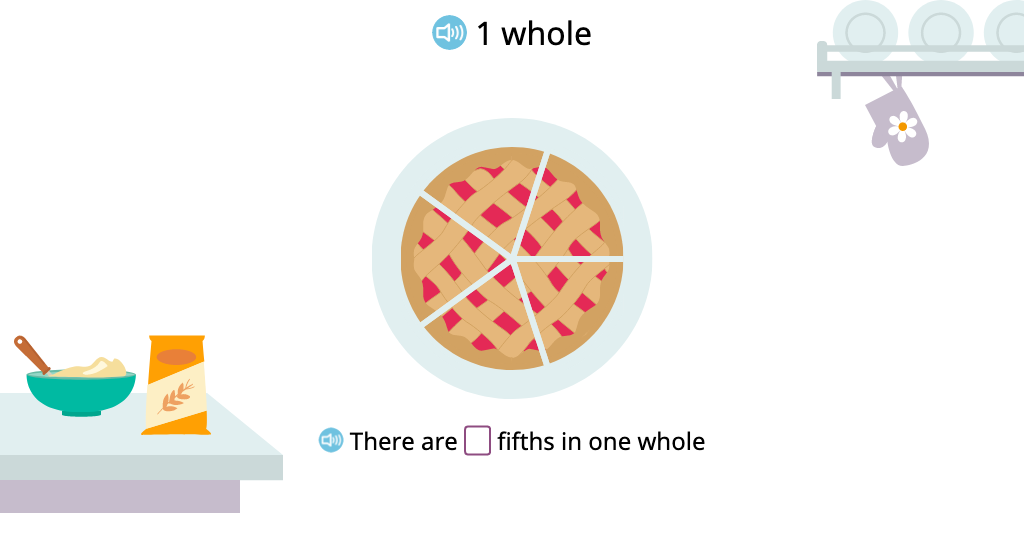
Determine the number of fractional parts in a whole
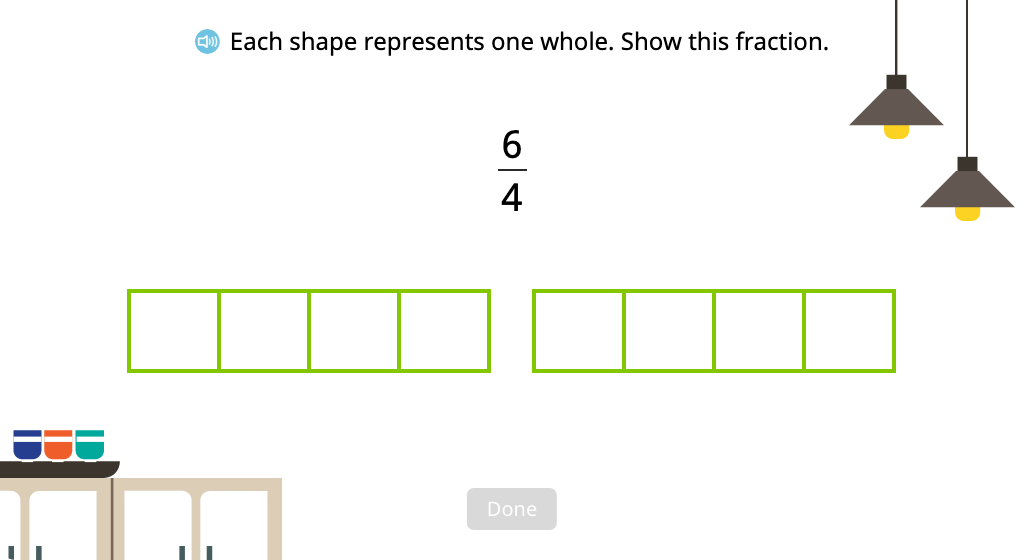
Solve problems involving multiple wholes and improper fractions

Identify a set of figures whose shading represents an improper fraction
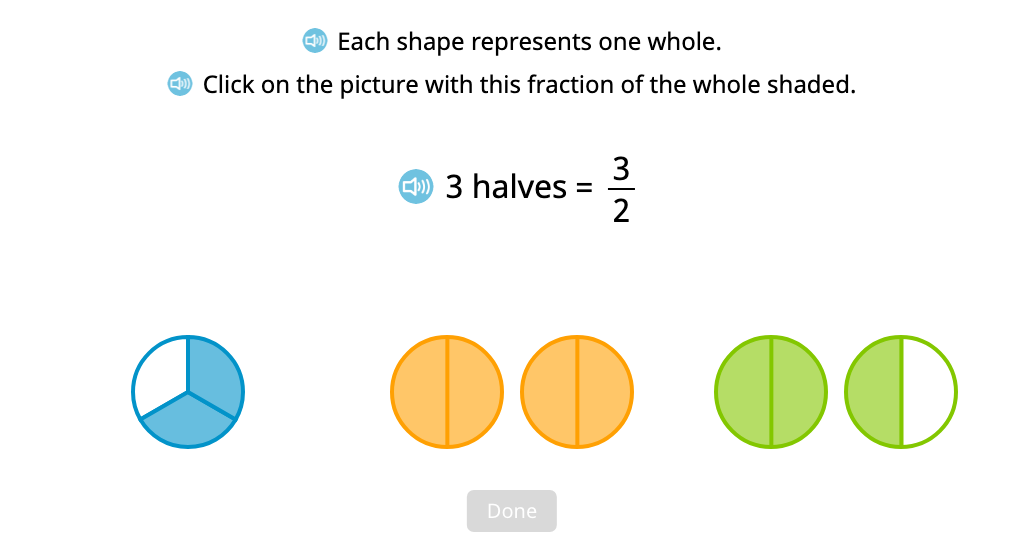
Label a set of figures whose shading represents an improper fraction
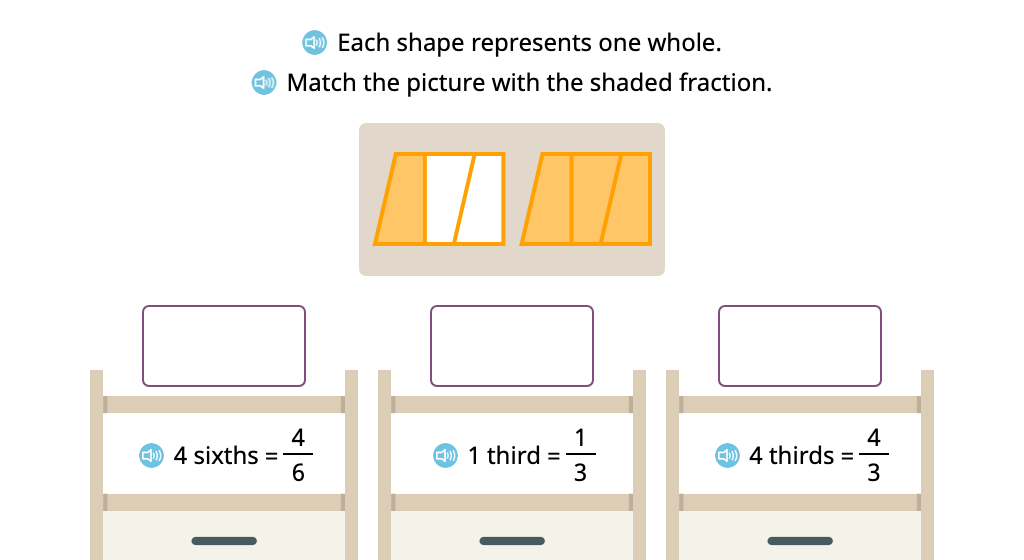
Divide and shade a set of figures to represent an improper fraction
Topic C: Comparing Unit Fractions and Specifying the Whole
Based on visual models, students learn that the more parts in a whole, the smaller each unit fraction. They then compare unit fractions using both words and symbols, and they relate the unit fraction to the whole.
Compare unit fractions based on a model
Compare unit fractions using <, =, and > with and without a model

Identify and label a unit fraction model that is greater or less than a given unit fraction model
Identify a whole based on a given unit fraction
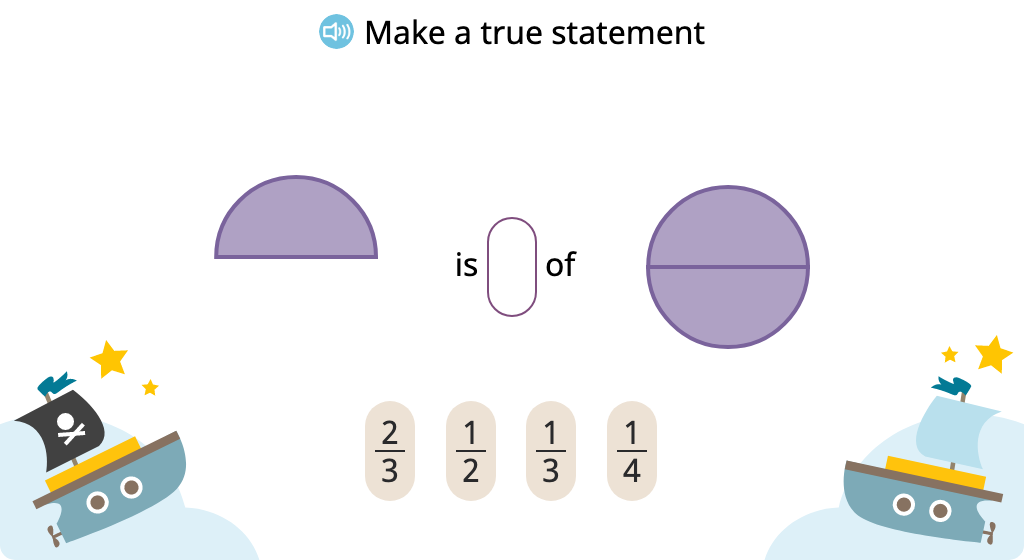
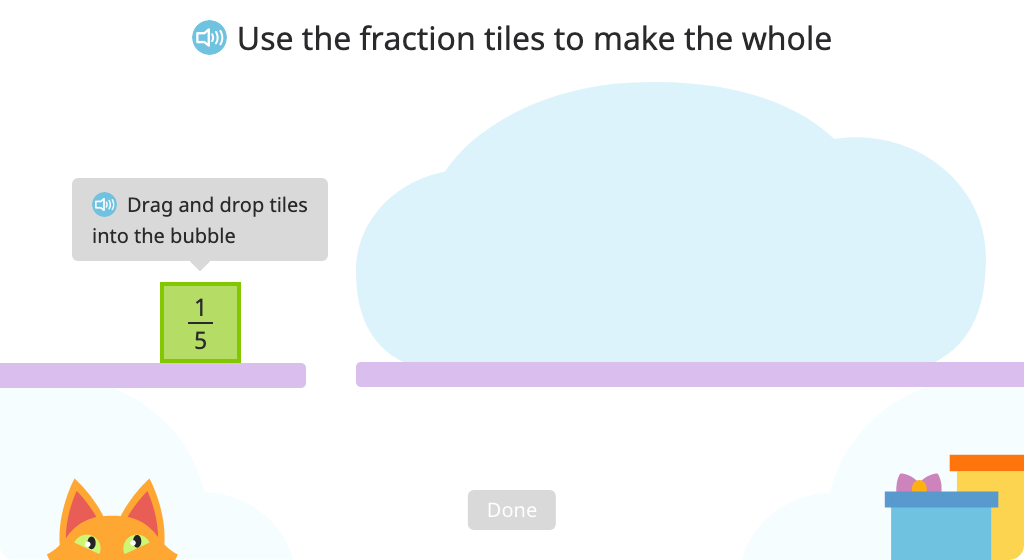
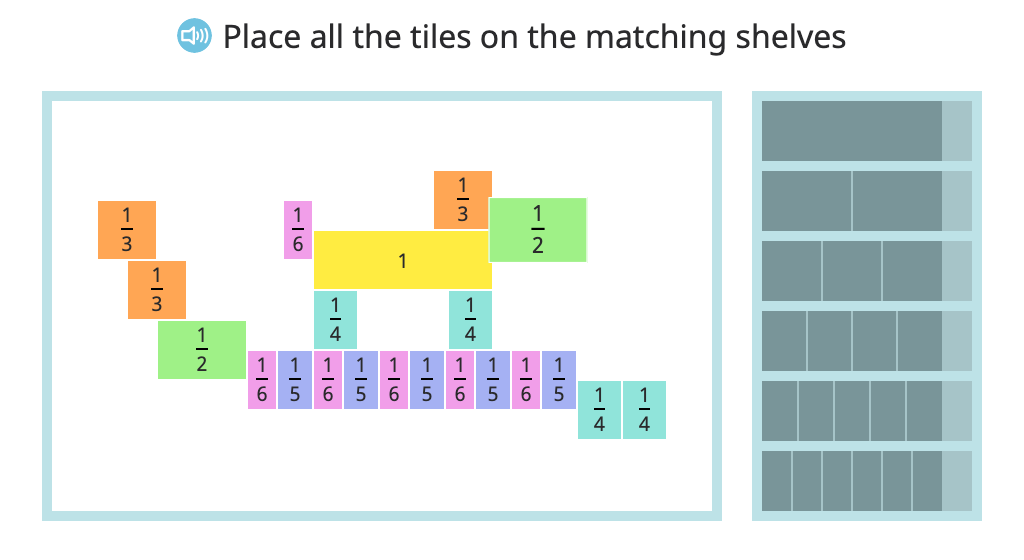
Build a whole using the correct number of unit fraction tiles
Topic D: Fractions on the Number Line
Students apply their understanding of fractions to numbers on a number line. They learn that there are numbers between the whole numbers on a number line and how to identify them. Using this tool, students are able to name equivalent whole number/fraction pairs, label fractions greater than 1, and compare fractions with unlike denominators.
Identify fractions on a number line and write 1 as a fraction

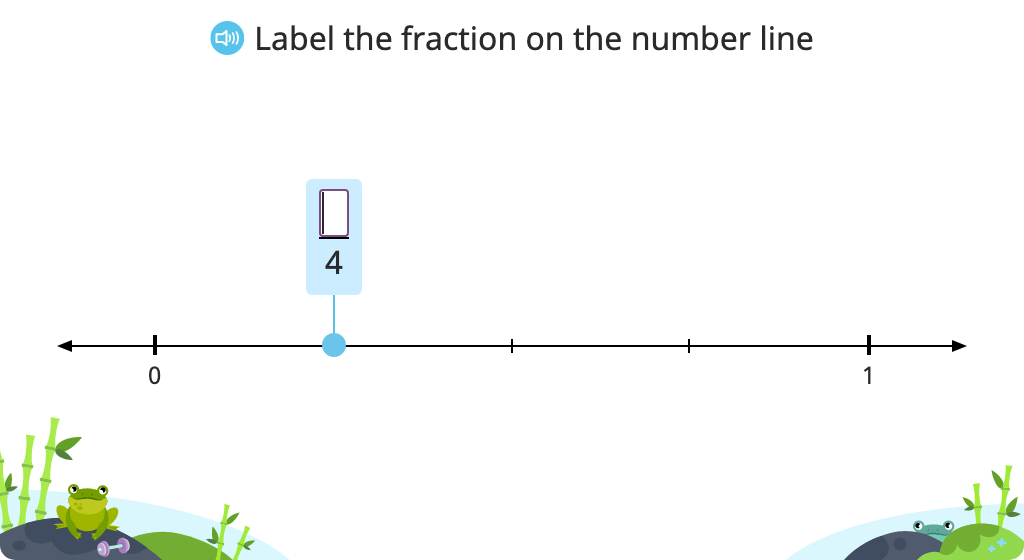
Label fraction numerators on a number line
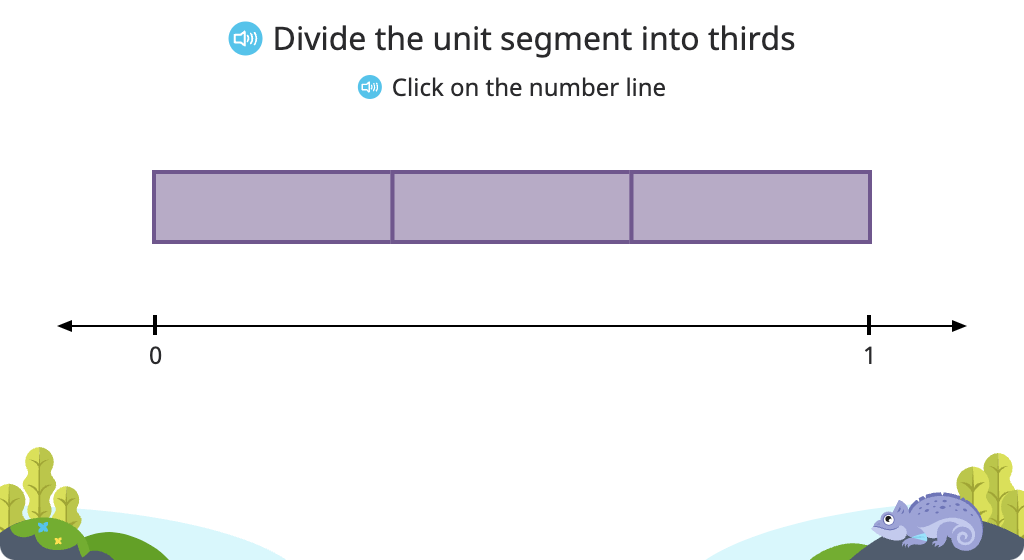
Label fractions on a number line (numerator and denominator)
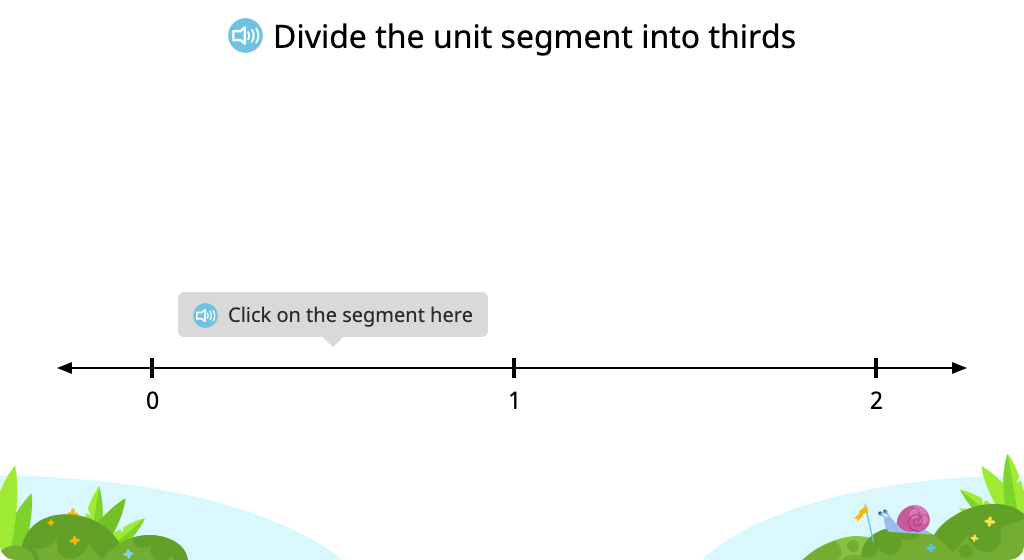
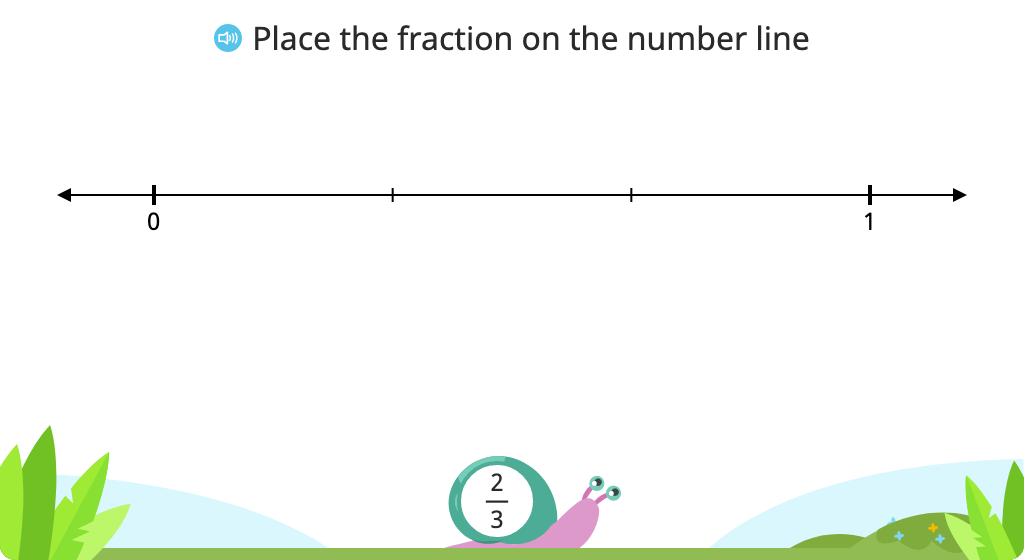
Segment a number line into fractions and place a given fraction on the number line
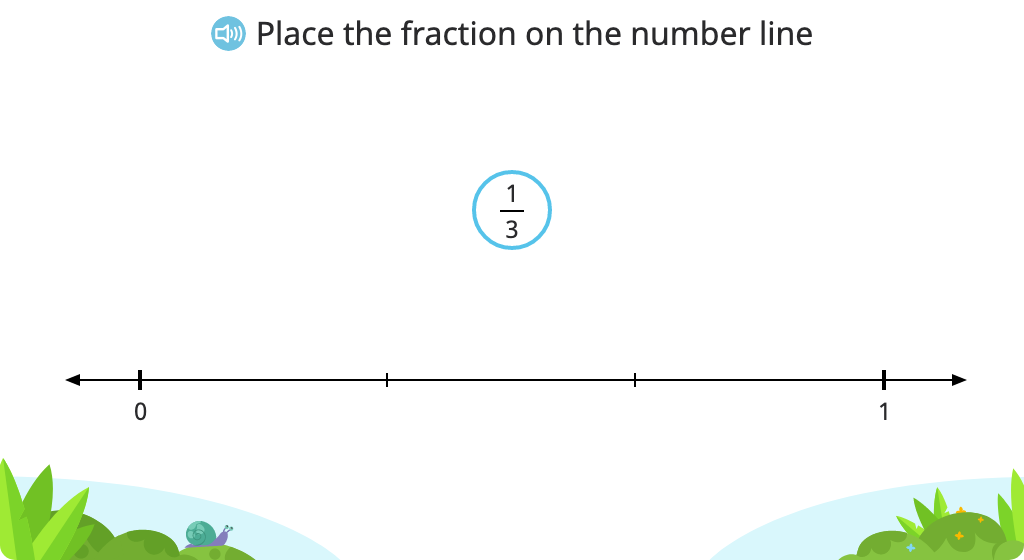
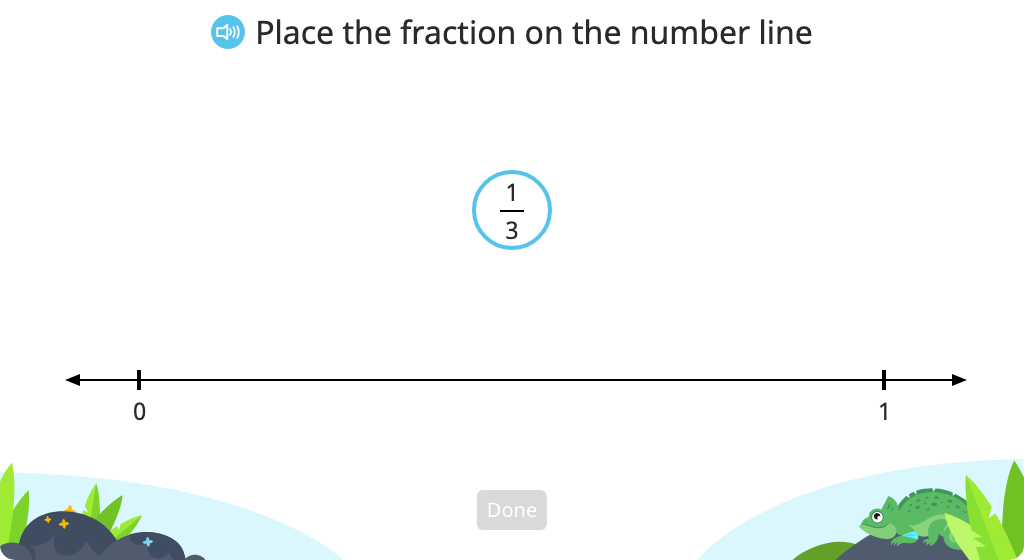
Place a given fraction on a number line visually (without hashmarks)
Label fraction numerators on a number line in numbers greater than 1
Identify a fraction that is equivalent to a whole number on a number line
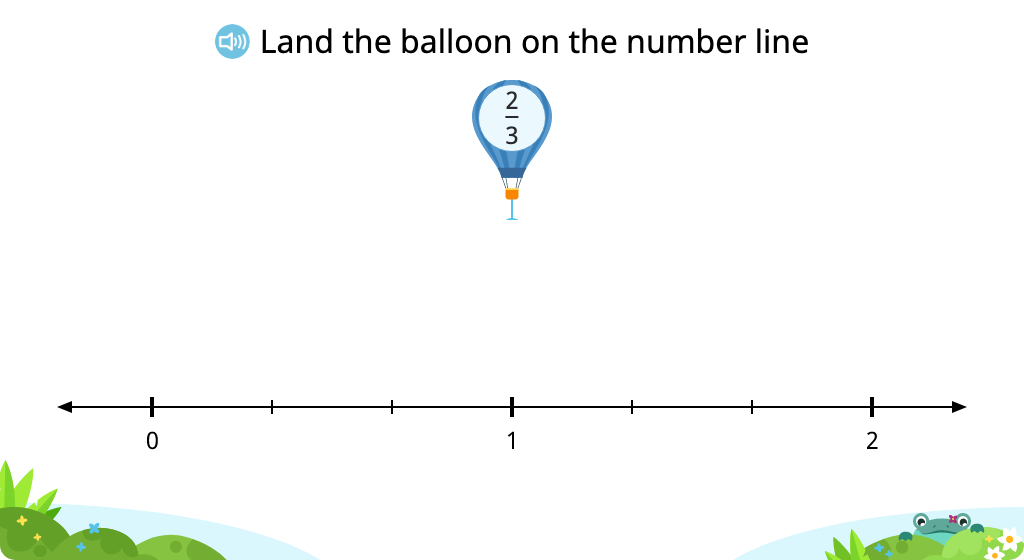
Place fractions greater than 1 on a number line
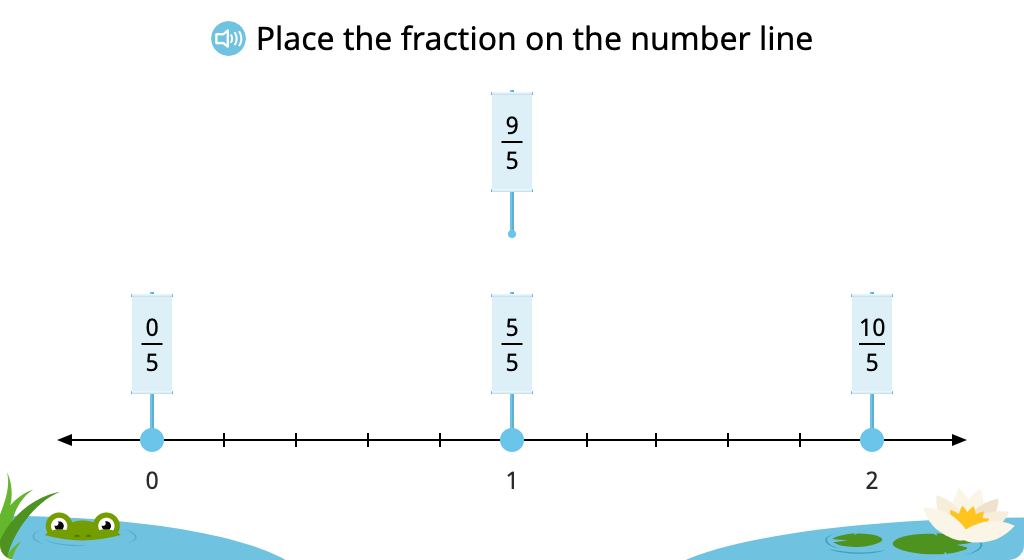
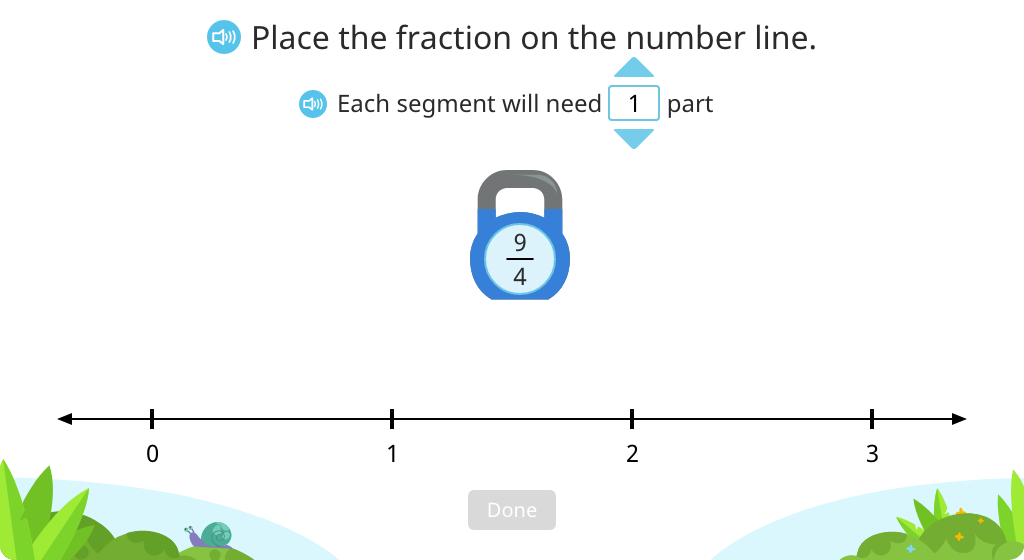
Segment a number line into fractions and place a given fraction (greater than 1) on the number line
Label fractions greater than 1 on a number line
Compare fractions with unlike denominators on a number line
Use <, =, or > to compare fractions with unlike denominators on a number line
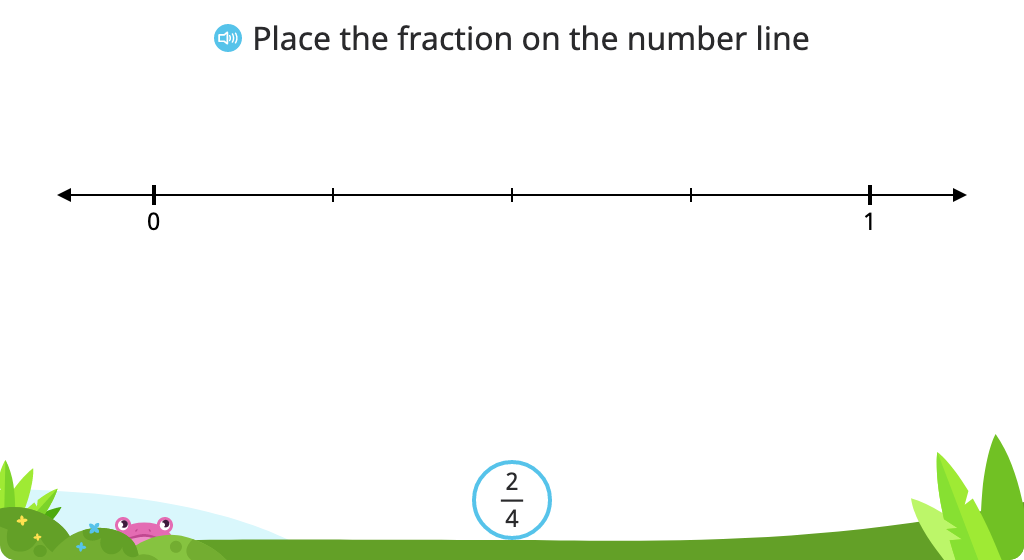
Topic E: Equivalent Fractions
Using familiar shaded models and the number line, students focus on concepts of equivalent fractions. They extend this understanding to include whole numbers and fractions greater than 1.
Create, label, identify, and compare equivalent fractions
Identify equivalent fractions using the number line (less than 1)

Identify equivalent fractions using the number line (greater than 1)
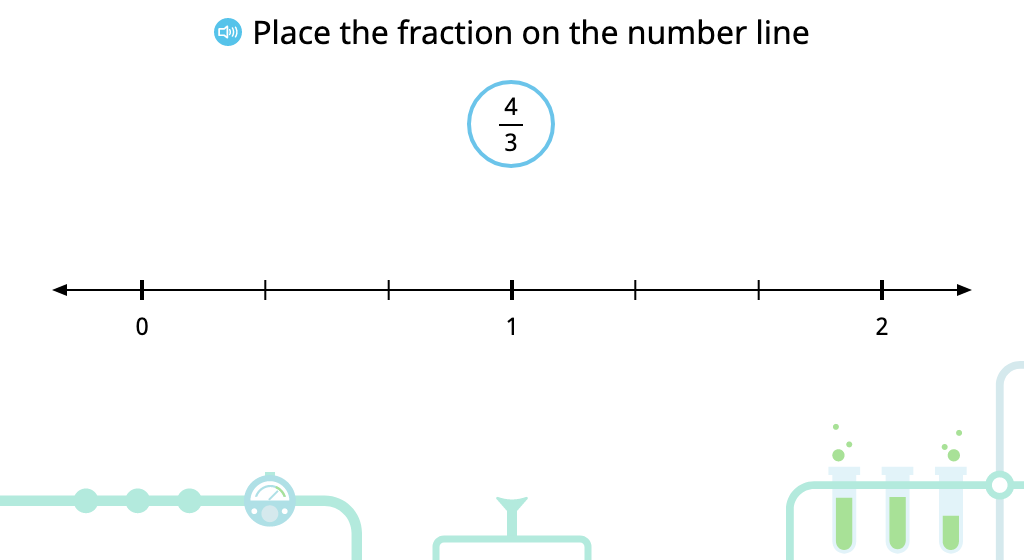
Label equivalent fractions on a number line
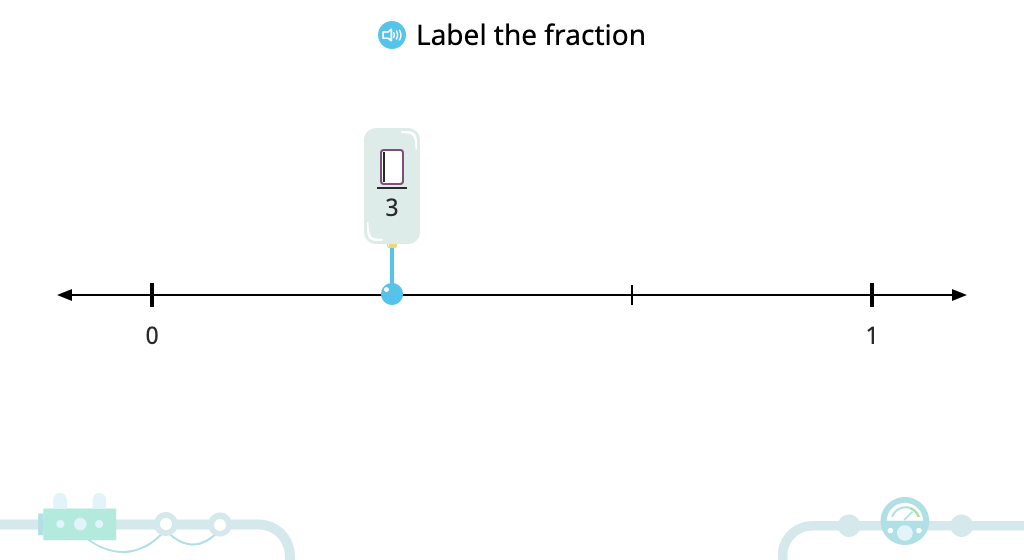
Label two equivalent fractions based on models
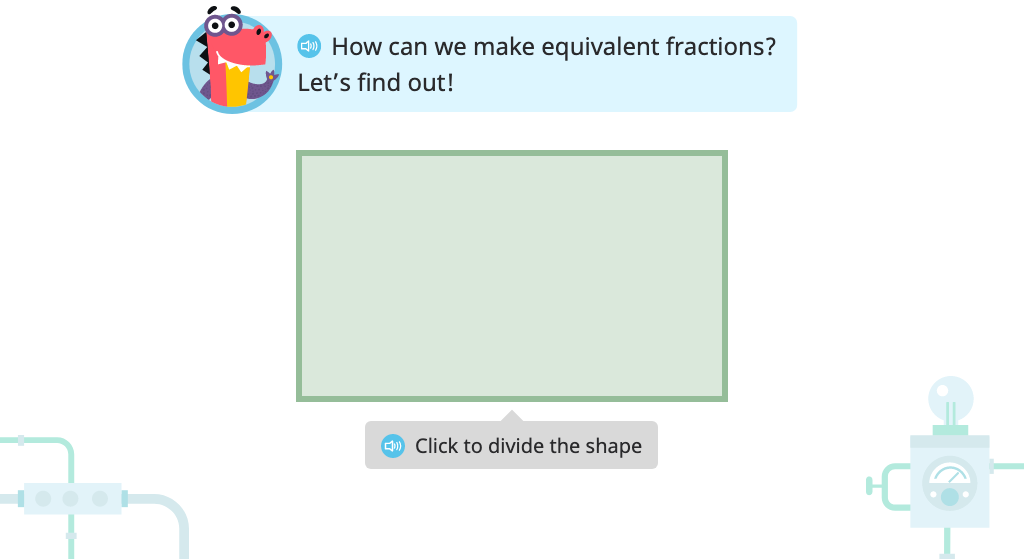
Label three equivalent fractions based on models
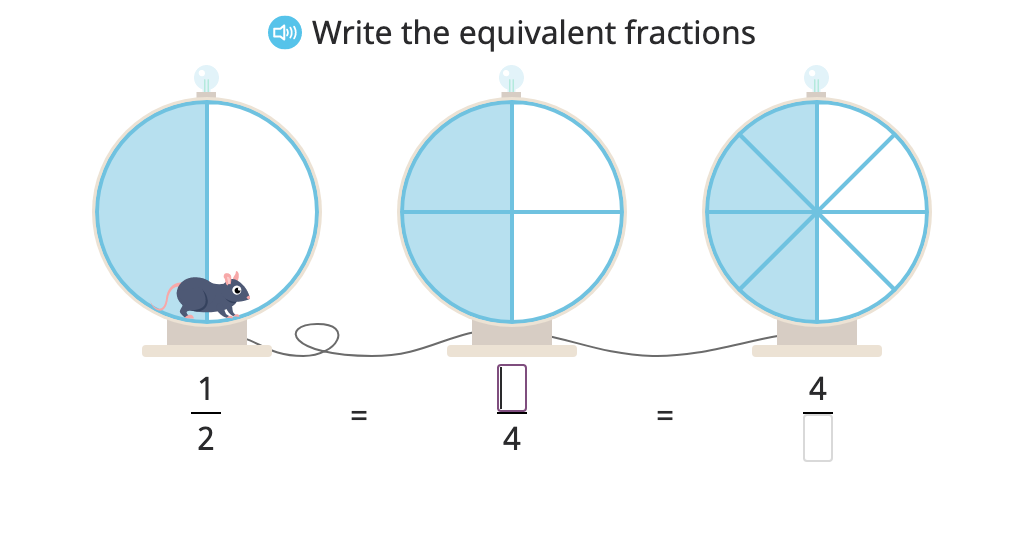
Label fractions equivalent to 1 whole
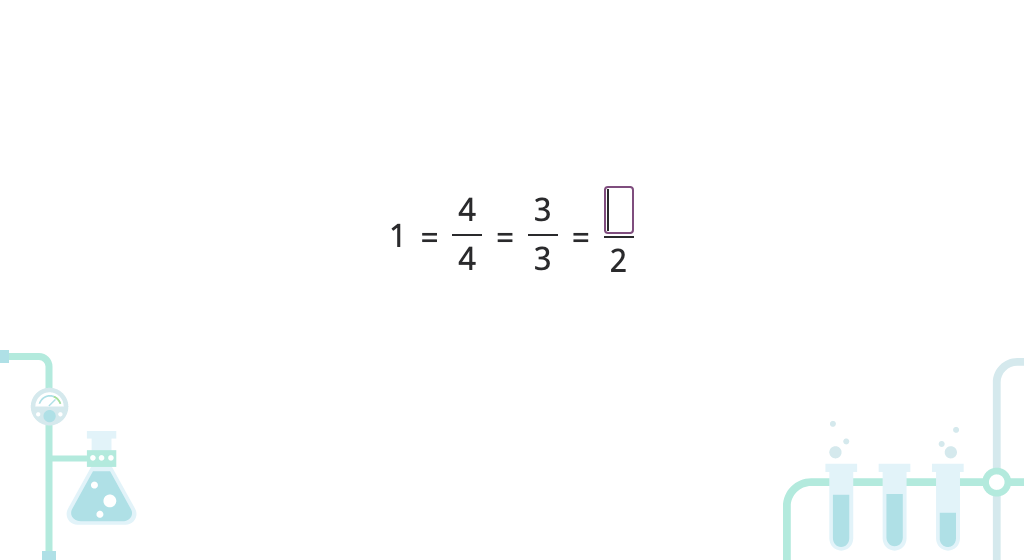
Write whole numbers as fractions (denominator of 1)
Write whole numbers as fractions (various denominators)
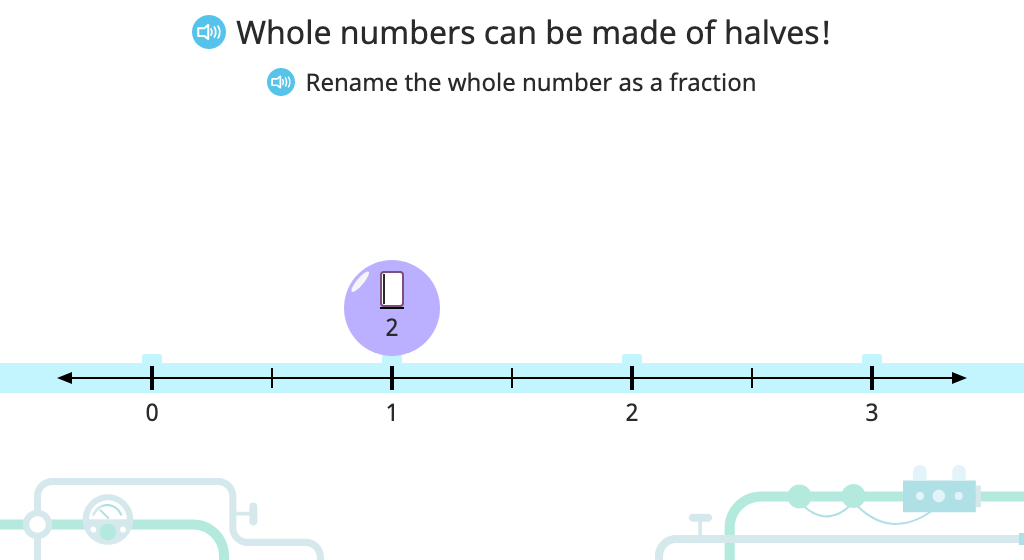
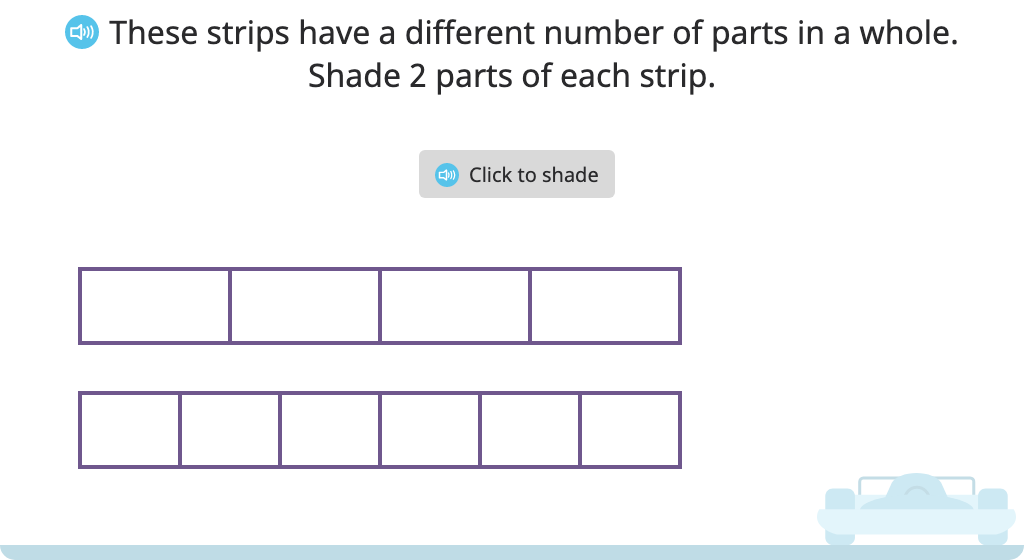
Topic F: Comparison, Order, and Size of Fractions
Based on visual models, students learn to compare two fractions with the same numerator or two fractions with the same denominator. To do so, they apply their understanding of creating and naming fractions, as well as using the <, =, and > symbols.
Compare fractions with the same numerator or the same denominator based on a model
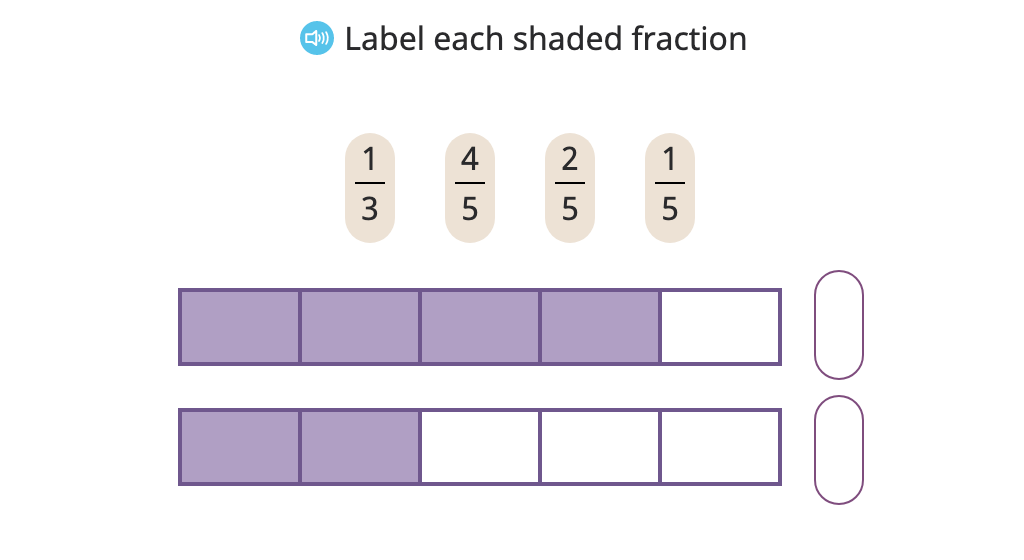
Shade and compare fractions with the same numerator based on a model
Label and compare fractions with the same numerator
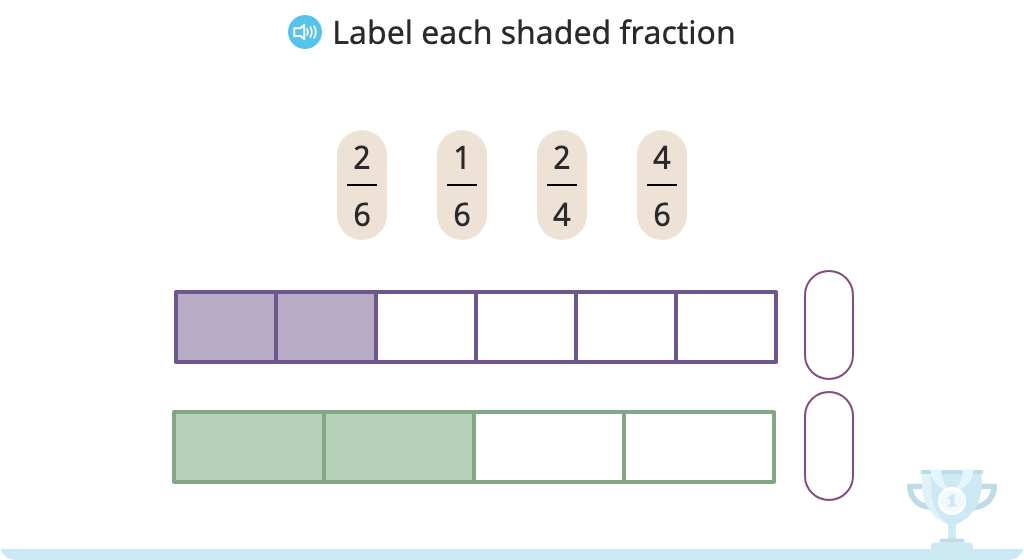
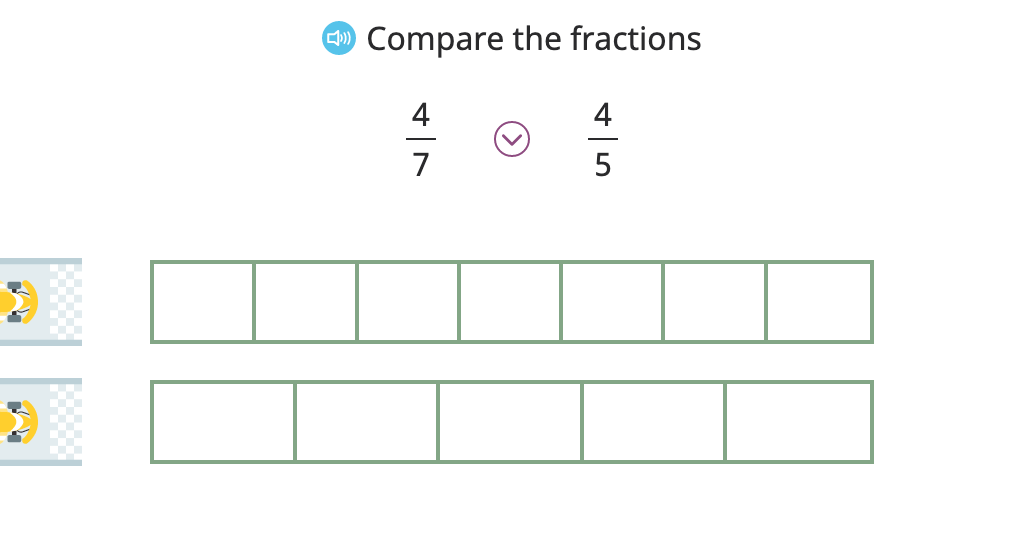
Compare fractions with the same numerator or the same denominator
MODULE 6. Collecting and Displaying Data
Topic A: Generate and Analyze Categorical Data
Students learn to create picture graphs and bar graphs, both scaled and unscaled. They learn to interpret data from these graphs and use them to solve word problems about the number of objects in categories.
Interpret data from a picture graph

Interpret data from scaled picture graphs (Level 1)

Interpret data from scaled picture graphs (Level 2)

Solve word problems based on data from a scaled picture graph

Interpret data from a horizontal bar graph

Interpret data from a vertical bar graph

Interpret data from a scaled bar graph (Level 1)

Interpret data from a scaled bar graph (Level 2)

Solve word problems based on data from a bar graph
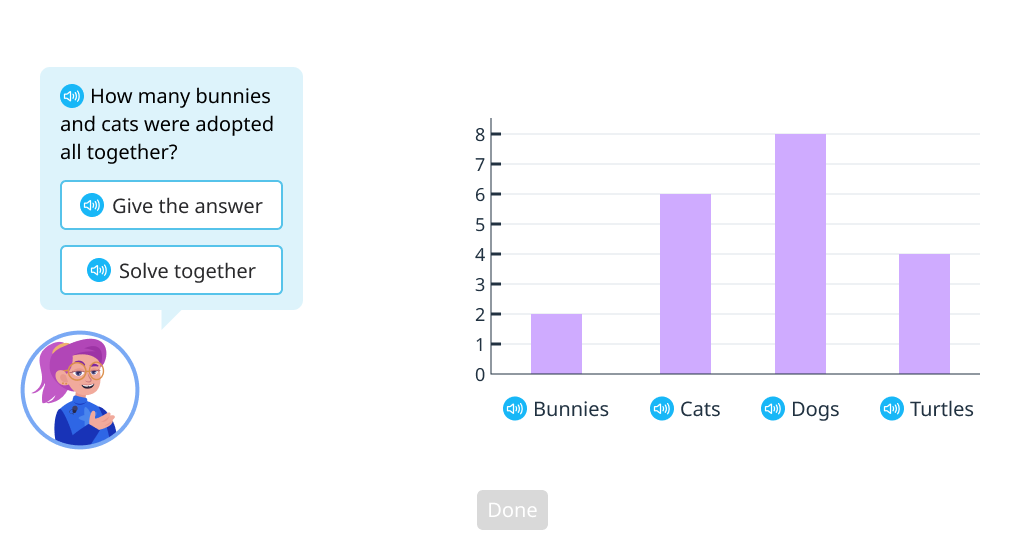
Solve word problems based on data from a scaled bar graph

MODULE 7. Geometry and Measurement Word Problems
Topic A: Attributes of Two-Dimensional Figures
Students learn that polygons are made of equal numbers of line segments and angles. They learn the names and attributes of common polygons and instances where the attributes intersect (i.e., squares and rhombuses).
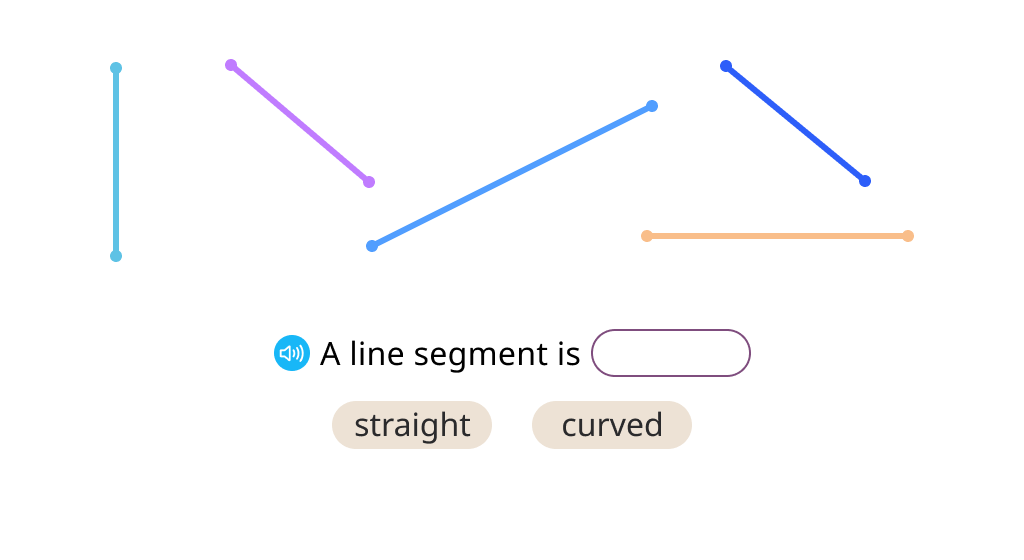
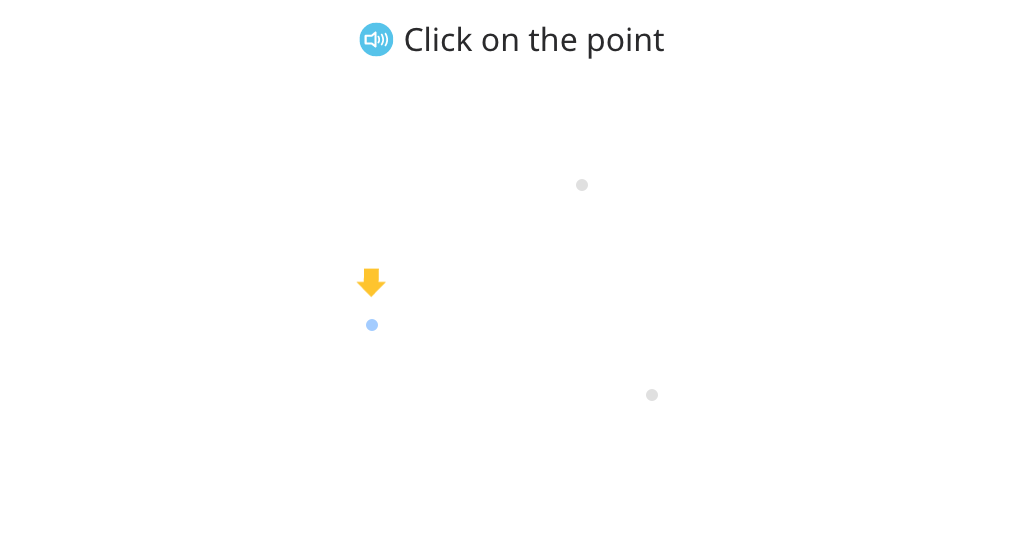
Explore the attributes of a line segment
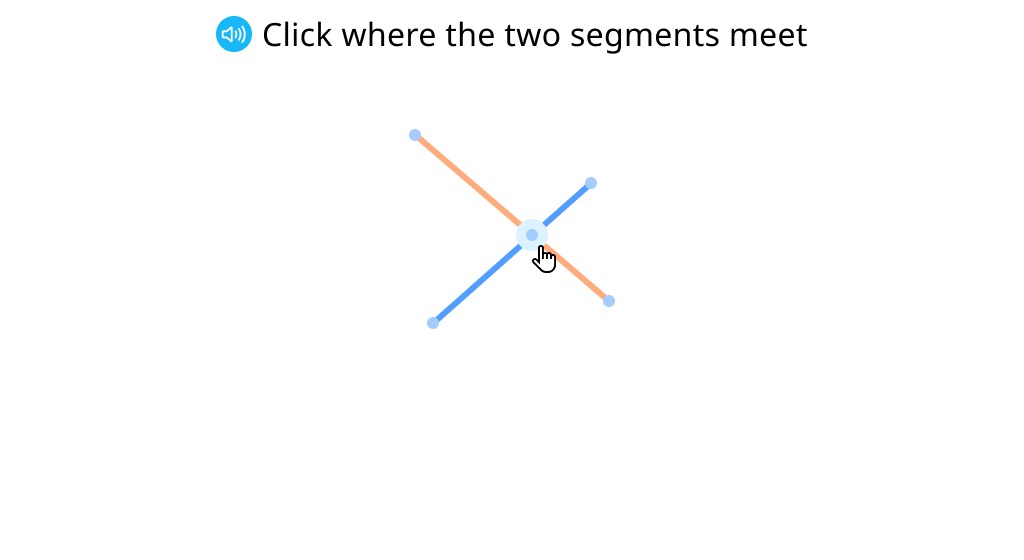
Identify common endpoints of line segments
Identify angles
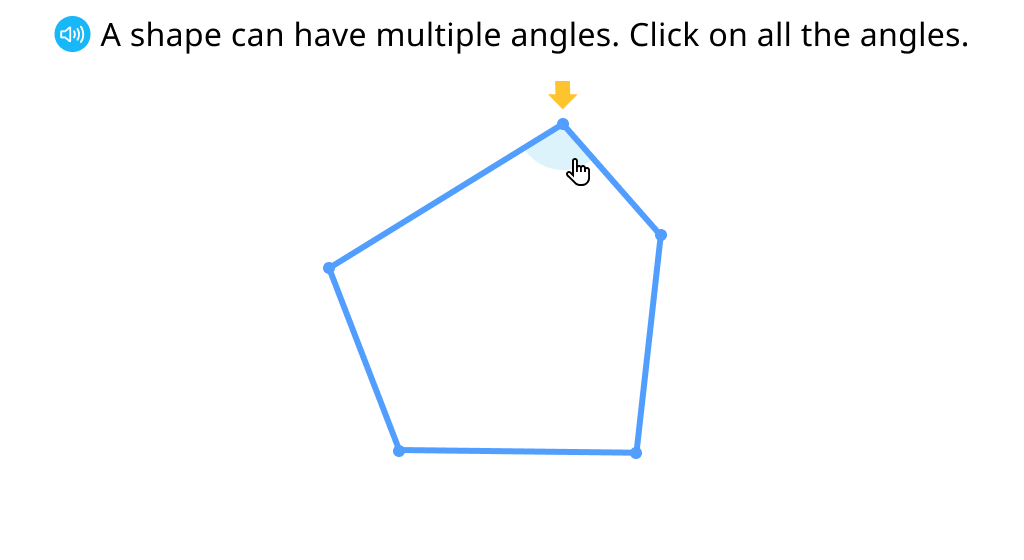
Identify the number of segments and angles in a triangle
Use a drafting triangle to identify right angles

Identify the number of segments and angles in a rectangle
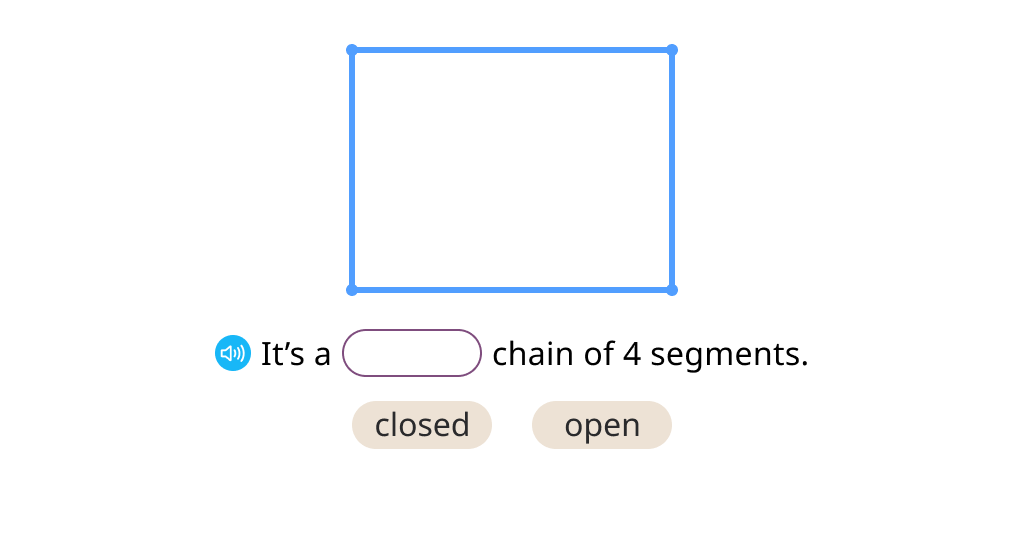
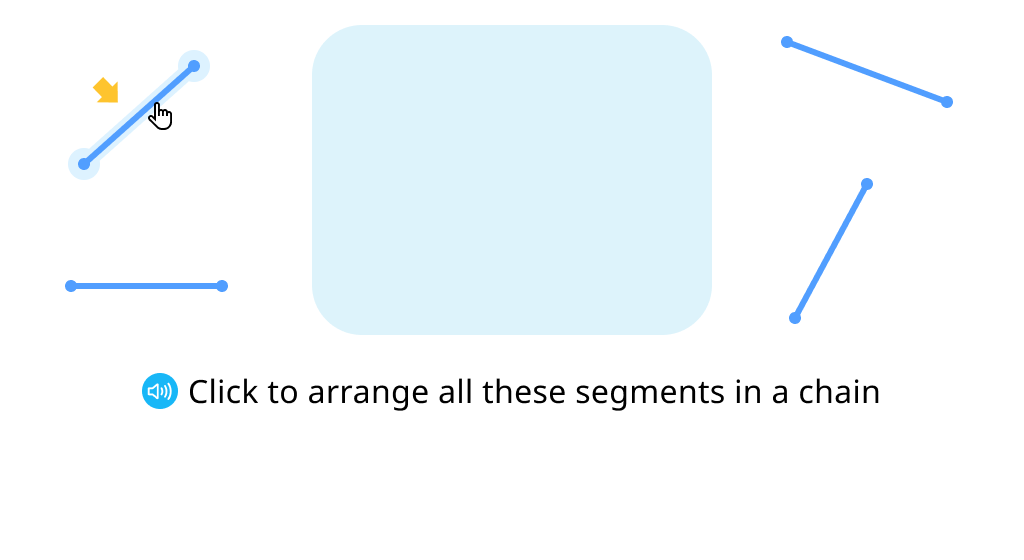
Create polygons with closed segment chains
Identify polygons
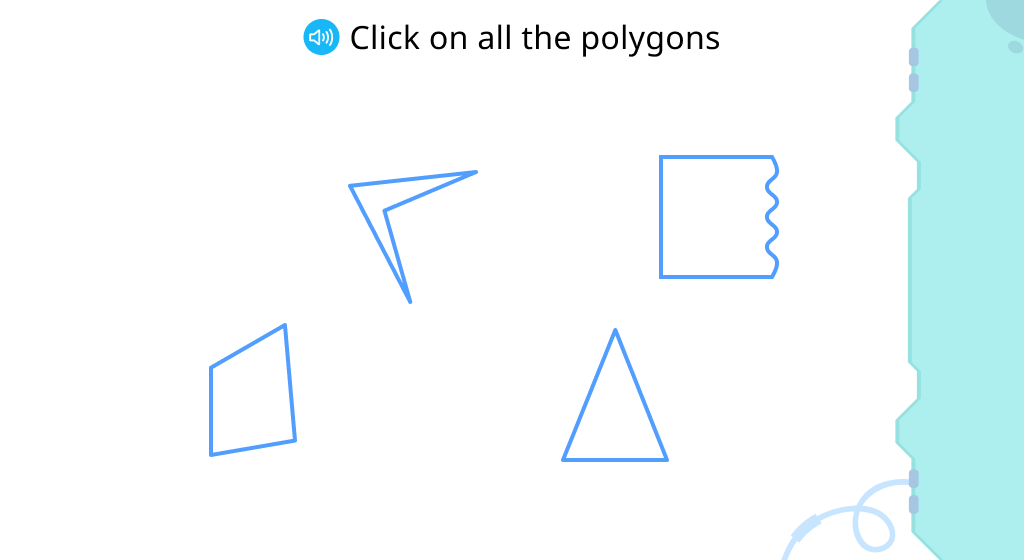
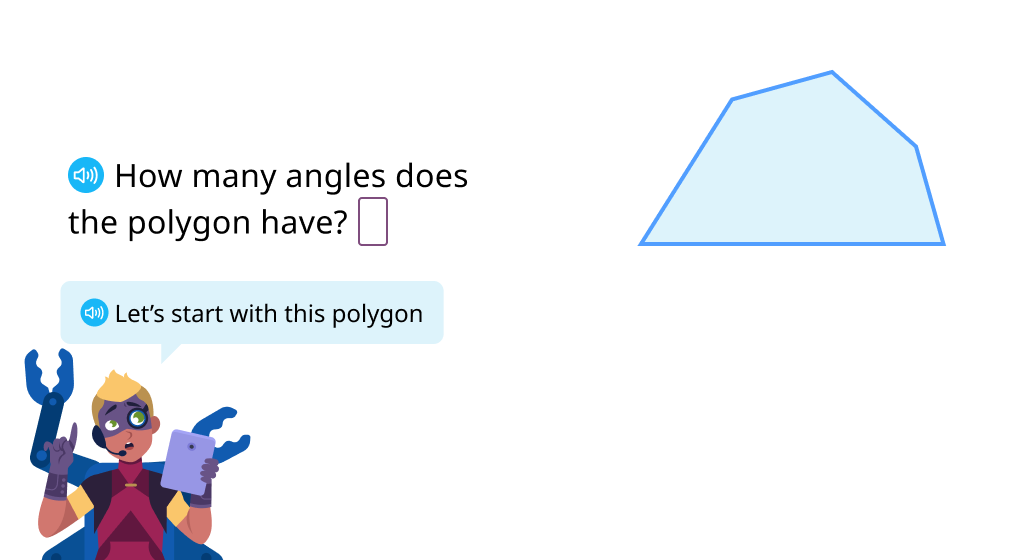
Determine the number of sides or angles of a given polygon (Level 1)
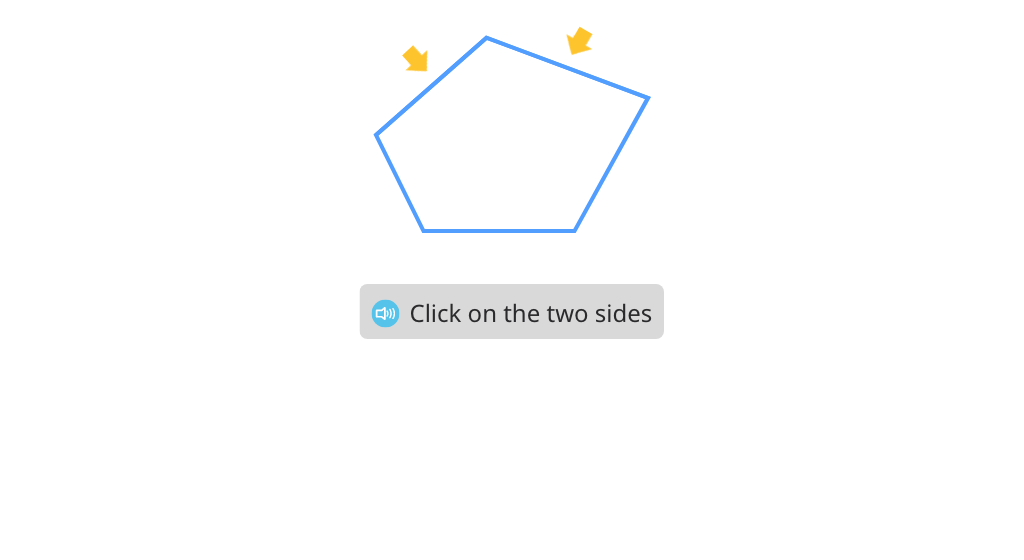
Determine the number of sides or angles of a given polygon (Level 2)

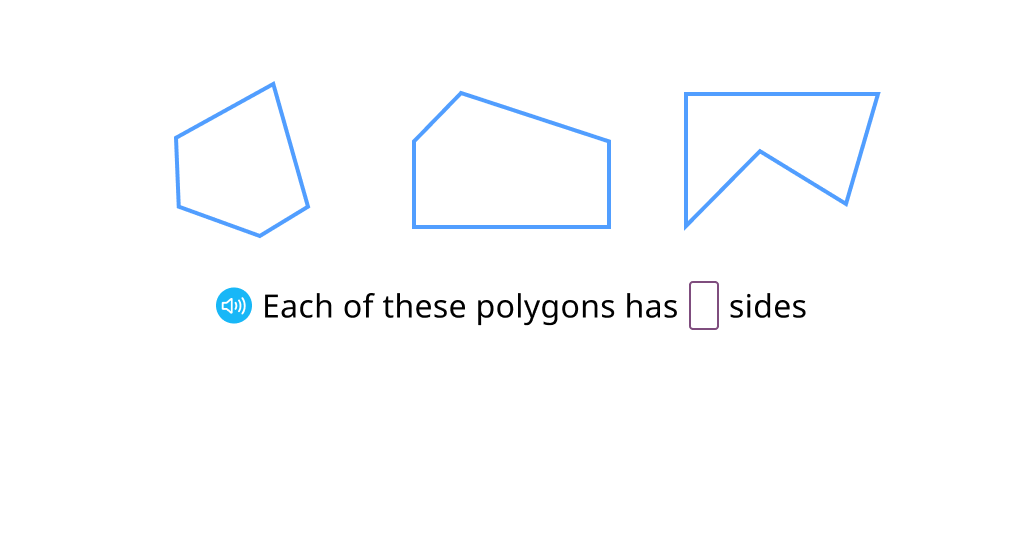
Determine how many sides a polygon can have
Identify quadrilaterals

Identify pentagons
Identify hexagons
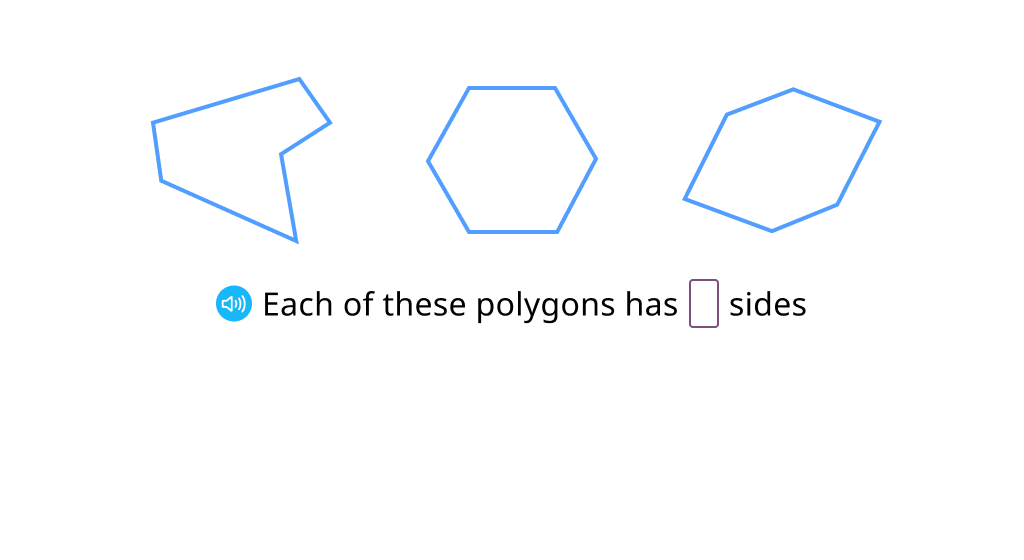
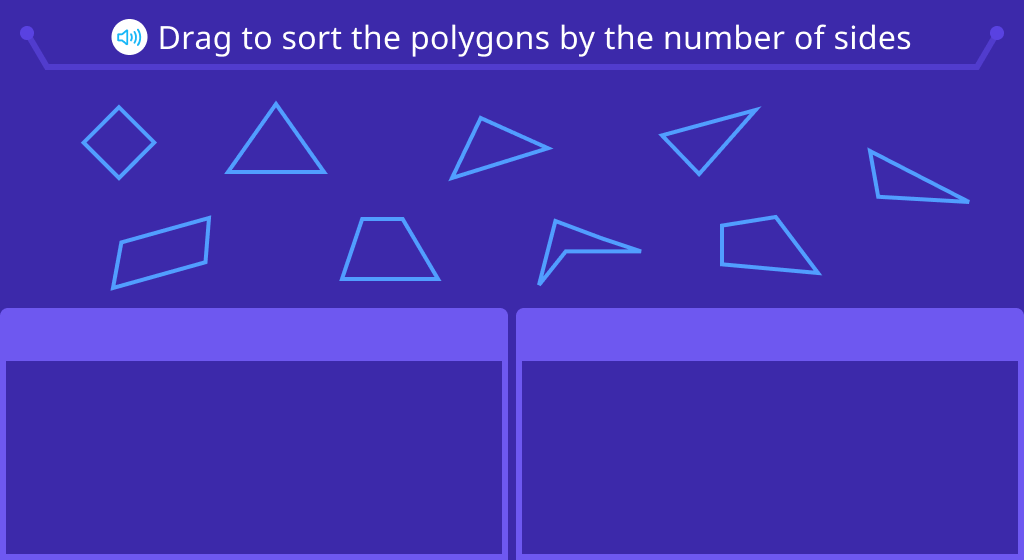
Sort and label polygons by the number of sides
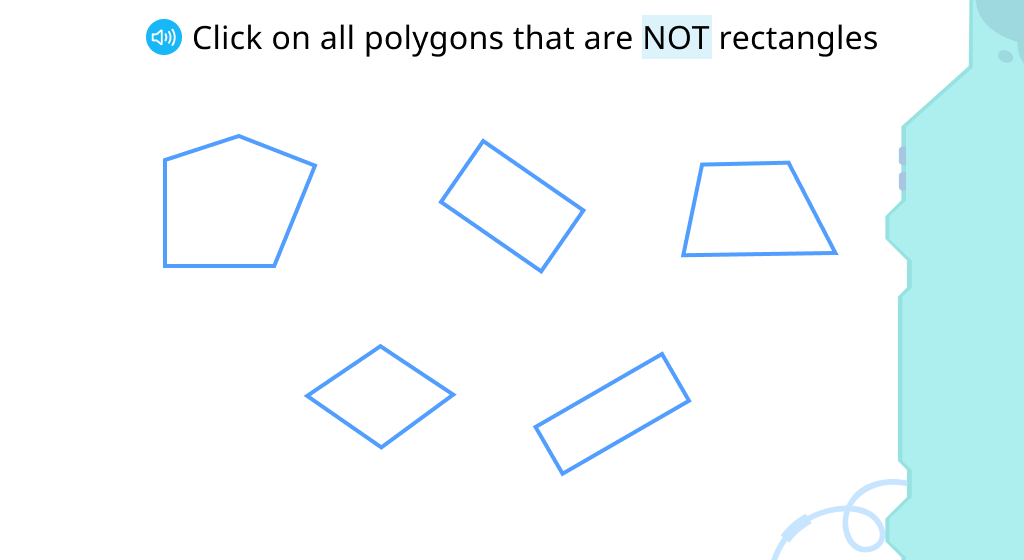
Explore attributes of a rectangle

Find opposite sides of a rectangle and their length
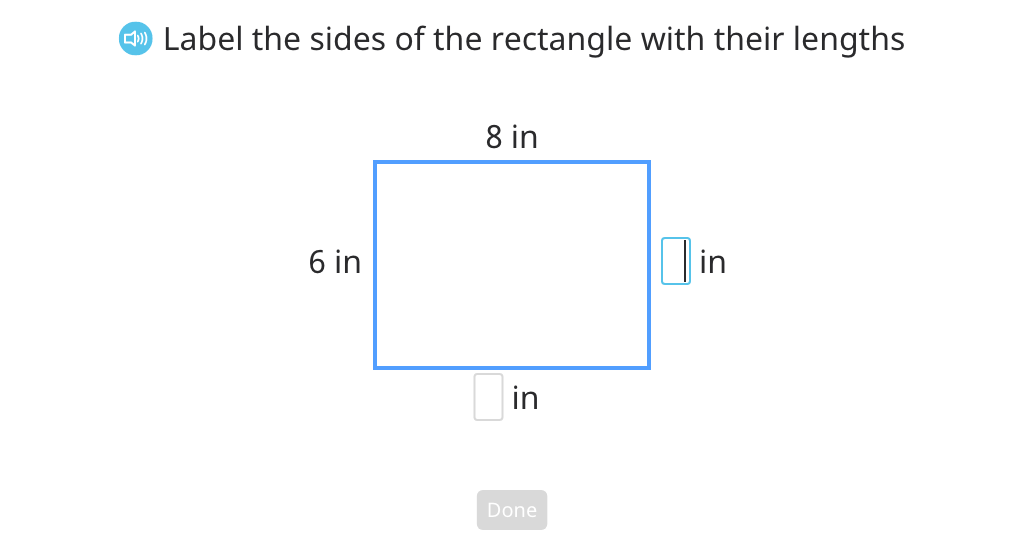
Find the lengths of a rectangle's sides
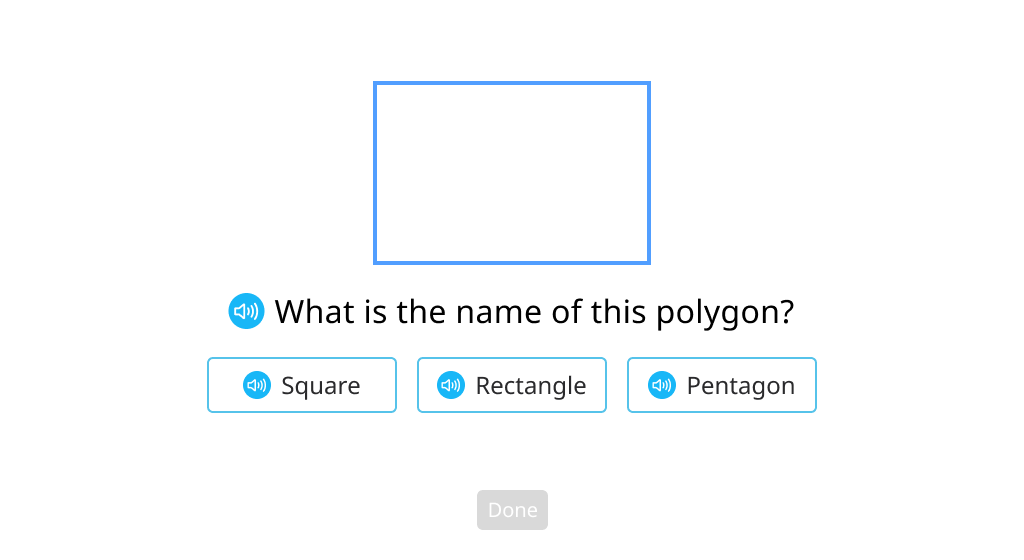
Solve riddles with the attributes of polygons
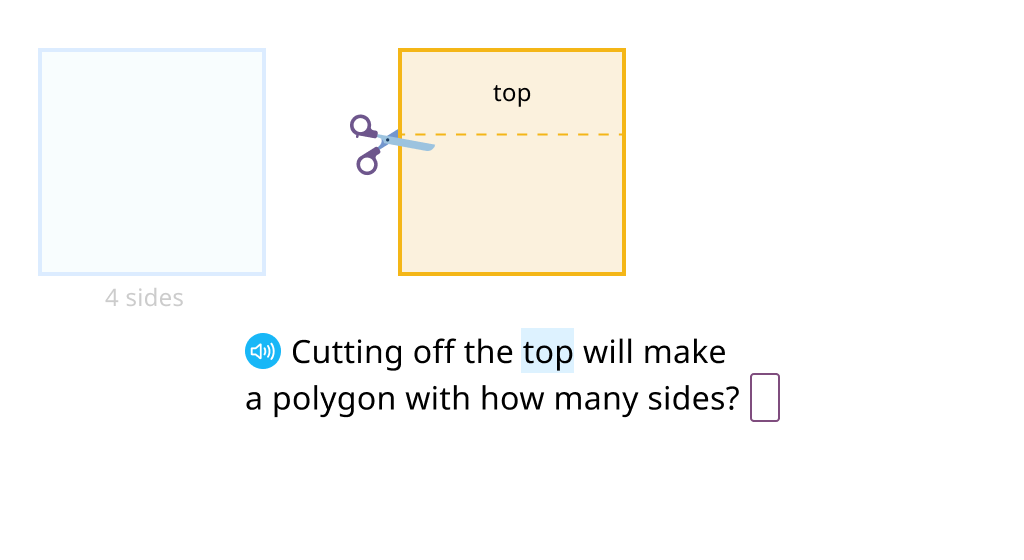
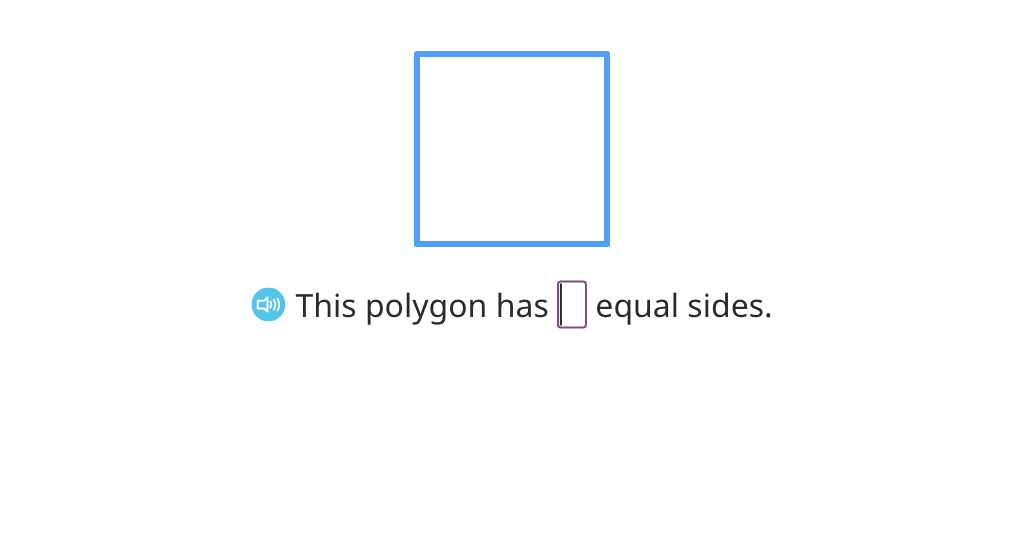
Explore attributes of a square
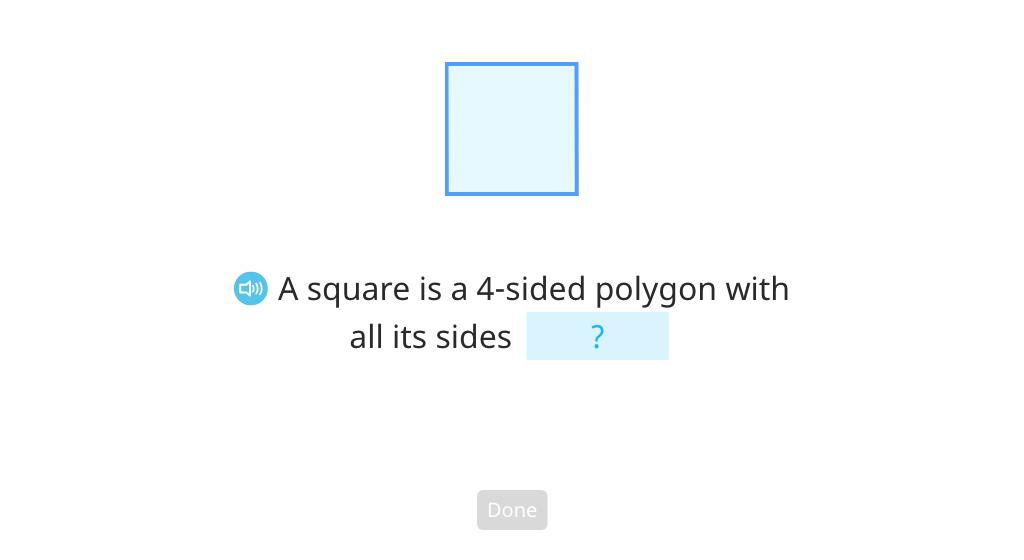
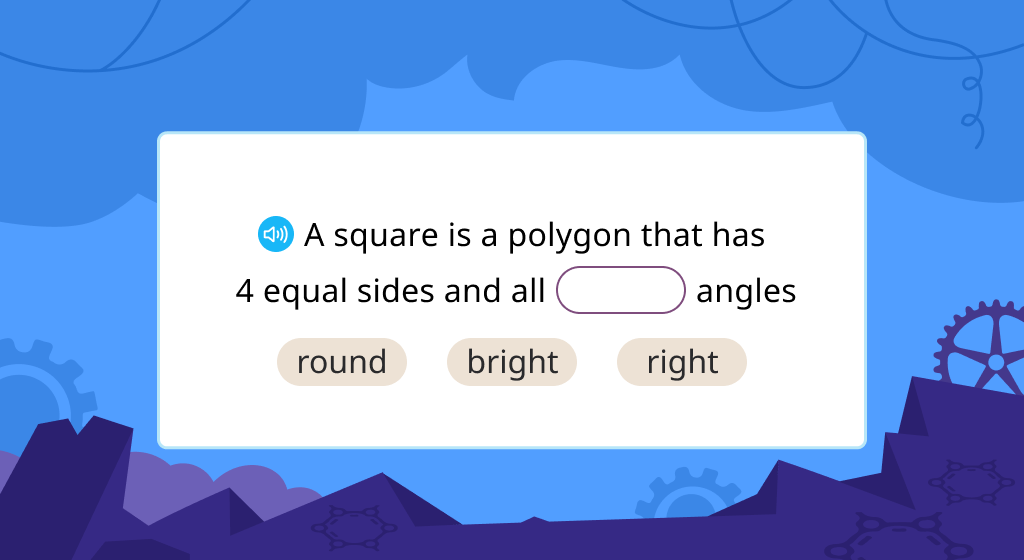
Review the attributes of squares, rectangles, and quadrilaterals
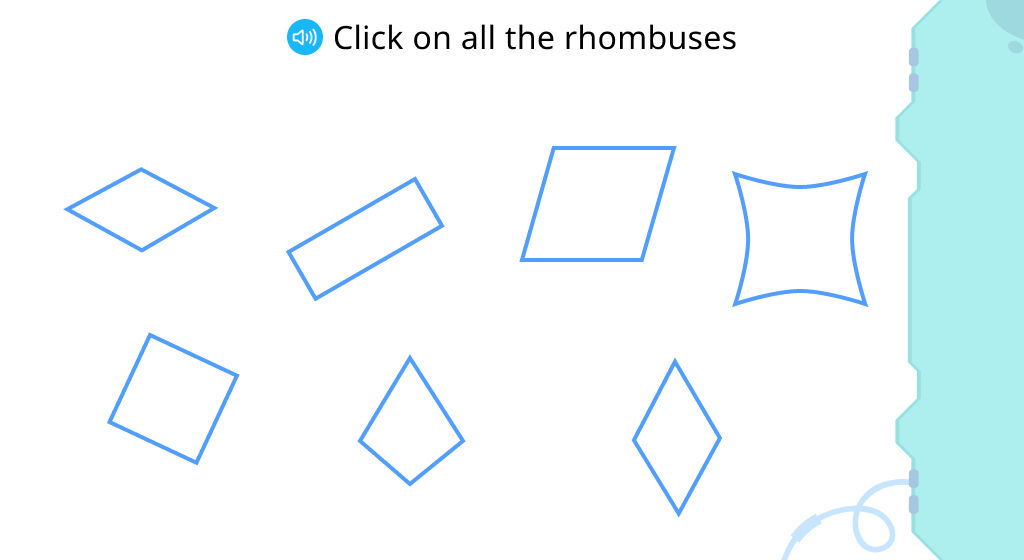
Explore attributes of a rhombus
Determine when a rhombus is also a square
Identify rhombuses and their attributes
Review attributes of polygons
Topic B: Problem Solving with Perimeter
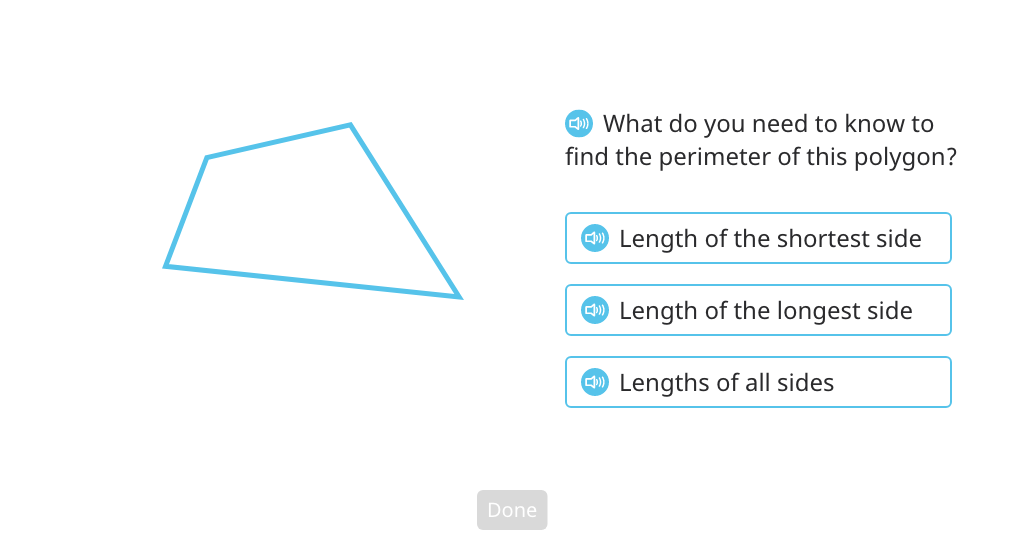
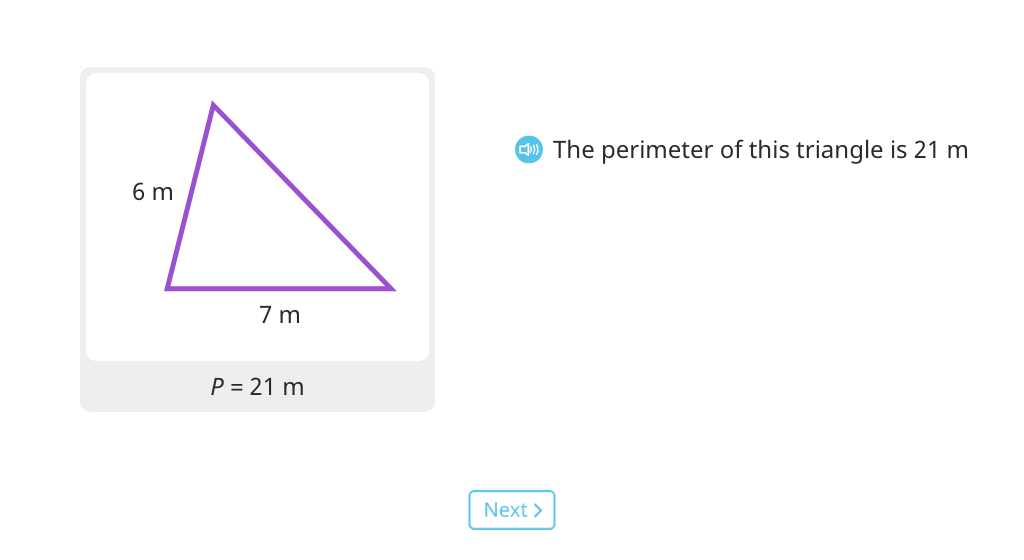
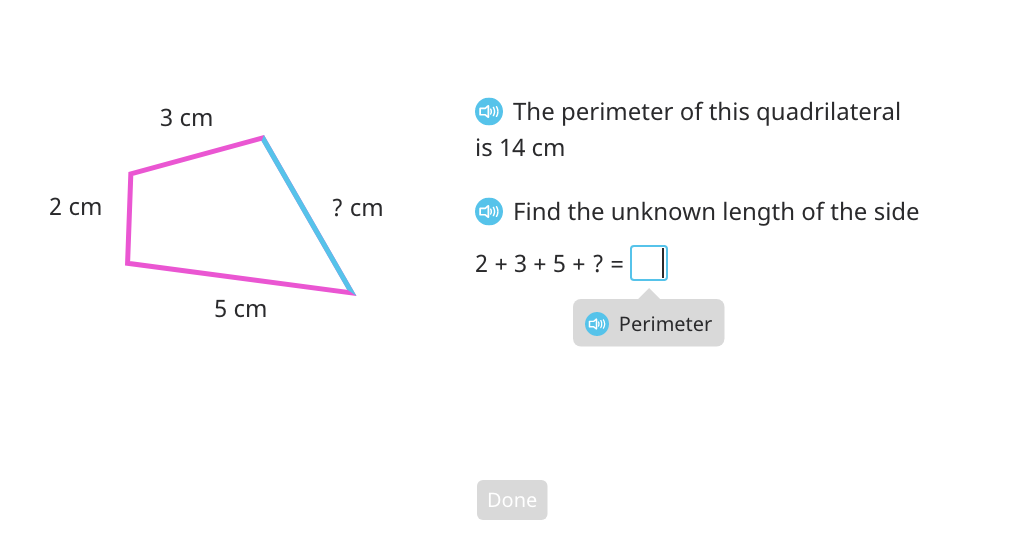
Students find the perimeter of a polygon by adding the lengths of its sides. They solve for the length of an unknown side and find the perimeters of equal-sided polygons.
Identify the perimeter of a polygon

Measure and add to find the perimeter of a polygon
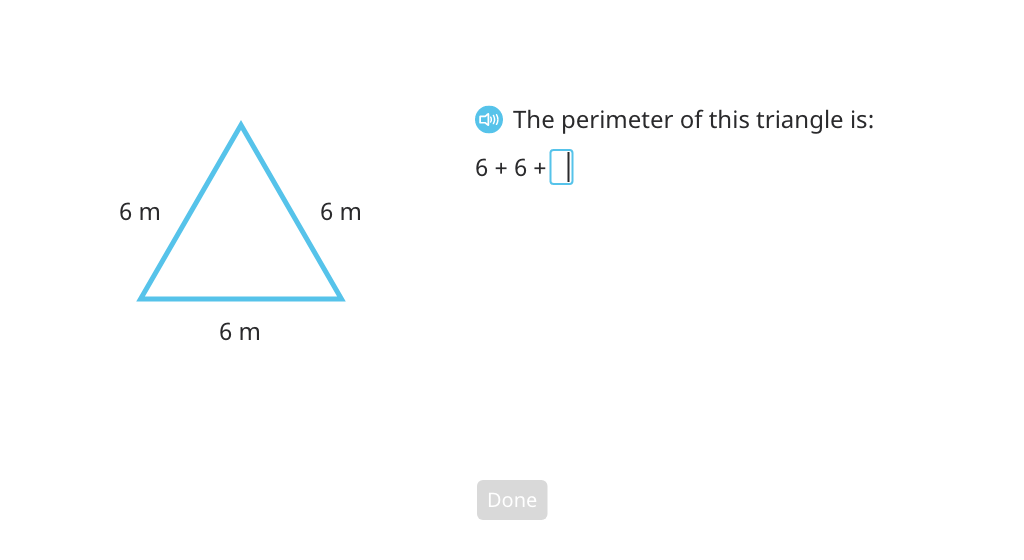
Find the perimeter of a triangle
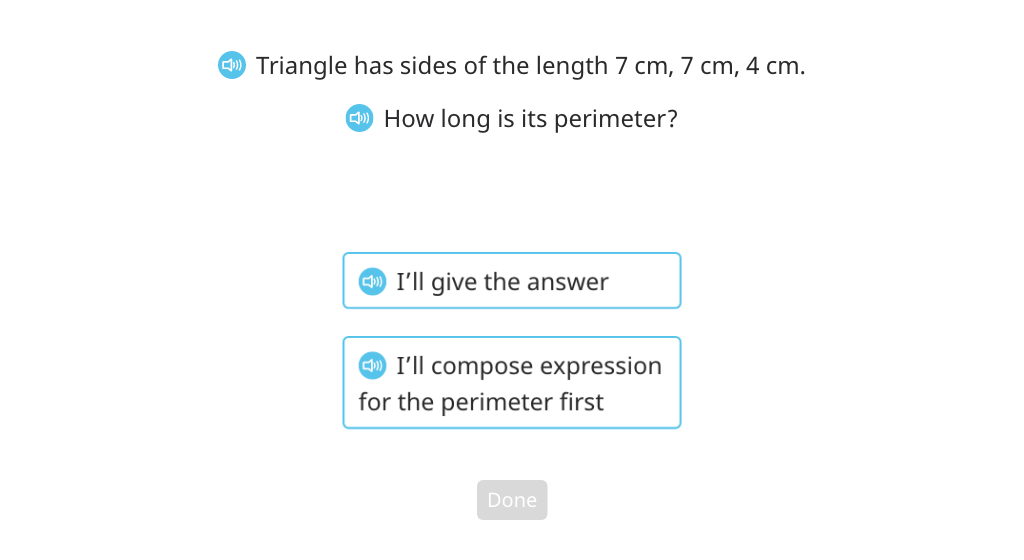
Find the perimeter of a rectangle
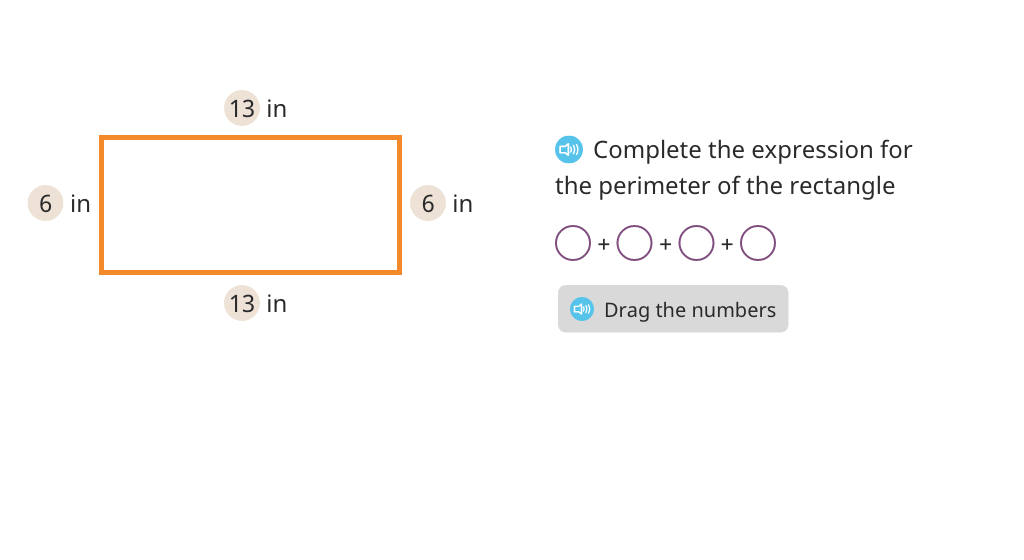
Find the perimeter of a polygon
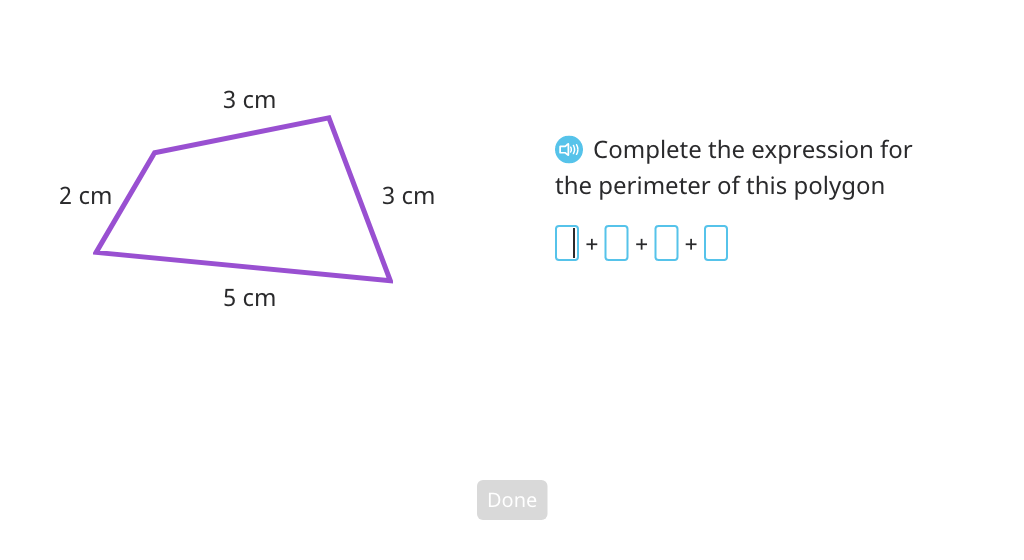
Find the perimeter of a pentagon
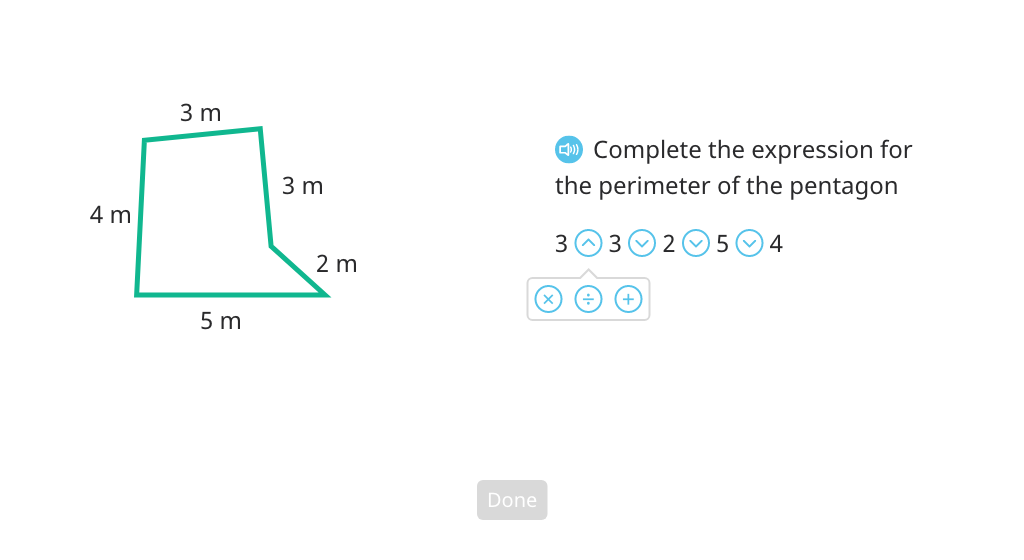
Find the length of an unknown side of a triangle
Find the length of an unknown side of a quadrilateral
Find the perimeter of a equal-sided polygon using multiplication