Curriculum for Grade 5
Grade Description: Students dig more deeply into place value patterns and operations. Their understanding grows to include decimals in the hundredths and thousandths, operations with fractions and decimals, multi-digit multiplication and division with remainders, area models, properties of multiplication and division, estimation, and measuring volume. We introduce the coordinate plane (quadrant I), which students use to solve problems.
MODULE 1. Place Value and Decimal Fractions
Topic A: Multiplicative Patterns on the Place Value Chart
Relying on solid understanding of the place value chart and powers of ten, students multiply and divide to solve problems with a decimal number as a factor or quotient.
Multiply by 10 with and without a place value chart

Multiply by 100 with and without a place value chart

Multiply by 1,000 with and without a place value chart

Multiply by 10, 100, and 1,000

Complete a pattern of multiplication by 10 or 100

Divide by 10 with and without a place value chart

Divide by 100 with and without a place value chart

Divide by 1,000 with and without a place value chart

Divide by 10, 100, and 1,000

Identify and complete a pattern of division by 10 or 100

Factor out powers of 10 to multiply numbers with a single non-zero digit

Multiply numbers with a single non-zero digit

Record the relationship between hundredths and thousandths using a place value chart

Multiply a decimal number by 10 with and without a place value chart

Multiply a decimal number by 100 with and without a place value chart

Multiply a decimal number by 1,000 with and without a place value chart

Multiply a decimal number by 10, 100, and 1,000

Complete a pattern of multiplication by 10, 100, and 1,000

Divide a decimal number by 10 with and without a place value chart

Divide a decimal number by 100 with and without a place value chart

Divide a decimal number by 1,000 with and without a place value chart

Divide a number by 10, 100, and 1,000

Complete a pattern of division by 10, 100, and 1,000

Represent repeated multiplication of 10 as 10 with an exponent

Represent 10 with an exponent as repeated multiplication

Multiply a decimal number by 10 with an exponent

Divide a number by 10 with an exponent

Topic B: Decimal Fractions and Place Value Patterns
Students use familiar symbols (<, =, >) to compare numbers to the thousandths place. They identify, compose, and arrange numbers of equal and unequal length.
Record a decimal number in expanded notation

Compare numbers to the hundredths place with and without a place value chart

Complete inequalities that compare numbers to the hundredths place

Arrange decimal numbers in order from smallest to greatest (Level 1)

Arrange decimal numbers in order from smallest to greatest (Level 2)

Arrange decimal numbers in order from smallest to greatest (Level 3)

Topic C: Place Value and Rounding Decimals
Students review the place value of decimal numbers. They use the basic algorithm for rounding whole numbers to round decimals to the ones, tenths, and hundredths place.
Review decimal place value

Use the basic algorithm to round decimals to the ones

Use the basic algorithm to round decimals to the tenths

Round decimal numbers to the tenths place (Level 1)

Round decimal numbers to the tenths place (Level 2)

Round decimal numbers to the tenths place (Level 3)

Use the basic algorithm to round decimals to the hundredths

Round decimal numbers to the hundredths place (Level 1)

Round decimal numbers to the hundredths place (Level 2)

Round the same decimal number to different place values (Level 1)

Round the same decimal number to different place values (Level 2)

Topic D: Adding and Subtracting Decimals
Based on the familiar disk model, students add and subtract numbers to the thousands place. They add and subtract in equations that require regrouping and learn to use the standard algorithm (column addition and column subtraction).
Add numbers to the hundredths place with regrouping using a disk model

Add numbers to the thousandths place with regrouping using a disk model

Add numbers to the thousandths place with regrouping using column addition and a disk model

Add numbers to the thousandths place with regrouping using column addition

Subtract numbers to the hundredths place with regrouping using a disk model

Subtract numbers to the thousandths place with regrouping using a disk model

Subtract numbers to the thousandths place with regrouping using column subtraction and a disk model

Subtract numbers of different lengths to the thousandths place with regrouping using column subtraction and a disk model

Subtract numbers to the thousandths place with regrouping using column subtraction

Topic E: Multiplying Decimals
Students take the first steps in understanding multiplication of a decimal number. Working with a single-digit whole number and a decimal number, students work step-by-step through the process using the familiar disk model. They trade disks to model regrouping and explore the importance of decimal point placement.
Multiply a decimal number with regrouping using a disk model

Multiply a decimal number with regrouping using a disk model and the standard algorithm

Compare multiplying a whole number with multiplying a decimal number with the same digits

Multiply a decimal number by converting it to a whole number and converting the product back to a decimal

Topic F: Dividing Decimals
Students rely on familiar models and procedures to apply their division knowledge to decimals. Step-by-step, they learn to correctly work through regrouping, using a new place value, using zeros, and placing a decimal in their quotient.
Divide a decimal number by a single-digit number based on a model

Divide a decimal number by a single-digit number with and without regrouping based on a model

Divide a decimal number by a single-digit number with and without regrouping based on a model

Divide a decimal number by a single-digit number with regrouping to a new place value based on a model

Divide a decimal number by a single-digit number with and without regrouping using long division and a model
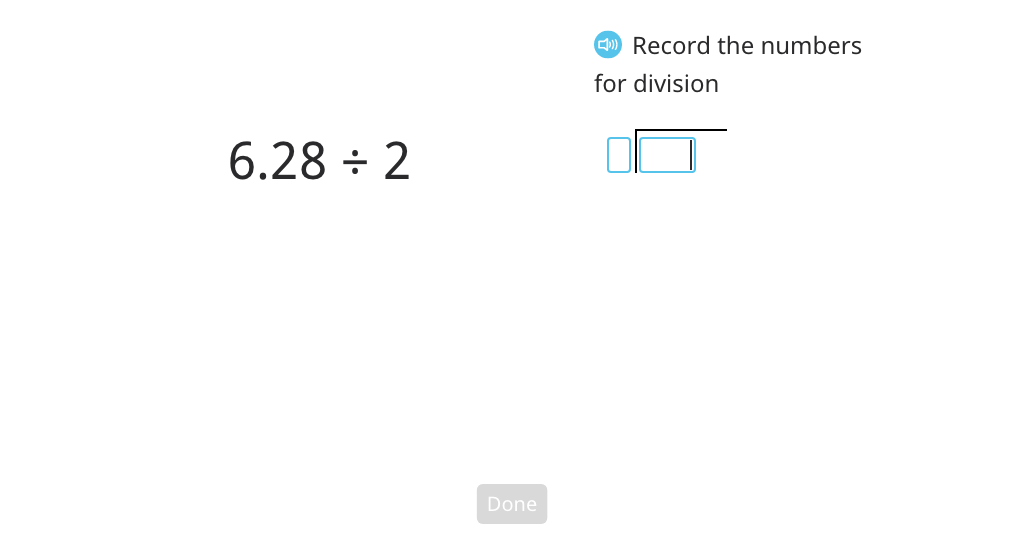
Use long division to divide a decimal number by a single-digit number with and without regrouping
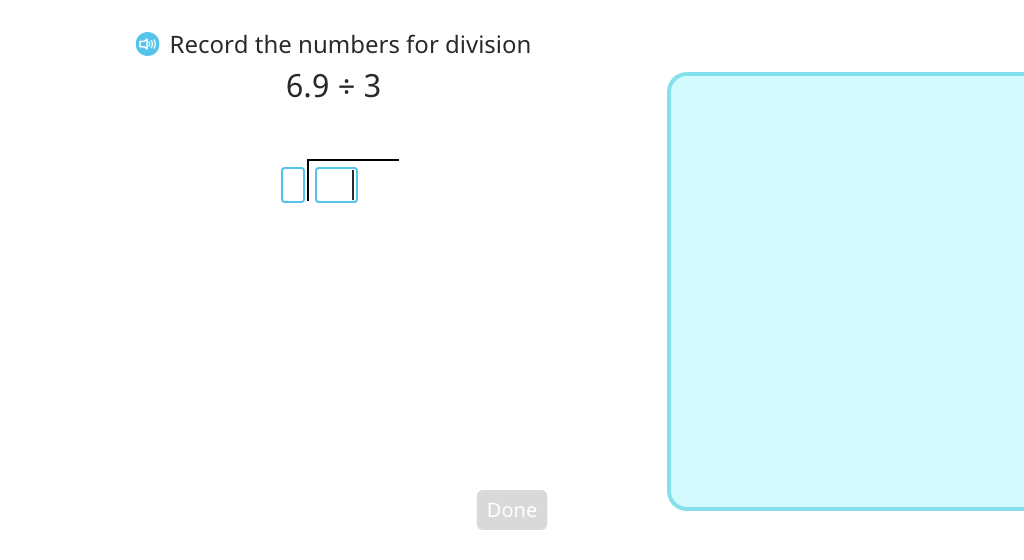
Use long division to divide a decimal number by a single-digit number with quotients that include 0

Use long division to divide a decimal number by a single-digit number with regrouping to a new place value

MODULE 2. Multi-Digit Whole Number and Decimal Fraction Operations
Topic A: Mental Strategies for Multi-Digit Whole Number Multiplication
Students work with round numbers in the tens, hundreds, and thousands to see how factoring out can make mental multiplication easier. In doing so, they apply properties of multiplication.
Factor out 10, 100, or 1,000 from a given number

Solve multiplication problems using the associative and commutative properties

Solve a multi-digit multiplication problem using factoring out and properties of multiplication (Level 1)

Solve a multi-digit multiplication problem mentally

Solve a multi-digit multiplication problem using factoring out and properties of multiplication (Level 2)

Round multi-digit numbers to estimate the area of a rectangle

Round multi-digit numbers to estimate the product

Topic B: The Standard Algorithm for Multi-Digit Whole Number Multiplication
Students hone their use of the standard algorithm for multiplication, working with multi-digit numbers. They master the use of regrouping and working across zeros. To further their conceptual understanding, the standard algorithm is presented alongside other strategies, such as the area model and factoring out powers of 10.
Solve multiplication problems using the standard algorithm (Level 1)

Solve multiplication problems using the standard algorithm (Level 2)

Multiply multi-digit numbers by factoring out powers of 10 and using the associative property

Develop and test an algorithm for multiplying by a factor with a single non-zero digit

Use the strategy of factoring out powers of 10 to solve multi-digit multiplication problems

Multiply two 2-digit numbers using the standard algorithm and the strategy of factoring out powers of ten (Level 1)

Multiply two 2-digit numbers using the standard algorithm and the strategy of factoring out powers of ten (Level 2)

Multiply two 2-digit numbers using the standard algorithm and the strategy of factoring out powers of ten (Level 3)

Use the area model to multiply two 2-digit numbers

Multiply two 2-digit numbers using the concept of partial products

Multiply multi-digit numbers using the concept of partial products (Level 1)

Multiply multi-digit numbers using the concept of partial products (Level 2)

Multiply multi-digit numbers using the concept of partial products (Level 3)

Multiply two 3-digit numbers using the concept of partial products (Level 1)

Multiply two 3-digit numbers using the concept of partial products (Level 2)

Multiply 3- and 4-digit numbers using the concept of partial products

Multiply up to 5-digit numbers using the concept of partial products

Topic C: Multiplying with Decimals and Multi-Digit Numbers
Students begin to multiply decimals in the tenths or hundredths by 2- or 3-digit whole numbers. They learn how to accurately place a decimal in their answer and how to estimate to check the reasonableness of their answer.
Multiply decimal numbers by powers of 10 and solve for missing factors

Multiply decimal numbers in the tenths by a whole number (Level 1)

Multiply decimal numbers in the hundredths by a whole number (Level 1)

Multiply decimal numbers in the tenths by a whole number (Level 2)

Multiply decimal numbers in the hundredths by a whole number (Level 2)

Factor out a power of 10 to multiply a decimal number by a tens or hundreds number (Level 1)

Factor out a power of 10 to multiply a decimal number by a tens or hundreds number (Level 2)

Round numbers to the leftmost place with a non-zero digit (Level 1)

Round numbers to the leftmost place with a non-zero digit (Level 2)

Estimate the product of a whole and decimal number by rounding (Level 1)

Estimate the product of a whole and decimal number by rounding (Level 2)

Find the estimated and actual products of a whole and decimal number

Topic D: Mental Strategies for Multi-Digit Whole Number Division
Students rely on their understanding of powers of 10, division, place value, and rounding to divide multi-digit whole numbers mentally.
Divide round numbers by powers of 10

Divide by factoring out powers of 10 from the divisor

Divide multi-digit round numbers mentally

List the multiples of a given 2-digit round number

Round a 3-digit number to the nearest multiple of a given 2-digit round number (Level 1)

Round a 3-digit number to the nearest multiple of a given 2-digit round number (Level 2)

Estimate a quotient by finding the nearest multiple

Estimate a quotient of a multi-digit division equation (Level 1)

Estimate a quotient of a multi-digit division equation (Level 2)
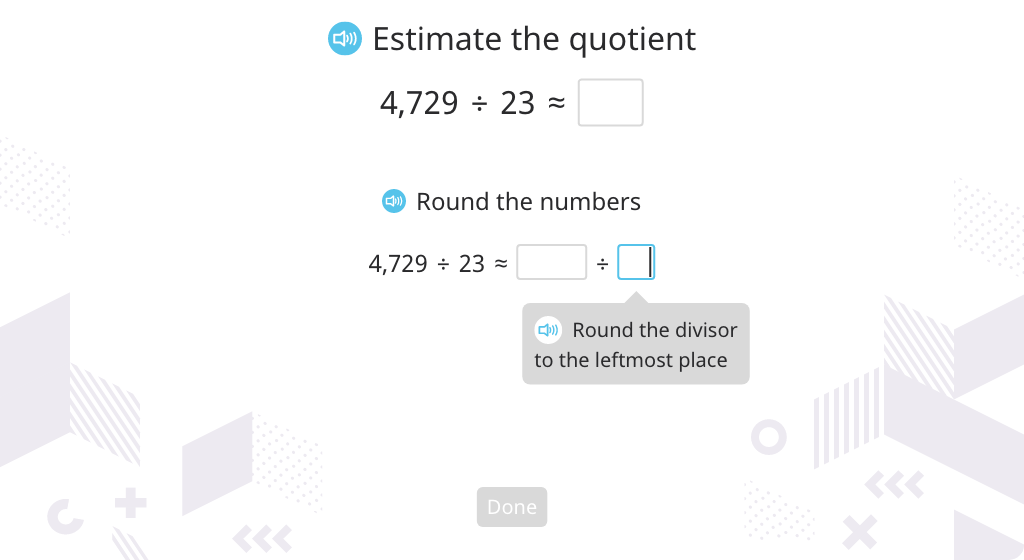
Topic E: Partial Quotients and Multi-Digit Whole Number Division
Students look under the hood of division to really understand the concept of a remainder as well as the steps involved in long division. Students work with one- or two- and three-digit dividends and one- and two-digit divisors. They use the standard algorithm for long division, but approach it in different ways to build math flexibility.
Divide a group of objects into groups of given size with a remainder

Find the quotient and remainder by using multiples of the divisor

Find the quotient and remainder by subtracting the divisor from the dividend (Part 1)

Find the quotient and remainder by subtracting the divisor from the dividend (Part 2)

Estimate the quotient, then solve using long division with a 1-digit quotient (Part 1)

Estimate the quotient, then solve using long division with a 1-digit quotient (Part 2)

Solve using long division with a 1-digit quotient
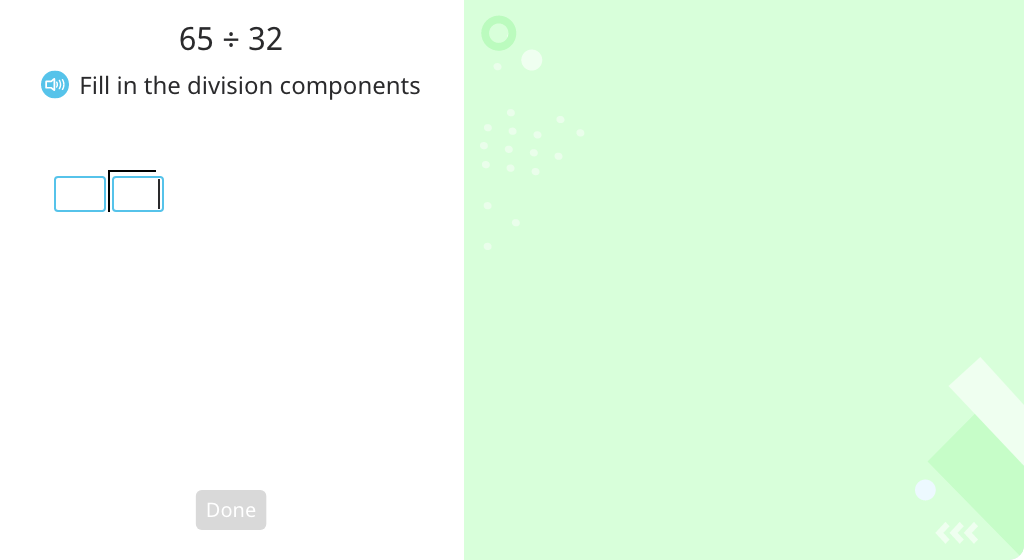
Solve using long division with a 1-digit quotient (overestimate)

Solve using long division with a 1-digit quotient (underestimate)

Solve using long division with a 1-digit quotient

Solve using long division with a 2-digit quotient (Part 1)

Solve using long division with a 2-digit quotient (over and underestimate)

Solve using long division with a 2-digit quotient (Part 2)

Solve using long division with a 3-digit quotient

Solve using long division with a 3-digit quotient (over and underestimate) (Part 1)

Solve using long division with a 3-digit quotient (over and underestimate) (Part 2)

Topic F: Partial Quotients and Multi-Digit Decimal Division
Students look under the hood of division to really understand the concept of a remainder as well as the steps involved in long division. Students work with one- or two- and three-digit dividends and one- and two-digit divisors. They use the standard algorithm for long division, but approach it in different ways to build math flexibility.
Rename decimal numbers in unit form

Rename a number in unit form as a decimal number

Rename a whole number in unit form and decimal form

Divide a decimal by a whole number (with and without using unit form)

Divide a decimal number by 10 or 100

Divide a decimal number by a multiple of 10 or 100

Estimate the quotient of a decimal number divided by a 2-digit number (Level 1)

Estimate the quotient of a decimal number divided by a 2-digit number (Level 2)

Solve long division to the tenths place
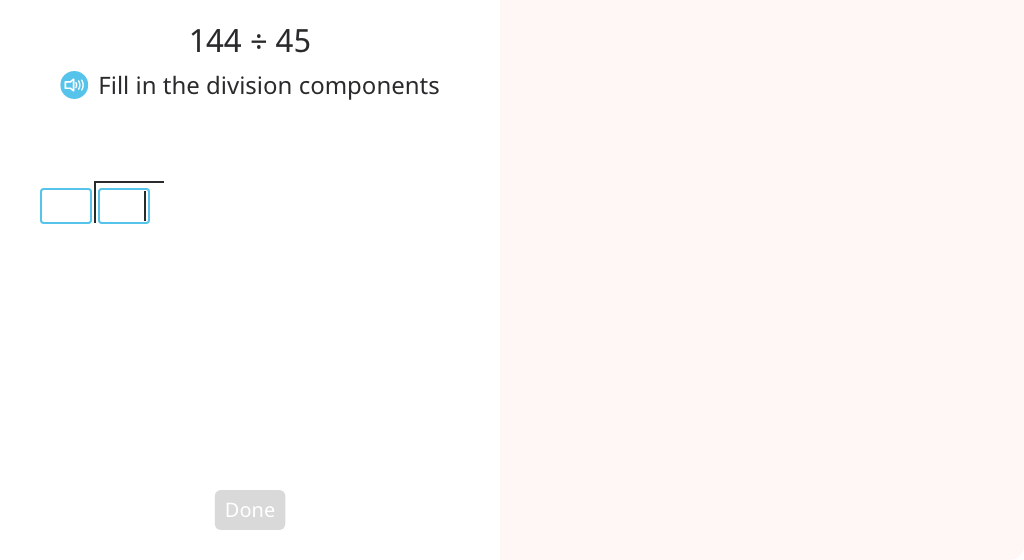
Solve long division to the hundredths place

Solve long division of a decimal number (Level 1)

Solve long division of a decimal number (Level 2)

Solve long division of a decimal number (Level 3)

Use long division to solve a word problem with a decimal quotient

Use long division to solve area problems with a decimal quotient

MODULE 3. Addition and Subtraction of Fractions
Topic A: Equivalent Fractions
Students are introduced to the basics of fraction equivalency. They learn to multiply to find an equivalent fraction and to divide to reduce a fraction. The concepts of common factors and greatest common factor are also introduced and applied.
Label the numerator and denominator in a fraction

Write an equivalent fraction (larger) based on a given multiple or denominator

Write an equivalent fraction (smaller) based on a given divisor, numerator, or denominator

Complete equivalent fractions

Identify common factors of two given numbers

Identify a common factor of two given numbers and divide both by the common factor

Reduce a fraction to its simplest form by dividing by the greatest common factor

Topic B: Making Like Units Pictorially
Students rely on their knowledge of fraction equivalence to work through all aspects of adding and subtracting with fractions and mixed numbers. With plenty of visual support and step-by-step prompting, they work with like and unlike denominators. Students learn to convert between mixed numbers and fractions to solve problems, write their answer in simplest form, and solve word problems.
Add fractions with like denominators

Rewrite an improper fraction as a mixed number

Add fractions with like denominators and rewrite the sum as a mixed number

Divide shapes into an equal number of parts (precursor to finding common denominators)

Add fractions with unlike denominators (multiply denominators to find a common denominator)

Rename fractions with unlike denominators (Level 1)

Rename fractions with unlike denominators (Level 2)

Add fractions with unlike denominators and rewrite the sum as a mixed number

Add fractions with unlike denominators and rewrite the sum in simplest form (Part 1)

Add fractions with unlike denominators and rewrite the sum in simplest form (Part 2)

Subtract fractions with like denominators

Subtract fractions with unlike denominators (multiply denominators to find a common denominator)

Subtract fractions with unlike denominators

Rewrite a mixed number as an improper fraction

Subtract a fraction from a mixed number with like denominators (rename the mixed number as a fraction)

Subtract a fraction from a mixed number with unlike denominators (rename the mixed number as a fraction)

Subtract a fraction from a mixed number with unlike denominators and rewrite the difference in simplest form

Subtract a fraction from a mixed number with unlike denominators to solve a word problem

Subtract a fraction from 1 whole to solve a word problem

Subtract two fractions from 1 whole to solve a word problem

Add fractions to solve a word problem

Topic C: Making Like Units Numerically
Students increase the complexity of the addition and subtraction operations they can solve by using mixed numbers. They reinforce and apply their understanding of number equivalence as they rename numbers to solve problems.
Add a mixed number and a whole number with like denominators

Subtract a fraction or a mixed number from a whole number with like denominators with and without a number line

Add a mixed number and a fraction with like denominators

Add mixed numbers with like denominators

Add mixed numbers with unlike denominators (Level 1)

Add mixed numbers with unlike denominators (Level 2)

Subtract mixed numbers with like denominators

Subtract mixed numbers with unlike denominators (Level 1)

Subtract a fraction from a mixed number with like denominators (rename the mixed number)

Subtract mixed numbers with unlike denominators (Level 2)

Subtract mixed numbers with unlike denominators (Level 3)

Topic D: Further Applications
To support more complex understanding of operations with fractions, students are supported by visual models, the number line, and diagrams. They apply their knowledge of fractions to estimate sums and differences and solve multi-step word problems with mixed numbers.
Compare fractions with unlike denominators to 1/2 to estimate the sum

Compare fractions with unlike denominators to a missing unit to estimate the sum

Compare fractions with unlike denominators to estimate the difference of a mixed number minus a fraction

Add multiple mixed numbers and fractions

Solve a multi-step word problem with mixed numbers with unlike denominators (Part 1)

Solve a multi-step word problem with mixed numbers with unlike denominators (Part 2)

MODULE 4. Multiplication and Division of Fractions and Decimal Fractions
Topic A: Line Plots of Fraction Measurements
Students combine their knowledge of measurement, rounding, and mixed numbers to create line plots. They then analyze the data, requiring them to perform operations with mixed numbers.
Round to the nearest half inch on a ruler

Round to the nearest half inch on a ruler to create a line plot and analyze the data

Round to the nearest quarter inch on a ruler

Round to the nearest quarter inch on a ruler to create a line plot and analyze the data

Round to the nearest eighth of a foot on a ruler

Round to the nearest eighth of an inch on a ruler to create a line plot and analyze the data

Topic B: Fractions as Division
To solidify their understanding of fractions as division, students work to convert between the two, using fractions greater than and less than one. They then work step by step to make sense of the remainder of a division problem as a fraction. Equipped with this understanding, students solve increasingly complex division word problems.
Rewrite division of whole numbers as a fraction based on a model

Rewrite division of whole numbers as a fraction and match a fraction to its related division equation

Relate division to fractions

Relate division to fractions greater than one

Divide and report the remainder as a fraction based on a model

Rename a fraction greater than one as a mixed number (Level 1)

Rename a fraction greater than one as a mixed number (Level 2)

Solve fraction word problems based on a model (Level 1)

Solve fraction word problems based on a model (Level 2)

Solve fraction word problems based on a model (Level 3)

Solve fraction word problems based on a model (Level 4)

Solve fraction word problems based on a model (Level 5)

Topic C: Multiplication of a Whole Number by a Fraction
Students begin by finding a unit fraction of a whole number and other fractions of a whole number using familiar models. They then relate that process to multiplication. To multiply a whole number by a fraction, students learn to find common factors and reduce either before or after multiplying.
Determine fractions of a whole number based on a model (Level 1)

Determine fractions of a whole number based on a model to solve a word problem

Determine fractions of a whole number based on a model (Level 2)

Determine fractions of a whole number based on a model (Level 3)

Determine a whole number given a fraction of that number based on a model

Multiply a whole number by a fraction

Relate a fraction of a whole number to multiplication and solve

Determine a fraction of a measurement by converting units and multiplying

Determine common factors of two whole numbers

Divide whole numbers by a common factor

Reduce a fraction by dividing by a common factor

Reduce factors before multiplying a whole number by a fraction (Level 1)

Reduce factors before multiplying a whole number by a fraction (Level 2)

Multiply a whole number by a fraction by reducing before or after multiplying

Topic D: Fraction Expressions and Word Problems
Students synthesize their understanding of fractions and operations to build and solve expressions. Familiar models support their learning, and word problems put the skills in context.
Match operations to the terms sum, difference, product, and quotient

Compose an expression based on text

Compose a compound expression based on text (Part 1)

Compose a compound expression based on text (Part 2)

Compose a compound expression based on text (Part 3)

Compose a compound equation based on a model and solve (Part 1)

Compose a compound equation based on a model and solve (Part 2)

Solve compound equations with parentheses and fractions

Solve a word problem by multiplying a whole number by a fraction (Level 1)

Solve a word problem by multiplying a whole number by a fraction (Level 2)

Topic E: Multiplication of a Fraction by a Fraction
Students learn to multiply fractions by starting with unit fractions and the support of an area model. They then progress to multiplication that involves mixed numbers, reducing, and units of measure.
Multiply unit fractions using an area model

Multiply fractions using an area model

Multiply fractions (reduce before multiplying)

Multiply fractions (reduce before or after multiplying)

Solve word problems by multiplying fractions using an area model

Rename a mixed number as a fraction to multiply by a fraction

Convert measurements by multiplying a whole number by a fraction

Convert measurements by multiplying fractions

Convert multiplication by a decimal to multiplication by a fraction and solve

Multiply by 0.1 using a place value chart

Multiply by 0.01 using a place value chart

Multiply by 0.1 or 0.01

Decompose a decimal number to multiply

Determine the placement of the decimal point in the product of two decimal numbers

Multiply two decimal numbers using column multiplication (Part 1)

Multiply two decimal numbers using column multiplication (Part 2)

Multiply two decimal numbers using column multiplication (Part 3)

Topic F: Multiplication of Fractions and Decimal Fractions
Students compare products with one of their factors, where the factors are a fraction or decimal number. They compose rules for instances where this factor is greater or less than 1. They also practice converting fractions to decimals.
Compare fractions with 1
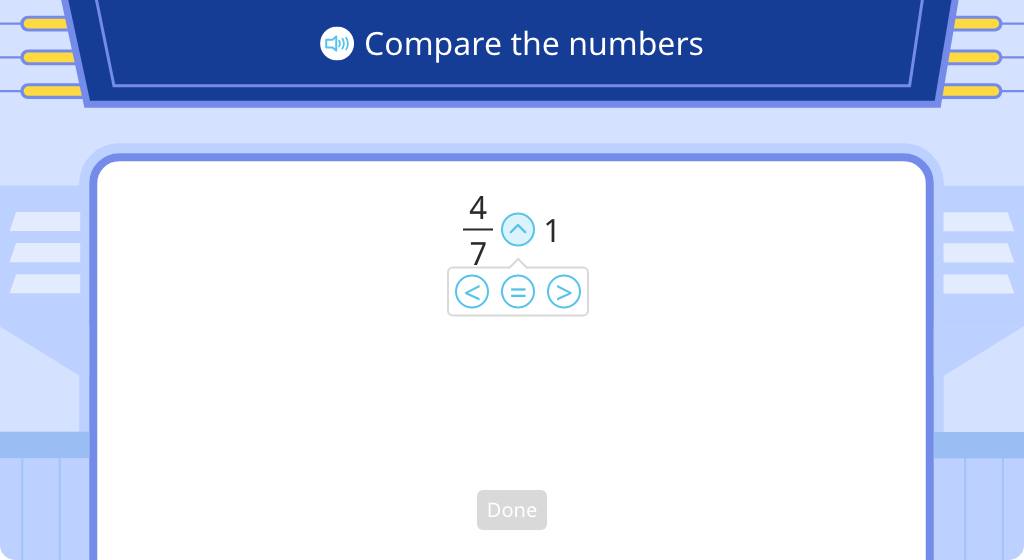
Compare a product with one of its factors (Level 1)
Compare a product with one of its factors (Level 2)
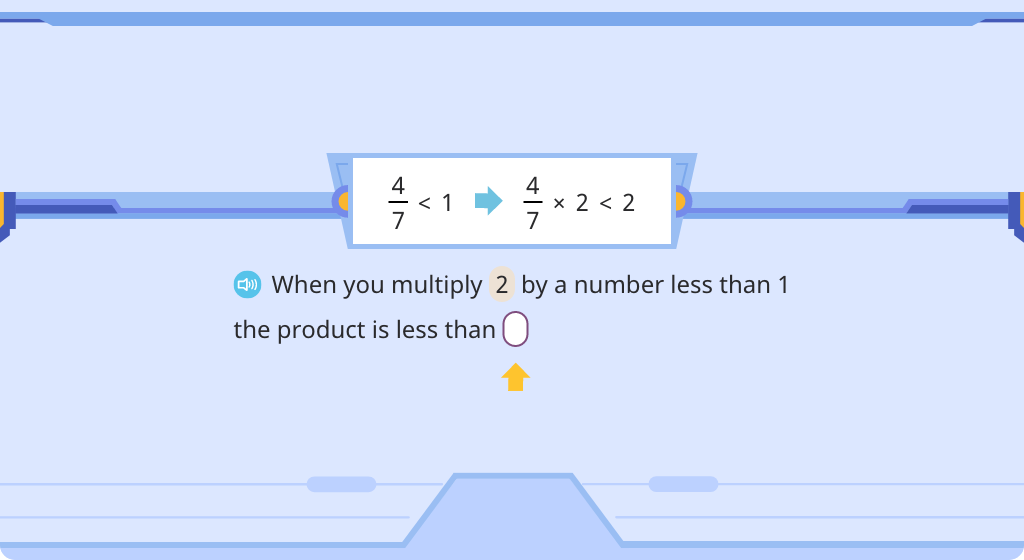
Compare a product with one of its factors (Level 3)
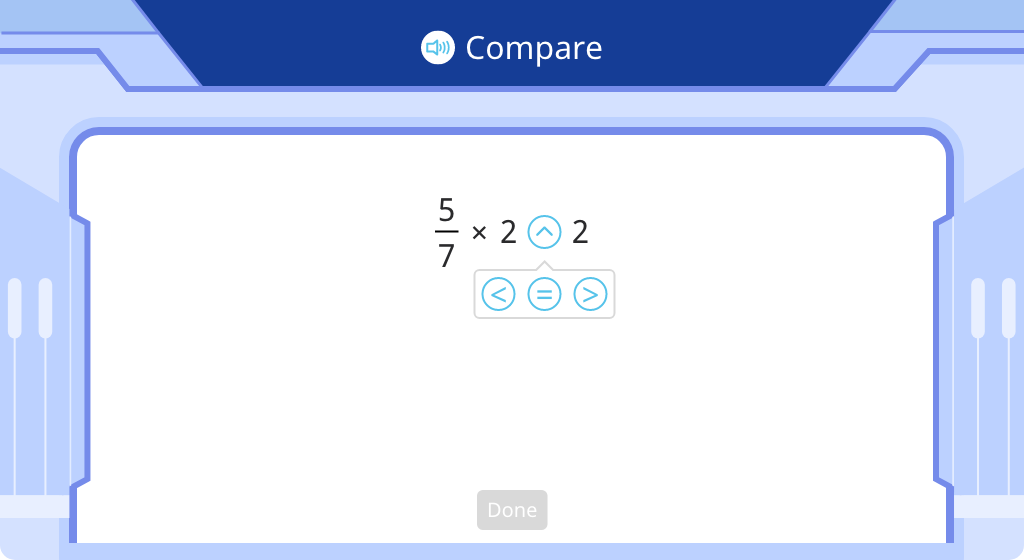
Compare a product with one of its factors (Level 4)
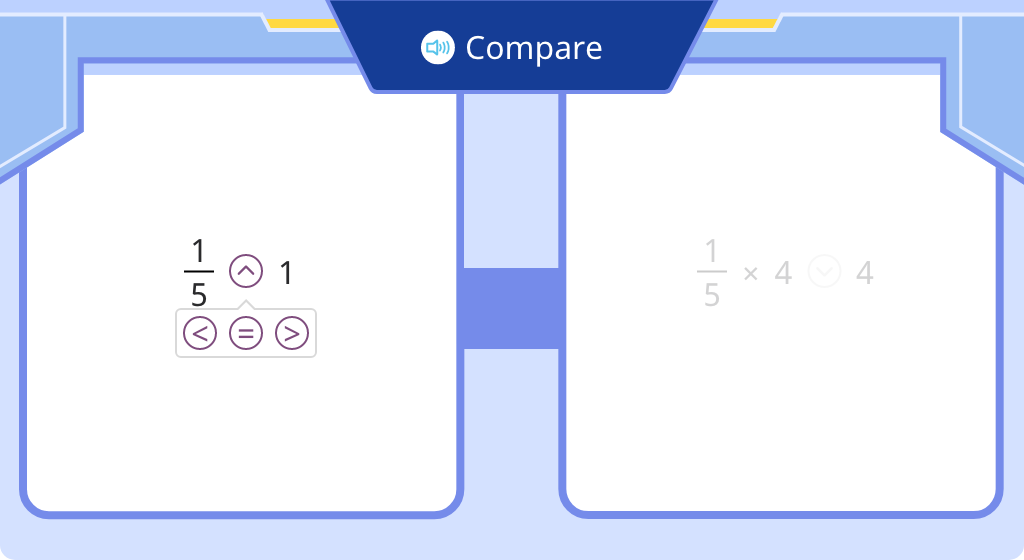
Compare a product with one of its factors (Level 5)
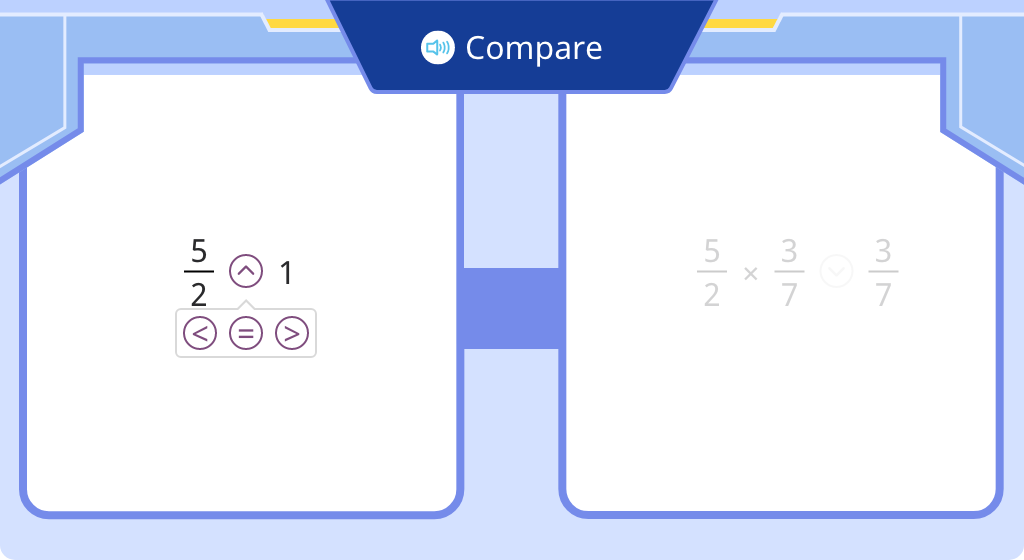
Compare a product with one of its factors (Level 6)
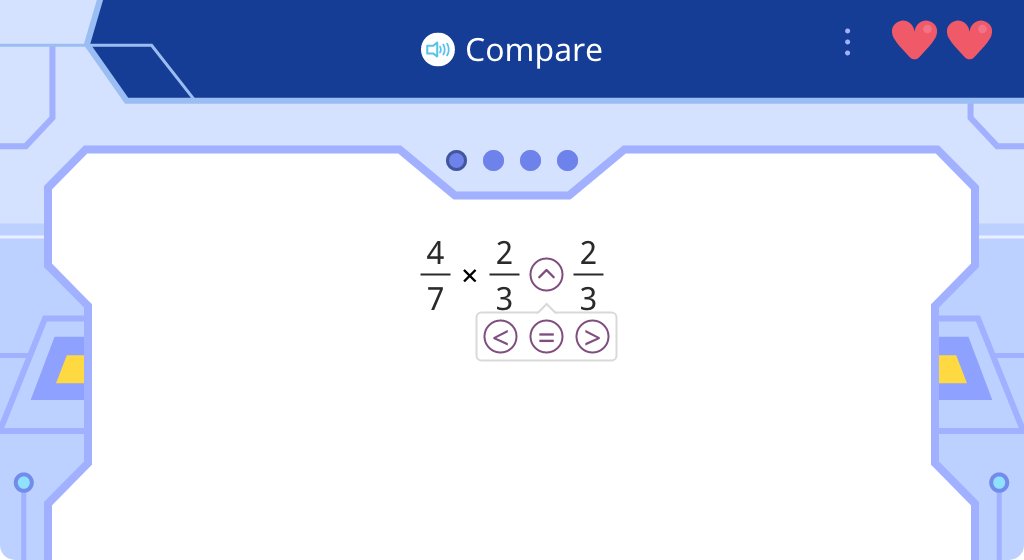
Compare a product to one of its factors in expressions with decimal numbers (Level 1)
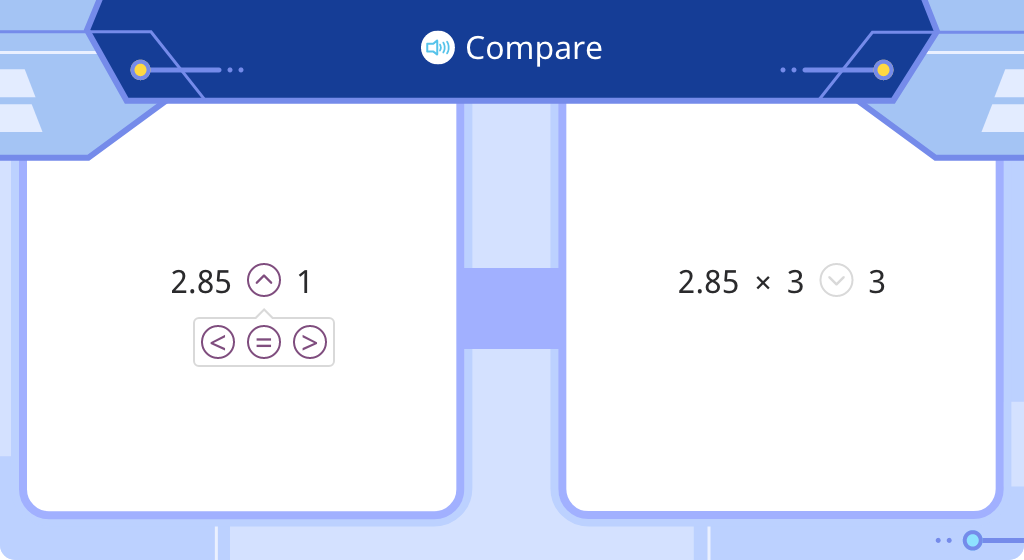
Compare a product to one of its factors in expressions with decimal numbers (Level 2)
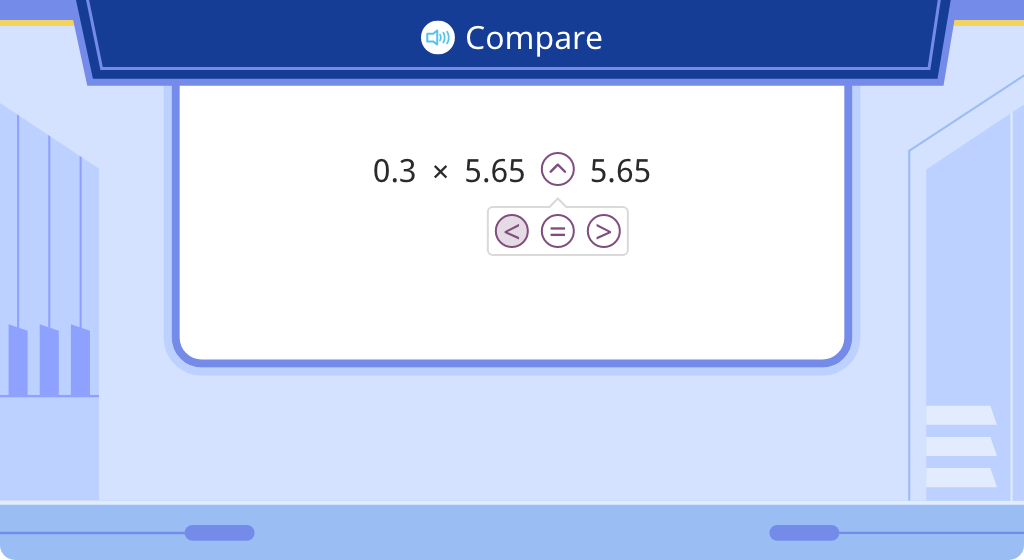
Compare a product to one of its factors in expressions with decimal numbers (Level 3)
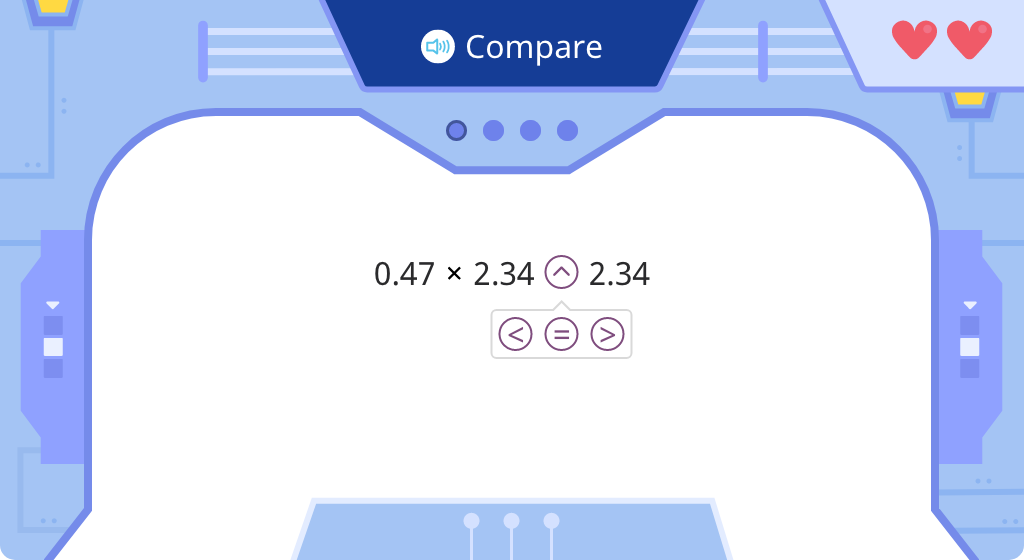
Identify the factor that will make an inequality true

Convert proper fractions to decimals (Level 1)
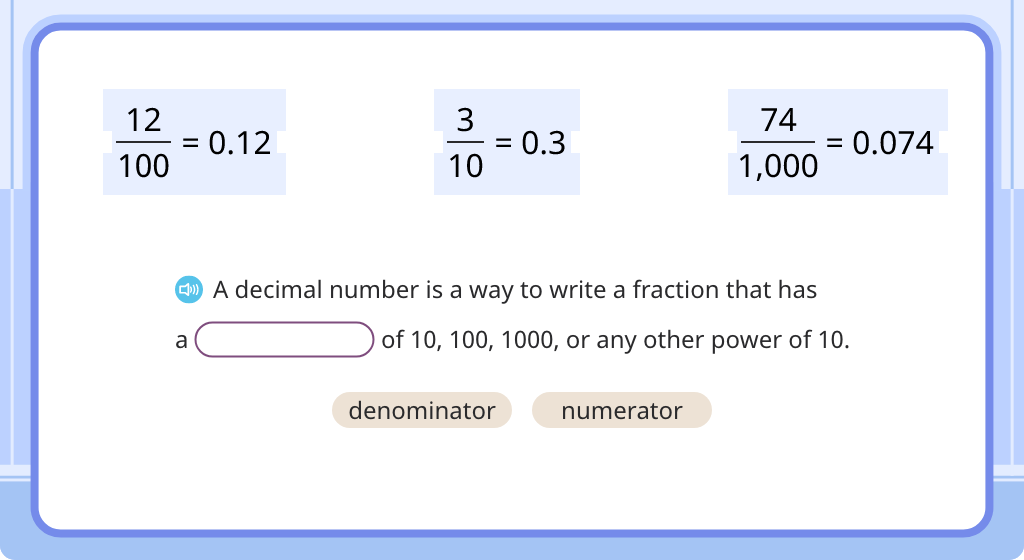
Convert proper fractions to decimals (Level 2)

Convert mixed numbers to decimals (Level 1)
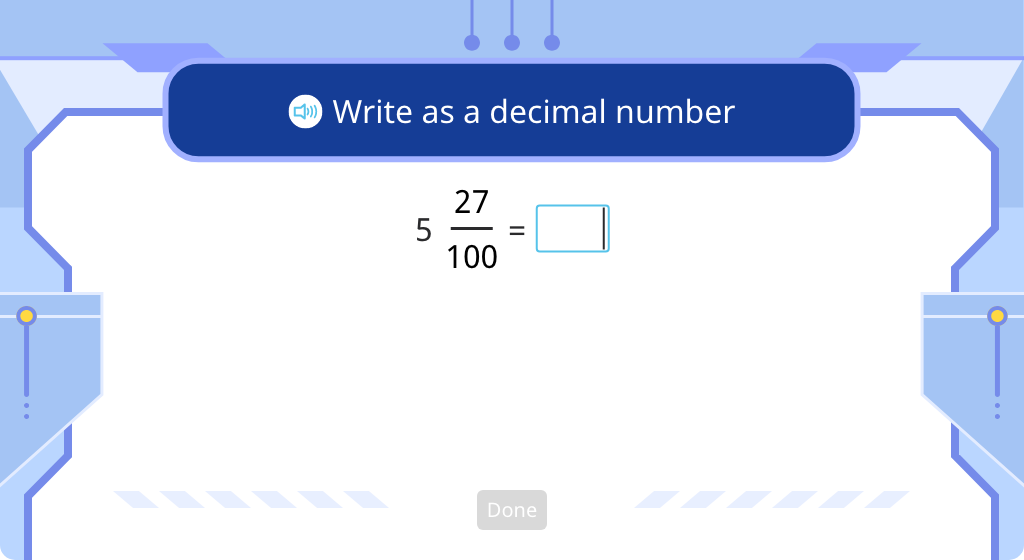
Convert mixed numbers to decimals (Level 2)
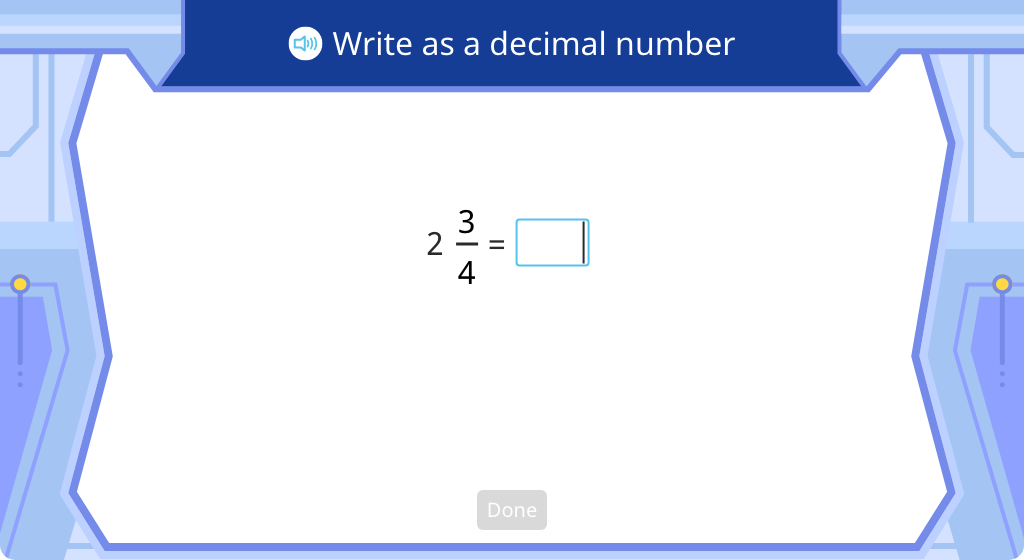
Convert proper fractions to decimals using long division

Convert improper fractions to decimals using long division
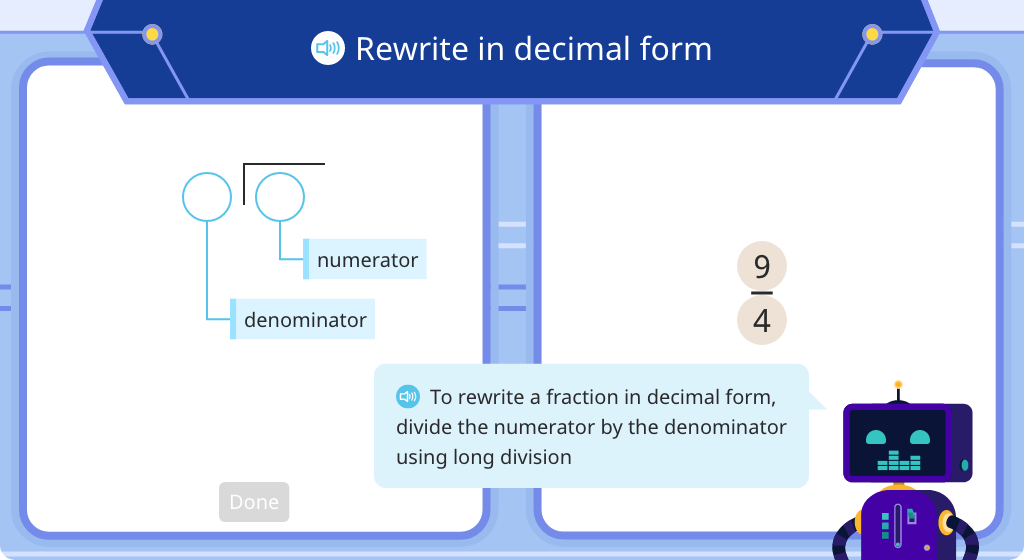
Topic G: Division of Fractions and Decimal Fractions
Students rely upon their understanding of multiplying fractions to learn how to divide fractions. With the assistance of familiar models such as tape diagrams and area models, they learn different ways to approach dividing with fractions. At this stage, they use unit fractions with whole numbers and unit fractions with unit fractions.
Rewrite an equation with multiplication by a fraction as a division equation based on a model

Compose a division equation with a fraction based on a model

Divide a whole number by a unit fraction based on a tape diagram

Relate division by a unit fraction to multiplication by the denominator

Divide a whole number by a unit fraction by multiplying by the denominator

Divide a whole number by a unit fraction

Divide a unit fraction by a whole number based on a tape diagram (Part 1)

Divide a unit fraction by a whole number based on a tape diagram (Part 2)

Divide a unit fraction by a whole number

Multiply a unit fraction by a unit fraction with and without an area model (Part 1)

Multiply a unit fraction by a unit fraction with and without an area model (Part 2)

Relate division by a whole number to multiplication by a unit fraction

Solve division equations with unit fractions and whole numbers

Multiply a decimal number by a power of ten

Simplify a fraction using the basic property of fractions

Convert a fraction to a given denominator using the basic property of fractions

Convert between division expressions and fractions

Complete fraction expressions using the basic property of fractions

Convert fractions with decimal denominators to fractions with whole number denominators (Level 1)

Convert fractions with decimal denominators to fractions with whole number denominators (Level 2)

Convert fractions with decimal denominators to fractions with whole number denominators (Level 3)

Convert fractions with decimal denominators to fractions with whole number denominators (Level 4)

Convert division expressions with decimal divisors to expressions with whole number divisors (Level 1)

Convert division expressions with decimal divisors to expressions with whole number divisors (Level 2)

MODULE 5. Addition and Multiplication with Volume and Area
Topic A: Concepts of Volume
Students find and compare the volumes of figures in standard units, including cubic units, cubic centimeters, and cubic inches. They also explore prisms and how to find their volume.
Explore the concept of volume

Find volume with unit cubes

Find and compare volumes with unit cubes (Level 1)

Find and compare volumes with unit cubes (Level 2)

Explore cubic centimeters as a standard unit of volume
Explore cubic inches as a standard unit of volume

Compare figures measured in cubic centimeters and cubic inches

Find the volume of a figure

Explore prisms
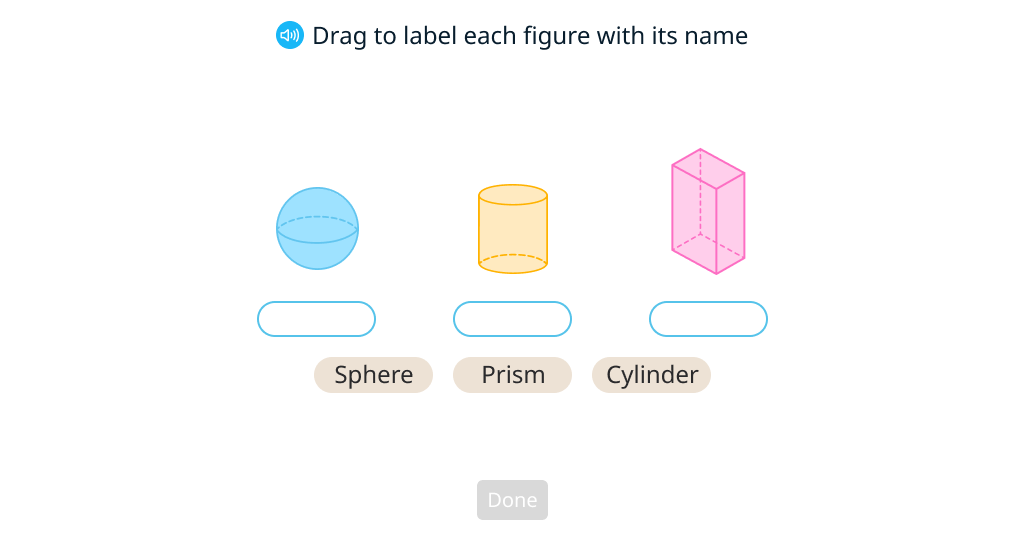
Find the volume of a prism

MODULE 6: Problem Solving with the Coordinate Plane
Topic A: Locate and Label Points on a Number Line and Coordinate Plane
Students explore the concept of coordinates on a number line and coordinate plane. They learn to define, label, and plot points.
Locate and label Points on a Number Line

Identify the origin and coordinate of a point on a number line

Explore coordinates on a number line

Use coordinates to find the distance between two points on a number line

Define a coordinate plane

Define points on a coordinate plane
Label coordinates on a coordinate plane

Plot points on a coordinate plane

Label points that lie on the coordinate axes

Use coordinates in purposeful ways

Explore patterns on a coordinate plane (Level 1)

Explore patterns on a coordinate plane (Level 2)

Topic B: Numerical Patterns on the Coordinate Plane
Students identify and generate numerical patterns for a data set based on one or two rules. They plot the data on a coordinate plane, discovering the relationships between coordinate points and the lines that connect them.
Identify and generate numerical patterns from a given rule

Identify and generate numerical patterns from two rules (Level 1)

Identify and generate numerical patterns from two rules (Level 2)

Plot table data on a coordinate plane
Plot and connect points on a coordinate plane

Find the relationship between coordinate points on a line

Discover the effect of the multiplication rule on the steepness of the resulting line
MODULE 7: Algebraic Expressions
Topic A: Solving Complex Missing Addend Equations
Students solve increasingly complex missing addend equations. In these pre-algebra equations, the challenge is not in the number values but in the logic of how numbers and equations can be combined to solve for numbers represented by symbols.
Solve missing addend equations

Solve multi-step missing addend equations

Solve for missing addends in paired equations (Level 1)

Solve for missing addends in a set of three equations

Solve for missing addends in paired equations (Level 2)

Solve missing addend equations containing a 0

Solve for missing addends in paired equations containing a 0
